Abstract
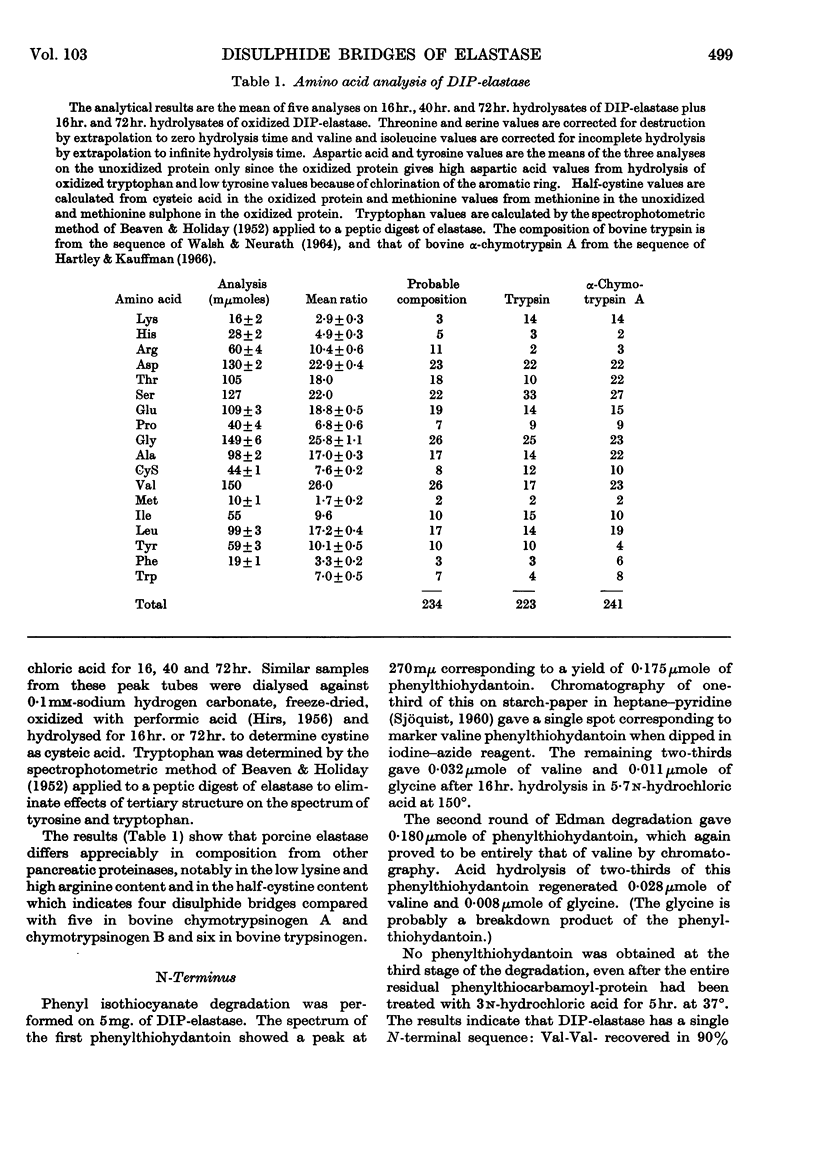
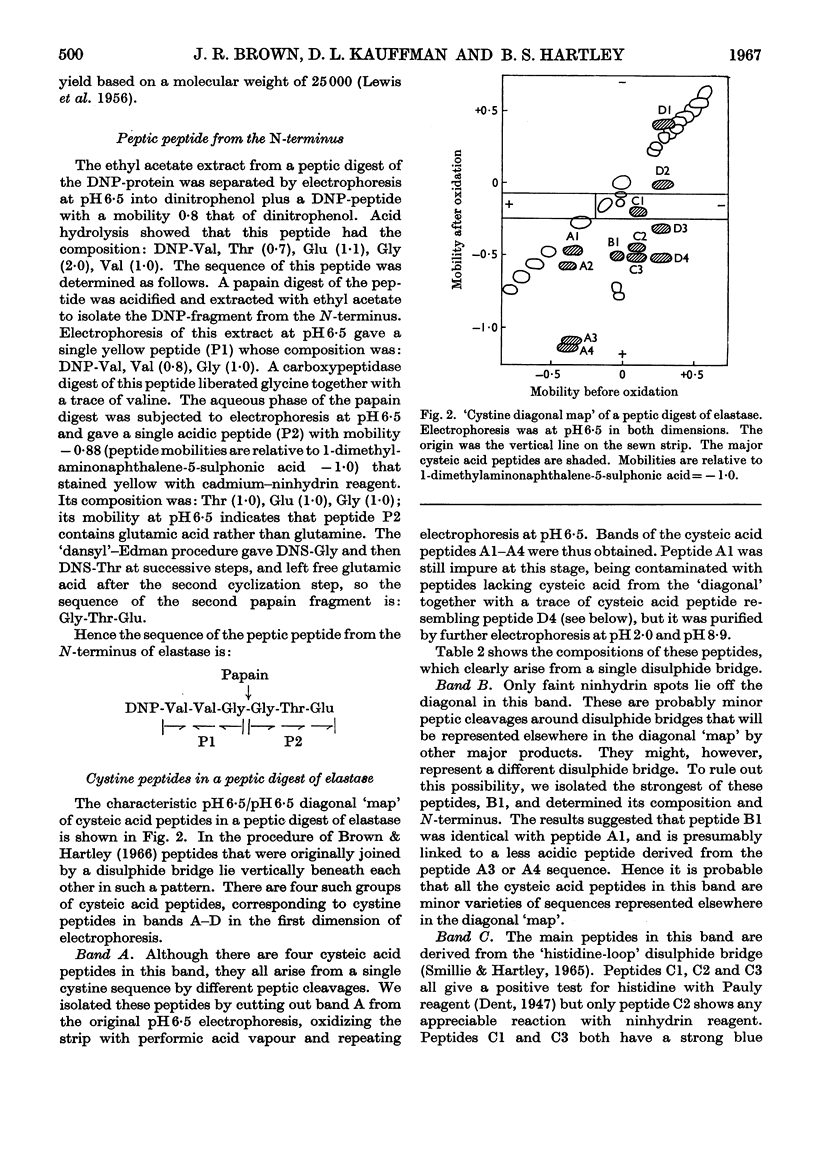
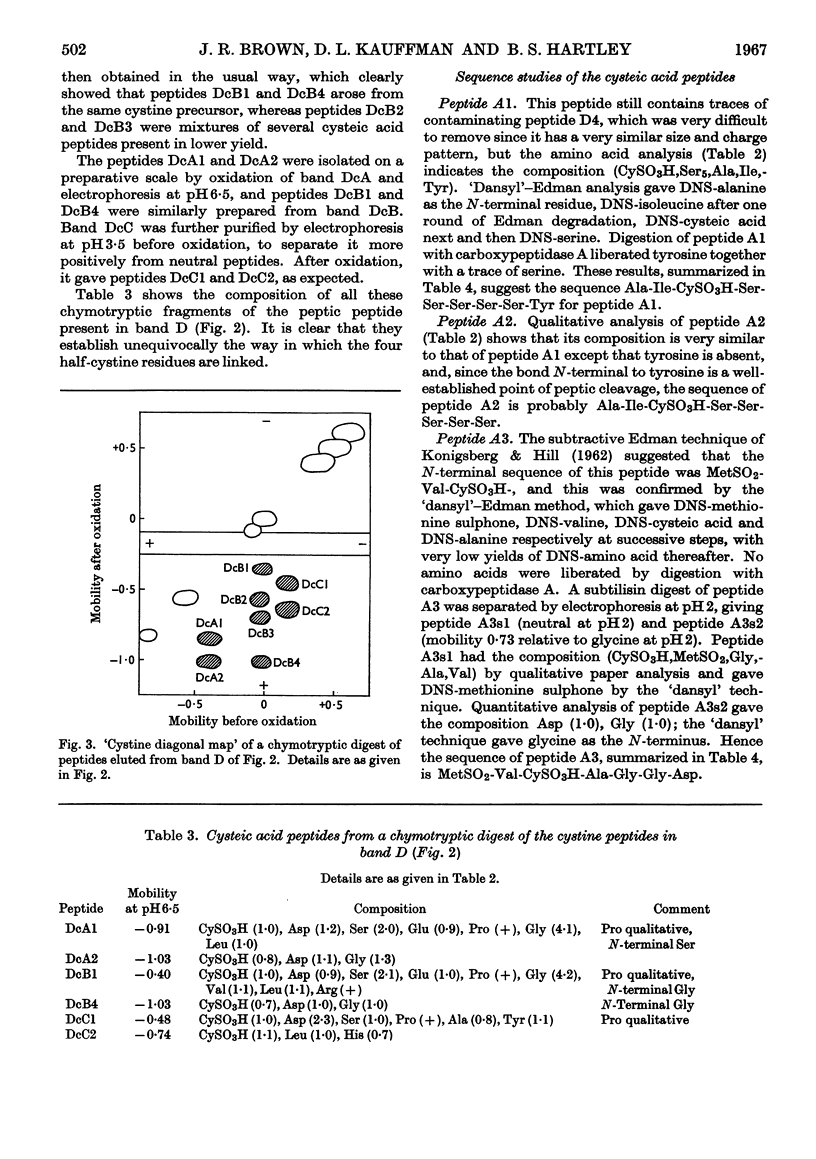
1. The amino acid composition and N-terminal groups of purified elastase show that it is a single peptide chain of 234 residues. 2. The N-terminal sequence is Val-Val-Gly-Gly-Thr-Glu-. 3. The sequences around the four disulphide bridges were determined by using a `diagonal' electrophoretic technique. 4. These four bridges are homologous with the four common to bovine trypsin and chymotrypsin. 5. Out of 83 residues of the elastase sequence so far determined, 43 are homologous with similar regions of trypsin and chymotrypsin. 6. The evolutionary ancestry of these enzymes is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEAVEN G. H., HOLIDAY E. R. Ultraviolet absorption spectra of proteins and amino acids. Adv Protein Chem. 1952;7:319–386. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENDER M. L., KEZDY J. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF PROTEOLYTIC ENZYMES. Annu Rev Biochem. 1965;34:49–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.34.070165.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINK N. G., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Pancreatic elastase: purification, properties, and function. J Biol Chem. 1956 Oct;222(2):705–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R., Hartley B. S. Location of disulphide bridges by diagonal paper electrophoresis. The disulphide bridges of bovine chymotrypsinogen A. