Abstract
The membrane fusion activity of murine leukaemia virus Env is carried by the transmembrane (TM) and controlled by the peripheral (SU) subunit. We show here that all Env subunits of the virus form disulphide-linked SU–TM complexes that can be disrupted by treatment with NP-40, heat or urea, or by Ca2+ depletion. Thiol mapping indicated that these conditions induced isomerization of the disulphide-bond by activating a thiol group in a Cys-X-X-Cys (CXXC) motif in SU. This resulted in dissociation of SU from the virus. The active thiol was hidden in uninduced virus but became accessible for alkylation by either Ca2+ depletion or receptor binding. The alkylation inhibited isomerization, virus fusion and infection. DTT treatment of alkylated Env resulted in cleavage of the SU–TM disulphide-bond and rescue of virus fusion. Further studies showed that virus fusion was specifically inhibited by high and enhanced by low concentrations of Ca2+. These results suggest that Env is stabilized by Ca2+ and that receptor binding triggers a cascade of reactions involving Ca2+ removal, CXXC-thiol exposure, SU–TM disulphide-bond isomerization and SU dissociation, which lead to fusion activation.
Keywords: disulphide-bond isomerase motif, fusion, retrovirus
Introduction
Retroviruses enter cells by fusing their envelope with the cell membrane (Hunter, 1997). The fusion mechanism has not yet been clarified, but is suggested to resemble the spring-loaded mechanism of influenza haemagglutinin (HA) (Carr and Kim, 1993; Skehel and Wiley, 2000). Similar to HA, the retroviral fusion protein Env is made as a homotrimer, which is cleaved into a complex of transmembrane (TM) and peripheral (SU) subunits. TM carries the fusion activity and SU the receptor-binding activity. In the unactivated Env, TM is probably trapped as a folding intermediate via its interactions with SU. Supposedly, dissociation of SU allows TM to resume folding and release its fusion potential before reaching a final inactive conformation. However, the way in which the fusion-suppressing ‘spring-catch', that is, the peripheral subunit, is removed in Env differs from that in HA. In a large number of retroviruses, Env activation is triggered by SU–receptor interaction and not by low pH as for influenza virus (Hernandez et al, 1996). Consequently, these retroviruses fuse at the plasma membrane (PM) and not in the endosome. In avian sarcoma and leucosis viruses (ASLV) however, the SU–receptor interaction only potentiates Env for subsequent low pH-induced activation in the endosome (Mothes et al, 2000).
It is noteworthy that the two subunits of both influenza HA and ASLV Env are disulphide-linked (Leamnson and Halpern, 1976; Skehel and Wiley, 2000). The linkage is likely to facilitate the synthesis and maintenance of the spring-loaded conformation of the fusion protein. On the other hand, its presence prevents subunit dissociation, which would be required for fusion activation. Therefore, a harsh triggering condition by acid might be necessary. In murine leukaemia viruses (MLV), a variable fraction of the Env subunits have been found to be disulphide-linked (Pinter et al, 1997). These Env subunits carry a disulphide-bond isomerase motif, Cys-X-X-Cys (CXXC) (Ferrari and Soling, 1999), in the C-terminal domain of SU, which in Friend (F)-MLV has been found to be disulphide-bonded to TM (Pinter et al, 1997). Therefore, it has been proposed that MLV uses a thiol–disulphide exchange activity to control the SU–TM subunit association and thereby its fusion activity. According to this model, one Cys residue of the motif is disulphide-bonded to TM, whereas the other carries a free thiol group that can induce isomerization of the SU–TM bond into a CXXC-disulphide. The isomerization is consistent with an earlier analysis of SU, released from F-MLV by freeze–thaw, which identified a disulphide in the CXXC motif (Linder et al, 1992). However, so far the isomerization has neither been directly demonstrated nor tested for functional significance. Furthermore, the partial linkage of Env subunits found in MLV preparations is inconsistent with the model. Nevertheless, we have shown that virtually all subunits of newly made MLV Env in cells are disulphide-bonded (Opstelten et al, 1998). The bond could be disrupted by NP-40 treatment in a manner that was temperature and pH dependent as well as Env alkylation sensitive. This suggested that MLV Env carries its own isomerization activity and that this can be induced artificially by solubilization. In the present study, we provide experimental evidence for a CXXC-linked isomerization activity in MLV Env, that receptor binding induces it, and that it controls the fusion function.
Results
SU and TM are disulphide-linked in MLV
We purified [35S]Cys-labelled Moloney(Mo)-MLV by floatation in a sucrose gradient and investigated the association of the Env subunits after lysis in the presence of the alkylating agent N-ethylmaleimide (NEM). Analyses of gradient fractions with anti-MLV polyclonal antibody (pAb) and reducing SDS–PAGE showed that the virus, with its SU and TM subunits and internal proteins, floated to the 35–40% sucrose interface (Figure 1A). Immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-SU pAb detected only the two Env subunits in the floating virus (Figure 1C). Quantification indicated that the SU (18 Cys residues) and TM (four Cys residues) subunits were present in an equimolar ratio. This suggested that there was no release of SU during virus isolation. The SU in the loading zone (lanes 7–8) most likely represents subunits released from the cells (Opstelten et al, 1998). We also detected a large, probably host-derived, protein with the anti-MLV pAb (Figure 1A, hp). Nonreducing SDS–PAGE revealed the majority of the virus-associated Env subunits (92%) as covalently linked SU–TM complexes and only a minor fraction (8%) as noncovalently linked subunits (Figure 1B and D). The host protein appeared as several bands together with free SU in the loading zone (Figure 1B). The possibility that the noncovalently linked subunits were generated artificially by SDS–PAGE was addressed with mAb 500. This reacts with an epitope only maintained in the SU–TM complexes (Chesebro et al, 1983). Accordingly, it reacted with SU–TM complexes in virions but not with free SU in the loading zone (Figure 1E). Surprisingly, it did react with the noncovalently linked SU in virions (lane 5), suggesting that this SU was liberated during sample preparation for SDS–PAGE. This was confirmed by eluting and re-running disulphide-linked SU–TM complexes (see Supplementary data). Thus, virtually all Env subunits form disulphide-linked SU–TM complexes in Mo-MLV. Similar results were obtained with F-MLV and MLV-like particles (VLPs) carrying Env of amphotropic MLV (Envampho) (data not shown).
Figure 1.
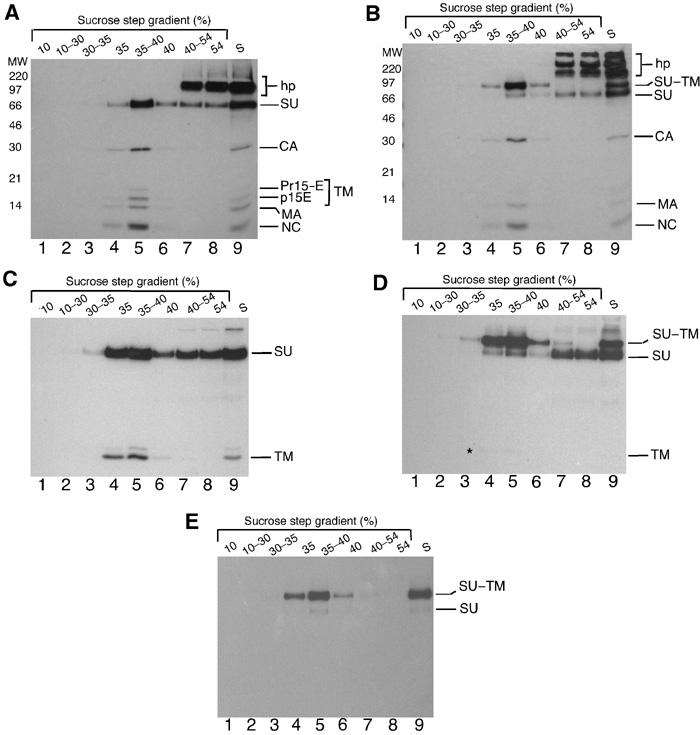
Disulphide-linked SU and TM in Mo-MLV. [35S]Cys-labelled virus was purified by floatation centrifugation. Fractions were subjected to IP with anti-MLV pAb (A,B), anti-SU pAb (C,D) or anti-Env mAb 500 (E) and analysed by reducing (A,C) or nonreducing (B–E) SDS–PAGE (12%). The disulphide-linked SU–TM complexes, the nonlinked SU and TM (Pr15E and p15E) subunits, the internal viral proteins capsid (CA), matrix (MA) and nucleocapsid (NC), and contaminating host protein (hp) are indicated. Internal viral protein p12 lacks Cys and is not detected. The asterisk in (D) indicates a weak TM band. Lane 9 in all panels shows unfractionated medium (s). Note that three times less of loading zone (54%) has been analysed as compared to other fractions.
