Abstract
Riboswitches and RNA interference are important emerging mechanisms found in many organisms to control gene expression. To enhance our understanding of such RNA roles, finding small regulatory motifs in genomes presents a challenge on a wide scale. Many simple functional RNA motifs have been found by in vitro selection experiments, which produce synthetic target-binding aptamers as well as catalytic RNAs, including the hammerhead ribozyme. Motivated by the prediction of Piganeau and Schroeder [(2003) Chem. Biol., 10, 103–104] that synthetic RNAs may have natural counterparts, we develop and apply an efficient computational protocol for identifying aptamer-like motifs in genomes. We define motifs from the sequence and structural information of synthetic aptamers, search for sequences in genomes that will produce motif matches, and then evaluate the structural stability and statistical significance of the potential hits. Our application to aptamers for streptomycin, chloramphenicol, neomycin B and ATP identifies 37 candidate sequences (in coding and non-coding regions) that fold to the target aptamer structures in bacterial and archaeal genomes. Further energetic screening reveals that several candidates exhibit energetic properties and sequence conservation patterns that are characteristic of functional motifs. Besides providing candidates for experimental testing, our computational protocol offers an avenue for expanding natural RNA's functional repertoire.
INTRODUCTION
RNA has a wonderful capacity to form complex, stable tertiary structures due to its conformational flexibility, modularity and versatility. This capacity enables RNA molecules to play essential roles in cellular processes of all organisms (1–4), mediated by ligand-binding, complementary base pairing and catalytic reactions. Recent discoveries have highlighted the regulatory roles of small functional RNA motifs in the control of gene expression. For example, riboswitches regulate translation via binding of mRNA to metabolites (5), and microRNAs suppress gene expression by complementary base pairing (6). Since ligand-binding and base pairing are fundamental aspects of RNA interactions and activities, many such small functional RNA motifs may exist inthe cell.
With rapidly growing interest in RNA structure and function, the central objective of increasing RNA's functional repertoire has led to various experimental and computational approaches. The current genome-wide searches for natural functional RNA molecules include genetic screening [e.g. the FANTOM Consortium and the RIKEN group (7,8) and others (9–11)], comparative genomics (12,13), neural networks (14), graph theory (15,16) and other complementary approaches (17). Unlike proteins, computational RNA genomics is still in its early stages of development, requiring new ideas and tools to advance the field.
Here, we develop and apply a method for finding small functional RNA motifs in genomic sequences based on synthetic functional motifs derived from in vitro selection experiments. In vitro selection is an iterative experimental process for uncovering small RNA molecules from a large pool of random sequences with a specific physical or chemical property (18,19) [reviewed in (20)]. Numerous target-binding nucleic acid molecules (known as ‘aptamers’) have been identified using this approach, with targeted molecules including organic molecules, antibiotics, peptides, proteins and whole viruses (20,21). In addition, in vitro selection experiments have led to the discovery of novel RNA enzymes (ribozymes) and to many applications in biomolecular engineering, e.g. allosteric ribozymes and biosensors (22–27). Clearly, in vitro selection has many important applications in biology, chemistry, medicine and biotechnology (22,24–26,28–30).
Although in vitro selection typically generates artificial, non-biological molecules, Szostak's group (31) recently found that the evolution-mimicking process of in vitro selection can recreate biologically active RNA motifs known in vivo, such as the hammerhead ribozyme. Moreover, recent findings show that metabolite-induced RNA conformational changes (i.e. natural RNA aptamers) control bacterial gene expression (5). Interestingly, Piganeau and Schroeder, in response to the Patel group's structural characterization of the streptomycin-binding aptamer (32), commented that ‘We can now predict that many biosynthetic pathways will be regulated by metabolite binding ‘natural aptamers,’ and we might even find a structure similar to the streptomycin aptamer in a bacterium producing streptomycin’ (33). Thus, experimental studies suggest that in vitro selected motifs may exist in vivo, and these findings imply that synthetic functional motifs may be exploited for expanding the repertoire of natural functional RNAs. Natural RNA motifs similar to synthetic aptamers are likely to exist because aptamers bind to certain targets that are prevalent in Nature (e.g. streptomycin produced by bacteria, ATP, FMN).
Currently, the Aptamer Database (34) lists ∼300 aptamer and artificial ribozyme sequences spanning diverse functions. This valuable information provides a unique opportunity for uncovering many small natural functional motifs in genomes. Our method involves extracting critical topological and sequence-specific features of in vitro selected motifs, searching for potential genomic sequences that may exhibit similar properties when folded and screening of candidate sequences using thermodynamics criteria for structural stability to eliminate spurious matches. After applying the method to several aptamers that bind either ATP, chloramphenicol, neomycin B or streptomycin, we find 37 candidate sequences that fold to the target aptamer motifs distributed among 9 bacterial and 4 archaeal genomes. Of these, several exhibit energetic properties and sequence conservation patterns that are characteristic of functional motifs. More generally, our study suggests that such ‘natural aptamers’ may be abundant in the genomes of various organisms.
The advantage of this computational approach to finding novel functional RNA motifs is that the biological activity is known a priori. Thus, the method is not limited to the existing repertoire of natural RNAs since the in vitro selected functional motifs can be expanded as needed, allowing identification of truly novel motifs not accessible by other techniques. In the near future, combining our computational prediction algorithm with experimental verification techniques has the potential to evolve a functional RNA motif discovery approach complementary to existing experimental and computational techniques.
METHODS
Overall approach
In brief, we extract the relevant structural and sequence information from in vitro selected aptamers that accounts for the molecule's functionality and search for genomic RNA sequences with the specified (sequence and structure) motif; we then assess the candidate sequences by performing thermodynamic stability and statistical significance tests which involve calculating heat-capacity curves, free energies, energy landscapes and expected motif occurrence frequency in random sequences. Although we develop the protocol to search for aptamers, it can be generalized to ribozyme motifs.
Our algorithm consists of four major steps:
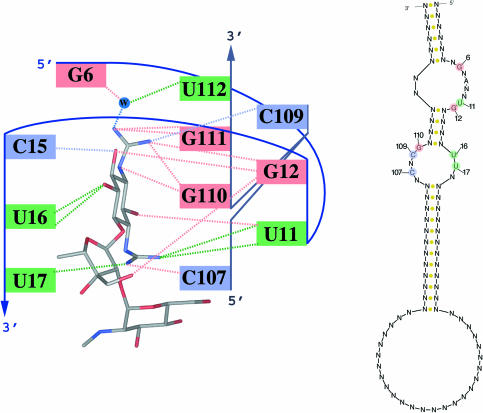
The motif descriptor is constructed manually by extracting the critical sequence and structural features from the in vitro selected functional RNA molecule that confer binding affinity (usually consensus sequences and secondary structures). If X-ray crystallography or NMR studies of aptamer motifs are available, detailed structural features are incorporated in the motif descriptor. Such studies help pinpoint important structural properties of the motif, including the overall qualitative structure (e.g. loops, bulges, hairpins, lengths of stems, etc.) and sequence information specifying critical hydrogen-bonding interactions (e.g. Figure 1 for the streptomycin–aptamer complex).
