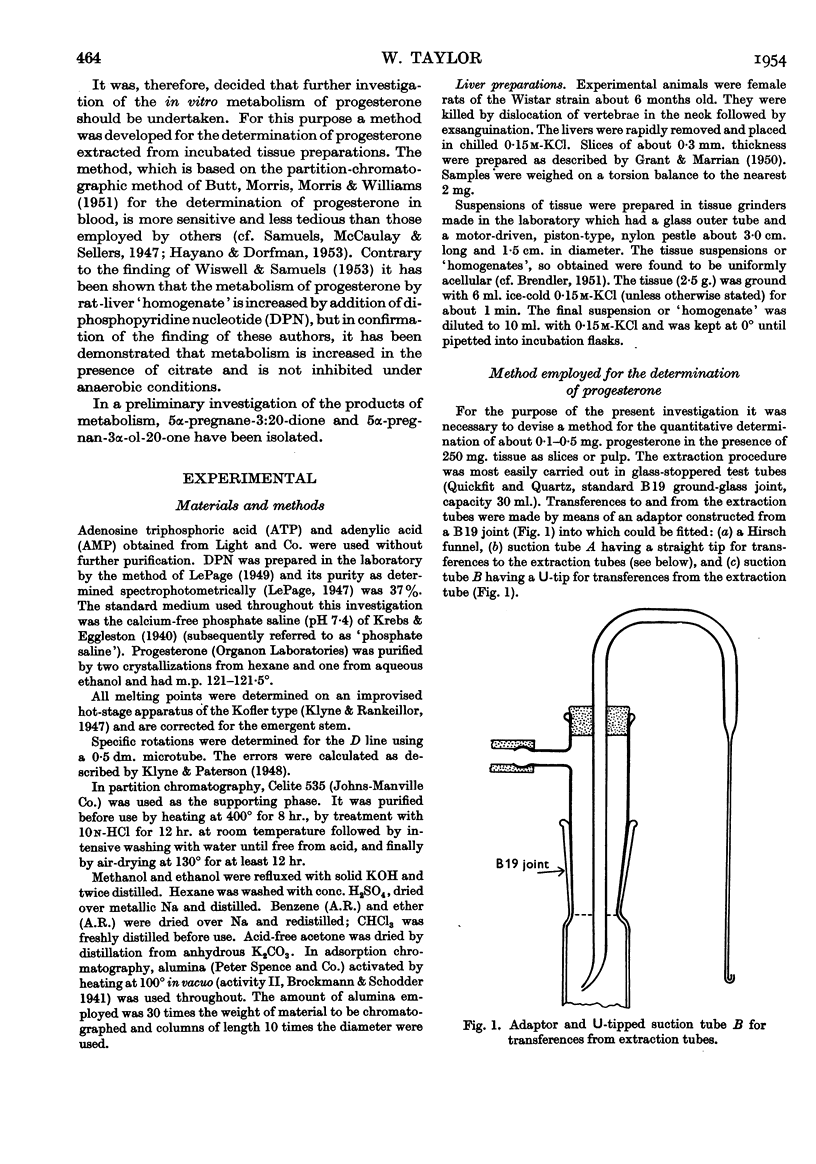
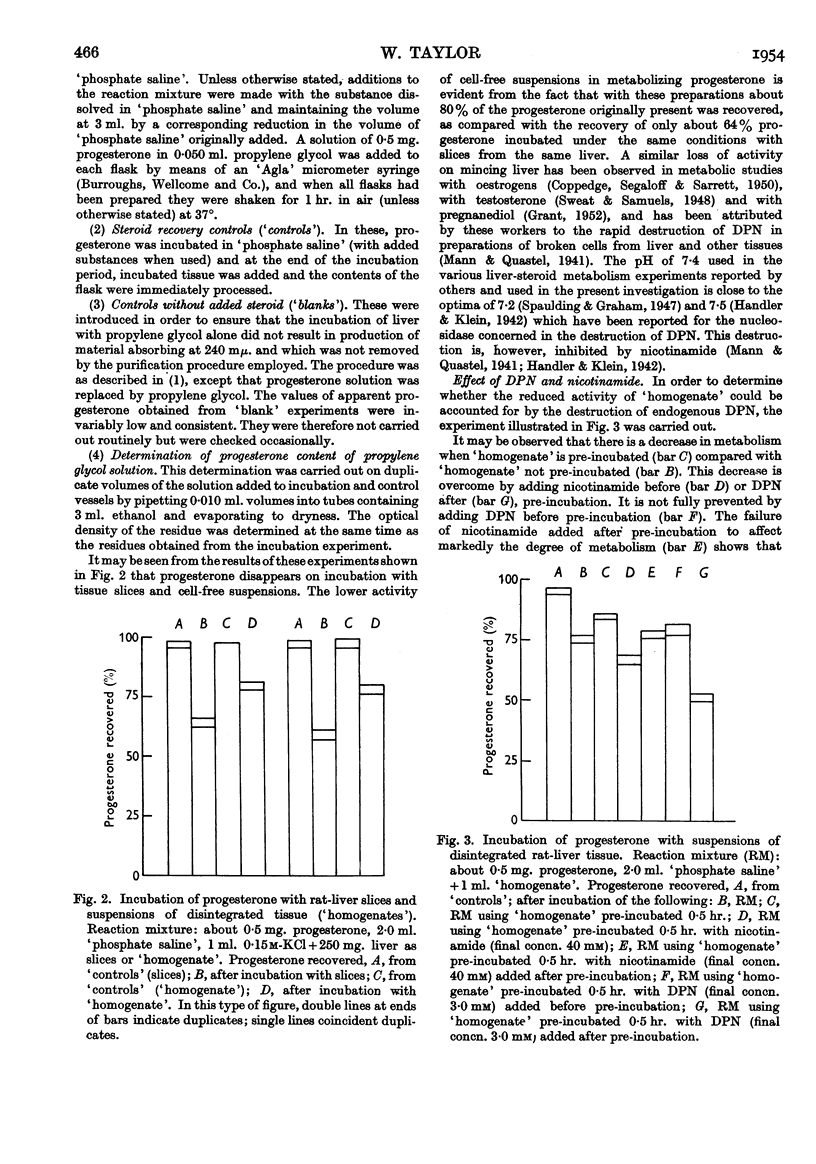
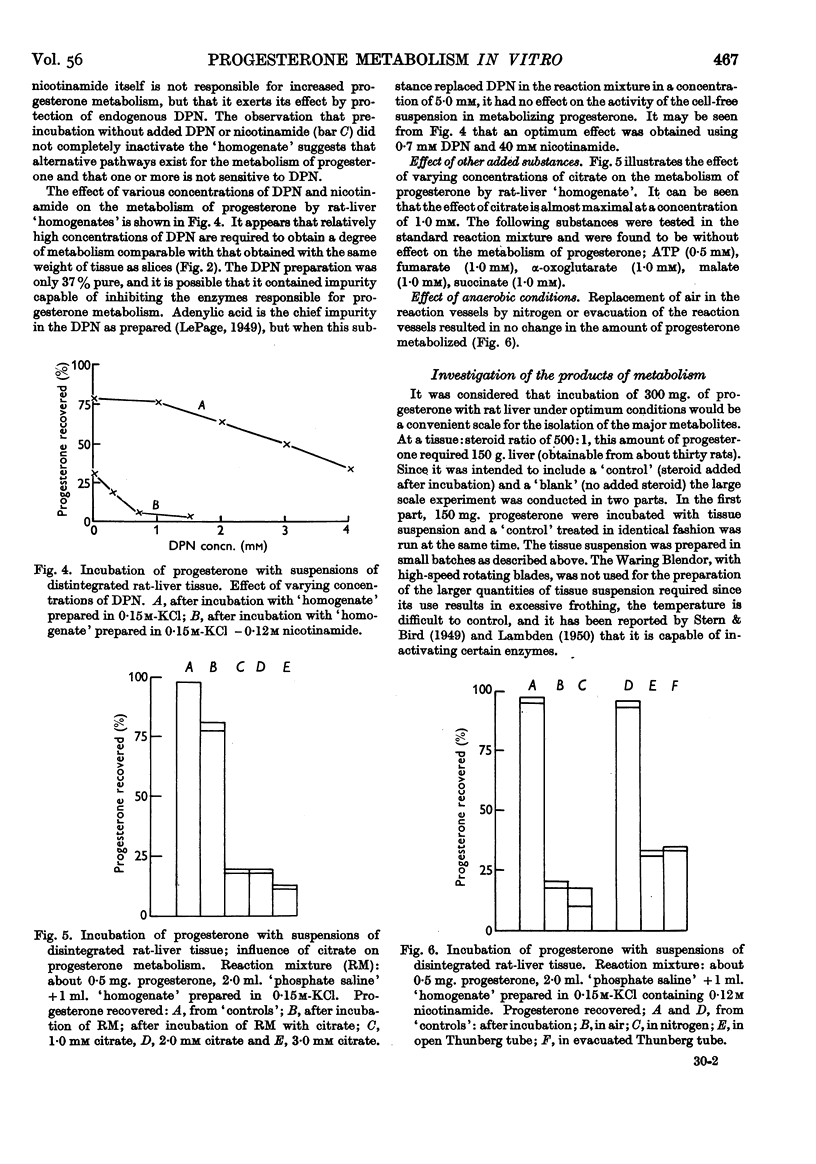
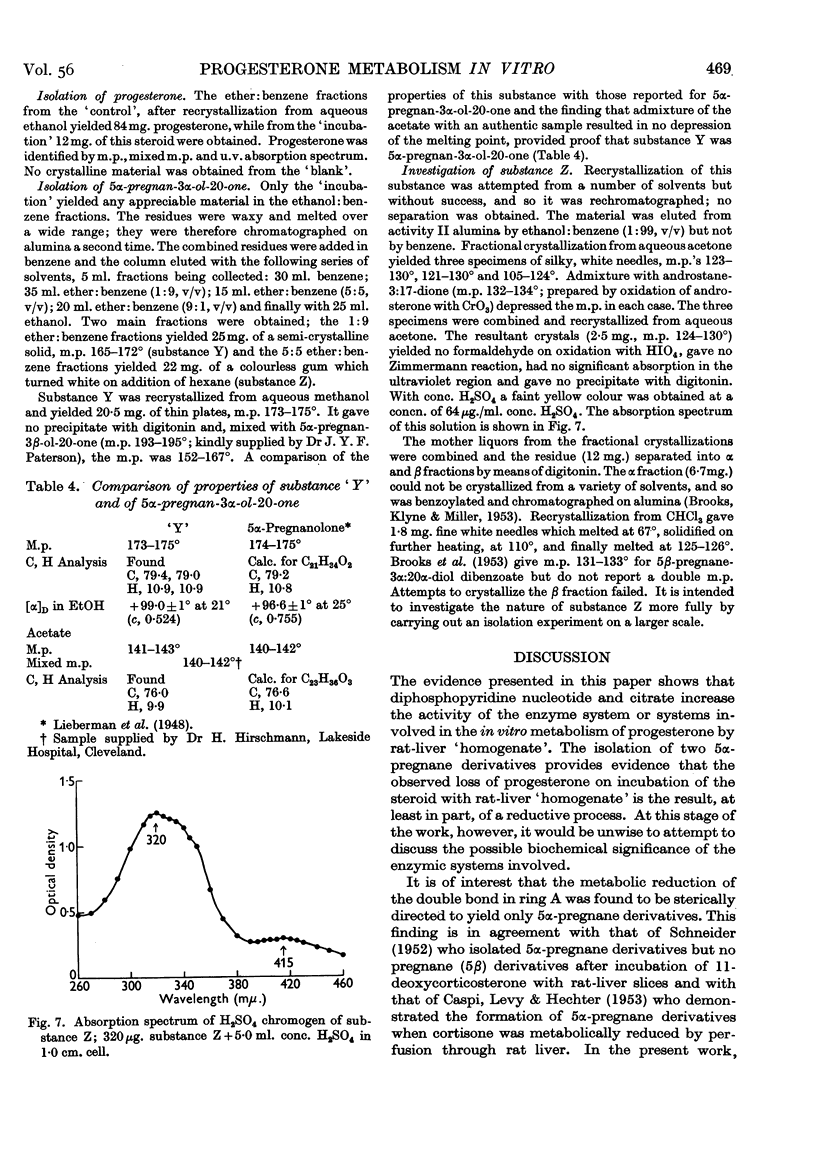
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRENDLER H. A simple, inexpensive microhomogenizer. Science. 1951 Jul 20;114(2951):61–62. doi: 10.1126/science.114.2951.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKS R. V., KLYNE W., MILLER E. The separation of steroid alcohols by chromatography of their benzoates on alumina. Biochem J. 1953 May;54(2):212–217. doi: 10.1042/bj0540212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTT W. R., MORRIS P., MORRIS C. J. O. R., WILLIAMS D. C. The polarographic estimation of steroid hormones. 5. Determination of progesterone in blood. Biochem J. 1951 Sep;49(4):434–438. doi: 10.1042/bj0490434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASPI E. Y., LEVY H., HECHTER O. M. Cortisone metabolism in liver. II. Isolation of certain cortisone metabolites. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Jul;45(1):169–182. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANT J. K., MARRIAN G. F. Studies on the metabolism of progesterone and related steroids in vitro; the metabolism of pregnane-3 alpha:20 alpha-diol by liver preparations. Biochem J. 1950 Oct;47(4):497–502. doi: 10.1042/bj0470497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANT J. K. Studies on the metabolism of progesterone and related steroids in vitro. 2. Factors influencing the metabolism of pregnane-3alpha:20alpha-diol by rat-liver homogenates, and the investigation of the products of metabolism. Biochem J. 1952 Jun;51(3):358–362. doi: 10.1042/bj0510358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYANO M., DORFMAN R. I. The enzymatic C-11 beta-hydroxylation of steroids. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):175–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KYLE T. I., MARRIAN G. F. The metabolic reduction of progesterone to allopregnane-3 alpha:20 alpha-diol in human subjects. Biochem J. 1951 Jul;49(2):162–164. doi: 10.1042/bj0490162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A., Eggleston L. V. The oxidation of pyruvate in pigeon breast muscle. Biochem J. 1940 Mar;34(3):442–459. doi: 10.1042/bj0340442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann P. J., Quastel J. H. Nicotinamide, cozymase and tissue metabolism. Biochem J. 1941 Apr;35(4):502–517. doi: 10.1042/bj0350502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proceedings of the Biochemical Society. Biochem J. 1948;42(1):i.1–i.x. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIEGEL B., HARTOP W. L., Jr, KITTINGER G. W. Studies on the metabolism of radioprogesterone in mice and rats. Endocrinology. 1950 Nov;47(5):311–319. doi: 10.1210/endo-47-5-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMUELS L. T., WEST C. D. The intermediary metabolism of the non-benzenoid steroid hormones. Vitam Horm. 1952;10:251–295. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60849-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER J. J. Conversion of desoxycorticosterone to four allopregnane metabolites by rat liver in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1952 Nov;199(1):235–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern R., Bird L. H. The use of the Waring blender in biochemical work. Biochem J. 1949;44(5):635–637. doi: 10.1042/bj0440635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISWELL J. G., SAMUELS L. T. The metabolism of progesterone by liver tissue in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