The Env of MLV and HTLV-1 but not RSV has a CXXC-linked SU–TM disulphide-bond isomerization activity
We have shown before that NP-40 induces an alkylation-sensitive disruption of the SU–TM disulphide-bond (Opstelten et al, 1998). To find out whether this is mediated by disulphide isomerization with the CXXC motif in SU, we mapped subunit-specific thiols in Envampho of [35S]Cys-labelled VLPs before and after NP-40-induced bond disruption. The CXXC-linked isomerization model predicts the disappearance of a free thiol in the CXXC motif of SU and the appearance of a new thiol in TM. The mapping was carried out by thiol alkylation with Nα-(3-maleimidylpropionyl)biocytin (MB) and subsequent streptavidin capture of alkylated subunits. To this end, one sample received MB before and another after solubilization. This resulted in the release of alkylated Env complexes with covalently linked and nonlinked SU and TM subunits, respectively. The linked SU–TM complexes and the two nonlinked subunits were isolated by nonreducing SDS–PAGE and glycanase F treated before being used for the analysis of subunit-specific thiols. A control analysis showed that the gel isolation of the SU–TM complexes resulted in some disruption of the SU–TM disulphide-bond (see SUox in Figure 2A, lane 1). When the complexes were reduced (lane 2) and the liberated subunits were subjected to streptavidin capture analysis, it was found that almost all SU was precipitated whereas most of TM remained in the supernatant (lanes 4 and 6). This shows that the SU–TM complex carries a free thiol group in the SU subunit. When the complexes were analysed in nonreduced form, we found that not only the intact complex but also the accompanying nonlinked SU was precipitated (lanes 3 and 5). This is consistent with the latter representing SU subunits of disulphide-linked complexes that were disrupted during gel isolation. Figure 2B (lanes 1 and 2) shows the migration of the gel-isolated SU and TM subunits that were alkylated in their nonlinked form. When these were subjected to the capture analysis, it was found that TM was efficiently precipitated (lanes 4 and 6,) whereas most of the SU remained in the supernatant (lanes 3 and 5). This demonstrates that NP-40-induced SU–TM disulphide-bond disruption is associated with the disappearance of an SU-thiol and the appearance of a TM-thiol, that is, a thiol switch in accordance with the CXXC-mediated isomerization model. A corresponding switch was also detected in Mo- and F-MLV upon lysis and in nonlysed Mo-MLV under Ca2+-free conditions, which, as demonstrated below, also induced disruption of the SU–TM disulphide-bond (data not shown). The free SU-thiol was further mapped by SDS–tricin–PAGE of trypsin-digested Envampho to a 12 kDa C-terminal fragment that included the CXXC motif (see Supplementary data).
Figure 2.
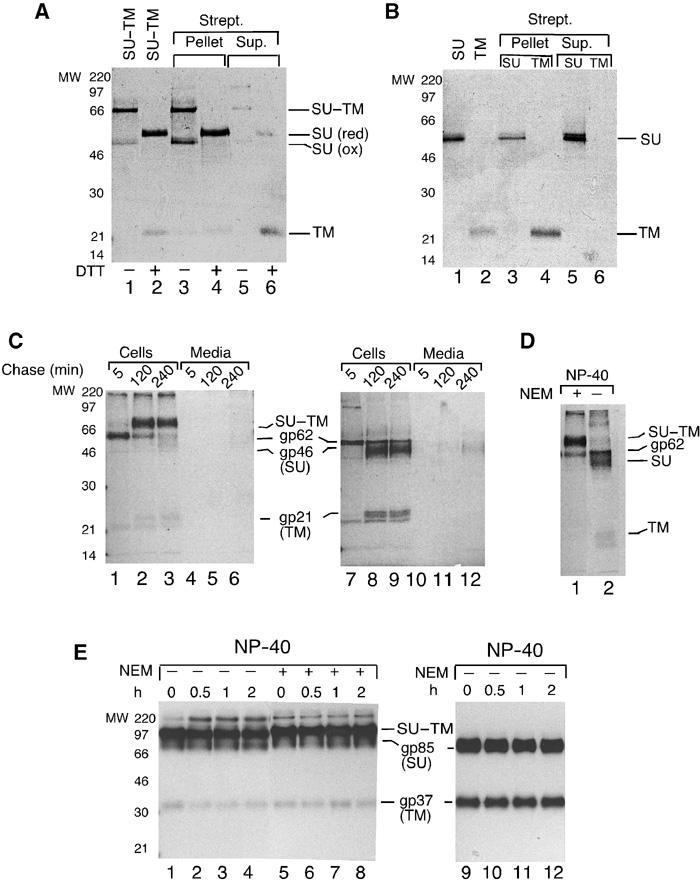
MLV and HTLV-1 Env carry isomerization activity. (A) Thiol mapping of disulphide-linked SU–TM subunits. SU–TM complexes of Envampho were alkylated with MB, gel isolated and glycanase F treated. Analyses of deglycosylated complexes by nonreducing (lane 1) and reducing (lane 2) SDS–PAGE. Note migration difference of reduced (red) and oxidized (ox) SU. Streptavidin capture of nonreduced (lanes 3 and 5) and reduced (lanes 4 and 6) complexes. (B) Thiol mapping of SU and TM after NP-40-induced SU–TM disulphide-bond disruption. Analyses of deglycosylated SU (lane 1) and TM (lane 2) by reducing SDS–PAGE. Streptavidin capture of SU (lanes 3 and 5) and TM (lanes 4 and 6). (C) SU and TM are disulphide-linked in HTLV-1 Env. BHK-21 cells expressing the HTLV-1 env gene were labelled with [35S]Cys for 30 min and chased for 5–240 min. Cells and media were lysed in the presence of NEM. Immunoprecipitated Env was analysed by nonreducing (lanes 1–6) or reducing (lanes 7–12) SDS–PAGE. (D) HTLV-1 Env can isomerize. Cells expressing HTLV-1 env at 2 h chase time were incubated in NP-40 lysis buffer for 40 min at 30°C with or without NEM. Immunoprecipitated Env was analysed by nonreducing SDS–PAGE. (E) RSV Env cannot isomerize. Cells expressing RSV env were labelled as above, chased for 2 h and lysed for 0–2 h at 30°C with or without NEM. Immunoprecipitated Env was analysed by nonreducing (lanes 1–8) or reducing (lanes 9–12) SDS–PAGE.
To obtain independent support for CXXC activity, we studied the isomerization capacities of the SU–TM disulphide-bonds in Env subunits of human T-cell leukaemia virus-1 (HTLV-1) and Rous sarcoma virus A (RSV). These are remotely related to MLV Env (23 and 20% identity, respectively) (GeneBank P03385, P90202 and O92955) (Pearson et al, 1997). Sequence analyses showed that EnvHTLV had conserved the CXXC motif of SU, whereas EnvRSV had not. The SU(gp85) and TM(gp37) subunits of EnvRSV have been shown to be linked by a disulphide-bond (Leamnson and Halpern, 1976), but its presence in EnvHTLV was unclear. Therefore, we expressed the HTLV-1 env gene in BHK-21 cells and followed Env synthesis by nonreducing SDS–PAGE. We observed the Env precursor molecule (gp62) and its maturation into a disulphide-linked SU(gp46)–TM(gp21) complex (MW, 70 kDa) (Figure 2C, lanes 1–3 and 7–9) (Pique et al, 1992). When tested for isomerization by NP-40 treatment, we found that the disulphide-bond was disrupted (Figure 2D, lane 2), unless NEM was included (lane 1). In contrast, the SU–TM disulphide-bond of EnvRSV remained essentially intact in the isomerization assay (Figure 2E, lanes 1–4). Thus, the results support the disulphide-bond isomerization activity of the CXXC motif. It should be noted that mutagenesis has been attempted as a way to study the activity of the motif but resulted in Env malfolding (Gu et al, 1995).
