Abstract
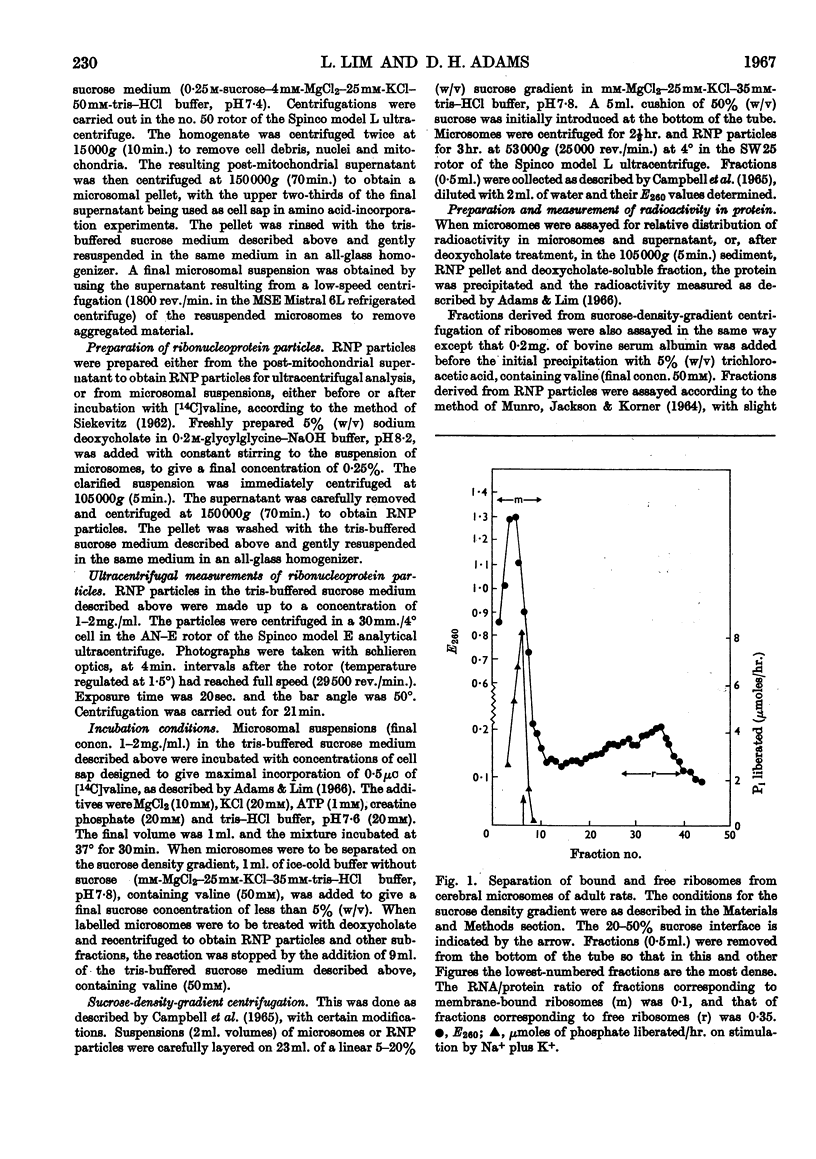
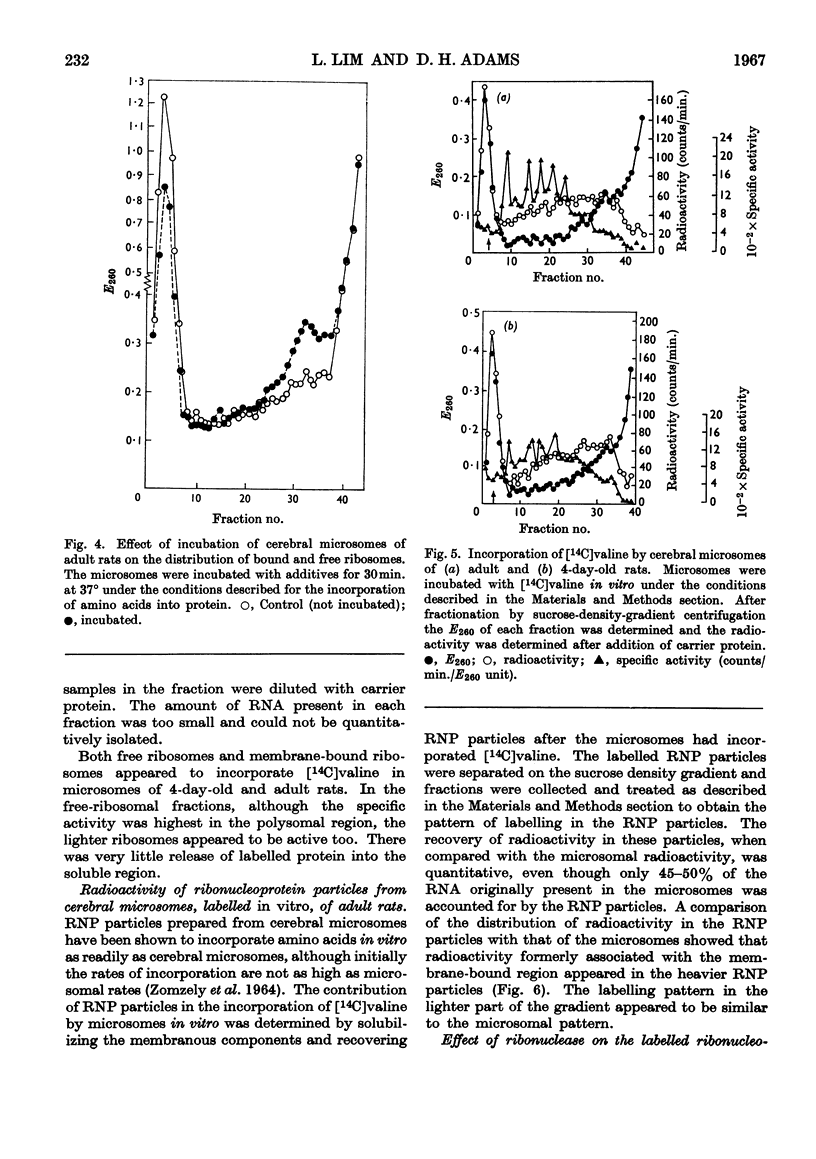
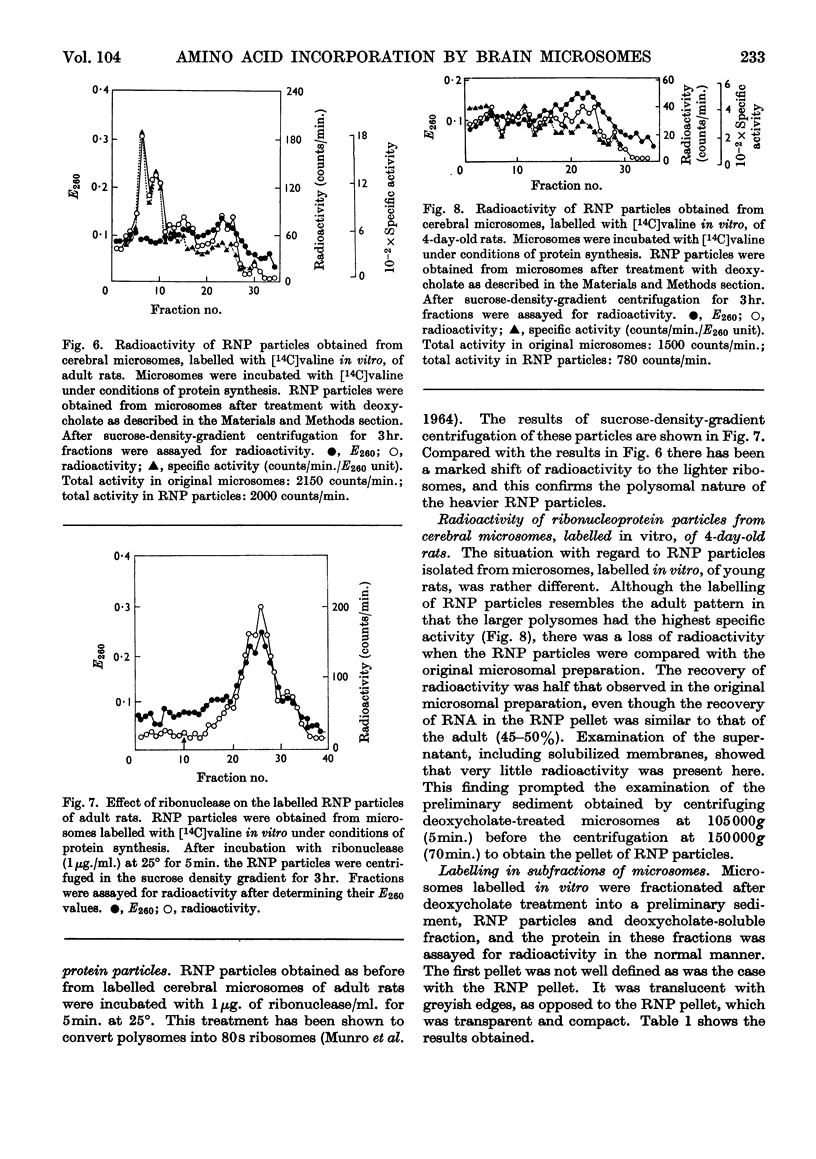
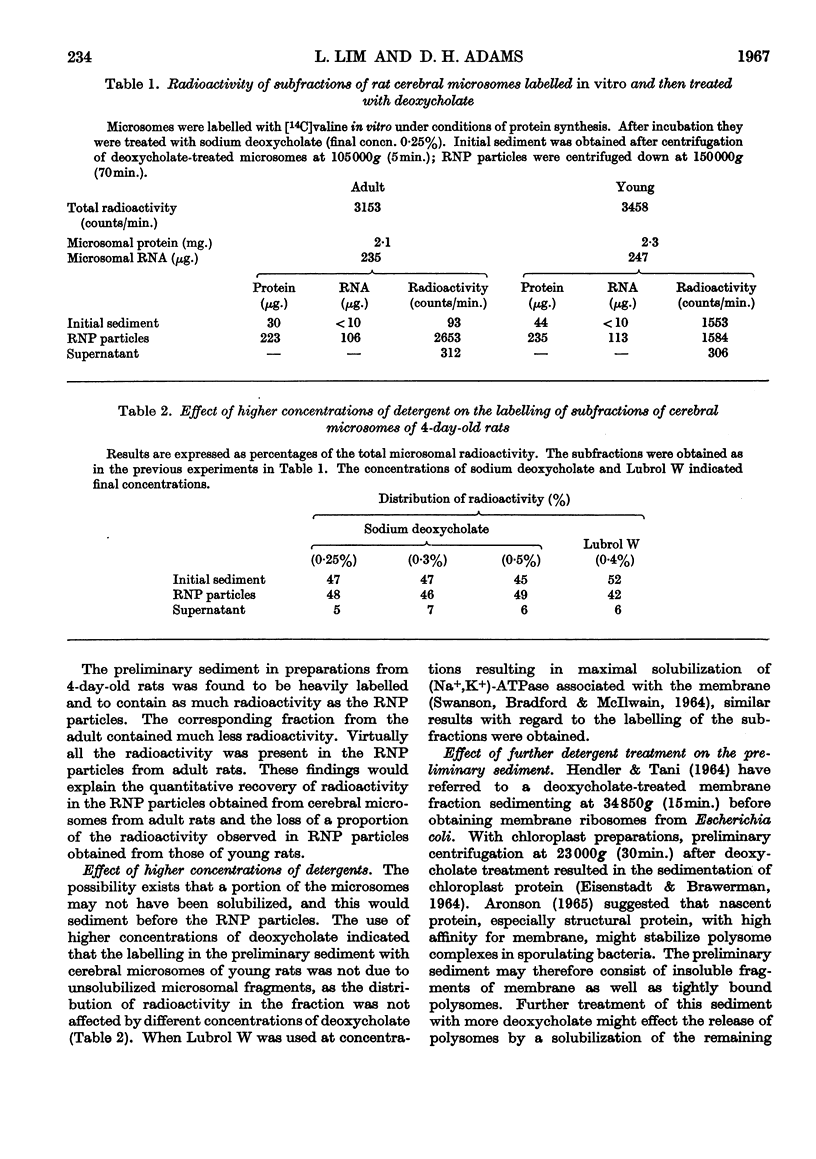
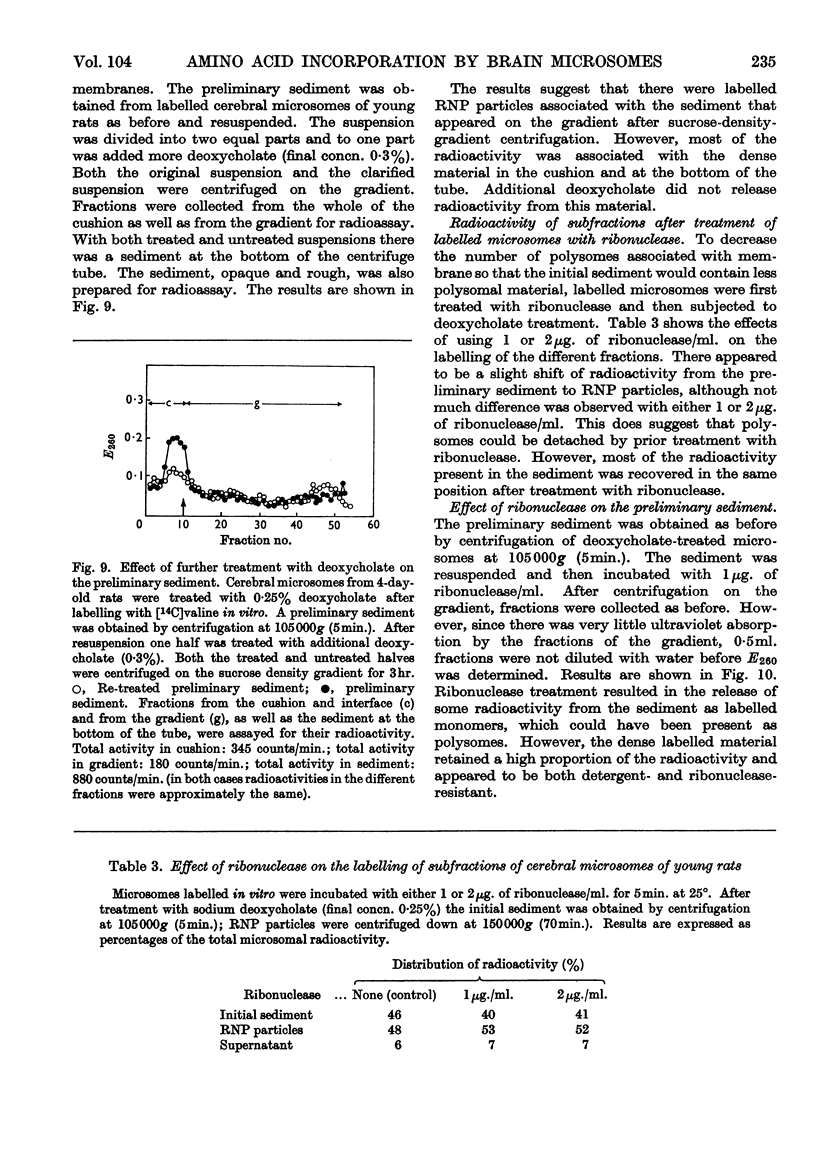
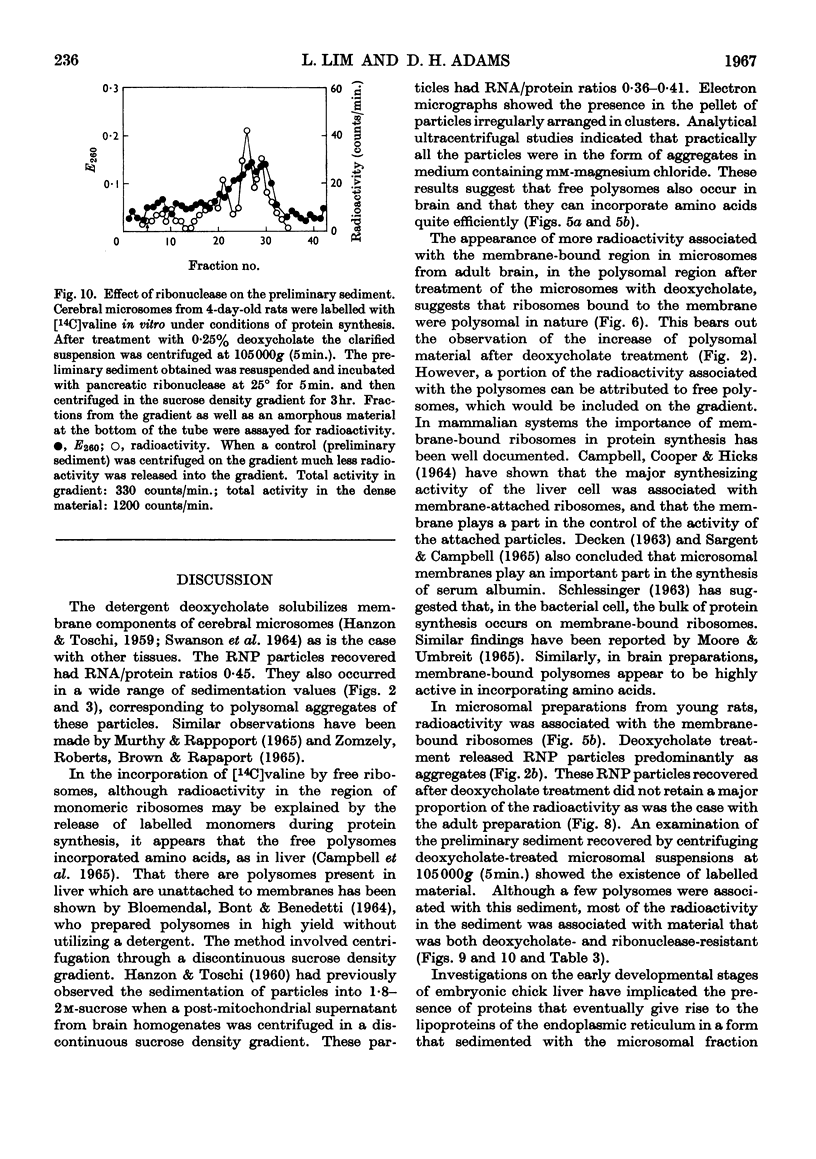
1. After incorporation of [14C]valine in vitro, cerebral microsomes were separated into membrane-bound and free ribosomes by sucrose-density-gradient centrifugation. 2. In preparations from both 4-day-old and adult rats, free and bound ribosomes incorporated [14C]valine. Free ribosomes could be found as polysomes, which were highly active. 3. Microsomes labelled with [14C]valine in vitro were fractionated after deoxycholate treatment into a preliminary sediment, sedimented at 105000g (5min.), and ribonucleoprotein particles, sedimented at 150000g (70min.), to determine the role of membrane-bound ribosomes. In the adult the ribonucleoprotein particles retained most of the radioactivity, whereas in the young the preliminary sediment was as highly labelled as the ribonucleoprotein particles. 4. The labelled preliminary sediment from young preparations was both ribonuclease- and deoxycholate-resistant, and the nature of this material is discussed in terms of a possible structural component of microsomal