Abstract
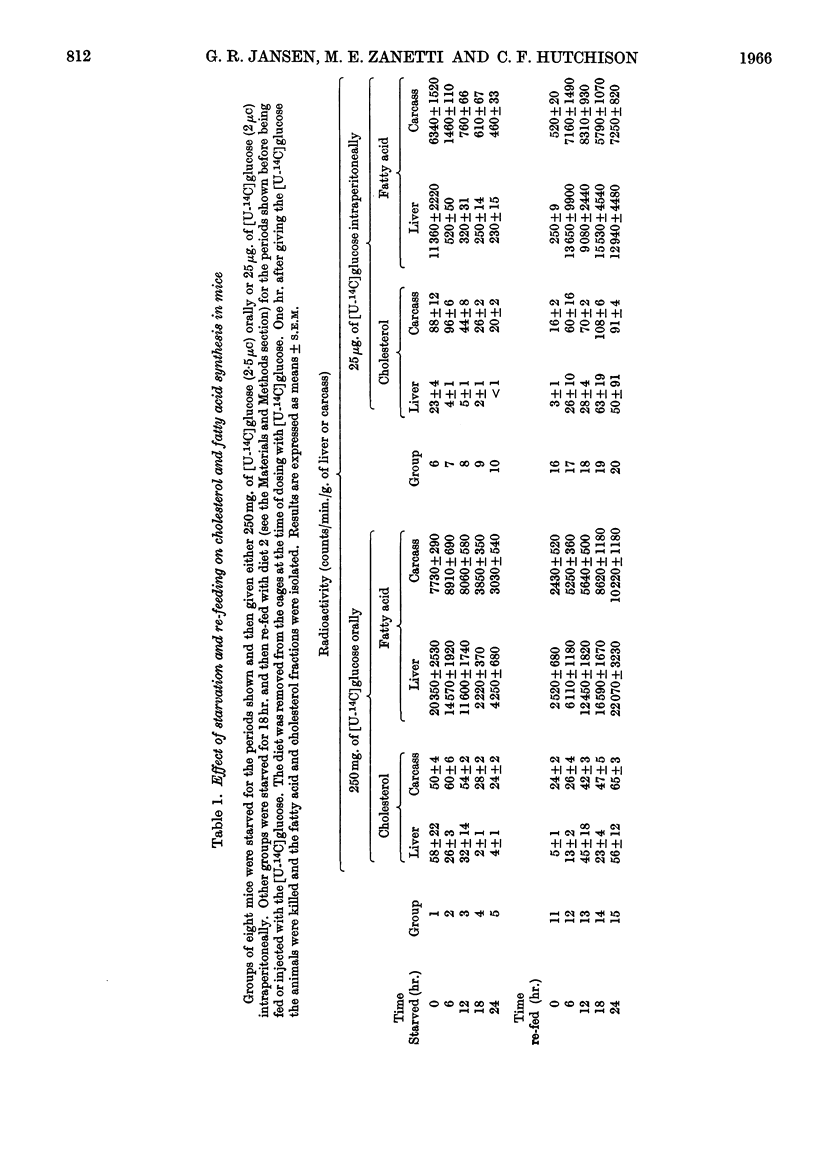
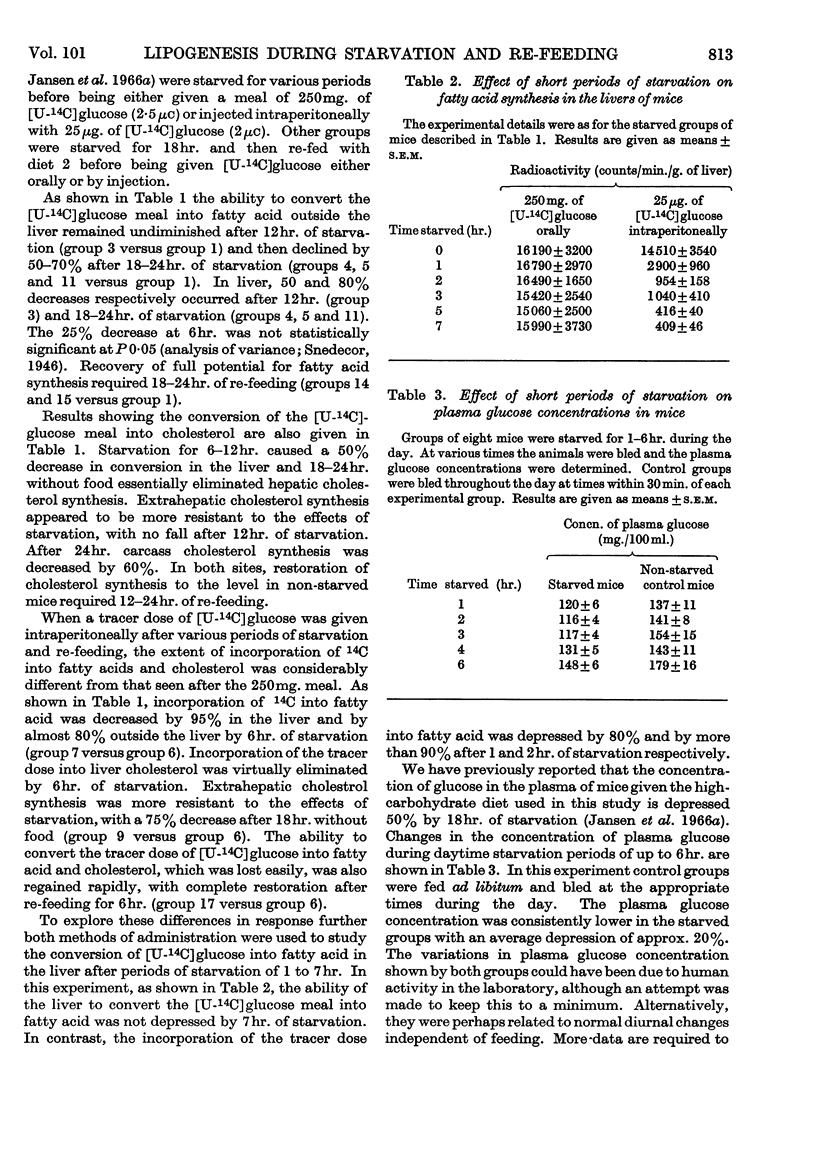
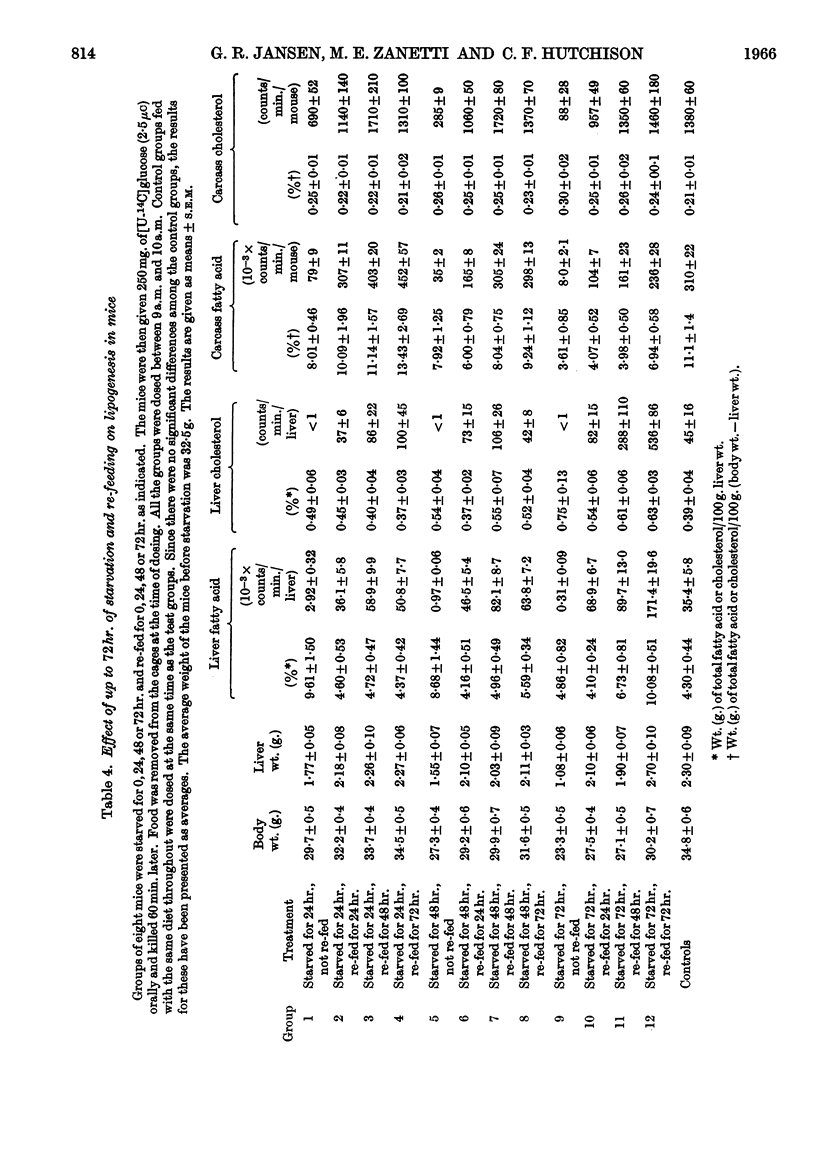
1. Lipogenesis in vivo has been studied in mice given a 250mg. meal of [U-14C]glucose (2·5μc) or given an intraperitoneal injection of 25μg. of [U-14C]glucose (2·0μc). 2. The ability to convert a [U-14C]glucose meal into fatty acid was not significantly depressed by 6–7hr. of starvation. In contrast, incorporation of 14C into fatty acid in the liver after the intraperitoneal dose of [14C]glucose was depressed by 80% and by more than 90% by 1 and 2hr. of starvation respectively. Carcass fatty acid synthesis from the [U-14C]glucose meal was not depressed by 12hr. of starvation, whereas from the tracer dose of [U-14C]glucose the depression in incorporation was 80% after 6hr. of starvation. 3. Re-feeding for 3 days, after 3 days' starvation, raised fatty acid synthesis and cholesterol synthesis in the liver fivefold and tenfold respectively above the levels in non-starved control mice. These increases were associated with an increased amount of both fatty acid and cholesterol in the liver. 4. After 18hr. of starvation incorporation of a [U-14C]glucose meal into carcass and liver glycogen were both increased threefold.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DIPIETRO D. L., SHARMA C., WEINHOUSE S. Studies on glucose phosphorylation in rat liver. Biochemistry. 