Ca2+ control of SU–TM disulphide-bond isomerization
As conditional triggering of isomerization could explain earlier findings about nonlinked SU and TM subunits in MLV, we tested several conditions for their effect on isomerization. We found that incubation of Mo-MLV in DMEM for up to 36 h at 37°C resulted in minor bond disruption (Figure 3A, lanes 1–4). In contrast, treatment with heat or urea resulted in complete isomerization within a few minutes (Figure 3B and C). Apparently, nonspecific perturbation of the Env structure triggers isomerization. Most significantly, this could also be induced in neutral TN (17 mM Tris, 8 mM HEPES, pH 7.45, 150 mM NaCl), or HN (15 mM HEPES, pH 7.45, 150 mM NaCl) buffers, in particular if the virus had been prewashed with EDTA buffer (HNE, 15 mM HEPES, pH 7.45, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM Na-EDTA). This is shown in Figure 3D (lanes 1–4) for virus that has been washed sequentially with HNE and HN by ultrafiltration and then incubated in TN at 37°C. In contrast, isomerization was suppressed in the low pH buffer MN (25 mM 2-[N-morpholino]ethanesulphonic acid (MES), pH 5.7, 150 mM NaCl) potentially due to protonation of CXXC-thiol (Figure 3E). Depletion of Ca2+ and/or Mg2+, the two divalent cations present in DMEM, could possibly trigger the isomerization in HNE/TN-treated Env. A specific involvement of Ca2+ was documented by demonstrating an inhibition of the TN-induced isomerization by 5 mM Ca2+, but not by 5 mM Mg2+ (Figure 3F, lanes 4–6 and 1–3) or 1 mM Zn2+ (data not shown). Furthermore, 37°C incubation in Ca2+-free DMEM caused efficient isomerization (Figure 3G, lanes 1–3). We conclude that Ca2+ controls the SU–TM disulphide-bond isomerization reaction by stabilizing an isomerization-suppressing Env conformation. Detailed analyses of isomerization kinetics at different pH values and concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ are presented in connection to their effects on Env function (Figures 6H and 7B). As incubation in TN containing the same concentration of Ca2+ as DMEM (1.8 mM) suppressed isomerization as efficiently as DMEM, we used this as the control condition in subsequent isomerization incubations.
Figure 3.
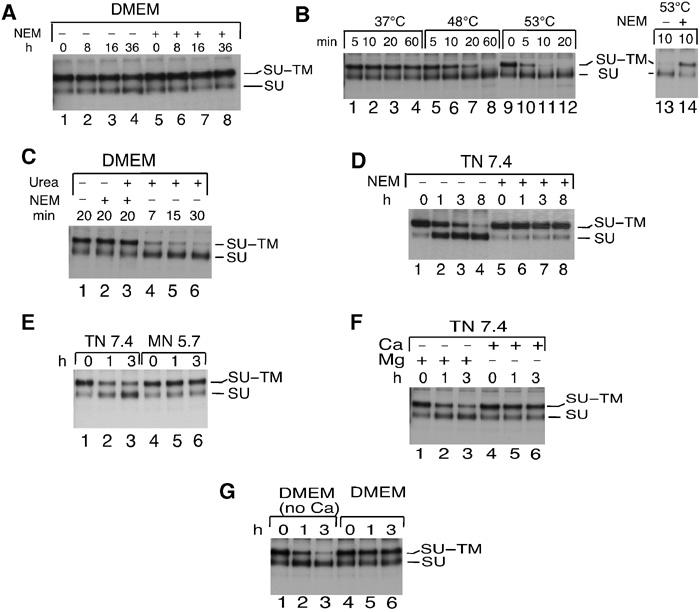
Induction of the SU–TM disulphide-bond isomerization in Mo-MLV. (A) Suppressed isomerization in DMEM. Virus, isolated by floatation centrifugation, was incubated for 0–36 h at 37°C in DMEM. NEM was added and the samples were subjected to IP with anti-MLV pAb and SU–TM disulphide-bond analyses by nonreducing SDS–PAGE (lanes 1–4). Samples that received NEM before the incubations were used as controls (lanes 5–8). (B) Heat induces isomerization. Virus in DMEM was incubated at elevated temperatures for 5–60 min before disulphide-bond analysis as in (A). (C) Urea induces isomerization. Virus was incubated in DMEM at 30°C with or without 2 M urea and NEM. (D) TN triggers isomerization. Virus in TN, pH 7.4, was incubated at 37°C with or without NEM. (E) Low pH inhibits isomerization. Virus was incubated in TN, pH 7.4, or MN, pH 5.7. (F) Ca2+, but not Mg2+, inhibits TN-induced isomerization. Virus in TN, pH 7.4, was incubated with Mg2+ (5 mM) or Ca2+ (5 mM). (G) DMEM without Ca2+ triggers isomerization. Mo-MLV was incubated in DMEM with or without Ca2+.
Figure 6.
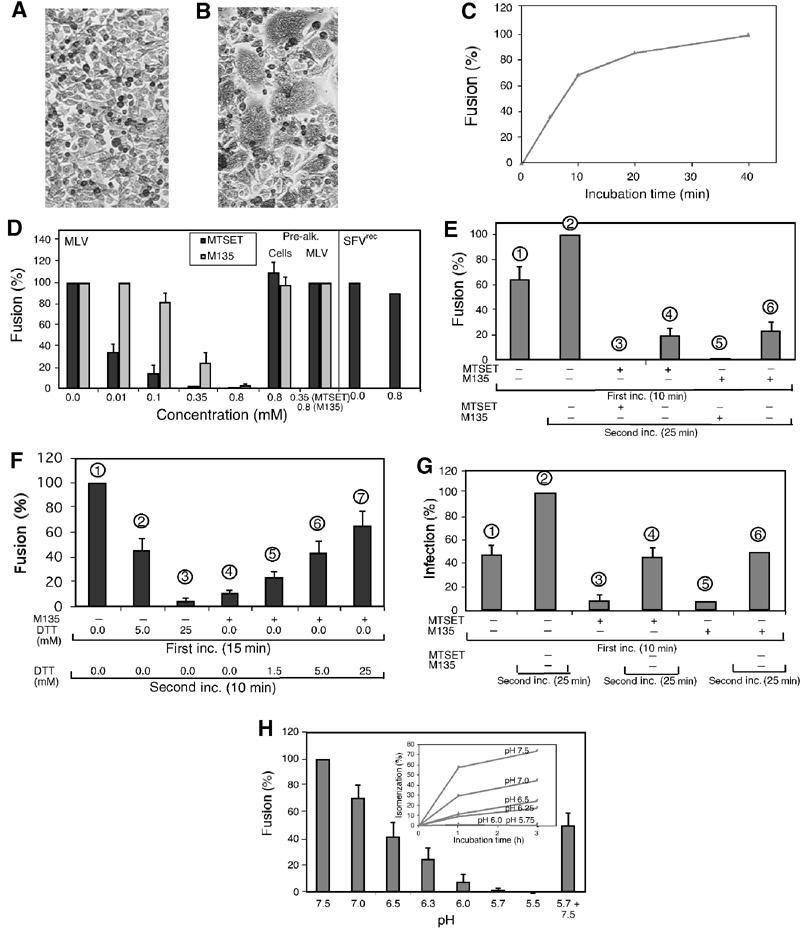
Isomerization inhibition suppresses MLV fusion and infectivity. (A,B) Mo-MLV induced fusion-from-without. Methylene-blue-stained XC cells before (A) and after (B) viral fusion (40 min at 37°C) and polykaryon formation. (C) Time course of Mo-MLV fusion in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+. Virus was fused with XC cells for 0–40 min before inactivation. The relative fusion efficiencies using fusion in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ for 40 min as control are shown. (D) Alkylation inhibits Mo-MLV but not SFVrec fusion. Mo-MLV fusion was performed for 10 min in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ with 0–0.8 mM M135 or MTSET. Fusion efficiencies are given in % of fusion in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ without drug. Fusion efficiencies with prealkylated cells or virus are also shown. SFVrec fusions were carried out by sequential incubations in TN (pH 7.4)/1.8 mM Ca2+ (5 min on ice), MN (pH 5.6)/1.8 mM Ca2+ (5 min at 37°C) and TN (pH 7.4)/1.8 mM Ca2+ (5 min at 37°C) with or without alkylator. (E) Rescue of M135- and MTSET-inhibited fusion by second, drug-free incubation. Mo-MLV fusion was carried out either for 10 min or 10+25 min in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ with or without 0.8 mM M135 or 0.35 mM MTSET. Fusion efficiencies are given in % of the 10+25 min fusion without drug. (F) DTT rescue of M135-inhibited fusion. Mo-MLV fusion was performed for 15 min in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ with M135 (0.8 mM) or DTT (5 and 25 mM), and for an additional 10 min in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ with or without DTT (1.5–25 mM). (G) Alkylation inhibits infectivity of MLV. 3T3 cells were infected with EnvMo-MLV-egfp vectors either for 10 min or for 10+25 min with or without alkylator. Infectivities (egfp-positive cells) are given in % of that of the 10+25 min infection without drug. (H) Inhibition of Mo-MLV fusion by low pH. Fusions were performed in DMEM/25 mM Tris or /MES at pH values ranging from 7.5 (control) to 5.5 for 15 min and expressed as % of control. The reversibility was shown by consecutive 15 min incubations at pH 5.7 and 7.4. (inset) Inhibition of isomerization by low pH. Isomerization was induced by incubating virus for 1–3 h at 37°C in TN or MN buffers at the indicated pH. Samples were analysed as in and isomerization is given in % of that in control samples, which received NEM before incubation.