membranes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACS G., NEIDLE A., WAELSCH H. Brain ribosomes and amino acid incorporation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jun 24;50:403–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90356-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. H., Lim L. Amino acid incorporation by preparations from the developing rat brain. Biochem J. 1966 May;99(2):261–265. doi: 10.1042/bj0990261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. Adsorption of polysomes to bacterial membranes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):505–514. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOEMENDAL H., BONT W. S., BENEDETTI E. L. PREPARATION OF RAT-LIVER POLYSOMES WITHOUT THE UTILIZATION OF DETERGENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 18;87:177–180. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEMENTE C. D. REGENERATION IN THE VERTEBRATE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1964;6:257–301. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60771-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLOUET D. H., RICHTER D. The incorporation of [35S] labelled methionine into the proteins of the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1959 Jan;3(3):219–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1959.tb12628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. N., Cooper C., Hicks M. Studies on the role of the morphological constituents of the microsome fraction from rat liver in protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):225–234. doi: 10.1042/bj0920225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. N., Serck-Hanssen G., Lowe E. Studies on the protein-synthesizing activity of the ribosomes of rat liver. The activity of free polysomes. Biochem J. 1965 Nov;97(2):422–431. doi: 10.1042/bj0970422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGMAN W., SPORN M. B. MOLECULAR THEORIES OF MEMORY. Science. 1964 Apr 3;144(3614):26–29. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3614.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENSTADT J. M., BRAWERMAN G. THE PROTEIN-SYNTHESIZING SYSTEMS FROM THE CYTOPLASM AND THE CHLOROPLASTS OF EUGLENA GRACILIS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Dec;10:392–402. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUMAGALLI R., GROSSI E., POLETTI P., POLETTI R. STUDIES ON LIPIDS IN BRAIN TUMOURS--I. J Neurochem. 