Abstract
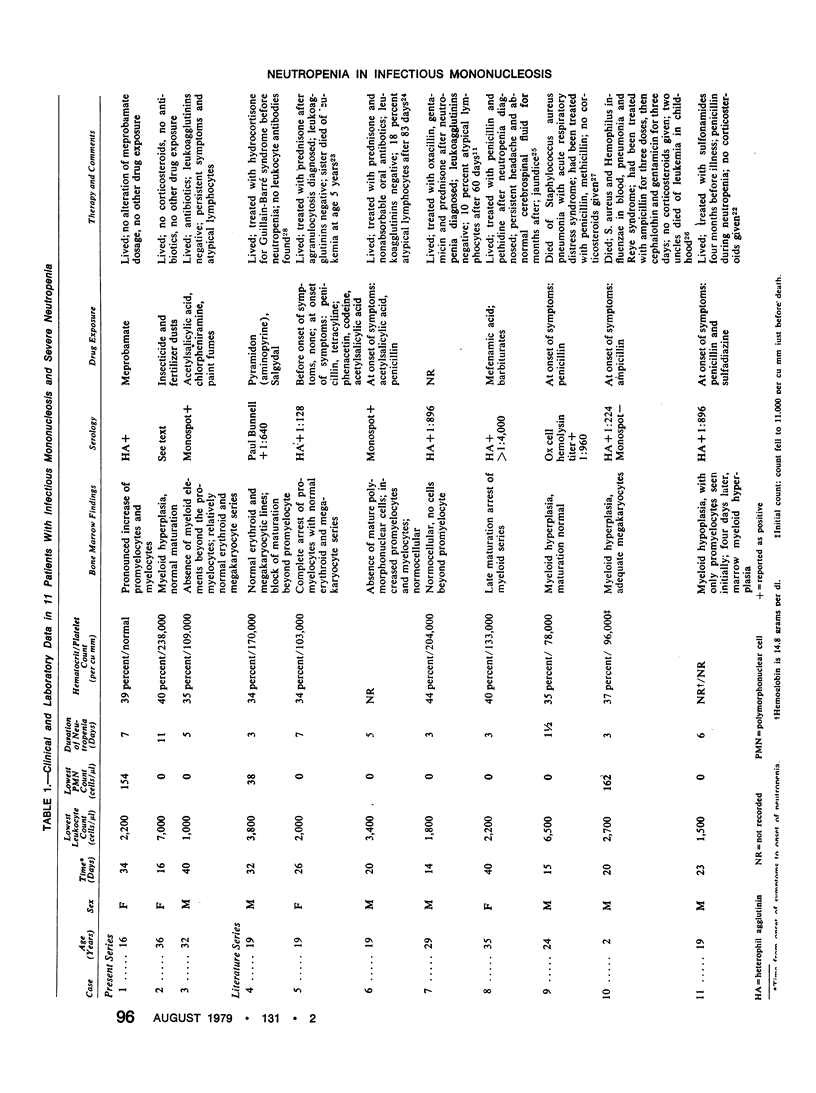
Mild neutropenia is a well-known concomitant of infectious mononucleosis caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) occurring in the first weeks of illness. However, severe neutropenia (less than 200 polymorphonuclear leukocytes per μl) is not generally regarded as a complication of infectious mononucleosis. Three patients were seen with severe neutropenia and EBV infection, and an additional eight cases were found in the literature. In two of the latter cases the neutropenia was fatal.