Figure 7.
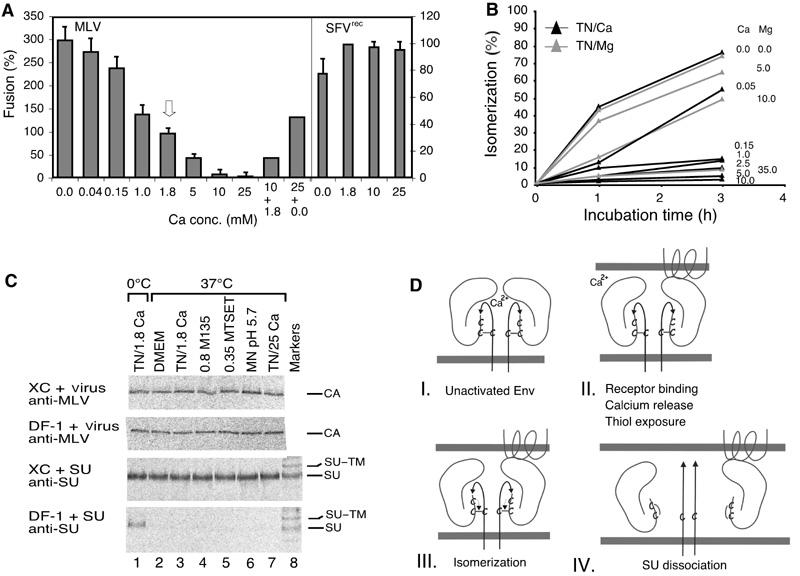
Isomerization induction enhances MLV fusion activity and infectivity. (A) Effect of Ca2+ on Mo-MLV and SFVrec fusion. Mo-MLV was fused to XC cells (left axis) for 15 min in TN, containing 0–25 mM Ca2+. Fusion at control conditions, 1.8 mM Ca2+, is highlighted by an arrow. In some experiments, the virus was first incubated in high Ca2+ (10 or 25 mM) for 15 min and then under control (1.8 mM) or Ca2+-free (0.0 mM) conditions for another 25 min. SFVrec fusions (right axis) were carried out for 10 min in MN, pH 5.6, in the presence of 0–25 mM Ca2+. (B) Effect of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on isomerization kinetics. Virus was taken up into TN containing Ca2+ or Mg2+ as indicated by dialysis and incubated at 37°C for 0–3 h. Isomerization was analysed as in (6H-inset). (C) Effect of alkylators, high Ca2+ and low pH on the specific SU–receptor and the unspecific virus–cell interactions. [35S]Cys-labelled Mo-MLV and accompanying free SU were produced in MOV-3 cells. Part of the culture supernatant was freed from virus by centrifugation and used for SU binding analyses. The unfractionated part was used for virus analyses. Virus and SU were bound to receptor-positive XC and receptor-negative DF-1 cells at 4°C for 1 h and then washed and incubated in control conditions (DMEM or TN/1.8 mM Ca2+), TN/1.8 mM Ca2+/0.8 mM M135, TN/1.8 mM Ca2+/0.35 mM MTSET, MN/pH 5.7/1.8 mM Ca2+ or TN/25 mM Ca2+ at 0°C (lane 1) or 37°C (lanes 2–7) for 15 min. Cell-bound SU or virus were immunoprecipitated with anti-SU or anti-MLV pAb and analysed by nonreducing SDS–PAGE. Note that only the CA band of cell-bound virus is shown. Note also that, in contrast to virus, free SU can only bind to the receptor-positive XC cells, and that alkylators, low pH and high Ca2+ do not significantly affect the specific SU–receptor or the unspecific virus–cell interactions. (D) Schematic model showing how the isomerization of the SU–TM disulphide-bond controls the fusion function in MLV Env. Four steps in the activation pathway (I–IV) are shown. The main events at each step are indicated. Two SU–TM complexes of the trimeric Env are depicted. Each consists of the membrane-anchored TM subunit, with the fusion peptide (arrow), and the peripheral SU subunit. The SU–TM disulphide-bond and the associated CXXC motif in SU are indicated. The target membrane at the top contains a multispanning Env-receptor protein.
Isomerization mediates dissociation of SU
The effects of isomerization on virus structure were studied by subjecting TN-treated Mo-MLV with partially or completely isomerized Env (Figure 4A, lanes 2 and 3) to floatation centrifugation. We found that isomerization was accompanied by SU dissociation from the particles (Figure 4B and C), and the released SU was found in the sample-loading zone together with the originally free SU. The SU-depleted particles also contained two new bands migrating slower and faster than CA (Figure 4C, lane 3). Elution and re-analyses under reducing conditions showed that the slower band was disulphide-linked TM and the faster band was disulphide-linked MA subunits (data not shown). We conclude that isomerization is accompanied by major alterations in Env structure, in particular dissociation of SU. However, it remained possible that the TN treatment by itself caused major conformational changes in Env and thus induced isomerization. This possibility was studied by following the effect of TN on Env structure in the presence or absence of NEM using mAb 500. The rationale was that if the TN treatment itself caused major alterations in the Env structure, changes should also take place when isomerization was blocked by alkylation of CXXC-thiol. mAb 500 should be a sensitive indicator for such changes as it is specific for the SU–TM complex. IP with anti-MLV pAb confirmed that NEM-sensitive isomerization was induced by TN (Figure 4D, lanes 1–6). The analyses with mAb 500 showed, as expected, that the SU of isomerized Env was not reactive (lanes 7–9). In contrast, the complex remained reactive when the TN-induced isomerization was inhibited by NEM (lanes 10–12). This suggests that TN treatment does not cause major conformational changes in Env, but that this is a consequence of isomerization.
Figure 4.
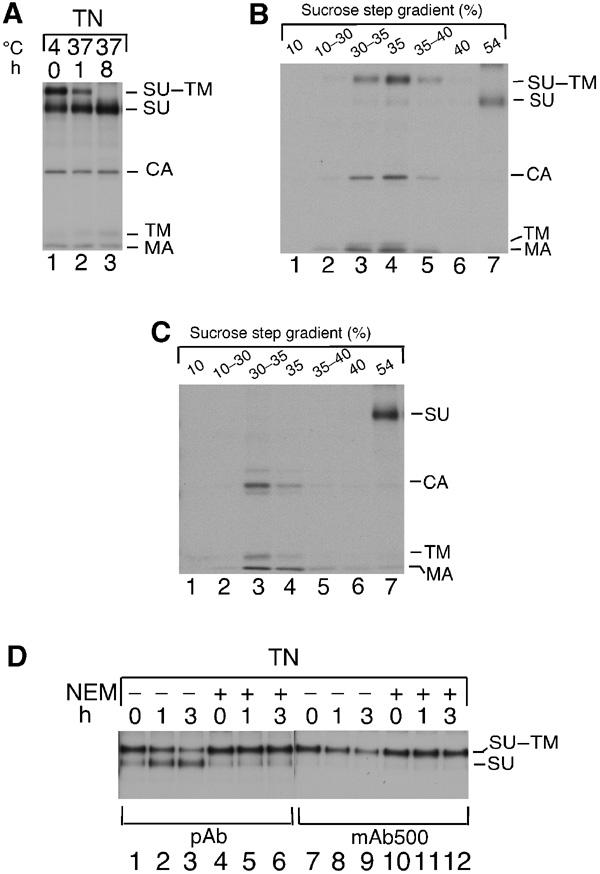
Isomerization results in SU dissociation. (A) Preparation of Mo-MLV with partially or completely isomerized SU–TM disulphide-bond. Mo-MLV was dialysed against TN, incubated as indicated, lysed in the presence of NEM, subjected to IP with anti-MLV pAb and analysed by nonreducing SDS–PAGE. (B,C) Isomerization results in dissociation of SU. Mo-MLV with partially (B) or completely (C) isomerized SU–TM disulphide-bond was subjected to floatation centrifugation. Fractions were immunoprecipitated and analysed by nonreducing SDS–PAGE. Note that four times less of loading zone (54%) has been analysed as compared to other fractions. (D) Conformational changes follow isomerization. Mo-MLV were incubated for 1–3 h at 37°C in TN with or without NEM, immunoprecipitated with pAb or mAb 500 and analysed by nonreducing SDS–PAGE.
