Abstract
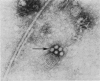
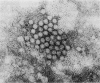
Within 1 week four separate incidents of gastroenteritis presumed to be foodborne were reported by guests of a Winnipeg hotel. Investigation revealed poor food-handling practices and illness among the kitchen staff. Elevated bacterial counts and Escherichia coli were found in 15 of 24 samples of food tested, and Staphylococcus aureus was isolated from 2 pastry samples. Culture of 14 stool samples for bacteria yielded Clostridium perfringens in 1 sample from a staff member and coagulase-positive S. aureus in 2 samples from staff members and 3 from guests. All of the S. aureus isolates were nonenterotoxigenic and had three different phage patterns. Electron microscopy and immunoelectron microscopy revealed the prototype Norwalk virus in five (56%) of nine stool samples; four samples were from guests, and one was from a kitchen employee. The employee had had diarrhea 24 hours before the first outbreak and was thus believed to be the source of the virus infection, possibly through food handling. This is the first report of Norwalk virus isolation and the first of foodborne Norwalk virus transmission in Canada. A review of foodborne Norwalk virus infections is presented.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleton H., Pereira M. S. A possible virus aetiology in outbreaks of food-poisoning from cockles. Lancet. 1977 Apr 9;1(8015):780–781. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92960-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklow N. R., Cukor G., Bedigian M. K., Echeverria P., Greenberg H. B., Schreiber D. S., Trier J. S. Immune response and prevalence of antibody to Norwalk enteritis virus as determined by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):903–909. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.903-909.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGLE J. H., BADGER G. F., FELLER A. E., HODGES R. G., JORDAN W. S., Jr, RAMMELKAMP C. H., Jr A study of illness in a group of Cleveland families. I. Plan of study and certain general observations. Am J Hyg. 1953 Jul;58(1):16–30. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gary G. W., Jr, Kaplan J. E., Stine S. E., Anderson L. J. Detection of Norwalk virus antibodies and antigen with a biotin-avidin immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):274–278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.274-278.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. R., Surowiec J. J., McCloskey D. I., Capuano B., Pierzynski B., Quinn M., Wojnarski R., Parkin W. E., Greenberg H., Gary G. W. Foodborne Norwalk virus. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Feb;115(2):178–184. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn R. A., Janowski H. T., Lieb S., Prather E. C., Greenberg H. B. Norwalk virus gastroenteritis following raw oyster consumption. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Mar;115(3):348–351. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Hazelton P. R., Chuang I., Klisko B. Improved detection of viruses by electron microscopy after direct ultracentrifuge preparation of specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):210–221. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.210-221.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heun E. M., Vogt R. L., Hudson P. J., Parren S., Gary G. W. Risk factors for secondary transmission in households after a common-source outbreak of Norwalk gastroenteritis. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Dec;126(6):1181–1186. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen A. M., Gill M., Bartlett C. L., Cubitt W. D., McSwiggan D. A. Two outbreaks of foodborne gastroenteritis caused by a small round structured virus: evidence of prolonged infectivity in a food handler. Lancet. 1987 Sep 5;2(8558):556–558. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92933-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. E., Feldman R., Campbell D. S., Lookabaugh C., Gary G. W. The frequency of a Norwalk-like pattern of illness in outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis. Am J Public Health. 1982 Dec;72(12):1329–1332. doi: 10.2105/ajph.72.12.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. E., Gary G. W., Baron R. C., Singh N., Schonberger L. B., Feldman R., Greenberg H. B. Epidemiology of Norwalk gastroenteritis and the role of Norwalk virus in outbreaks of acute nonbacterial gastroenteritis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 1):756–761. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leers W. D., Kasupski G., Fralick R., Wartman S., Garcia J., Gary W. Norwalk-like gastroenteritis epidemic in a Toronto hospital. Am J Public Health. 1987 Mar;77(3):291–295. doi: 10.2105/ajph.77.3.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb S., Gunn R. A., Medina R., Singh N., May R. D., Janowski H. T., Woodward W. E. Norwalk virus gastroenteritis. An outbreak associated with a cafeteria at a college. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Feb;121(2):259–268. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. L., Guzewich J. J., Hanrahan J. P., Stricof R., Shayegani M., Deibel R., Grabau J. C., Nowak N. A., Herrmann J. E., Cukor G. Widespread outbreaks of clam- and oyster-associated gastroenteritis. Role of Norwalk virus. N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 13;314(11):678–681. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603133141103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. M., Grohmann G. S., Christopher P. J., Lopez W. A., Davey G. R., Millsom R. H. An Australia-wide outbreak of gastroenteritis from oysters caused by Norwalk virus. Med J Aust. 1979 Oct 6;2(7):329–333. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1979.tb104133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil A. E., Richen D., Lundrie P. A waterborne epidemic of acute infectious non-bacterial gastroenteritis in Alberta, Canada. Can J Public Health. 1985 May-Jun;76(3):199–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. A., Caul E. O., White D. G., Palmer S. R. Role of infected food handler in hotel outbreak of Norwalk-like viral gastroenteritis: implications for control. Lancet. 1988 Aug 6;2(8606):321–323. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92367-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan T., Wills A. An outbreak of gastroenteritis in a psycho-geriatric hospital associated with a small round structured virus. J Hosp Infect. 1986 Nov;8(3):296–299. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(86)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer L. A., Murphy J. J., Kaplan J. E., Pinsky P. F., Chacon D., Walmsley S., Schonberger L. B., Phillips A., Forward K., Goldman C. 25- to 30-nm virus particle associated with a hospital outbreak of acute gastroenteritis with evidence for airborne transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 Jun;127(6):1261–1271. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornhill T. S., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Pattern of shedding of the Norwalk particle in stools during experimentally induced gastroenteritis in volunteers as determined by immune electron microscopy. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):28–34. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truman B. I., Madore H. P., Menegus M. A., Nitzkin J. L., Dolin R. Snow Mountain agent gastroenteritis from clams. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Sep;126(3):516–525. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K. E., Osterholm M. T., Mariotti J. A., Korlath J. A., Lawrence D. H., Ristinen T. L., Greenberg H. B. A foodborne outbreak of Norwalk virus gastroenteritis. Evidence for post-recovery transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Jul;124(1):120–126. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]