Abstract
1. The metabolism of the phosphorothionate parathion in vitro was examined by using [32P]parathion and microsomes isolated from the livers of various animal species. 2. The major metabolic products of parathion in this system in vitro were identified as diethyl 4-nitrophenyl phosphate (paraoxon), diethyl hydrogen phosphate, diethyl hydrogen phosphorothionate and p-nitrophenol. 3. The reaction leading to the formation of diethyl hydrogen phosphorothionate and p-nitrophenol requires the same cofactors (NADPH and oxygen) required for metabolism of parathion to its active anti-acetylcholinesterase paraoxon. 4. The enzyme activity towards parathion per unit weight of liver is increased some 65–130% by pretreatment of male rats with phenobarbital and 3,4-benzopyrene. 5. The metabolism of parathion is inhibited by incubation in a nitrogen atmosphere and in an atmosphere containing carbon monoxide. Pure oxygen is also inhibitory. These results are discussed in terms of a deficiency of oxygen for maximal activity as well as the lability of some component of the system to oxidation.
Full text
PDF


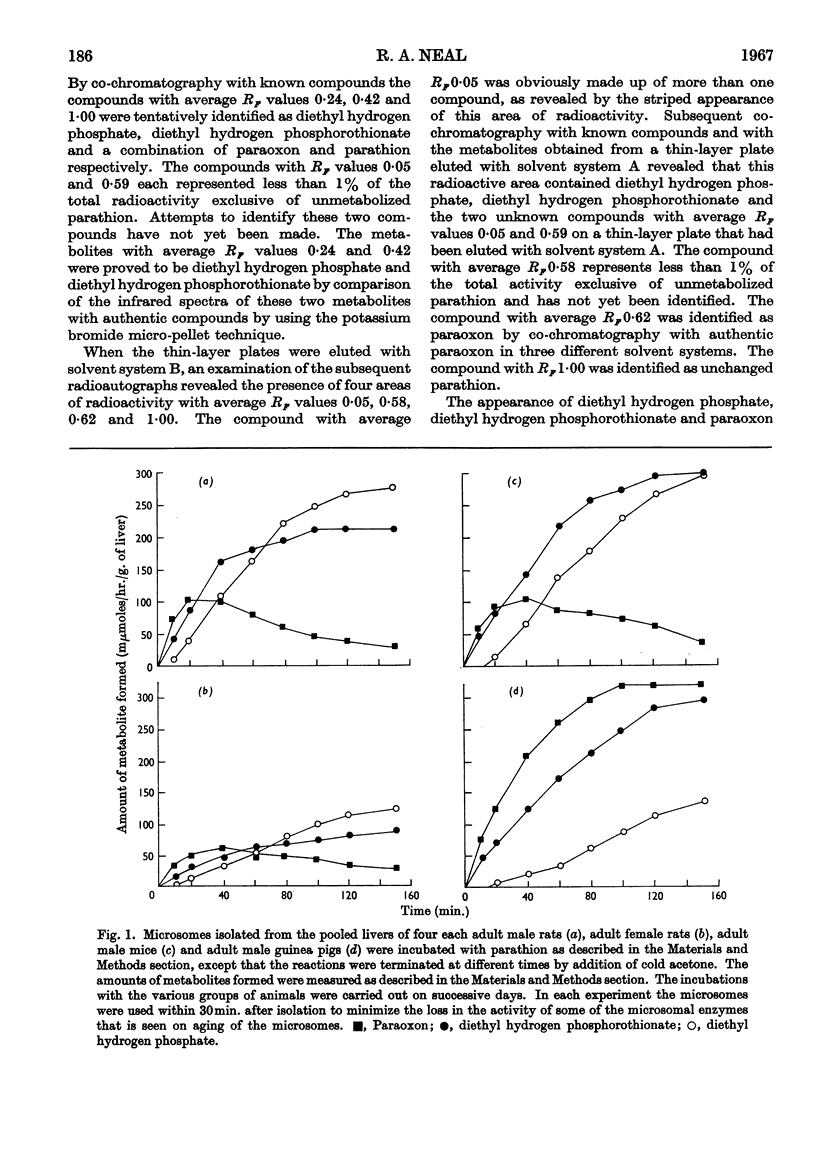
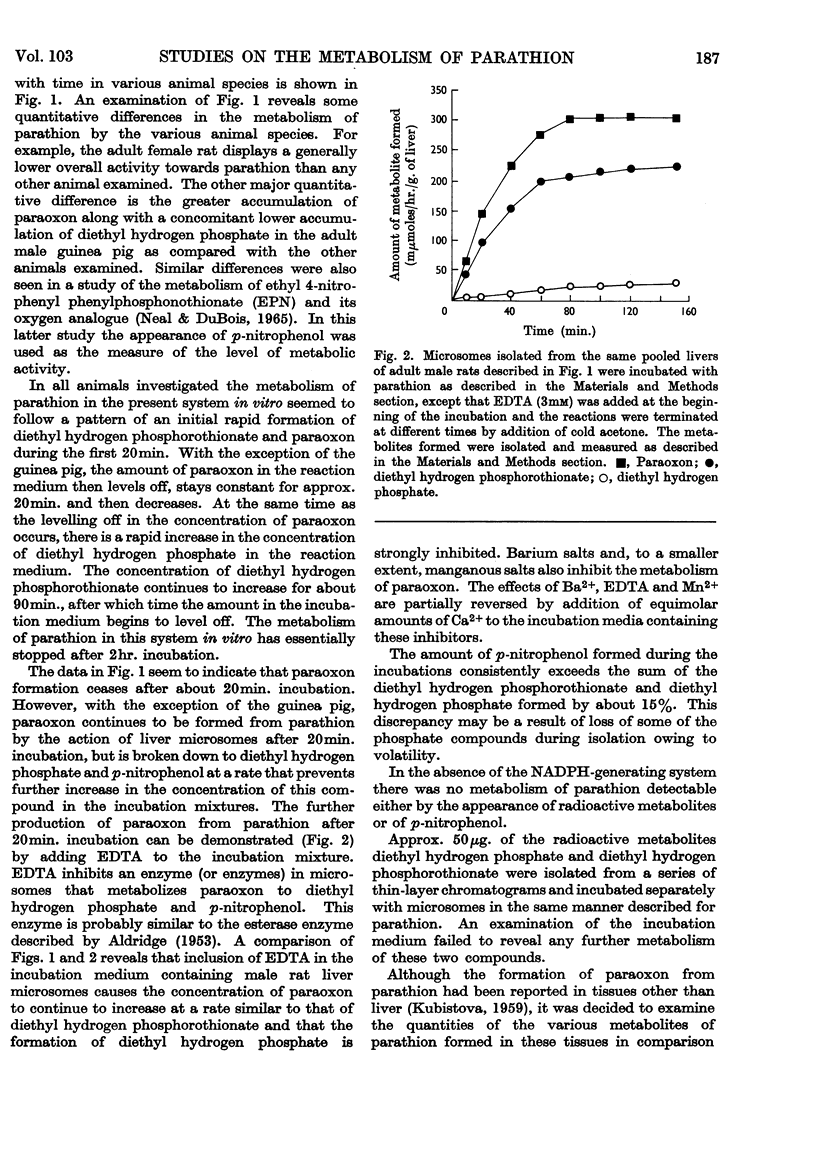




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Serum esterases. I. Two types of esterase (A and B) hydrolysing p-nitrophenyl acetate, propionate and butyrate, and a method for their determination. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):110–117. doi: 10.1042/bj0530110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALL W. L., SINCLAIR J. W., CREVIER M., KAY K. Modification of parathion's toxicity for rats by pretreatment with chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticides. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1954 Jul;32(4):440–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER D. Y., LEVIN S., NARASIMHULU S., ROSENTHAL O. PHOTOCHEMICAL ACTION SPECTRUM OF THE TERMINAL OXIDASE OF MIXED FUNCTION OXIDASE SYSTEMS. Science. 1965 Jan 22;147(3656):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3656.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cram R. L., Juchau M. R., Fouts J. R. Stimulation by chlordane of hepatic drug metabolism in the squirrel monkey. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Dec;66(6):906–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON A. N. The conversion of schra dan (OMPA) and parathion into inhibitors of cholinesterase by mammalian liver. Biochem J. 1955 Oct;61(2):203–209. doi: 10.1042/bj0610203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIGGLE W. M., GAGE J. C. Cholinesterase inhibition by parathion in vivo. Nature. 