Abstract
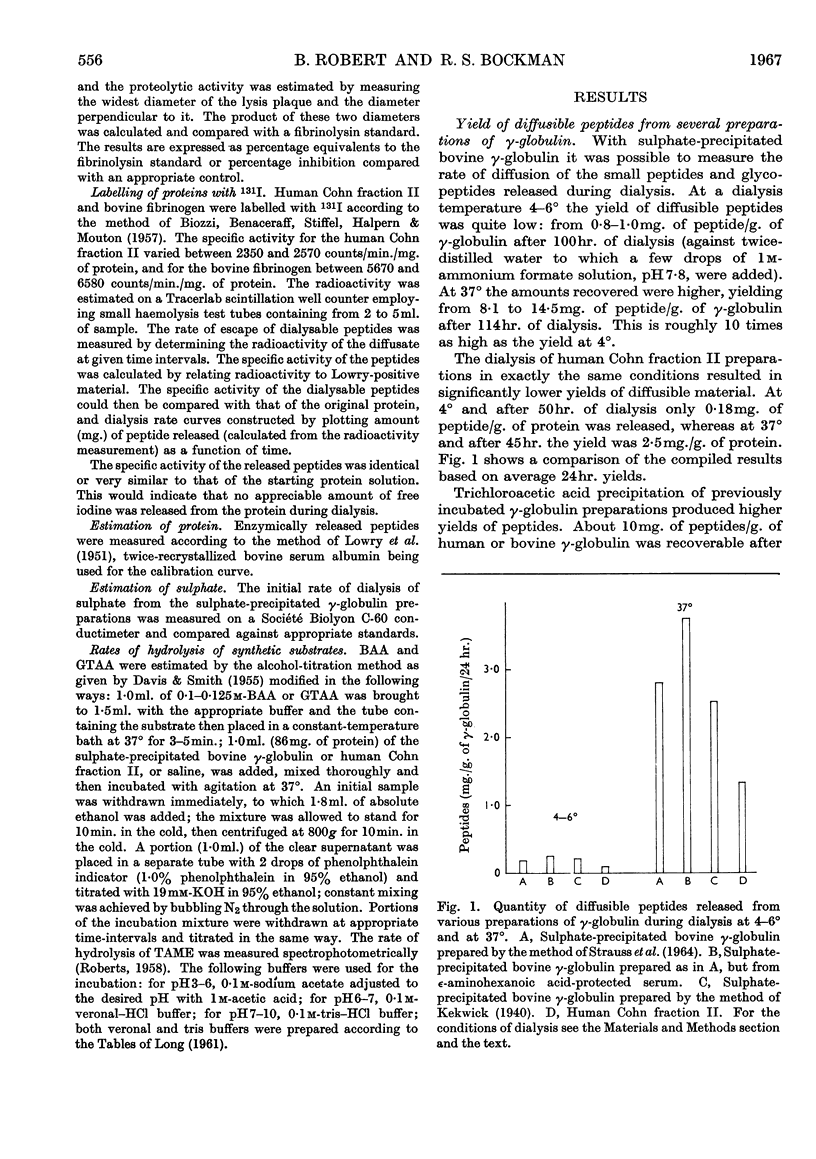
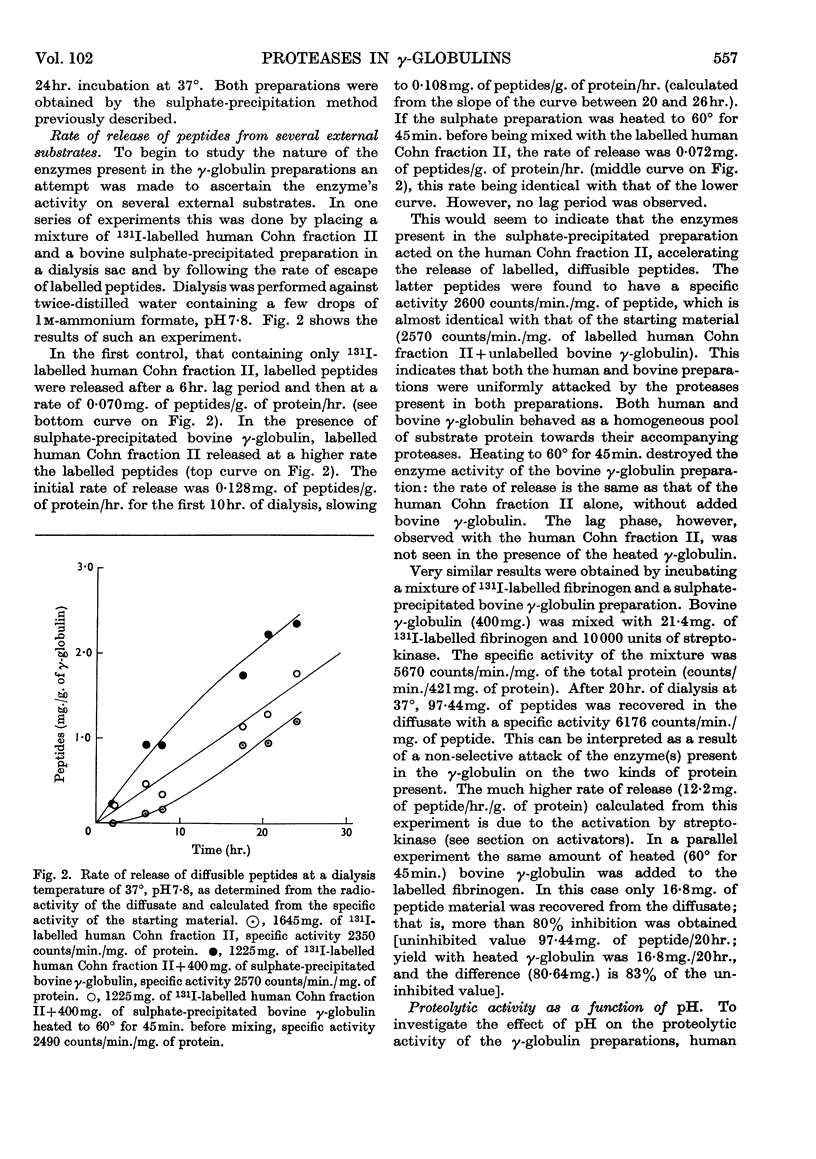
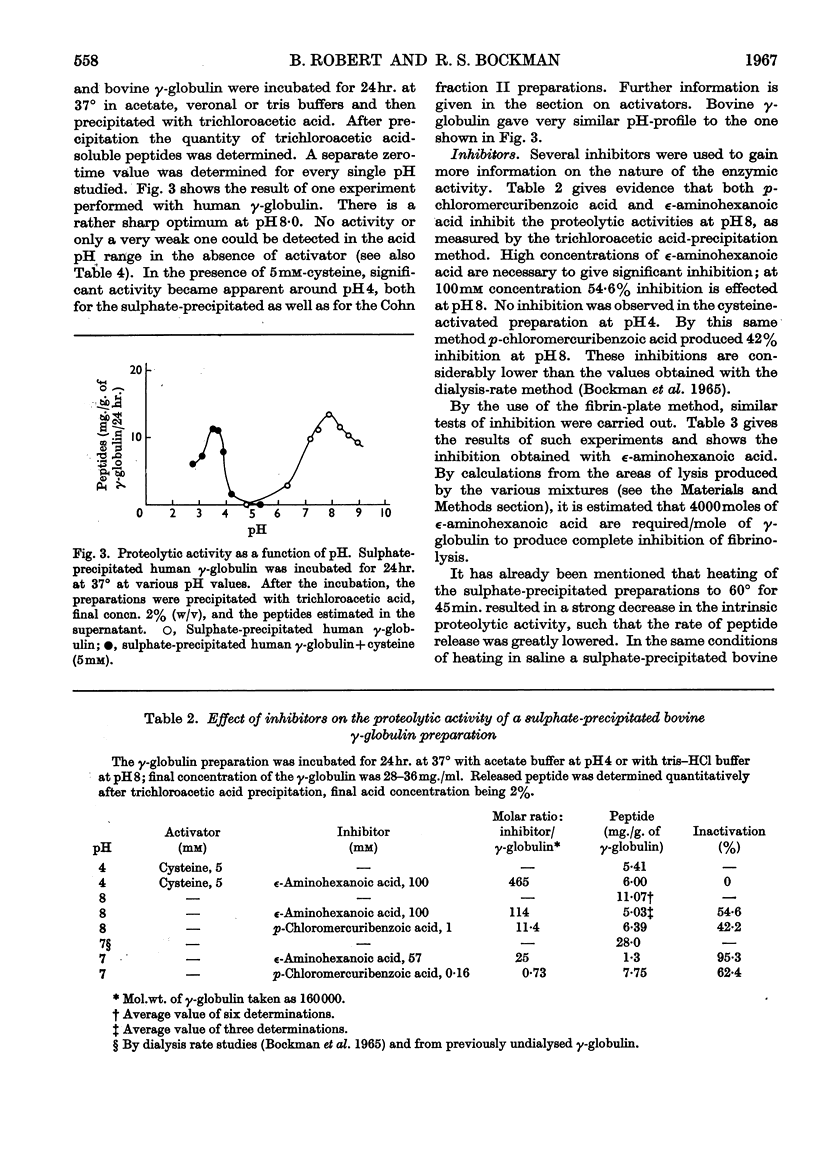
1. The proteolytic activities of several γ-globulin preparations were tested. These included sulphate-precipitated human and bovine preparations and human and bovine Cohn fraction II preparations as well as purified γ-globulin preparations. Up to 14mg. of diffusible peptides and glycopeptides/g. of γ-globulin was liberated after dialysis and up to 10mg. of peptides/g. after incubation and trichloroacetic acid precipitation, as products of the degradation process in incubated γ-globulin. 2. ∈-Aminohexanoic acid and p-chloromercuribenzoic acid, as well as heating at 60° for 40min., were shown to inhibit strongly these proteolytic activities. Streptokinase was shown to activate strongly the proteolytic activity of all the human preparations (sulphate-precipitated, Cohn fraction II, and purified γ-globulin). 3. Two distinct pH optima were shown for human and bovine γ-globulin preparations: one at pH8, the other at pH3·8 (the latter activity could be demonstrated only in the presence of cysteine). 4. Both 131I-labelled human Cohn fraction II and bovine fibrinogen were attacked by a sulphate-precipitated preparation of γ-globulin. Of the synthetic substrates tested toluene-p-sulphonyl-l-arginine methyl ester was hydrolysed by both the sulphate-precipitated and Cohn fraction II preparations, as was benzoyl-l-arginine amide at pH5, but only in the presence of cysteine. 5. These data are interpreted to indicate that at least two enzymes are present in γ-globulin preparations, one being similar to the plasmin system, the other similar to cathepsin B.