The genomes of selected organisms are searched using the RNAMotif program (35), a motif scanning tool, for the structure specified by the motif descriptor. The program searches for sequences in genomes that could potentially fold into the specified secondary structure based on base pairing rules (Watson–Crick, wobbles and non-canonical base pairs).
The sequence hits are then folded using the Vienna RNA Package (36), a secondary structure prediction algorithm. Although the algorithm is imperfect (pseudoknots and magnesium ions are excluded), it is known to be reasonably accurate for the short sequences we study, <100 nt. Genomic sequences that fold to the target motifs define our candidate natural aptamer motifs.
The candidates are further subjected to statistical significance and thermodynamic stability tests to assess their quality and eliminate likely false-positives. The stability test involves assessing the candidates' thermodynamic variables and energy landscapes in comparison with those for randomly shuffled sequences; the statistical significance test is established by calculating expected motif occurrence frequency in random sequences with a uniform base composition. These tests are described in detail below.
Figure 1.
The hydrogen-bonding scheme of the streptomycin-binding aptamer from crystal structure [adapted from (32)]. The dotted lines represent hydrogen bonds between the streptomycin molecule (center) and the nucleotides in the binding pocket. Information about binding specificity is critical for creating accurate aptamer motif descriptors.
Aptamer motif descriptors
Creating motif descriptors requires biological intuition and experimentation. Generally, the results of many in vitro selection studies include a family of similar sequences with the desired function. Therefore, based on sequence conservation, it is possible to judge how much variability to allow in certain parts of the structure. This sequence conservation has been used by experimentalists to produce minimal (shorter), active aptamers binding antibiotic targets (37,38). Our motif descriptors are designed for these aptamers, though they do not necessarily match the raw sequences from in vitro selection experiments. The motif descriptors for antibiotic and ATP-binding aptamers are shown in Figure 2, and their RNAMotif descriptor files are available in Supplementary Data.
Figure 2.
The four experimental aptamers (left side of each set), constructed motif descriptors (middle) and candidate natural aptamers (right). Regions with many N's are variable in length. The nucleic acid base symbols are defined as follows: N = any base; V = A, C, or G; S = C or G. We search the genomes for any sequence that fits the descriptor consensus (allowing for slight mismatches). The experimental papers associated with the aptamers are (a) ATP (38), (b) chloramphenicol (41), (c) neomycin B (42,43) and (d) streptomycin (37).
ATP-binding aptamers
All ATP-binding aptamers have a small, highly conserved consensus sequence embedded within a common secondary structure. The smallest secondary structure model for ATP aptamer was supported by deletion analysis as well as dimethylsulfate modification experiments (38). The structure model has a simple hairpin structure with an asymmetric bulge containing the consensus sequence (GGAAGAAACUG), which mediates the binding; the two helices surrounding the bulge are variable in length (we allow 6–14 bp). The constructed descriptor reflects exactly this information (Figure 2a); it also matches several in vitro selected ATP sequences in refs (39,40).
Chloramphenicol-binding aptamers
Several of the selected chloramphenicol aptamer sequences exhibit sequence conservation and the ability to fold into similar secondary structures. The secondary structure model is supported through deletion–selection analysis and RNase S1 sensitivity analysis (41). The structure is composed of a hairpin with two adenine-rich asymmetric bulges which are responsible for binding. The helix in between the two bulges is only slightly variable in length (4–6 bp), while the two outer helices allow higher variability.
Neomycin B-binding aptamers
The neomycin B descriptor is a simple hairpin structure originally elucidated by footprinting experiments (42,43). The common sequence feature is that the hairpin loop is composed of three G-U wobble pairs followed by a G-C pair right before the loop starts. The loop exhibits a consensus where the first nucleotide is a guanine and the rest of the loop is adenine-rich; the loop is closed off by a non-canonical A-G pair. NMR experiments elucidate how the RNA binds the neomycin B and verifies that the conserved sequences are actually critical for the binding to take place (43).
Streptomycin-binding aptamers
The streptomycin-binding aptamer was also discovered as a motif with a consensus sequence in the bulges (32,37). The raw sequences are ∼75 nt long whereas the corresponding minimally active structure is only ∼40 nt in length. The minimal structure is composed of two asymmetric bulges in a hairpin structure, with the middle helix relatively not variable in length, and the other two helices highly variable. The structure was initially elucidated using a variety of techniques, including probing though Pb2+-induced RNA cleavage, dimethylsulfate and kethoxal. Later, the structure of the RNA–streptomycin complex was solved by X-ray crystallography (32), allowing the identification of the specific nucleotides in the aptamer that confer binding specificity. Specifically, the experimental sequence for the 5′ asymmetric bulge is 5′-G6-C7-A8-U9-U10-U11-G12, but based on the information in Figures 1 and 2d, only the first nucleotide and the last 2 nt (G and UG respectively) are involved in the hydrogen-bonding network. Therefore, it is possible to search for the sequence motif GNANNUG in the asymmetric bulge.
Melting curve analysis of candidate sequences
Biological molecules generally possess stable structures at physiological temperatures. The stability of RNA secondary structures with respect to temperature change can be analyzed using heat-capacity curves (‘melting’ curves). These curves represent the amount of energy absorbed per unit change in temperature at any given temperature (i.e. dH/dT versus T, where H is the RNA's conformational enthalpy). For each candidate sequence, we compute the melting curve using tools available in the Vienna RNA Package (36). Additionally, to discriminate random from probable functional RNA sequences, we randomly shuffle each candidate sequence 1000 times and compute the corresponding melting curves. The melting temperature, Tm, is defined as the temperature at the highest peak; it may also be interpreted as the transition temperature at which the RNA molecule's secondary structure experiences significant disruption. For each sequence (the candidate and the randomly shuffled ones), we plot the melting temperature (Tm) against the free energy () as a further indicator of stability. We then use principal component analysis to compute a 90% confidence ellipse to determine whether the original sequence is significantly more stable than its randomly shuffled sequences.
Conformational energy landscapes for candidate sequences
Functional RNA molecules likely have a steeper conformational energy landscape compared with random sequences since they are expected to favor a native, intrinsic fold and must attain the native fold relatively fast (44). Thus, examination of the shape of the energy landscape offers an alternative approach for discriminating RNA-like from non-RNA-like molecules. The energy landscape is defined as a plot of RNA's internal energy (E) versus the base pair dissimilarity ‘distance’ (D) between the minimum energy structure and each suboptimal structure. More precisely, for a numbered sequence, D is defined as the number of dissimilarly numbered base pairs between two secondary structures (36). In practice, the suboptimal structures are calculated up to a given energy level (e.g. 5 kcal/mol above the minimum).
To characterize and quantify the conformational energy landscapes, we compute the ‘Valley index,’ described in (45), which provides a measure of the overall shape of the landscape (i.e. steepness and number of minima). The Valley index, V, is computed by forming the Boltzmann-weighted average of distances between all pairs of structures (minimum energy and suboptimal):
with
where Dij is the base dissimilarity distance between structure i and structure j, and Ei is the energy of structure i. Similar to the procedure for the melting curves, we randomly shuffle the candidate sequence 1000 times and plot the Valley index V versus the ensemble free energy and assess the relative stability of the target sequence using a 90% confidence ellipse.