In the 11 cases the severe neutropenia began 14 to 40 days after illness and usually lasted for three to seven days. At the time of severe neutropenia, studies of marrow specimens showed increased proportions of promyelocytes and myelocytes. Our data suggest that EBV infection is the proximate cause of the severe neutropenia in some patients with infectious mononucleosis and that in such cases close observation and early treatment of suspected superinfections is necessary.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar R. S., DeLor C. J., Clausen K. P., Hurtubise P., Henle W., Hewetson J. F. Fatal infectious mononucleosis in a family. N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 14;290(7):363–367. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402142900704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantow E. F., Kostinas J. E. Studies on infectious mononucleosis. IV. Changes in the granulocytic series. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jul;46(1):43–47. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/46.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. L. Granulocyte changes in infectious mononucleosis. J Clin Pathol. 1966 May;19(3):279–283. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman J. M., Glick T. H., Shannon D. C., Galdabini J., Walker A. Complications of infectious mononucleosis. A fatal case in a 2-year-old child. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Aug;128(2):239–243. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110270113023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher B. D. Neutropenia in infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 22;288(12):633–633. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303222881214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habib M. A., Babka J. C., Burningham R. A. Profound granulocytopenia associated with infectious mononucleosis. Am J Med Sci. 1973 Apr;265(4):339–346. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197304000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz C. A., Henle W., Henle G., Polesky H., Balfour H. H., Jr, Siem R. A., Borken S., Ward P. C. Heterophil-negative infectious mononucleosis and mononucleosis-like illnesses. Laboratory confirmation of 43 cases. Am J Med. 1977 Dec;63(6):947–957. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90550-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz C. A., Henle W., Henle G., Schmitz H. Clinical evaluation of patients with infectious mononucleosis and development of antibodies to the R component of the Epstein-Barr virus-induced early antigen complex. Am J Med. 1975 Mar;58(3):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90599-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koziner B., Hadler N., Parrillo J., Ellman L. Agranulocytosis following infectious mononucleosis. JAMA. 1973 Sep 3;225(10):1235–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Davidsohn I., Panczyszyn O. Horse agglutinins in infectious mononucleosis. II. The spot test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jan;49(1):12–18. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/49.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng-Lévy J., Castaing R., Aubertin J., Leng B., Marion J., Lacut J. Y., Lardeau P. Mononucléose infectieuse et syndrome de Guillan-Barré. Bord Med. 1970 Sep;3(9):2065–2070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro A. H., Degnen F., Munro J. F. Infectious mononucleosis and agranulocytosis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1971;3(3):249–250. doi: 10.3109/inf.1971.3.issue-3.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel E. U. Infectious mononucleosis. Death due to agranulocytosis and pneumonia. JAMA. 1976 Sep 27;236(13):1493–1494. doi: 10.1001/jama.236.13.1493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman H. G. Extreme neutropenia in glandular fever. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jan;21(1):48–49. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman H. G. Fatal infectious mononucleosis: a critical review. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Dec;23(9):765–771. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.9.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provisor A. J., Iacuone J. J., Chilcote R. R., Neiburger R. G., Crussi F. G. Acquired agammaglobulinemia after a life-threatening illness with clinical and laboratory features of infectious mononucleosis in three related male children. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 10;293(2):62–65. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507102930202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Cassel C. K., Yang J. P., Harper R. X-linked recessive progressive combined variable immunodeficiency (Duncan's disease). Lancet. 1975 Apr 26;1(7913):935–940. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., DeFlorio D., Jr, Hutt L. M., Bhawan J., Yang J. P., Otto R., Edwards W. Variable phenotypic expression of an X-linked recessive lymphoproliferative syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 17;297(20):1077–1080. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711172972001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T. Opportunistic non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in X-linked recessive immunodeficiency and lymphoproliferative syndromes. Semin Oncol. 1977 Sep;4(3):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T. Pathogenesis and phenotypes of an X-linked recessive lymphoproliferative syndrome. Lancet. 1976 Oct 23;2(7991):882–885. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90542-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEVENS J. E., BAYRD E. D., HECK F. J. Infectious mononucleosis; a study of 210 sporadic cases. Am J Med. 1951 Aug;11(2):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(51)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulff H. R. Acute agranulocytosis following infectious mononucleosis. Report of a case. Scand J Haematol. 1965;2(3):179–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1965.tb01294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


