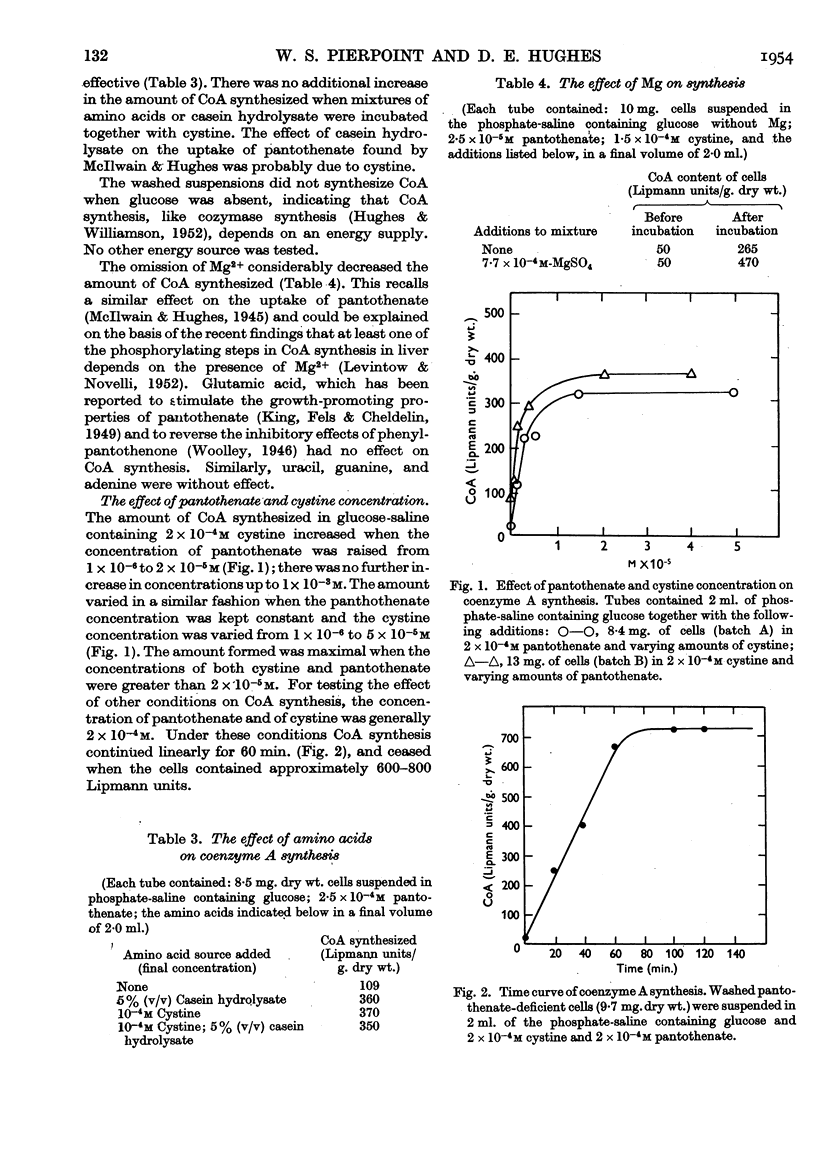
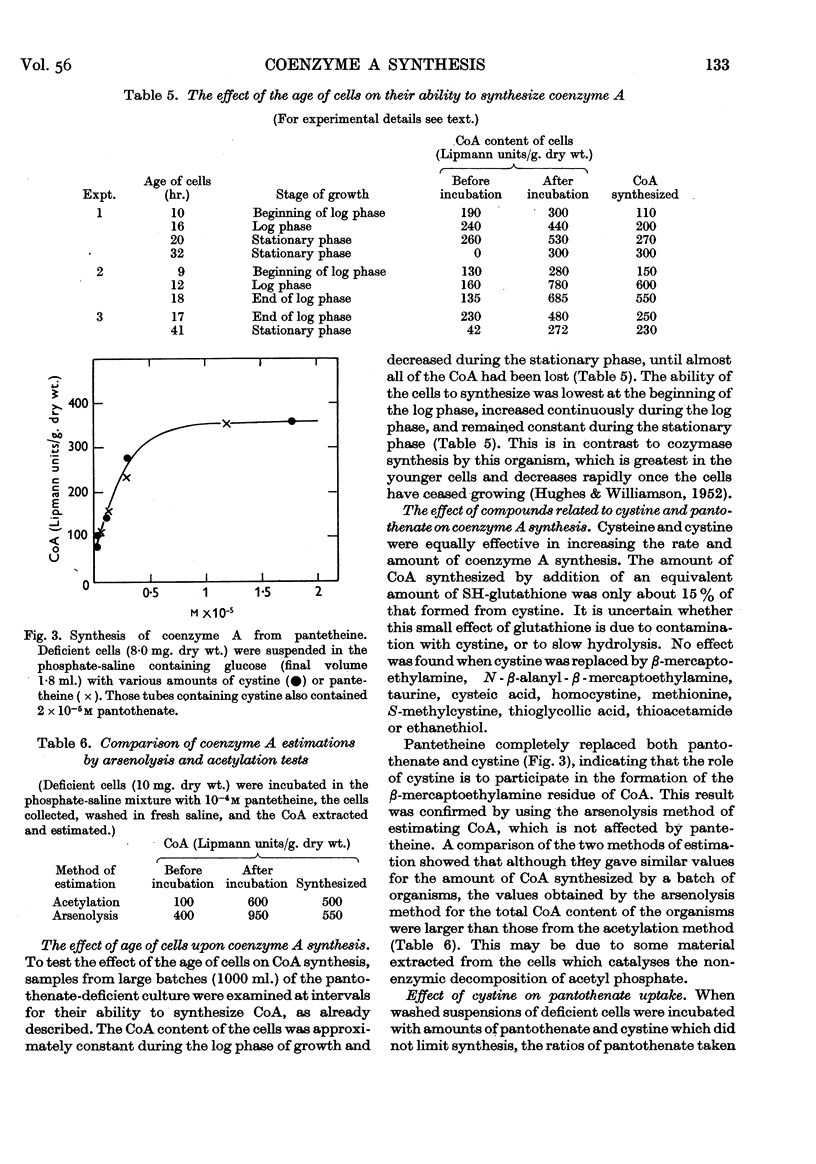
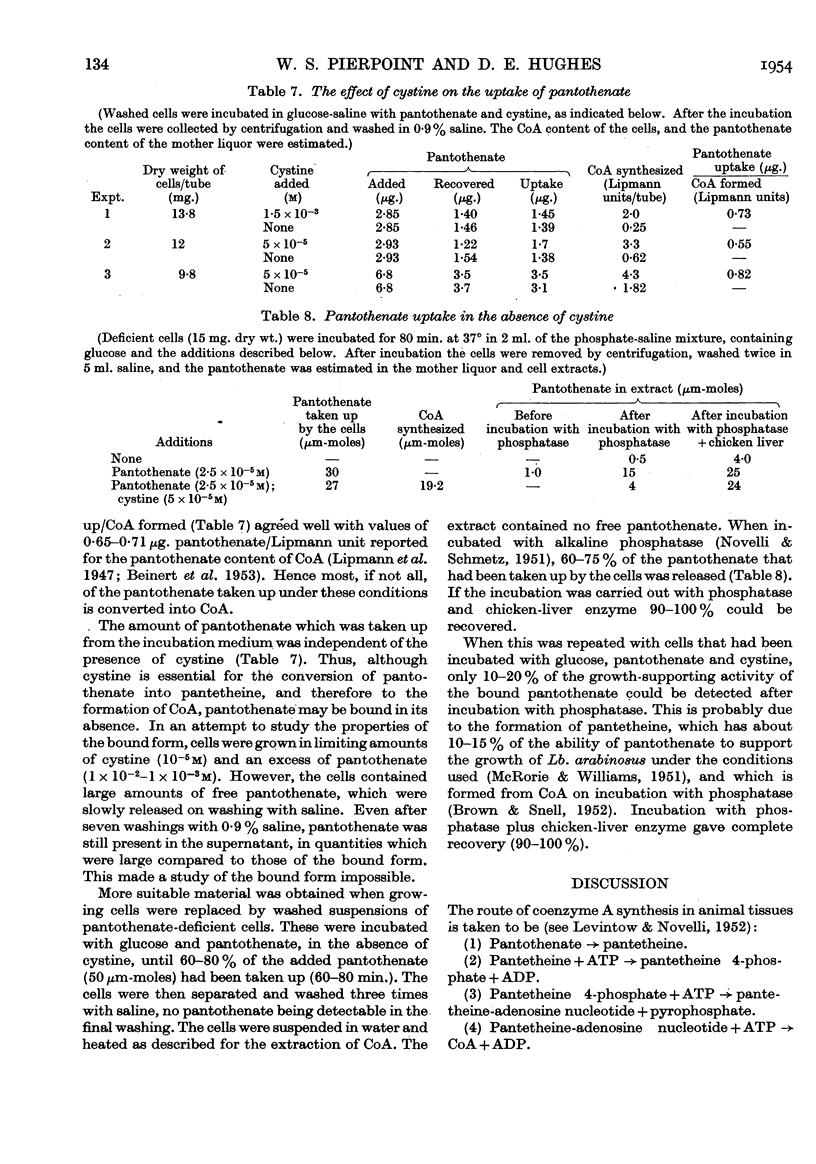
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEINERT H., VON KORFF R. W., GREEN D. E., BUYSKE D. A., HANDSCHUMACHER R. E., HIGGINS H., STRONG F. M. A method for the purification of coenzyme A from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jan;200(1):385–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN G. M., SNELL E. E. The relationship of pantethine to naturally occurring forms of the Lactobacillus bulgaricus factor. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):375–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenblum I., Chain E. An improved method for the colorimetric determination of phosphate. Biochem J. 1938 Feb;32(2):295–298. doi: 10.1042/bj0320295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAIG J. A., SNELL E. E. The comparative activities of pantethine, pantothenic acid, and coenzyme A for various microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1951 Mar;61(3):283–291. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.3.283-291.