Since the Valley index is a Boltzmann-weighted average of the distances between two structures, competing low-energy structures that are ‘far’ from each other (i.e. have highly distinct structures) will contribute significantly to the Valley index, giving it a large value. Functional RNA molecules are likely to have smaller Valley index values compared with random sequences since they are expected to favor a native, intrinsic fold.
Statistical analysis
The theoretical frequency of observing a given motif in a random sequence of nucleotides can be estimated (46), allowing assessment of the statistical over or under-representation of the motif in the genome of a specific organism. Since the motif descriptors of aptamers allow for variability of length and sequence, analytic computation based on the motif's information content is complex (46–48). Thus applying a Monte Carlo method to calculate the frequency is appropriate.
We consider a 1 Mb random sequence of nucleotides (25% A, U, C, G) as a random vector X and define φ(X) as the number of times the given motif is found in X; we then estimate the expected value E[φ(X)] using a sample-mean method that, for each iteration, generates a 1 Mb uniformly distributed sequence of nucleotides [using the Mersenne Twister algorithm (49)] and counts the number of times that the given motif is observed in the sequence (using RNAMotif). We average this number over one million iterations and estimate the standard error to define the number of hits a specific target motif can be expected to be found in a genome. The deviation from this estimate allows us to assess the significance of our actual findings.
Selected bacterial and archaeal genomes
We choose 10 bacterial and 16 archaeal species (>100 complete genomes are available). Since the Streptomyces species produce many known antibiotics (including those used here), we use the two available Streptomyces genomes. Additionally, we choose Escherichia coli genomes since they are among the best characterized bacterial species. Other bacterial genomes were selected randomly. For the searches involving the ATP aptamer, we use 16 of the available archaeal genomes at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
Computational performance
The computational speed depends on both the genome size and the complexity of the descriptor. The searches using the RNAMotif program are very fast for bacterial-sized genomes (∼10 Mb): for the streptomycin-binding aptamer in Figure 2d, <1 min is required for the largest genome searched (Streptomyces avermitilis, ∼9 Mb). Subsequently, the sequence hits are ‘folded’ using the RNAfold program. For a sequence <100 nt, the predicted secondary structure is computed in several seconds.
The screening analyses (step iv) are more computationally intensive. Generating suboptimal structures for energy landscape assessment is relative efficient, taking only a few minutes for 200 000 structures. However, calculating heat-capacity curves can take several minutes. Since we generate 1000 curves for each sequence, the process can take up to several CPU hours. The computation of the theoretical expected frequency of each motif is most intensive since we perform on the order of one million iterations of the sample-mean method. The combined calculations (genome scanning, suboptimal structures and expected frequency) require several weeks of computation. All computations were performed on a SGI 300 MHz MIPS R12000 IP27 processor with 4 GB of memory.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
We search for three aptamer motifs for the antibiotics chloramphenicol (41), streptomycin (32,37) and neomycin B (42,43) in bacterial genomes, as well as for an ATP-binding aptamer (38) in archaeal genomes. The four motif descriptors are shown in Figure 2 (middle structure). Tables 1 and 2 summarize our initial search results from the RNAMotif program for sequence hits in bacterial and archaeal genomes matching the four aptamer target descriptors (without filtering by sequence folding and energetic analyses). There is a total of 46 (3 × 10 + 1 × 16) aptamer motif/genome pairs. To determine statistical significance, Tables 1 and 2 also report the expected number of motif matches for each genome computed from searches in random sequences (‘Exp.’); thus, when the number of hits (under ‘Obs.’) is greater than the number of expected hits (under ‘Exp.’), a potential significant finding may arise.
Table 1.
The number of matches to the antibiotic-binding aptamer descriptors in bacterial genomes (‘Obs.’) and the expected number of matches calculated using random sequences with uniformly distributed nucleotides (‘Exp.’)
| Genome (NCBI accession number) | Size (Mb) | Chloramphenicol | Streptomycin | Neomycin B | Total Obs. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs. | Exp. | Obs. | Exp. | Obs. | Exp. | |||
| Streptomyces avermitilis (NC_003155) | 9.2 | 0 | 3.1 | 2 | 0.7 | 6 | 19.8 | 8 |
| Streptomyces coelicolor (NC_003888) | 8.8 | 0 | 2.9 | 1 | 0.7 | 1 | 18.9 | 2 |
| Escherichia coli K12 (U00096) | 4.7 | 7 | 1.6 | 1 | 0.4 | 11 | 10.1 | 19 |
| Escherichia coli O157:H7 (BA000007) | 5.6 | 7 | 1.9 | 1 | 0.4 | 17 | 12.0 | 25 |
| Escherichia coli O157:H7 EDL933 (AE005174) | 5.6 | 7 | 1.9 | 1 | 0.4 | 19 | 12.0 | 27 |
| Escherichia coli CFT073 (AE014075) | 5.3 | 7 | 1.8 | 0 | 0.4 | 17 | 11.4 | 24 |
| Neisseria meningitidis MC58 (AE002098) | 2.3 | 1 | 0.8 | 0 | 0.2 | 9 | 4.9 | 10 |
| Neisseria meningitidis Z2491 (AL157959) | 2.2 | 5 | 0.7 | 0 | 0.2 | 9 | 4.7 | 14 |
| Sinorhizobium meliloti (AL591688) | 3.7 | 1 | 1.2 | 1 | 0.3 | 3 | 7.9 | 5 |
| Chlamydia trachomatis (NC_000117) | 1.1 | 4 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.1 | 1 | 2.4 | 5 |
| Total | 39 | 7 | 93 | 139 | ||||
The motif matches are generated by the RNAMotif program without any filtering.
Table 2.
The number of matches to the antibiotic-binding aptamer descriptors in archaeal genomes (‘Obs.’) along with the expected number of matches calculated using random sequences with uniformly distributed nucleotides (‘Exp.’)
| Genome (NCBI accession number) | Size (Mb) | ATP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obs. | Exp. | ||
| Aeropyrum pernix (NC_000854) | 1.7 | 6 | 1.6 |
| Archaeoglobus fulgidis DSM 4304 (NC_000917) | 2.2 | 6 | 2.1 |
| Halobacterium sp. NRC-1 (NC_002607, NC_002608, NC_001869) | 2.6 | 4 | 2.5 |
| Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum str. (NC_000916) | 1.8 | 6 | 1.7 |
| Methanococcus jannaschii (NC_000909, NC_001732, NC_01733) | 1.7 | 4 | 1.6 |
| Methanopyrus kandleri AV19 (NC_003551) | 1.7 | 3 | 1.6 |
| Methanosarcina acetivorans C2A (NC_003552) | 5.8 | 12 | 5.5 |
| Methanosarcina mazei Goe1 (NC_003901) | 4.1 | 5 | 3.9 |
| Pyrobaculum aerophilum (NC_003364) | 2.3 | 2 | 2.2 |
| Pyrococcus abyssi (NC_000868) | 1.8 | 3 | 1.7 |
| Pyrococcus furiosus DSM 3638 (NC_003413) | 1.9 | 8 | 1.8 |
| Pyrococcus horikoshii (NC_000961) | 1.8 | 3 | 1.7 |
| Sulfolobus solfataricus (NC_002754) | 3.0 | 2 | 2.8 |
| Sulfolobus tokodaii (NC_003106) | 2.7 | 4 | 2.5 |
| Thermoplasma acidophilum (NC_002578) | 1.6 | 2 | 1.5 |
| Thermoplasma volcanium (NC_002689) | 1.6 | 2 | 1.5 |
| Total | 72 | ||
No additional filtering is applied to the motif matches found by the RNAMotif program.