1962 May 25;1:455–462. doi: 10.1021/bi00909a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECHTER O., HALKERSTON I. D. EFFECTS OF STEROID HORMONES ON GENE REGULATION AND CELL METABOLISM. Annu Rev Physiol. 1965;27:133–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.27.030165.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks S. E., Allmann D. W., Gibson D. M. Inhibition of hyperlipogenesis with puromycin or actinomycin D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 4;106(2):441–444. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen G. R., Hutchon C. F., Zanetti M. E. Studies on lipogenesis in vivo. Effect of dietary fat or starvation on conversion of [14]glucose into fat ad turnover of newly synthsized fat. Biochem J. 1966 May;99(2):323–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0990323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen G. R., Zanetti M. E., Hutchison C. F. Stdies on lipogenesis in vivo. Effects of starvation andre-feeding, and studies on cholesterol synthesis. Biochem J. 1966 May;99(2):333–340. doi: 10.1042/bj0990333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Randle P. J. Regulation of glucose uptake by muscle. 7. Effects of fatty acids, ketone bodies and pyruvate, and of alloxan-diabetes, starvation, hypophysectomy and adrenalectomy, on the concentrations of hexose phosphates, nucleotides and inorganic phosphate in perfused rat heart. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):641–651. doi: 10.1042/bj0930641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER V. R., ONO T. Enzyme patterns in rat liver and Morris hepatoma 5123 during metabolic transitions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:355–362. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J. Fuel and power in the control of carbohydrate metabolism in mammalian muscle. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1964;18:129–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STETTEN M. R., STETTEN D., Jr A study of the nature of glycogen regeneration in the intact animal. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN H. M., TEPPERMAN J. The hexosemonophosphate shunt and adaptive hyperlipogenesis. Diabetes. 1958 Nov-Dec;7(6):478–485. doi: 10.2337/diab.7.6.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN J., TEPPERMAN H. M. Effects of antecedent food intake pattern on hepatic lipogenesis. Am J Physiol. 1958 Apr;193(1):55–64. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN J., TEPPERMAN H. M. Metabolism of glucose-1-C-14 and glucose-6-C-14 by liver slices of refed rats. Am J Physiol. 1961 May;200:1069–1073. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.5.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINUELA E., SALAS M., SOLS A. Glucokinase and hexokinase in liver in relation to glycogen synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1963 Mar;238:1175–1177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