Receptor binding induces isomerization
The accessibility of CXXC-thiol for alkylation in intact virus, that is, virus in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+, was analysed by incubating Mo-MLV with the membrane-impermeate alkylating reagent 4-(N-maleimido)benzyl-α-trimethylammonium iodide (M135). As complete removal of alkylator after treament was a problem, we treated virus that was immobilized by unspecific binding to receptor-negative DF-1 chicken cells (Pizzato et al, 1999) (Figure 5A, first inc.). This facilitated efficient alkylator removal by washing. The virus–cell sample was then lysed and the degree of CXXC-thiol alkylation was determined indirectly, by following its inhibitory effect on the isomerization reaction induced by lysis (second inc.). Figure 5A (lane 3) shows that isomerization is complete in the absence of alkylator. Surprisingly, treatments with 1.0 or 2.5 mM M135 for 1 h could not inhibit the lysis-induced isomerization (Figure 5A, lanes 4 and 5). Thus, CXXC-thiol was inaccessible for alkylation. However, if alkylation was carried out during lysis, as little as 0.05 mM was effective (lane 1) and 0.75 mM resulted in virtually complete isomerization inhibition (lane 2). Similarly, if alkylation treatment during the first incubation was carried out in TN, that is, conditions that induce roughly 50% isomerization (see lane 2 in Figure 3D), it was effective, causing inhibition of the subsequent lysis-induced isomerization (Figure 5, lanes 6–8). The alkylation in TN was studied in more detail by following directly the inhibitory effects of different concentrations of M135 or [2-(trimethylammonium)ethyl]methanethiosulphonate bromide (MTSET), another membrane-impermeant alkylator, on the kinetics of TN-induced isomerization in free virus. In this case, the subsequent lysis was performed in the presence of NEM (20 mM) to exclude completely any lysis-induced isomerization. It was found that most of the TN-induced isomerization was inhibited at 0.8 mM M135 or 0.1 mM MTSET (Figure 5B). We conclude that CXXC-thiol is hidden in intact Env but becomes exposed when isomerization is induced. Apparently, alkylators can then modify the exposed thiol before it is able to attack the SU–TM disulphide-bond. Thus, the alkylated Env represents an intermediate, which is arrested at an early stage in the isomerization process. Further studies with DF-1 cell-bound virus showed that induction of isomerization was also associated with exposure of the SU–TM disulphide-bond. Intact Env was resistant towards reduction with DTT (Figure 5C), whereas Env that had been induced to isomerize with TN and arrested by alkylation was sensitive (Figure 5D).
Figure 5.
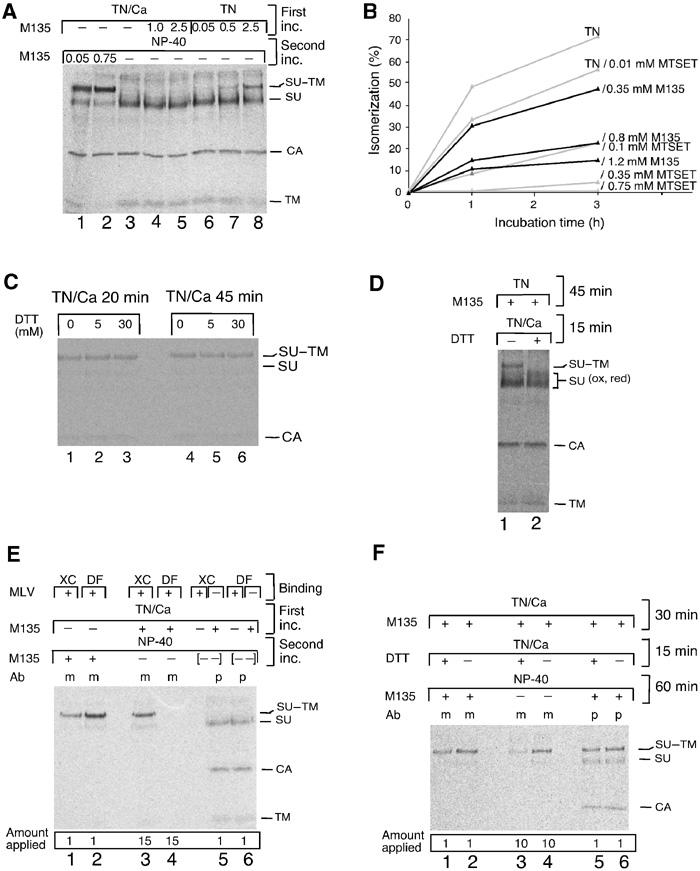
Receptor binding in the presence of alkylator generates an isomerization-arrested Env intermediate. (A) Induction of isomerization exposes CXXC-thiol for alkylation. Mo-MLV was adsorbed to DF-1 cells, washed two times with TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ and incubated for 1 h at 37°C in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ (lanes 1–5), or washed two times with TN/0.05 mM EDTA and incubated in TN (lanes 6–8), with or without M135 (0.05–2.5 mM) (first inc.). The cells were washed and lysed in NP-40 buffer for 40 min at 30°C with or without alkylator (second inc.). Viral proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-MLV pAb and analysed by nonreducing SDS–PAGE. (B) Inhibition of TN-induced isomerization by M135 and MTSET in free virus. Mo-MLV in TN was incubated for 0–3 h at 37°C in the presence of 0–1.2 mM alkylator. NEM was added, samples were lysed and viral proteins were analysed as in (A). Isomerization was estimated from the decrease of SU–TM complexes as compared to a control sample incubated in TN with 20 mM NEM and is given in %. (C) The SU–TM disulphide-bond of intact virus is DTT resistant. Mo-MLV was adsorbed to DF-1 cells and incubated for 20 or 45 min at 37°C in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ with 0–30 mM DTT. NEM was added, samples were lysed and the SU–TM disulphide-bond was analysed as in (A). (D) The SU–TM disulphide-bond of isomerization-induced/M135-arrested Env is DTT sensitive. Mo-MLV was adsorbed to DF-1 cells and incubated first for 45 min at 37°C in TN with 1.5 mM M135 and then, after adding Ca2+ to 1.8 mM, for an additional 15 min with or without 10 mM DTT. Samples were washed, lysed without NEM and disulphide-bonds were analysed as in (A). Note that the M135 isomerization-arrested SU–TM complexes (lane 1) were reduced by DTT (lane 2). (E) Receptor binding exposes CXXC-thiol for alkylation. Mo-MLV was bound to XC or DF-1 cells and incubated for 40 min at 37°C in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ with or without M135 (1.2 mM) (first inc.). The cultures were washed and lysed in NP-40 buffer for 60 min at 30°C with or without alkylator (second inc.). Viral proteins were immunoprecipitated with mAb 500 (m) or anti-MLV pAb (p) and analysed by nonreducing SDS–PAGE. Samples 5 and 6 are controls where lysates of alkylated XC or DF-1 cells have been mixed ([- -]) with nonalkylated virus–cell samples. The complete isomerization observed indicates that the alkylator has been efficiently removed after the first incubation. Note relative differences between the amounts of samples that have been applied on the gel. (F) Receptor-bound Env, arrested in isomerization by alkylation, is sensitive to SU–TM disulphide-bound reduction. Mo-MLV was bound to XC cells and incubated and analysed as in (E), but including 15 min incubation in TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ with or without 5 mM DTT before incubation with NP-40. Note that SU of cleaved complexes is not seen by mAb 500 (lane 3).