The filtering step, folding each sequence and discarding those that fold into structures that are not similar to the target experimental motif structure, reduces the number of sequence hits from 211 to 37, which define our candidate sequences (Table 3); for the streptomycin aptamer, only one candidate sequence remains. Table 3 also reports results from thermodynamic tests of candidates.
Table 3.
The candidate natural aptamer sequences that fold to the target structures
| Sequence | Genome | Location | Gene | (kcal/mol) | Tm (°C) | test | V | test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloramphenicol | |||||||||
| 1 | 5′-TCAGAGCTGA AAAACTGGCC CCGGGTGCAG CTAAAAACTG A | E.coli K12 | 1 172 203 | Mfd | −11.90 | 78.0 | − | 1.09 | − |
| 2 | 5′-TCAGAGCTGA AAAACTGGCC CCGAGTGCAG CTAAAAACTG A | E.coli O157:H7 | 1 532 105 | ECs1492 | |||||
| 3 | E.coli O157:H7 EDL933 | 1 617 201 | Mfd | −10.58 | 72.6 | − | 2.40 | − | |
| 4 | 5′-GGGAAACGCA AAAATCAGGT ACAGGCAGAC GACGGTGGCG TAAAACTCCC | N.meningitidis Z2491 | 2 179 300 | Non-coding | −9.17 | 54.4 | − | 5.28 | − |
| 5 | 5′-GCAACGGAAA AAGCTGCTTT GCCCTTGAAG GCGGGGGGTG ATTCGGAAAA TGC | S.meliloti | 493 471 | Non-coding | −14.44 | 48.8 | − | 6.18 | − |
| Streptomycin | |||||||||
| 6 | 5′-GTACCCGGAC GTGCCCTTCC AGGCGTCCAT GGAGGCCTGG CTCGGGGCGG TGC | S.avermitilis | 7 323 209 | Non-coding | −28.64 | 111.4 | − | 0.84 | − |
| ATP | |||||||||
| 7 | 5′-GCTGGTCGAA GACACTGGCT GTCGCTGTCG ACGGCGATCA GC | Halobacterium sp. NRC1 | pNRC200 92 229 | Non-coding | |||||
| 8 | Halobacterium sp. NRC1 | pNRC100 92 229 | Non-coding | −19.43 | 71.6 | + | 4.54 | + | |
| 9 | 5′-TCTGTCCAAC CAGAGGAAAC TGGCTTCCAA AGTTCTCGGA TGCGGGCTTG ATAGG | M.acetivorans C2A | 1 295 025 | MA1090 | −16.04 | 71.2 | − | 6.40 | − |
| 10 | 5′-CAAGGGCTGA AGAAAATGCT GTGGTTATAT CCTACCAGGG TGACGGGGAC CTTG | M.mazei Goe1 | 3 868 884 | vorA | −13.71 | 69.4 | − | 8.46 | − |
| 11 | 5′-CTTGCTTTGA AAAAACTGGC AAATTCAACA AGGATTGCGA AGTACG | P.furiosus; DSM 3638 | 168 991 | PF0158 | −7.48 | 63.8 | − | 9.49 | − |
| Neomycin B | |||||||||
| 12 | 5′-TGAGCAGGGG CGAGAAGTTT TTCCTTG | E.coli K12 | 3 430 475 | smf_1 | −5.37 | 67.2 | − | 8.23 | − |
| 13 | E.coli K12 | 1 832 073 | Non-coding | ||||||
| 14 | 5′-TGTGTCGGGC GTAGAGTTTT GCGAG | E.coli O157:H7 EDL933 | 2 508 764 | Non-coding | −4.12 | 59.6 | − | 3.25 | − |
| 15 | E.coli CFT073 | 1 987 894 | Non-coding | ||||||
| 16 | 5′-CTGCGGGGGA ACACTTTGGT G | E.coli K12 | 3 973 740 | wecE | −3.54 | 60.0 | − | 4.27 | − |
| 17 | 5′-AGTCTGGTGG GCGATATGTT TATTATGAT | E.coli K12 | 1 324 039 | yciQ | −6.10 | 57.8 | + | 2.24 | − |
| 18 | E.coli O157:H7 | 1 826 735 | ECs1840 | ||||||
| 19 | E.coli O157:H7 EDL933 | 2 260 441 | Z2542 | ||||||
| 20 | E.coli CFT073 | 1 569 619 | yciQ | ||||||
| 21 | E.coli O157:H7 | 1 373 724 | ECs1300 | ||||||
| 22 | 5′-ATTCACTGGG CGACATGTTT GATGAAT | E.coli O157:H7 EDL933 | 1 457 496 | Z1560 | −5.55 | 61.4 | − | 1.41 | − |
| 23 | E.coli O157:H7 EDL933 | 1 061 889 | Z1121 | ||||||
| 24 | E.coli CFT073 | 1 130 797 | c1166 | ||||||
| 25 | E.coli O157:H7 | 1 037 740 | ECs0954 | ||||||
| 26 | 5′-AATGGGCGCA GAGTTTGTT | E.coli O157:H7 EDL933 | 1 039 400 | Z1102 | −3.65 | 60.8 | − | 1.33 | − |
| 27 | E.coli CFT073 | 960 757 | c1001 | ||||||
| 28 | E.coli O157:H7 | 3 148 310 | Non-coding | ||||||
| 29 | 5′-CCAGCGGGCG CAGAGTTTAT GGG | E.coli O157:H7 EDL933 | 3 218 265 | Non-coding | −4.98 | 57.4 | − | 0.42 | − |
| 30 | E.coli CFT073 | 2 704 642 | Non-coding | ||||||
| 31 | 5′-TGCGGGCGAA CAGTTTGCA | E.coli O157:H7 EDL933 | 5 503 670 | Non-coding | −7.61 | 81.0 | + | 1.12 | + |
| 32 | 5′-TTGAGCAGGG GCGTGAAGTT TTTGCTTTG | E.coli CFT073 | 3 864 206 | Smf | −10.79 | 83.4 | + | 1.44 | + |
| 33 | 5′-TTCCTGAAGG GGGACGACTT TGATGGGGA | N.meningitidis MC58 | 1 221 920 | Non-coding | −7.44 | 65.2 | − | 8.29 | − |
| 34 | N.meningitidis Z2491 | 1 283 084 | Non-coding | ||||||
| 35 | 5′-ACGAGGGCGG TAAGTTTTTT T | N.meningitidis MC58 | 1 468 213 | Non-coding | −2.55 | 51.6 | − | 1.22 | − |
| 36 | N.meningitidis Z2491 | 1 553 595 | Non-coding | ||||||
| 37 | 5′-GCAGGTGGGC GCAGAGTTTG CCATT | C.trachtomatis | 604 373 | yjeE | −9.07 | 83.0 | − | 0.76 | − |
The physical properties, energetic test results, and location(s) of each candidate sequence are reported. , Tm, and V denote the free energy, melting temperature and Valley index, respectively. The and test results (+ or −) at 90% confidence level are calculated using the thermodynamic scatter plots (see text and Figure 4). Location refers to the position of the start site of a candidate sequence (by nucleotide number) and Gene refers to the gene's name (GenBank annotations) or non-coding region containing the candidate sequence. The locations of sequences 7 and 8 are in the associated species' plasmids. The most promising candidates are numbered in bold.