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABLONDI F. B., HAGAN J. J., PHILIPS M., DE RENZO E. C. Inhibition of plasmin, trypsin and the streptokinase-activated fibrinolytic system by 6-aminocaproic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90100-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. xi-Aminocaproic acid: an inhibitor of plasminogen activation. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):832–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., BIOZZI G., HALPERN B. N., MOUTON D., STIFFEL C. Influence de la quantité d'iode fixee sur les proteines seriques normales et modifiees par la chaleur sur la phagocytose de ces colloïdes par les cellules du S.R.E. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1957 Jan;92(1):89–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOCKMAN R., CREPIN Y., ROBERT B. M'ECANISME DE LA LIB'ERATION DES PEPTIDES DIALYSABLES 'A PARTIR DES GAMMA-GLOBULINES. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 22;260:3515–3518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES G. E., LOWE J. S. PRESENCE OF KALLIKREIN IN THE GAMMA-GLOBULIN PERMEABILITY FACTOR OF GUINEA-PIG SERUM. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Dec;21:491–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb02017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES G. E., LOWER J. S. The effects of guinea-pig gamma globulins on capillary permeability and serum complement. Immunology. 1961 Oct;4:289–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong R., Nisonoff A. Relative labilities of the two types of interchain disulfide bond of rabbit gamma G-immunoglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3883–3891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES K., HENNEY C. S., STANWORTH D. R. STRUCTURAL CHANGES OCCURRING IN 7S GAMMA-GLOBULINS. Nature. 1964 May 9;202:563–566. doi: 10.1038/202563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A. The serum proteins in multiple myelomatosis. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1248–1257. doi: 10.1042/bj0341248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERT B., DENES Y., CREPIN Y. MISE EN 'EVIDENCE DE PEPTIDES DIALYSABLES ACCOMPAGNANT LES GAMMA-GLOBULINES DANS LEUR PR'EPARATION. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1965 Jan 11;260:734–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS P. S. Measurement of the rate of plasmin action on synthetic substrates. J Biol Chem. 1958 May;232(1):285–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKVARIL F., GRUNBERGER D. Inhibition of spontaneous splitting of gamma-globulin preparations with episilon-aminocaproic acid. Nature. 1962 Nov 3;196:481–482. doi: 10.1038/196481a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBER H. A., PETERSON E. A. Protein chromatography on ion exchange cellulose. Fed Proc. 1958 Dec;17(4):1116–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS A. J., KEMP P. G., Jr, VANNIER W. E., GOODMAN H. C. PURIFICATION OF HUMAN SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULIN FOR IMMUNOLOGIC STUDIES: GAMMA-GLOBULIN FRAGMENTATION AFTER SULFATE PRECIPITATION AND PROLONGED DIALYSIS. J Immunol. 1964 Jul;93:24–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALLAN H. H., JONES M. E., FRUTON J. S. On the proteolytic enzymes of animal tissues. X. Beef spleen cathepsin C. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):793–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROLL W., SHERRY S., WACHMAN J. The action of plasmin on synthetic substrates. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIMER H. E., MOSHIN J. R. Serum glyco protein concentrations in experimental tuberculosis of guinea pigs. Am Rev Tuberc. 1953 Oct;68(4):594–602. doi: 10.1164/art.1953.68.4.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