If receptor binding induces isomerization, the formation of a limited amount of isomerization-arrested, DTT-sensitive Env intermediates was expected when virus was bound to receptor-positive cells and incubated with M135. This was tested with Mo-MLV bound to XC rat cells. After incubation with the alkylator (Figure 5E, first inc.), cells were washed and lysed (second inc.). As Env subunits not in complex with receptors isomerize during lysis, it was possible to use mAb 500 to capture selectively the receptor-bound and isomerization-arrested Env subunits (lane 3). The fraction of unbound Env in the virus was measured with mAb 500 in parallel samples that received M135 before lysis but not during initial incubation. This treatment converted all unbound Env subunits into isomerization-arrested intermediates (lane 1). Virus adsorbed to the receptor-negative DF-1 cells were used as control (lanes 2 and 4). About 8% of the Env could be captured as arrested complexes after 40 min incubation of XC cell-bound virus in the presence of alkylator (compare lanes 1 and 3, and note the different amounts applied). No complexes were detected in virus adsorbed to DF-1 cells (lanes 4 and 2). In Figure 5F (lanes 3 and 4), we show that the M135-arrested, receptor-bound Env complexes were, like the corresponding complexes in TN-induced virus (Figure 5D), also sensitive to DTT. We conclude that receptor binding triggers the isomerization process in Env. The verification of this conclusion with a soluble receptor fragment was not carried out due to difficulties in designing a suitable fragment of the receptor, which is a multiple membrane-spanning amino-acid transporter (Wang et al, 1991).
SU–TM disulphide-bond isomerization controls the fusion activity of Env
The possibility that isomerization controls the fusion activity was tested by analysing Mo-MLV fusion and infectivity under conditions that either inhibited or induced isomerization. The fusion was studied as virus-induced polykaryon formation in XC cells (fusion-from-without). Fusion of cell-bound virus is induced by incubation at 37°C and terminated by pH 3.0 treatment. In confluent cultures (Figure 6A), the fusion will merge cells, and with time these will rearrange into polykaryons (Figure 6B). Preliminary testing demonstrated that TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ supported fusion as effectively as DMEM (data not shown). Therefore, TN/1.8 mM Ca2+ was used as the control condition. The time course of the fusion process is shown in Figure 6C.
We first studied the effect that alkylation-mediated inhibition of isomerization had on fusion. To avoid adverse effects due to alkylation of internal viral proteins, we used the membrane-impermeant reagents M135 and MTSET. We observed a concentration-dependent inhibition of fusion with both reagents (Figure 6D, MLV), which correlated with the effect of the alkylators on TN-induced isomerization in free virus (Figure 5B). This suggests that the fusion inhibition results from suppressed isomerization due to alkylation of CXXC-thiol. Control experiments showed that the alkylators did not affect the specific SU–receptor nor the unspecific virus–cell interactions of cell-bound virus (Pizzato et al, 1999) (Figure 7C, lanes 4 and 5 in all panels). Any inhibition due to unspecific alkylation of virus and/or cells was studied by complementing a 10 min fusion reaction in the presence of alkylator with a second incubation (25 min), without the drug. We expected that Env complexes that were not bound to receptors, and hence not isomerization arrested by the alkylator, should be able to fuse during the second incubation, unless the reaction was inhibited unspecifically. About 60% of the fusion that occurred during the second incubation in the control without alkylator (Figure 6E, difference of columns 1 and 2) was rescued (columns 4 and 6). The specificity was further substantiated by the fact that alkylation of either cells or virus before virus binding did not inhibit subsequent virus-induced fusion (Figure 6D, pre-alk.) and that fusion of XC cells by SFVrec was not inhibited by alkylation (Figure 6D). SFVrec is a nonreplicative Semliki Forest virus vector (SFV1-gagMo), which can fuse cells from without at acidic pH.
If M135 inhibited fusion by generation of isomerization-arrested, alkylated Env (see above), it should be possible to reduce the SU–TM disulphide-bond with DTT and possibly rescue fusion. This was tested by treating M135 fusion-inhibited virus with 1.5–25 mM DTT for 10 min. We found that incubation without DTT resulted in limited rescue (Figure 6F, column 4), as expected from the fusion time course shown in Figure 6C, whereas 25 mM DTT restored most of the fusion activity (column 7). Interestingly, DTT treatment efficiently inhibited fusion without M135 (columns 2 and 3). It is possible that DTT mediates the reduction of the SU–TM disulphide-bond in receptor-bound Env before natural isomerization takes place and that this leads to premature, nonproductive fusion activation.
The effect of MTSET on MLV infectivity was studied in 3T3 mouse cells with EnvMo-MLV-egfp vectors and scored by egfp-positive cells. The analysis showed that ∼80% of the infectivity of a 10 min incubation was inhibited by 0.35 mM MTSET or 0.8 mM M135 (Figure 6G, columns 3 and 5). However, a subsequent incubation without alkylator for 25 min restored the infectivity to a level (columns 4 and 6) that corresponded to the difference between the 10 min (column 1) and 10+25 min incubation (column 2) without drug. Thus, the alkylation effect on infectivity concords with that on fusion.
We showed above that isomerization was inhibited by protonation of CXXC-thiol. Interestingly, Portis et al (1985) have shown that low pH also inhibits MLV fusion. To find out whether the low pH effects on isomerization and fusion correlated, we studied them in parallel. Both functions were similarly inhibited by low pH (Figure 6H with inset). Unspecific inhibition of fusion by low pH was unlikely in view of the fact that both ASLV and SFV require low pH for fusion (Hernandez et al, 1996; Mothes et al, 2000). Furthermore, the virus–cell interactions of cell-bound virus were largely unaffected by low pH (Figure 7C, lane 6 in all panels) and the fusion inhibition was partially (∼50%) reversible (Figure 6H, 5.5+7.5).
As Ca2+ depletion induced isomerization of Env, we tested its effect on virus fusion. The fusion activity increased when the Ca2+ concentration in TN was decreased below control level (1.8 mM Ca2+) (Figure 7A, MLV). A three-fold increase was observed in TN without Ca2+. The enhanced fusion in TN was paralleled by increased infectivity of Mo-MLV in TN (data not shown). It was not effective with receptor-negative BHK-21 and DF-1 cells and was inhibited by 0.35 mM MTSET and 0.8 mM M135 (data not shown). This suggests that the fusion enhancement results from Ca2+-depletion-facilitated Env isomerization of receptor-bound virus. Accordingly, SFVrec fusion was not enhanced in TN (Figure 7A, SFVrec, 0.0). We noticed that isomerization in free virus was less sensitive to low Ca2+ (∼50% efficiency at ∼0.05 mM Ca2+) (Figure 7B) than virus fusion on XC cells (∼50% efficiency at ∼1.0 mM Ca2+) (Figure 7A). However, such a difference would be expected if Ca2+ deprivation and receptor binding cooperates in isomerization induction (see below). Altogether we conclude that the SU–TM disulphide-bond isomerization reaction controls the fusion activity in the Env of MLV.
Ca2+ release activates isomerization in Env after receptor binding
The difference in dependence of the fusion and isomerization on Ca2+ concentration is consistent with either a fusion process in which receptor binding and Ca2+ deprivation cooperate in the same activation pathway or by using two separate pathways (a natural one, which is receptor mediated, and an artificial one, which is Ca2+-depletion-driven). To sort out these possibilities, we tested whether TN containing high concentrations of Ca2+ inhibited virus fusion. This should be the case in a common pathway, but not in separate pathways. The analysis showed that 10 mM Ca2+ reduced fusion to 14% of the control level and 25 mM almost abolished fusion (Figure 7A). Control experiments showed that high Ca2+ did not significantly affect the virus–cell interactions of cell-bound virus (Figure 7C, lane 7 in all panels) and that the fusion activity was partially restored by a second incubation under control or Ca2+-free conditions (Figure 7A, 10+1.8 and 25+0.0). Furthermore, we found that high Ca2+ had no significant effect on SFVrec fusion (Figure 7A). Therefore, we conclude that Ca2+ represents a natural, isomerization-controlling mediator in the fusion-activation pathway of Env.