Statistical analysis reveals over or under-representation of aptamer motifs in genomes
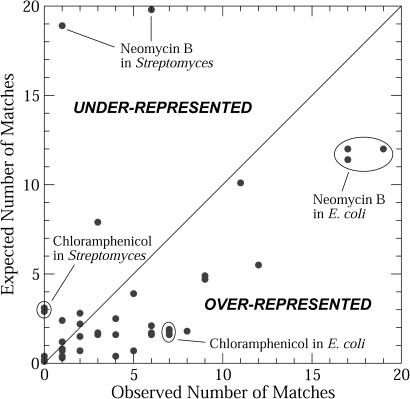
Knowing the over or under-representation of motifs in a given genome helps determine the biological significance of sequence hits. Figure 3 plots the expected versus observed matches for all 46 motif/genome pairs in our study. The expected number of matches for a genome is calculated from the average number of matches per million base pairs for a sequence of random nucleotides (Table 4). As shown in Tables 1 and 2 and Figure 3, the observed number of matches deviates from the expected number of matches for many motif/genome pairs. Significantly, most of the aptamer motif/genome pairs are over-represented, meaning that their occurrence frequencies in genomes cannot be accounted for by chance. For instance, as highlighted in Figure 3, the expected numbers of matches are considerably lower than the observed numbers of matches to the chloramphenicol (7 versus 1.8 expected matches) and neomycin B (∼16 versus 11 expected matches) aptamer motifs in E.coli genomes. In contrast, neomycin B and chloramphenicol aptamer motifs are under-represented in Streptomyces.
Figure 3.
Expected number of matches versus the observed number of matches for 46 aptamer motif/genome pairs; the expected number is calculated using random sequences. Deviations from the diagonal line represent genomes with either an over or under-representation of the given motif.
Table 4.
The expected frequency of each aptamer descriptor per 1 and 10 million base pairs of random sequence with uniformly distributed nucleotides
| Descriptor | Frequency ± 1 standard error | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Mb | 10 Mb | |
| Chloramphenicol | 0.3320 ± 0.0007 | 3.320 ± 0.007 |
| Streptomycin | 0.0778 ± 0.0003 | 0.778 ± 0.003 |
| Neomycin B | 2.1471 ± 0.0015 | 21.47 ± 0.015 |
| ATP | 0.9424 ± 0.0009 | 9.424 ± 0.009 |
Specifically, the average number of matches to the neomycin B aptamer motif in Streptomyces genomes is 4, while the average number in E.coli is four times greater. Since the average Streptomyces genome size is almost twice that of the average E.coli genome (∼9 versus ∼5 Mb), these trends are significant because probability alone would predict the number of matches in Streptomyces genomes to be about twice as many matches as E.coli, not one-fourth as obtained. This might indicate a biological preference/discrimination for/against this aptamer, i.e. either Streptomyces is significantly missing this structure, or E.coli has a significantly large occurrence of it.
In general, the number of matches for the ATP motif in archaeal genomes shows that most genomes do not exhibit a significant number of matches over or under the expected number (Table 2). However, Aeropyrum pernix, Archaeoglobus fulgidis DSM 4304, Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum, Methanosarcina acetivorans C2A and Pyrococcus furiosus DSM 3638 all produce far more matches for the ATP aptamer than the expected number, even though their nucleotide compositions are uniformly distributed.
To estimate the expected number of sequence matches, we used random sequences with a uniform nucleotide composition [i.e, the T(U):C:A:G should be 1:1:1:1]. Judging by the nucleotide composition data in Table 5, most genomes are nearly uniformly distributed. If the nucleotide composition of a genome deviates significantly from uniform the expected number of matches should be calculated using random sequences with the same nucleotide composition. By using the biased nucleotide distribution of Streptomyces (30% A/T and 70% G/C), we do not find a significant deviation in the expected number of matches. Calculation of expected matches using complex random sequence models, such as higher-order Markov chains (dinucleotide, trinucleotide, etc. distributions), may also be considered to generate more accurate estimates (46,47,50) but are not expected to produce significant changes in the results.
Table 5.
The nucleotide distribution of genomes
| T(U) (%) | C (%) | A (%) | G (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptomyces avermitilis | 14.6 | 35.4 | 14.7 | 35.3 |
| Streptomyces coelicolor | 14.0 | 36.0 | 13.9 | 36.1 |
| Escherichia coli K12 | 24.6 | 25.4 | 24.6 | 25.4 |
| Escherichia coli O157:H7 | 24.7 | 25.2 | 24.8 | 25.3 |
| Escherichia coli O157:H7 EDL933 | 24.7 | 25.2 | 24.8 | 25.2 |
| Escherichia coli CFT073 | 24.7 | 25.3 | 24.8 | 25.2 |
| Neisseria meningitidis MC58 | 24.3 | 25.6 | 24.2 | 26.0 |
| Neisseria meningitidis Z2491 | 24.2 | 25.9 | 24.0 | 25.9 |
| Sinorhizobium meliloti | 18.6 | 31.5 | 18.6 | 31.2 |
| Chlamydia trachomatis | 29.3 | 20.6 | 29.4 | 20.7 |
| Aeropyrum pernix | 22.1 | 28.4 | 21.6 | 28.0 |
| Archaeoglobus fulgidis DSM 4304 | 25.6 | 24.2 | 25.8 | 24.4 |
| Halobacterium sp. NRC-1 | 17.1 | 33.0 | 17.0 | 33.0 |
| Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum str. ΔH | 25.4 | 24.7 | 25.1 | 24.8 |
| Methanococcus jannaschii | 34.3 | 15.5 | 34.4 | 15.7 |
| Methanopyrus kandleri AV19 | 19.4 | 30.7 | 19.5 | 30.4 |
| Methanosarcina acetivorans C2A | 28.8 | 21.4 | 28.5 | 21.3 |
| Methanosarcina mazei Goe1 | 29.2 | 20.7 | 29.3 | 20.8 |
| Pyrobaculum aerophilum | 24.1 | 25.4 | 24.5 | 25.9 |
| Pyrococcus abyssi | 27.7 | 22.4 | 27.6 | 22.3 |
| Pyrococcus furiosus DSM 3638 | 29.6 | 20.4 | 29.6 | 20.4 |
| Pyrococcus horikoshii | 29.1 | 21.2 | 29.0 | 20.7 |
| Sulfolobus solfataricus | 32.3 | 17.9 | 31.9 | 17.9 |
| Sulfolobus tokodaii | 33.8 | 16.3 | 33.4 | 16.5 |
| Thermoplasma acidophilum | 26.8 | 22.9 | 27.2 | 23.1 |
| Thermoplasma volcanium | 29.9 | 19.9 | 30.2 | 20.0 |
Energetic analysis discriminates natural from random RNA sequences
With the significantly smaller pool of filtered sequences (following RNAfold), we now proceed to thermodynamic evaluation of the 37 candidates in Table 3 using melting temperature ( plot) and Valley index () tests. The scatter plot for a promising candidate sequence should have favorable energetic characteristics compared with randomized sequences. We analyze the scatter plots using an ellipse oriented along the principal component axes that contains 90% of the points. As a check of the test, we applied it to five known biological RNAs. Table 6 shows that all the biological sequences land outside the confidence ellipse; similar results are obtained for a dozen RNAs. A previous study using the free energy criterion alone did not yield sufficient discrimination for functional RNAs (51). The plots for four candidate aptamer sequences (numbered 7/8, 17–20, 31 and 32 in Table 3) are shown in Figure 4. The candidate aptamer sequences for ATP (sequence 7/8 in Halobacterium sp.) and neomycin B (sequences 17–20, 31 and 32 in E.coli) lie outside this ellipse and away from the bulk of random sequences; as noted before, the neomycin B motif is over-represented in the E.coli genomes. We observe that the candidate aptamers have favorable energetic parameters even though they do not have the lowest free energies or highest melting temperatures compared with some randomized sequences.