1951 Dec 8;168(4284):998–998. doi: 10.1038/168998a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIGGLE W. M., GAGE J. C. Cholinesterase inhibition in vitro by OO-diethyl O-p-nitrophenyl thiophosphate (parathion, E 605). Biochem J. 1951 Sep;49(4):491–494. doi: 10.1042/bj0490491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS K. P., THURSH D. R., MURPHY S. D. Studies on the toxicity and pharmacologic actions of the dimethoxy ester of benzotriazine dithiophosphoric acid (DBD, guthion). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Feb;119(2):208–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAGE J. C. A cholinesterase inhibitor derived from OO-diethyl O-p-nitrophenyl thiophosphate in vivo. Biochem J. 1953 Jun;54(3):426–430. doi: 10.1042/bj0540426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., ISHERWOOD F. A. Separation of the phosphoric esters on the filter paper chromatogram. Nature. 1949 Dec 31;164(4183):1107-12, illust. doi: 10.1038/1641107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUBISTOVA J. Parathion metabolism in female rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1959 Feb 1;118(3-4):308–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAIN A. R. The purification of the enzyme hydrolysing diethyl p-nitrophenyl phosphate (paraoxon) in sheep serum. Biochem J. 1960 Jan;74:10–20. doi: 10.1042/bj0740010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAIN A. R. The role of A-esterase in the acute toxicity of paraoxon, TEPP, and parathion. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1956 Mar;34(2):197–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY S. D., DUBOIS K. P. Enzymatic conversion of the dimethoxy water of benzotriazine dithiophosphoric acid to an anticholinesterase agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Apr;119(4):572–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYERS D. K., MENDEL B., GERSMANN H. R., KETELAAR J. A. A. Oxidation of thiophosphate insecticides in the rat. Nature. 1952 Nov 8;170(4332):805–807. doi: 10.1038/170805b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKATSUGAWA T., DAHM P. A. PARATHION ACTIVATION ENZYMES IN THE FAT BODY MICROSOMES OF THE AMERICAN COCKROACH. J Econ Entomol. 1965 Jun;58:500–509. doi: 10.1093/jee/58.3.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEAL R. A., DUBOIS K. P. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF DETOXIFICATION OF CHOLINERGIC PHOSPHOROTHIOATES. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 May;148:185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'BRIEN R. D. Activation of thionophosphates by liver microsomes. Nature. 1959 Jan 10;183(4654):121–122. doi: 10.1038/183121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER J. L., O'BRIEN R. D. PARATHION ACTIVATION BY LIVERS OF AQUATIC AND TERRESTRIAL VERTEBRATES. Science. 1964 Apr 3;144(3614):55–57. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3614.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