Discussion
In this study we show that the Env of Mo-MLV can isomerize its SU–TM disulphide-bond. The activity is induced by receptor binding and is required for virus entry into cells. Isomerization results in SU displacement and subsequent activation of the fusion function in TM. The activity is linked to a typical disulphide-isomerase-active motif, CXXC, which is located in the C-terminal portion of SU. In the unactivated Env, the CXXC motif is disulphide-bonded to the last Cys residue of a CX6CC motif in a conserved region of TM (Fass et al, 1996; Pinter et al, 1997; Kobe et al, 1999). This probably undergoes chain reversal during fusion activation to facilitate virus and cell membrane contacts (Maerz et al, 2000). Consequently, the maintenance of a conditionally isomerization-competent CXXC–CX6CC disulphide-bond in Env appears as an elegant way to prevent chain reversal and the subsequent activation of the fusion function until required. The conservation of the isomerization activity in MLVs and HTLV-1, as shown in the present work, as well as the observation of disulphide-linked SU and TM subunits in bovine leukaemia virus (BLV) (Johnston and Radke, 2000), suggests that this control mechanism is common to all retroviruses with an (SU)CXXC–CX6CC(TM) disulphide bridge.
The fact that ASLV can fuse without isomerization of its SU–TM disulphide-bond constitutes an apparent contradiction to the model. EnvASLV contains a CX6CC motif in TM but no CXXC motif in SU. However, it has been shown that fusion activation of EnvASLV requires low pH in addition to receptor (Mothes et al, 2000). The low pH probably weakens the SU–TM interaction to an extent that TM can undergo fusion activating conformational changes even in the presence of an SU–TM disulphide-bond.
The lentivirus has a CX6C sequence in the TM subunit but no disulphide bridge to the peripheral one (Chan et al, 1997). Strikingly, HIV-1 entry is inhibited by thiol-blocking agents (Gallina et al, 2002; Matthias et al, 2002). In particular, it has been shown that trivalent arsenicals react with redox-active dithiols in domain 2 of the HIV-1 receptor CD4 and in the active sites of receptor-associated PDI and soluble thioredoxin. This suggests that corresponding structures participate in the fusion activation of the viral Env. Such mechanisms do not apply for MLV, however, because trivalent arsenicals were ineffective against infection of 3T3 cells with MSLV pseudotyped with Enveco and infection of Sup T1 cells with HIV-1 pseudotyped with Envampho (Gallina et al, 2002). Furthermore, we showed here that MLV fusion and infection were unaffected by prealkylation of target cell membranes.
Recently, an intersubunit disulphide-bond was engineered into EnvHIV. This prevented virus fusion if not reduced with DTT during infection (Abrahamyan et al, 2003). The finding supports the general role of an intersubunit disulphide-bond as a fusion suppressor.
Our observation that Ca2+ controls the isomerization activity of MLV Env is intriguing. The data suggest that Ca2+ stabilizes the intact, unactivated form of Env and that Ca2+ removal mediates isomerization upon receptor binding. As calmodulin-like Ca2+-binding motifs are absent in Env, and Ca2+ has been found not to bind to the crystallized receptor-binding fragment (RBD) of F-MLV or to SU released from BLV-infected cells, Ca2+ might be coordinated by amino-acid residues that are part of separate subunits in the Env oligomer (Fass et al, 1997; Gatot et al, 2002). It is possible that receptor binding disturbs the coordination of Ca2+, leading to its release and subsequent Env destabilization, CXXC-thiol activation, SU–TM disulphide-bond isomerization and triggering of the fusion function in TM. An evident advantage to stabilize Env in this way would be that receptor binding of only one SU subunit of the trimeric Env could induce Ca2+ removal and thus trigger the fusion function in all three subunits. Env destabilization caused by Ca2+ removal could also explain how it is possible for wt SU or its RBD to rescue a fusion-arrested, and presumably also isomerization-arrested, RBD mutant of MLV at the PM (Lavillette et al, 2000). The model is summarized in Figure 7D.
Experimental procedures
Cells
BHK-21 cells were grown as described (Opstelten et al, 1998). XC, DF-1 and 3T3 cells (American type culture collection, Rockville, MD), and MOV-3 cells (G Schmidt, GSF-National Research Center for Environment and Health, Neuherberg, Germany) were maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM; GIBCO BRL) supplemented with 10% FCS, 20 mM HEPES and L-glutamine. Fr-57 cells were generated by transfection of 3T3 cells with F-MLV proviral DNA (BW Chesebro, Rocky Mountain Laboratories, Hamilton, MT).
Antibodies
We used the mouse mAb 500 against MLV Env protein (BW Chesebro), the mouse pAb against RSV A TM (J White, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA), the goat pAbs HE885 against MLV proteins and HE698 against MLV SU (Viromed Biosafety Laboratories, Camden, NJ) and an anti-HTLV-1 antisera (NL Paul, Institute of Cancer Research, London, UK).
Vectors
SFV viral vectors (∼5 × 107 IU/ml) expressing retrovirus proteins, VLPs and MLV-egfp vectors (∼7 × 105 IU/ml) were produced as described (Liljestrom and Garoff, 1991; Li and Garoff, 1996). SFV RNA replicons encoding gag and env genes were transcribed from pSFV1-gagMo, pSFV1-envampho and pSFV1-envMo (Suomalainen and Garoff, 1994; Li and Garoff, 1996), pSFV1-gp62HTLV−1 (MT-2 strain from NL Paul) and pSFV1-envRSV (RSV-A strain from J White). pSFV-1-LN3I-GFP with the green fluorescent protein gene (egfp) in an MLV vector was subcloned from pEGFP-N3 (BD Biosciences Clonentech, Palo Alto, CA) into the LN3I vector (Li and Garoff, 1996) and was provided by H Andersson (Karolinska Institute).
Preparation of particles and lysates
Metabolic labelling of viral proteins in cells was carried out with [35S]Cys (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Amersham, UK) as described (Opstelten et al, 1998). Labelled VLPs and MLV were produced in SFV vector-infected BHK-21 cells and in MOV-3 or Fr-57 cells, respectively, by 14 h labelling in DMEM containing 5% FCS. Unlabelled MLV (∼106 IU/ml) was prepared correspondingly. MLV was purified by floatation centrifugation in a step gradient, composed of 5 ml/55% (w/w) (loading zone), 2 ml/40%, 2 ml/35%, 1 ml/30% and 1 ml/10% sucrose in 50 mM Tris, pH 7.4/150 mM NaCl, for 16 h at 160 000 g and 4°C in a Beckman SW 41 rotor. MOV-3 culture supernatant with virions and free SU was virus depleted by centrifugation at 120 000 g for 2 h at 4°C. Cells, virus or VLPs were lysed on ice in NP-40 buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA, 1% NP-40) with or without NEM (20 mM) (SIGMA-Aldrich Chemie, Munich, Germany) or other alkylators as indicated. IP, SDS–PAGE, autoradiography and quantification of labelled proteins on gels have been described (Opstelten et al, 1998).
Thiol mapping
Thiols in subunits of disulphide-linked SU–TM complexes were alkylated by incubation of VLPs or virus with 2 mM of the biotinylated agent MB (Molecularprobes, Eugen, OR) in NP-40 lysis buffer for 1 h at 4°C in the dark. To map thiols in nonlinked SU and TM subunits, the particles were incubated for 40 min at 30°C in lysis buffer or for 1 h at 37°C in TN before MB treatment. A 10 times molar excess of NEM was added and SU–TM complexes and nonlinked subunits, respectively, were isolated by nonreducing SDS–PAGE and eluted into TNE/0.1% SDS at 20°C. Asn-linked sugars were removed by N-glycanase F (Roche Biochemicals, Basel, Switzerland) for 18 h at 37°C in lysis buffer and the subunits were tested for MB modification by incubation with streptavidin–agarose (SIGMA-Aldrich Chemie) for 24 h at 4°C in the same buffer. The captured subunits were washed and prepared for SDS–PAGE as immunoprecipitates. Noncaptured subunits were analysed directly.