Table 6.
The physical properties and stability test results for five biological RNA sequences
| Sequences | RNA | NCBI accession | (kcal/mol) | Tm (°C) | test | V | test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 5′-GGAUACGGCC AUACUGCGCA GAAAGCACCG CUUCCCAUCC GAACAGCGAA GUUAAGCUGC GCCAGGCGGU GUUAGUACUG GGGUGGGCGA CCACCCGGGA AUCCACCGUG CCGUAUCCU | 5S RNA | M34003 | −61.78 | 93.6 | + | 4.13 | + |
| B2 | 5′-GGUCCUAUGG UCUAGUGGUC AGGACAUUGG ACUCUGAAUC CAGUAACCCG AGUUCAAAUC UCGGUAGGAC CU | Gln tRNA | −29.65 | 87.4 | + | 2.65 | + | |
| B3 | 5′-AGCACCGCCU GCUACUUACA UCGCAUUUAU CUUUCGCCUU UUACUAAAGA UAGCCGUGAG UGAGCAGGCA CUGCGGUGCA UUGACCCAAU UUUUGGAGCC CCCUCAAAAG GGCA | U5 RNA | AF095839 | −42.96 | 86.8 | + | 7.25 | + |
| B4 | 5′-UGCAGUUUGC UGCGCUAUUA GUUUGGAACA ACACUGAGAA GAUUAGCAUG GCCCCUGCGC AAGGACGGCA UCUUUCUUUG AGAGGUGUGC UGGGCUCGCC CAGCUUUU | U6 RNA | AF053588 | −38.43 | 67.4 | + | 18.06 | − |
| B5 | 5′-GACGUGUUAC AGCUCUUUUA GAAUUUGUCU AGUAGGCUUU CUGGCUUUUC ACCGGAAAGC CCCU | U7 RNA | M17910 | −19.45 | 93.4 | + | 8.85 | + |
, Tm and V denote the free energy, melting temperature and Valley index, respectively. The and test results (+ or −) at 90% confidence level are calculated using the thermodynamic scatter plots (see text and Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Free energy versus melting temperature Tm (left column) and free energy versus Valley index V (middle column) for four good candidate aptamers (diamond symbol; right column) and their 1000 randomly shuffled sequences. Points in the ellipses cover 90% of sequences. Sequence numbers refer to those in Table 3.
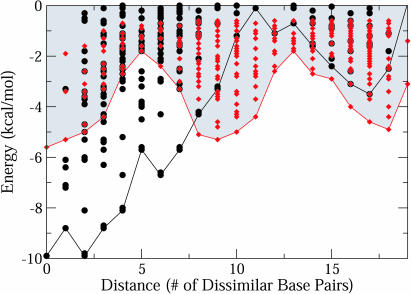
Similarly, we analyze the conformational energy landscape and assess the corresponding plot for each candidate sequence. Figure 5 shows the energy landscape plot for neomycin B candidate sequences 32 and 33/34 from E.coli and Neisseria meningitidis, respectively. The good candidate sequence 32 possesses a steep single-minimum landscape conformational energy landscape with a small V value of 1.44, whereas the poor candidate 33/34 has multiple low minima with V = 8.29. The Valley index, a quantitative measure of the conformational energy landscape, allows for a specific and rigorous quantitative test and accounts for the much higher-dimensional quality of the pair-wise distances between all suboptimal structures.
Figure 5.
Examples of good and poor conformational energy landscapes. The good landscape is represented by candidate sequence 32 (black filled circles, shaded) and the poor landscape by candidate sequence 33/34 (red, diamonds) for the neomycin B antibiotic. The good candidate sequence exhibits a sharp, steep slope while the poor candidate sequence has multiple low-energy minima. The optimal and suboptimal structures are generated using the Vienna RNA Package.
Similar to the plots in Figure 4, we use 1000 randomized permutations and 90% confidence ellipse in plots to assess biological significance of candidate sequences. For biological sequences (5S, tRNA, U5, U6, U7), Table 6 shows that 4/5 cases pass the Valley index test [i.e. their sequences lie outside the 90% confidence ellipse (45)], suggesting that the test is reasonable. Applying the Valley index test to the 37 candidate aptamer sequences in Table 3, we find that candidate sequences 7/8, 31 and 32 pass the test. Thus, except for candidate 17/18/19/20, candidates that pass the melting temperature test also pass the Valley index test.
In Table 3, we retain all 37 correctly folded aptamer candidates, even though most do not pass the thermodynamic tests, because these tests are imperfect, especially for small RNA motifs. More importantly, most false-positive sequences are already eliminated by the folding step; for example, we observe that for tRNA >95% of the false-positive tRNA sequences matching the tRNA motif are eliminated by the folding step.
The thermodynamic tests measure the specificity of the search algorithm. Also important is the algorithm's sensitivity, i.e. the success in detecting a known RNA class. We assess this sensitivity of our algorithm for E.coli K12 tRNAs by using the tRNA motif descriptor in the RNAMotif package. The tRNA descriptor identifies 74 out of 86 known E.coli K12 tRNAs, yielding a high success rate of 86%. Of the 74 tRNA sequences detected, only 33% (25 sequences) fold correctly to the tRNA shape by the RNAfold algorithm. Of the remaining 25, 17 pass the melting temperature test, yielding a success rate of 68%. Thus, for tRNA the overall sensitivity of our algorithm is ∼20%. Clearly, sensitivity depends on specific RNA classes, and the weak component of our overall protocol is the RNAfold folding application. If we were to extrapolate from the tRNA findings, the number of possible aptamer motifs in genomes might be five times the number of detected aptamer sequences.