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):214–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1010214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent C. E. The amino-aciduria in Fanconi syndrome. A study making extensive use of techniques based on paper partition chromatography. Biochem J. 1947;41(2):240–253. doi: 10.1042/bj0410240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY W. R., HARTLEY B. S. THE STRUCTURE OF A CHYMOTRYPTIC PEPTIDE FROM PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:379–380. doi: 10.1042/bj0890379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTLEY B. S., NAUGHTON M. A., SANGER F. The amino acid sequence around the reactive serine of elastase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:243–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S., Brown J. R., Kauffman D. L., Smillie L. B. Evolutionary similarities between pancreatic proteolytic enzymes. Nature. 1965 Sep 11;207(5002):1157–1159. doi: 10.1038/2071157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S., Kauffman D. L. Corrections to the amino acid sequence of bovine chymotrypsinogen A. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):229–231. doi: 10.1042/bj1010229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INAGAMI T. THE MECHANISM OF THE SPECIFICITY OF TRYPSIN CATALYSIS. I. INHIBITION BY ALKYL AMMONIUM IONS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:787–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONIGSBERG W., HILL R. J. The structure of human hemoglobin. III. The sequence of amino acids in the tryptic peptides of the alpha chain. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2547–2561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARES-GUIA M., SHAW E. STUDIES ON THE ACTIVE CENTER OF TRYPSIN. THE BINDING OF AMIDINES AND GUANIDINES AS MODELS OF THE SUBSTRATE SIDE CHAIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1579–1585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAUGHTON M. A., SANGER F., HARTLEY B. S., SHAW D. C. The amino acid sequence around the reactive serine residue of some proteolytic enzymes. Biochem J. 1960 Oct;77:149–163. doi: 10.1042/bj0770149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAUGHTON M. A., SANGER F. Purification and specificity of pancreatic elastase. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:156–163. doi: 10.1042/bj0780156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH I. Colour reactions on paper chromatograms by a dipping technique. Nature. 1953 Jan 3;171(4340):43–44. doi: 10.1038/171043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smillie L. B., Hartley B. S. Histidine sequences in the active centres of some 'serine' proteinases. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):232–241. doi: 10.1042/bj1010232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smillie L. B., Hartley B. S. The disulphide bridges of chymotrypsinogen B. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):933–936. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80341-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSH K. A., NEURATH H. TRYPSINOGEN AND CHYMOTRYPSINOGEN AS HOMOLOGOUS PROTEINS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:884–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