Induction of isomerization in Env
Virus in DMEM was subjected to sequential ultrafiltration (Nanose OMEGA 300 kDa MW cutoff filters, Pall Corporation, Ann Arbor, MN) at 4°C with HNE and HN and mixed with a given incubation buffer. Alternatively, buffer conditions were changed by dialysis at 4°C (15 or 300 kDa MW cutoff membranes, Spectrum Laboratories Inc., Rancho Dominguez, CA). In a third protocol, Mo-MLV was adsorbed to receptor-negative DF-1 cells and buffer conditions changed by washing. Isomerization inductions were carried out at 37°C with or without Ca2+, Mg2+ or alkylating reagent (M135 or MTSET, Toronto Research Chemicals Inc., North York, Canada). Heat and urea inductions were carried out by mixing virus with preheated or urea-containing DMEM and NP-40 inductions by incubation in lysis buffer at 30°C. Isomerization was terminated by adding NEM to 20 mM and the samples were analysed by IP and SDS–PAGE. The degree of isomerization was estimated from the resolution of the SU–TM complex into SU and TM subunits as compared to control samples that received NEM before induction of isomerization.
Assays for virus functions
Mo-MLV or SFVrec was bound to confluent XC cells in six-well (35 mm) dishes for 1 h at 4°C in DMEM with polybrene (8 μg/ml) (MLV) or bovine serum albumin (0.1%) (SFVrec), and incubated under various fusion conditions. Fusion was terminated by incubation in 40 mM sodium citrate, pH 3.0, 10 mM KCl and 135 mM NaCl for 1 min at 20°C. Virus-fused cells rearranged into polykaryons by incubation in DMEM for 3 h. The cells were stained in methanol/methylene blue (0.5%), and the number of cells (ncell) and nuclei (nnuclei) were counted and the fusion index (Fi=1−ncell/nnuclei) calculated. Parallel 1.5- to 3-fold dilution series under test and control conditions were measured and the relative fusion efficiency (% of control) was obtained by matching the Fi values of the two series. Only Fi values in the range of 0.05–0.85, which according to initial experiments were directly proportional to virus amount, were used. Standard deviations were based on data from 3–5 experiments. 3T3 cells were infected with EnvMo-MLV-egfp vectors using the protocol for fusion. After virus inactivation, 3T3 cells were incubated for 36 h and egfp-positive cells were counted.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Data
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge BW Chesebro, J White, NL Paul and H Andersson for Abs and plasmids, and M Sjöberg and M Suomalainen for discussions. Swedish Science Foundation grants 5107 and 13279 to HG supported the work.
References
- Abrahamyan LG, Markosyan RM, Moore JP, Cohen FS, Melikyan GB (2003) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Env with an intersubunit disulfide bond engages coreceptors but requires bond reduction after engagement to induce fusion. J Virol 77: 5829–5836 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr CM, Kim PS (1993) A spring-loaded mechanism for the conformational change of influenza hemagglutinin. Cell 73: 823–832 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan DC, Fass D, Berger JM, Kim PS (1997) Core structure of gp41 from the HIV envelope glycoprotein. Cell 89: 263–273 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B, Britt W, Evans L, Wehrly K, Nishio J, Cloyd M (1983) Characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with murine leukemia viruses: use in analysis of strains of Friend MCF and Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. Virology 127: 134–148 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass D, Davey RA, Hamson CA, Kim PS, Cunningham JM, Berger JM (1997) Structure of a murine leukemia virus receptor-binding glycoprotein at 2.0 angstrom resolution. Science 277: 1662–1666 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass D, Harrison SC, Kim PS (1996) Retrovirus envelope domain at 1.7 angstrom resolution. Nat Struct Biol 3: 465–469 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari DM, Soling HD (1999) The protein disulphide-isomerase family: unravelling a string of folds. Biochem J 339: 1–10 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallina A, Hanley TM, Mandel R, Trahey M, Broder CC, Viglianti GA, Ryser HJ (2002) Inhibitors of protein-disulfide isomerase prevent cleavage of disulfide bonds in receptor-bound glycoprotein 120 and prevent HIV-1 entry. J Biol Chem 277: 50579–50588 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatot JS, Callebaut I, Van Lint C, Demonte D, Kerkhofs P, Portetelle D, Burny A, Willems L, Kettmann R (2002) Bovine leukemia virus SU protein interacts with zinc, and mutations within two interacting regions differently affect viral fusion and infectivity in vivo. J Virol 76: 7956–7967 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J, Parthasarathi S, Varela-Echavarria A, Ron Y, Dougherty JP (1995) Mutations of conserved cysteine residues in the CWLC motif of the oncoretrovirus SU protein affect maturation and translocation. Virology 206: 885–893 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez LD, Hoffman LR, Wolfsberg TG, White JM (1996) Virus–cell and cell–cell fusion. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 12: 627–661 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E (1997), In Viral Entry and Receptors, Retroviruses, Coffin JM, Hughes SH, Varmus HE (eds) pp 71–119. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston ER, Radke K (2000) The SU and TM envelope protein subunits of bovine leukemia virus are linked by disulfide bonds, both in cells and in virions. J Virol 74: 2930–2935 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobe B, Center RJ, Kemp BE, Poumbourios P (1999) Crystal structure of human T cell leukemia virus type 1 gp21 ectodomain crystallized as a maltose-binding protein chimera reveals structural evolution of retroviral transmembrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 4319–4324 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavillette D, Ruggieri A, Russell SJ, Cosset FL (2000) Activation of a cell entry pathway common to type C mammalian retroviruses by soluble envelope fragments. J Virol 74: 295–304 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leamnson RN, Halpern MS (1976) Subunit structure of the glycoprotein complex of avian tumor virus. J Virol 18: 956–968 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li KJ, Garoff H (1996) Production of infectious recombinant Moloney murine leukemia virus particles in BHK cells using Semliki Forest virus-derived RNA expression vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 11658–11663 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljestrom P, Garoff H (1991) A new generation of animal cell expression vectors based on the Semliki Forest virus replicon. Biotechnology (NY) 9: 1356–1361 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder M, Linder D, Hahnen J, Schott HH, Stirm S (1992) Localization of the intrachain disulfide bonds of the envelope glycoprotein 71 from Friend murine leukemia virus. Eur J Biochem 203: 65–73 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maerz AL, Center RJ, Kemp BE, Kobe B, Poumbourios P (2000) Functional implications of the human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein helical hairpin structure. J Virol 74: 6614–6621 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthias LJ, Yam PT, Jiang XM, Vandegraaff N, Li P, Poumbourios P, Donoghue N, Hogg PJ (2002) Disulfide exchange in domain 2 of CD4 is required for entry of HIV-1. Nat Immunol 3: 727–732 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mothes W, Boerger AL, Narayan S, Cunningham JM, Young JA (2000) Retroviral entry mediated by receptor priming and low pH triggering of an envelope glycoprotein. Cell 103: 679–689 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opstelten DJ, Wallin M, Garoff H (1998) Moloney murine leukemia virus envelope protein subunits, gp70 and Pr15E, form a stable disulfide-linked complex. J Virol 72: 6537–6545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson WR, Wood T, Zhang Z, Miller W (1997) Comparison of DNA sequences with protein sequences. Genomics 46: 24–36 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A, Kopelman R, Li Z, Kayman SC, Sanders DA (1997) Localization of the labile disulfide bond between SU and TM of the murine leukemia virus envelope protein complex to a highly conserved CWLC motif in SU that resembles the active-site sequence of thiol–disulfide exchange enzymes. J Virol 71: 8073–8077 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pique C, Pham D, Tursz T, Dokhelar MC (1992) Human T-cell leukemia virus type I envelope protein maturation process: requirements for syncytium formation. J Virol 66: 906–913 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzato M, Marlow SA, Blair ED, Takeuchi Y (1999) Initial binding of murine leukemia virus particles to cells does not require specific Env-receptor interaction. J Virol 73: 8599–8611 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis JL, McAtee FJ, Evans LH (1985) Infectious entry of murine retroviruses into mouse cells: evidence of a postadsorption step inhibited by acidic pH. J Virol 55: 806–812 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel JJ, Wiley DC (2000) Receptor binding and membrane fusion in virus entry: the influenza hemagglutinin. Annu Rev Biochem 69: 531–569 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen M, Garoff H (1994) Incorporation of homologous and heterologous proteins into the envelope of Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol 68: 4879–4889 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H, Kavanaugh MP, North RA, Kabat D (1991) Cell-surface receptor for ecotropic murine retroviruses is a basic amino-acid transporter. Nature 352: 729–731 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Data