The results of both the melting temperature and Valley index tests are summarized in Table 3 for all 37 candidate sequences that are predicted to fold into target structures. Of these 37 matches, there are 21 distinct sequences (since many of the sequences occur in multiple organisms in multiple locations). The table shows that four of the sequences pass the test (sequences 7/8, 17–20, 31 and 32), while only three of the sequences pass the test (sequences 7/8, 31 and 32). Taken together, we produce the promising candidates for experimental verification, i.e. binding of candidate motifs to antibiotics, as: 7/8, 17/18/19/20, 31 and 32. It is also possible that few sequences pass the tests because they are so short. Even some biological sequences may fail the energetic tests because functional properties might not be revealed by such tests; for example, many snoRNAs, which interact extensively with ribosomal RNAs via base pairing, do not pass such tests. Biological sequences are generally longer (more than 70 nt). This means that the predictive algorithms can characterize their properties better than short sequences, such as the ones in Table 3. Furthermore, in all tested cases, the Valley index test is more stringent than the melting temperature test.
The above 2D correlation analyses involving free energy, melting temperature and Valley index can be generalized to three or higher dimensions. For ellipsoidal confidence analysis, it can be shown that the confidence level increases as the dimensionality decreases. Thus, for a fixed confidence level, screening in higher dimensions is more stringent than that for lower dimensions. Currently, 1D thermodynamic screening criteria use either free energy or Valley index. We have used 2D analyses to improve on these screening criteria.
In addition to the above energetic tests, we also assess the stability of the candidate sequences within larger sequences for those candidates occurring in known genes (see Table 3). We fold the entire gene sequence with and without constraining the aptamer's structure to determine the change in the optimal free energy (). The optimal energy of the constrained structure is always higher than that for its unconstrained structure. A significant limitation of this assessment is that RNA fold predictions are not accurate for long sequences (the gene sequences are ∼1000 nt). Still, we find that for candidate sequences 1, 2, 3, 25 and 26, the values are between −1 and 0 kcal/mol, indicating that these aptamer structures are likely stable within the larger sequence context. For candidate sequences 32 and 37, is −4 kcal/mol compared with aptamer energies of about −10 kcal/mol; for other candidate aptamers (9–12,17–24) within genes, the values are comparable to their aptamer energies.
Yet another test of the candidate natural aptamers' stability is to fold them within a slightly larger sequence context. We perform this test for all the four good candidates (sequences 7/8, 17–20, 31 and 32). Specifically, we extend these candidate sequences by 10 nt at the 3′ and 5′ ends and refold them. Encouragingly, the key motif elements (A-rich bulge of ATP aptamer and stem–loop motif of Neomycin B aptamer) of all the shorter (original) sequences responsible for binding are maintained, indicating their stability within the larger sequence context.
Sequence conservation and four promising candidate natural aptamer sequences
The physical and statistical analyses above helped us evaluate the candidate sequences that are most likely to have the properties of biological molecules. Based on such analyses, the promising natural aptamer sequences are 7/8 (42 nt), 17/18/19/20 (29 nt), 31 (23 nt) and 32 (19 nt). Further support for these candidates is provided by their sequence conservation. Candidate aptamers 7 and 8 are identical 42 nt non-coding sequences found in plasmids pNRC200 and pNRC100, respectively, of Halobacterium sp. Most interestingly, the 39 nt sequences 17–20 are identical copies found in hypothetical genes (yciQ, ECs1849, Z2542) of four different E.coli species. It is unlikely that candidate sequences 7/8 and 17/18/19/20 occur by chance. Table 3 shows that several other mostly shorter sequences (2–3, 13–15, 21–24, 25–27, 28–30, 33–34, 35–36) also exist in multiple copies. However, candidate sequences 31 and 32 exist as unique sequences in E.coli genomes; sequence 31 occurs in the non-coding region and sequence 32 in gene Smf.
Thus, sequences 7/8 (ATP) and 17/18/19/20 (neomycin B) are promising candidates for natural aptamers based on energetic and statistical tests, and sequence conservation; sequences 31 (neomycin B) and 32 (neomycin B) are judged to be good candidates based on energetic and statistical tests. These final sequences 7/8, 17/18/19/20, 31 and 32 (Table 3) comprise our best candidates for experimental testing. The functions of these candidate aptamers could be verified by performing ligand-binding experiments in vitro, and their existence in vivo could be determined using standard gene expression assays.
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
Our method for searching for artificial aptamer motifs in the genomes of various organisms includes a series of statistical, thermodynamic and biological (sequence conservation) tests to screen and produce the most promising candidates. In our application to ATP, chloramphenicol, neomycin B and streptomycin aptamers, we have found several promising natural aptamer motifs (sequences 7/8, 17/18/19/20, 31 and 32 in Table 3). These candidates, possessing characteristics of functional RNA molecules (stable folds and sequence conservation), are found in coding and non-coding regions of bacterial and archaeal genomes. Collaborations are underway to test these candidates in the laboratory.
Many algorithmic improvements can be envisioned so that our tool will provide a general resource to screen and discover aptamer motifs in genomes. Automating the analyses so that the algorithm can be applied to all genomes comprehensively as well as to the numerous aptamers catalogued in the Aptamer Database (34) is highly desirable. Better ways to eliminate false-positives from our search results are also needed. With experimental feedback, further computational and biological improvements can be made. The resulting computational tool in conjunction with in vitro technology has the potential to help the effort of expanding known RNA repertoire by identifying novel RNA genes or RNA-based regulatory mechanisms.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Supplementary Data are available at NAR Online.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Marco Avellaneda, Andres Jäschke, Dinshaw Patel, Renée Schroeder and Mike Waterman for constructive discussions and many suggestions related to this work. The authors thank Tom Macke and Ivo Hofacker for technical assistance with RNAMotif and the Vienna RNA package, respectively. The authors also thank Elizabeth Moran for help creating Figures 1, 2 and 4, and Yanli Wang for help preparing Figure 1. The authors thank Dave Scicchitano for supporting this study through the Department of Biology, and the authors also gratefully acknowledge the support of the NSF (DMS-0201160) (including undergraduate VIGRE support through Oliver Bühler), Howard Hughes Medical Institute (for an undergraduate summer research fellowship through the Honors Summer Institute at NYU) and the Human Frontier Science Program. Funding to pay the Open Access publication charges for this article was provided by NSF (DMS-0201160).
