Abstract
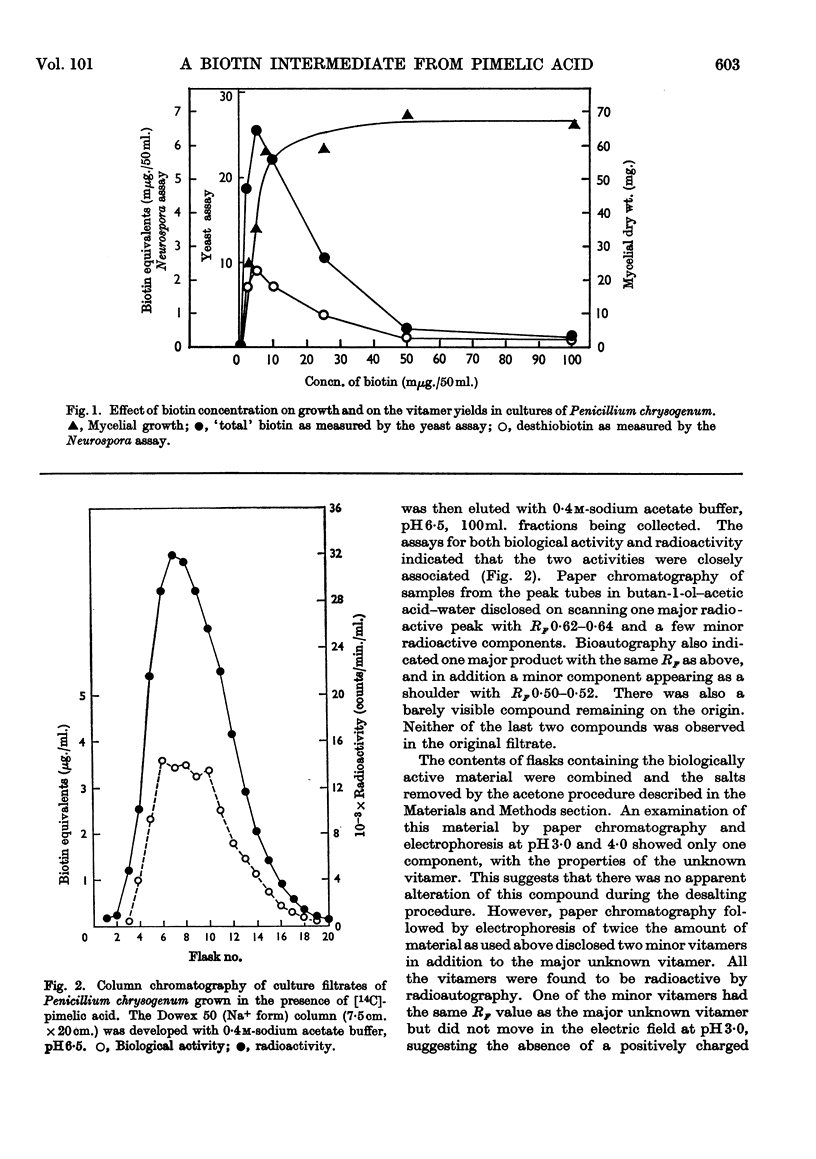
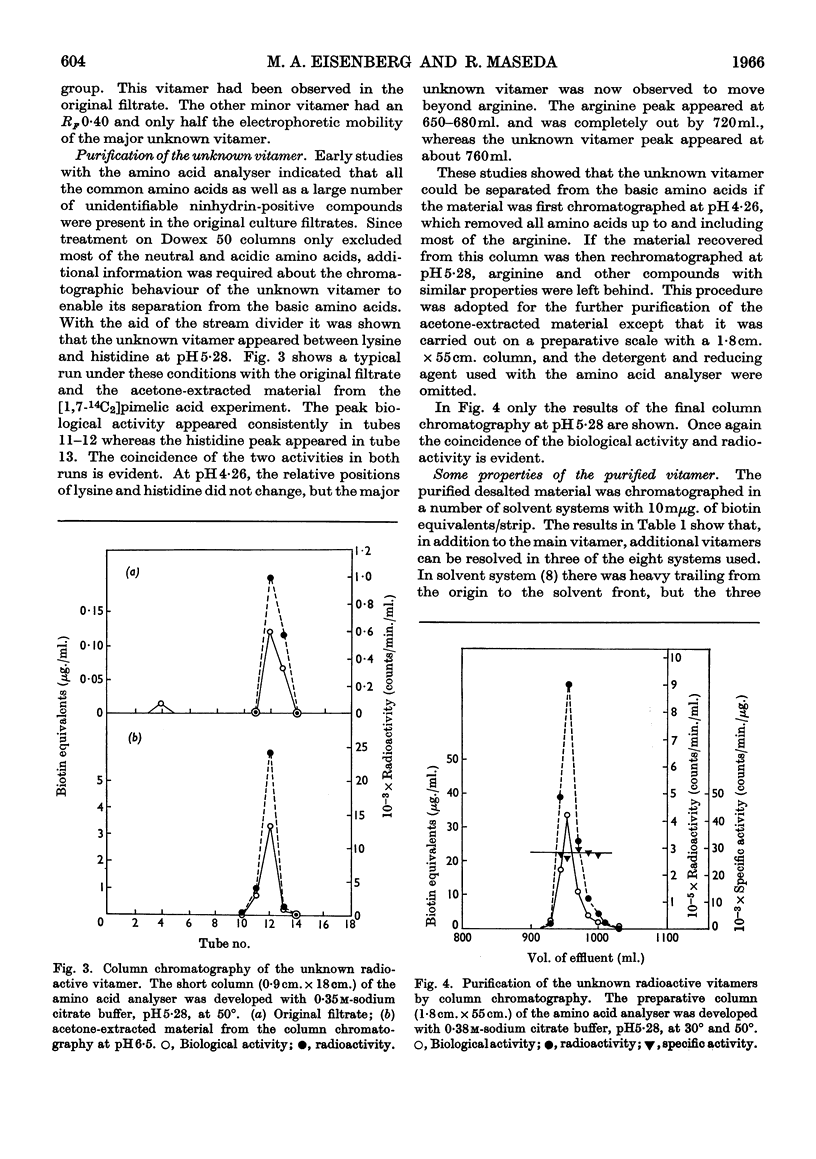
1. An unknown biotin vitamer was obtained in high yields in culture filtrates of Penicillium chrysogenum. 2. Production of this vitamer and desthiobiotin is controlled by the biotin concentration in the medium. 3. The unknown vitamer becomes labelled when the organism is grown in the presence of radioactive pimelic acid. 4. Chromatographic procedures were developed for the purification of the radioactive vitamer. 5. The vitamer is extremely stable in concentrated acid but gives rise to new vitamers under certain conditions. 6. The intermediate role of this vitamer in the synthesis of biotin is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EISENBERG M. A. BIOTIN BIOSYNTHESIS. I. BIOTIN YIELDS AND BIOTIN VITAMERS IN CULTURES OF PHYCOMYCES BLAKESLEEANUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:673–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.673-680.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENBERG M. A. The incorporation of 1,7 C14 pimelic acid into biotin vitamers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Aug 31;8:437–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEZIUS A., RINGELMANN E., LYNEN F. [On the biochemical function of biotin. IV. The biosynthesis of biotin]. Biochem Z. 1963;336:510–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAI C. H., LICHSTEIN H. C. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF BIOTIN IN MICROORGANISMS. II. MECHANISM OF THE REGULATION OF BIOTIN SYNTHESIS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Apr 12;100:36–42. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90424-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


