Abstract
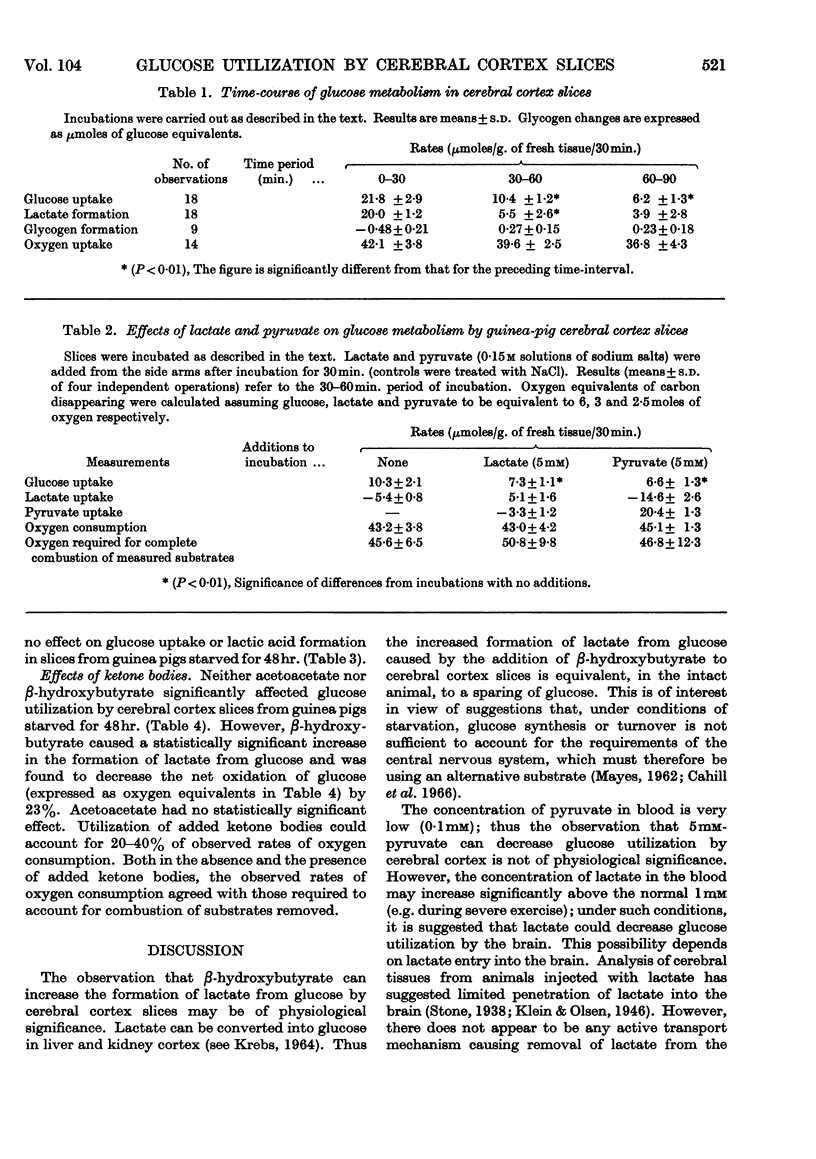
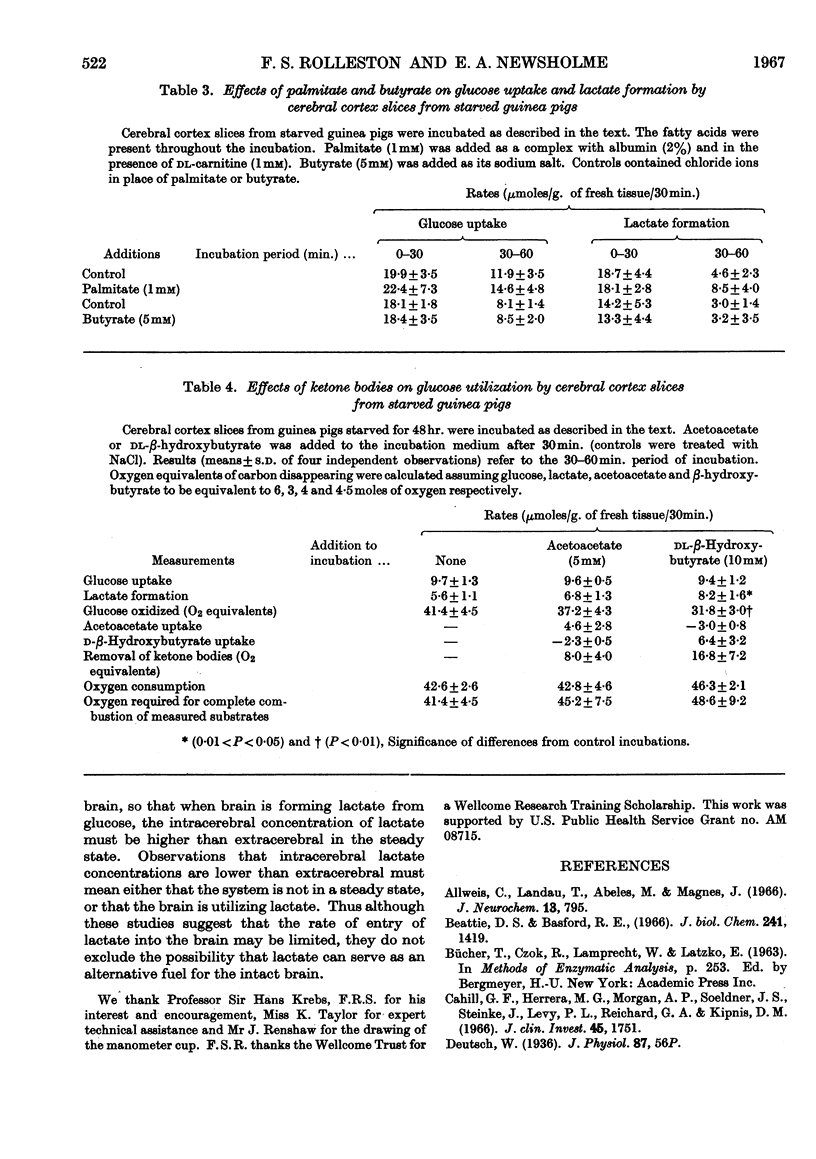
1. Starvation did not affect the rates of glucose utilization or lactate formation by guinea-pig cerebral cortex slices. 2. Palmitate (1mm), butyrate (5mm) or acetoacetate (5mm) did not affect glucose utilization or lactate formation by cerebral cortex slices from guinea pigs starved for 48hr. 3. dl-β-Hydroxybutyrate (10mm) increased the formation of lactate without affecting glucose utilization by cerebral cortex slices from guinea pigs starved for 48hr. This implies that β-hydroxybutyrate decreased the rate of glucose oxidation. 4. Metabolism of added ketone bodies can account for 20–40% of observed rates of oxygen consumption. 5. Lactate or pyruvate (5mm) decreased the rates of glucose utilization by guinea-pig cerebral cortex slices.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allweis C., Landau T., Abeles M., Magnes J. The oxidation of uniformly labelled albumin-bound palmitic acid to CO2 by the perfused cat brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Sep;13(9):795–804. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb05874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott K. A., Greig M. E., Benoy M. P. The metabolism of lactic and pyruvic acids in normal and tumour tissues: Rat liver, brain and testis. Biochem J. 1937 Jul;31(7):1003–1020. doi: 10.1042/bj0311003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gevers W., Krebs H. A. The effects of adenine nucleotides on carbohydrate metabolism in pigeon-liver homogenates. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):720–735. doi: 10.1042/bj0980720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaister D., Kerly M. The oxygen consumption and carbohydrate metabolism of the retractor muscle of the foot of Mytilus edulis. J Physiol. 1936 Jun 10;87(1):56–66. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jowett M., Quastel J. H. Studies in fat metabolism: The formation and breakdown of acetoacetic acid in animal tissues. Biochem J. 1935 Sep;29(9):2181–2191. doi: 10.1042/bj0292181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARMANOVA I. G. Effects of partial sympathectomy on the production of photogenic catalepsy. Fed Proc. 1963 Mar-Apr;Suppl 22:271–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINZELLER A., RYBOVA R. Glycogen synthesis in brain cortex slices and some factors affecting it. J Neurochem. 