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Doudna J.A., Cech T.R. The chemical repertoire of natural ribozymes. Nature. 2002;418:222–228. doi: 10.1038/418222a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Storz G. An expanding universe of noncoding RNAs. Science. 2002;296:1260–1263. doi: 10.1126/science.1072249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gibbs W.W. The unseen genome: gems among the junk. Sci. Am. 2003;289:26–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gesteland R.F., Cech T., Atkins J.F. The RNA World. The Nature of Modern RNA Suggests a Prebiotic RNA. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Winkler W., Nahvi A., Breaker R.R. Thiamine derivatives bind messenger RNAs directly to regulate bacterial gene expression. Nature. 2002;419:952–956. doi: 10.1038/nature01145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Filipowicz W., Jaskiewicz L., Kolb F.A., Pillai R.S. Post-transcriptional gene silencing by siRNAs and miRNAs. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005;15:331–341. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2005.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Okazaki Y., Furuno M., Kasukawa T., Adachi J., Bono H., Kondo S., Nikaido I., Osato N., Saito R., Suzuki H., et al. Analysis of the mouse transcriptome based on functional annotation of 60,770 full-length cDNAs. Nature. 2002;420:563–573. doi: 10.1038/nature01266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Numata K., Kanai A., Saito R., Kondo S., Adachi J., Wilming L.G., Hume D.A., Hayashizaki Y., Tomita M. Identification of putative noncoding RNAs among the RIKEN mouse full-length cDNA collection. Genome Res. 2003;13:1301–1306. doi: 10.1101/gr.1011603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huttenhofer A., Kiefmann M., Meier-Ewert S., O'Brien J., Lehrach H., Bachellerie J.P., Brosius J. RNomics: an experimental approach that identifies 201 candidates for novel, small, non-messenger RNAs in mouse. EMBO J. 2001;20:2943–2953. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.11.2943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wassarman K.M., Repoila F., Rosenow C., Storz G., Gottesman S. Identification of novel small RNAs using comparative genomics and microarrays. Genes Dev. 2001;15:1637–1651. doi: 10.1101/gad.901001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yuan G.Z., Klambt C., Bachellerie J.P., Brosius J., Huttenhofer A. RNomics in Drosophila melanogaster: identification of 66 candidates for novel non-messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:2495–2507. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eddy S.R. Computational Genomics of noncoding RNA genes. Cell. 2002;109:137–140. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00727-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rivas E., Klein R.J., Jones T.A., Eddy S.R. Computational identification of noncoding RNAs in E-coli by comparative genomics. Curr. Biol. 2001;11:1369–1373. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Carter R.J., Dubchak I., Holbrook S.R. A computational approach to identify genes for functional RNAs in genomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:3928–3938. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.19.3928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kim N., Shiffeldrim N., Gan H.H., Schlick T. Candidates for novel RNA topologies. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;341:1129–1144. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.06.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gan H.H., Pasquali S., Schlick T. Exploring the repertoire of RNA secondary motifs using graph theory; implications for RNA design. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:2926–2943. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lim L.P., Lau N.C., Weinstein E.G., Abdelhakim A., Yekta S., Rhoades M.W., Burge C.B., Bartel D.P. The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev. 2003;17:991–1008. doi: 10.1101/gad.1074403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ellington A.D., Szostak J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990;346:818–822. doi: 10.1038/346818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tuerk C., Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 1990;249:505–510. doi: 10.1126/science.2200121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wilson D.S., Szostak J.W. In vitro selection of functional nucleic acids. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999;68:611–647. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.68.1.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hermann T., Patel D.J. Biochemistry: adaptive recognition by nucleic acid aptamers. Science. 2000;287:820–825. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5454.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jaschke A. Artificial ribozymes and deoxyribozymes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001;11:321–326. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(00)00208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jaschke A., Seelig B. Evolution of DNA and RNA as catalysts for chemical reactions. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2000;4:257–262. doi: 10.1016/s1367-5931(00)00086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Soukup G.A., Breaker R.R. Engineering precision RNA molecular switches. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1999;96:3584–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Soukup G.A., Breaker R.R. Nucleic acid molecular switches. Trends Biotechnol. 1999;17:469–476. doi: 10.1016/s0167-7799(99)01383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Soukup G.A., Breaker R.R. Allosteric nucleic acid catalysts. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000;10:318–325. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(00)00090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hodgson D.R., Suga H. Mechanistic studies on acyl-transferase ribozymes and beyond. Biopolymers. 2004;73:130–150. doi: 10.1002/bip.10518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jaschke A., Seelig B. Evolution of DNA and RNA as catalysts for chemical reactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000;4:257–262. doi: 10.1016/s1367-5931(00)00086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pearson N.D., Prescott C.D. RNA as a drug target. Chem. Biol. 1997;4:409–414. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(97)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sullenger B.A., Gilboa E. Emerging clinical applications of RNA. Nature. 2002;418:252–258. doi: 10.1038/418252a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Salehi-Ashtiani K., Szostak J.W. In vitro evolution suggests multiple origins for the hammerhead ribozyme. Nature. 2001;414:82–84. doi: 10.1038/35102081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tereshko V., Skripkin E., Patel D.J. Encapsulating Streptomycin within a small 40-mer RNA. Chem. Biol. 2003;10:175–187. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(03)00024-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Piganeau N., Schroeder R. Aptamer structures. A preview into regulatory pathways? Chem. Biol. 2003;10:103–104. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(03)00028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lee J.F., Hesselberth J.R., Meyers L.A., Ellington A.D. Aptamer database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:D95–D100. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Macke T.J., Ecker D.J., Gutell R.R., Gautheret D., Case D.A., Sampath R. RNAMotif, an RNA secondary structure definition and search algorithm. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:4724–4735. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.22.4724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hofacker I.L. Vienna RNA secondary structure server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3429–3431. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wallace S.T., Schroeder R. In vitro selection and characterization of streptomycin-binding RNAs: recognition discrimination between antibiotics. RNA. 1998;4:112–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sassanfar M., Szostak J.W. An RNA motif that binds ATP. Nature. 1993;364:550–553. doi: 10.1038/364550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Vaish N.K., Larralde R., Fraley A.W., Szostak J.W., McLaughlin L.W. A novel, modification-dependent ATP-binding aptamer selected from an RNA library incorporating a cationic functionality. Biochemistry. 2003;42:8842–8851. doi: 10.1021/bi027354i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jhaveri S., Rajendran M., Ellington A.D. In vitro selection of signaling aptamers. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000;18:1293–1297. doi: 10.1038/82414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Burke D.H., Hoffman D.C., Brown A., Hansen M., Pardi A., Gold L. RNA aptamers to the peptidyl transferase inhibitor chloramphenicol. Chem. Biol. 1997;4:833–843. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(97)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wallis M.G., Vonahsen U., Schroeder R., Famulok M. A Novel RNA motif for neomycin recognition. Chem. Biol. 1995;2:543–552. doi: 10.1016/1074-5521(95)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jiang L.C., Majumdar A., Hu W.D., Jaishree T.J., Xu W.K., Patel D.J. Saccharide-RNA recognition in a complex formed between neomycin B and an RNA aptamer. Structure Fold. Des. 1999;7:817–827. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rangan P., Masquida B., Westhof E., Woodson S.A. Assembly of core helices and rapid tertiary folding of a small bacterial group I ribozyme. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:1574–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0337743100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kitagawa J., Futamura Y., Yamamoto K. Analysis of the conformational energy landscape of human snRNA with a metric based on tree representation of RNA structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:2006–2013. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Reinert G., Schbath S., Waterman M.S. Probabilistic and statistical properties of words: an overview. J. Comput. Biol. 2000;7:1–46. doi: 10.1089/10665270050081360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Durbin R., Eddy S., Krogh A., Mitchison G. Biological Sequence Analysis Probabilistic Models of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cover T.M., Thomas J.A. Elements of Information Theory. NY: Wiley; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Matsumoto M., Nishimura T. A 623-dimensionally equidistributed uniform pseudorandom number generator. ACM TOMACS: Uniform Random Number Generation. 1998;8:3–30. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tomso D.J., Bell D.A. Sequence context at human single nucleotide polymorphisms: overrepresentation of CpG dinucleotide at polymorphic sites and suppression of variation in CpG islands. J. Mol. Biol. 2003;327:303–308. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rivas E., Eddy S.R. Secondary structure alone is generally not statistically significant for the detection of noncoding RNAs. Bioinformatics. 2000;16:583–605. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/16.7.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.