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGGLESTON L. V., HEMS R. Separation of adenosine phosphates by paper chromotography and the equilibrium constant of the myokinase system. Biochem J. 1952 Sep;52(1):156–160. doi: 10.1042/bj0520156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOVIER W. M., GIBBONS A. J. II. Some observations on the fate of injected coenzyme A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Jul;32(2):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90281-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANDSCHUMACHER R. E., MUELLER G. C., STRONG F. M. An improved enzymatic assay for coenzyme A. J Biol Chem. 1951 Mar;189(1):335–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. E., WILLIAMSON D. H. The synthesis of cozymase from nicotinic acid and its derivatives by Lactobacillus arabinosus 17-5. Biochem J. 1952 Jun;51(3):330–338. doi: 10.1042/bj0510330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAAS W. K. Pantothenate studies. III. Description of the extracted pantothenate-synthesizing enzyme of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):23–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H., Hughes D. E. Biochemical characterization of the actions of chemotherapeutic agents: 2. A reaction of haemolytic streptococci, involving pantothenate-usage, inhibited by pantoyltaurine, and associated with carbohydrate metabolism. Biochem J. 1944;38(2):187–195. doi: 10.1042/bj0380187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H., Hughes D. E. Biochemical characterization of the actions of chemotherapeutic agents: 3. Relationships between metabolic and growth inhibitions by pantothenate analogues: their structural and species specificity. Biochem J. 1945;39(2):133–139. doi: 10.1042/bj0390133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRORIE R. A., WILLIAMS W. L. Studies on the relationship between the Lactobacillus bulgaricus factor and pantothenic acid. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jun;61(6):737–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.6.737-745.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVELLI G. D., SCHMETZ F. J., Jr An improved method for the determination of pantothenic acid in tissues. J Biol Chem. 1951 Sep;192(1):181–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R., NOVELLI G. D., LIPMANN F. Coenzyme A function in and acetyl transfer by the phosphotransacetylase system. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jul;191(1):365–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