1957;2(1):45–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A., BENNETT D. A., DE GASQUET P., GASQUET P., GASCOYNE T., YOSHIDA T. Renal gluconeogenesis. The effect of diet on the gluconeogenic capacity of rat-kidney-cortex slices. Biochem J. 1963 Jan;86:22–27. doi: 10.1042/bj0860022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. THE CROONIAN LECTURE, 1963. GLUCONEOGENESIS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Mar 17;159:545–564. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBARON F. N. The resynthesis of glycogen by guinea pig cerebral-cortex slices. Biochem J. 1955 Sep;61(1):80–85. doi: 10.1042/bj0610080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYES P. A. A calorie deficiency hypothesis of ketogenesis. Metabolism. 1962 Aug;11:781–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCILWAIN H., TRESIZE M. A. The glucose, glycogen and aerobic glycolysis of isolated cerebral tissues. Biochem J. 1956 Jun;63(2):250–257. doi: 10.1042/bj0630250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J., Newsholme E. A., Garland P. B. Regulation of glucose uptake by muscle. 8. Effects of fatty acids, ketone bodies and pyruvate, and of alloxan-diabetes and starvation, on the uptake and metabolic fate of glucose in rat heart and diaphragm muscles. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):652–665. doi: 10.1042/bj0930652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone W. E. The effects of anaesthetics and of convulsants on the lactic acid content of the brain. Biochem J. 1938 Nov;32(11):1908–1918. doi: 10.1042/bj0321908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIGNAIS P. M., GALLAGHER C. H., ZABIN I. Activation and oxidation of long chain fatty acids by rat brain. J Neurochem. 1958;2(2-3):283–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLK M. E., MILLINGTON R. H., WEINHOUSE S. Oxidation of endogenous fatty acids of rat tissues in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1952 Apr;195(2):493–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARBURG O., KRIPPAHL G. [Further development of manometric methods (carbonate mixtures)]. Z Naturforsch B. 1960 Jun;15B:364–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON D. H., MELLANBY J., KREBS H. A. Enzymic determination of D(-)-beta-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid in blood. Biochem J. 1962 Jan;82:90–96. doi: 10.1042/bj0820090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