1964 Aug;11:561–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb11453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURST S., LAJTHA A., WAELSCH H. Amino acid and protein metabolism of the brain. III. Incoporation of lysine into the proteins of various brain areas and their cellular fractions. J Neurochem. 1958;2(2-3):216–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANZON V., TOSCHI G. Centrifugation of brain microsomes in a density gradient. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Nov;21:332–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDLER R. W., TANI J. ON THE CYTOLOGICAL UNIT FOR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN VIVO IN E. COLI. II. STUDIES WITH INTACT CELLS OF TYPE B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 17;80:294–306. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSHAW E. C., BOJARSKI T. B., HIATT H. H. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY FREE AND BOUND RAT LIVER RIBOSOMES IN VIVO AND IN VITRO. J Mol Biol. 1963 Aug;7:122–129. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLBERT R. B., SCHMITZ H., BRUMM A. F., POTTER V. R. Nucleotide metabolism. II. Chromatographic separation of acid-soluble nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jul;209(1):23–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURTHY M. R., RAPPOPORT D. A. BIOCHEMISTRY OF THE DEVELOPING RAT BRAIN. VI. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF RIBOSOMES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 11;95:132–145. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. D., Umbreit W. W. Membrane-associated protein synthesis in Streptococcus faecalis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 15;103(3):466–477. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro A. J., Jackson R. J., Korner A. Studies on the nature of polysomes. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):289–299. doi: 10.1042/bj0920289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALAY S. L., PALADE G. E. The fine structure of neurons. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Jan;1(1):69–88. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollak J. K., Ward K., Shorey C. D. The formation of a membranous reticulum by the interaction of reticulosomes and micellar phospholipids. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):564–567. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMACHANDRAN K., WALKER T. K. Glucose metabolism in Candida species. Biochem J. 1957 Jan;65(1):20–24. doi: 10.1042/bj0650020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SATAKE M., MASE K., TAKAHASHI Y., OGATA K. Incorporation of leucine into microsomal protein by a cell-free system of guinea-pig brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 1;41:366–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLESSINGER D. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY POLYRIBOSOMES ON PROTOPLAST MEMBRANES OF B. MEGATERIUM. J Mol Biol. 1963 Nov;7:569–582. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson P. D., Bradford H. F., McIlwain H. Stimulation and solubilization of the sodium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase of cerebral microsomes by surface-active agents, especially polyoxyethylene ethers: actions of phospholipases and a neuraminidase. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):235–247. doi: 10.1042/bj0920235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zomzely C. E., Roberts S., Brown D. M., Rapaport D. Isolation of 55-S ribonucleoprotein particles with amino acid-incorporating activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 15;103(3):529–531. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der DECKEN Labeling with 14C amino acids of albumin-like protein by rat liver ribonucleoprotein particles. J Cell Biol. 1963 Mar;16:471–481. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]