Abstract
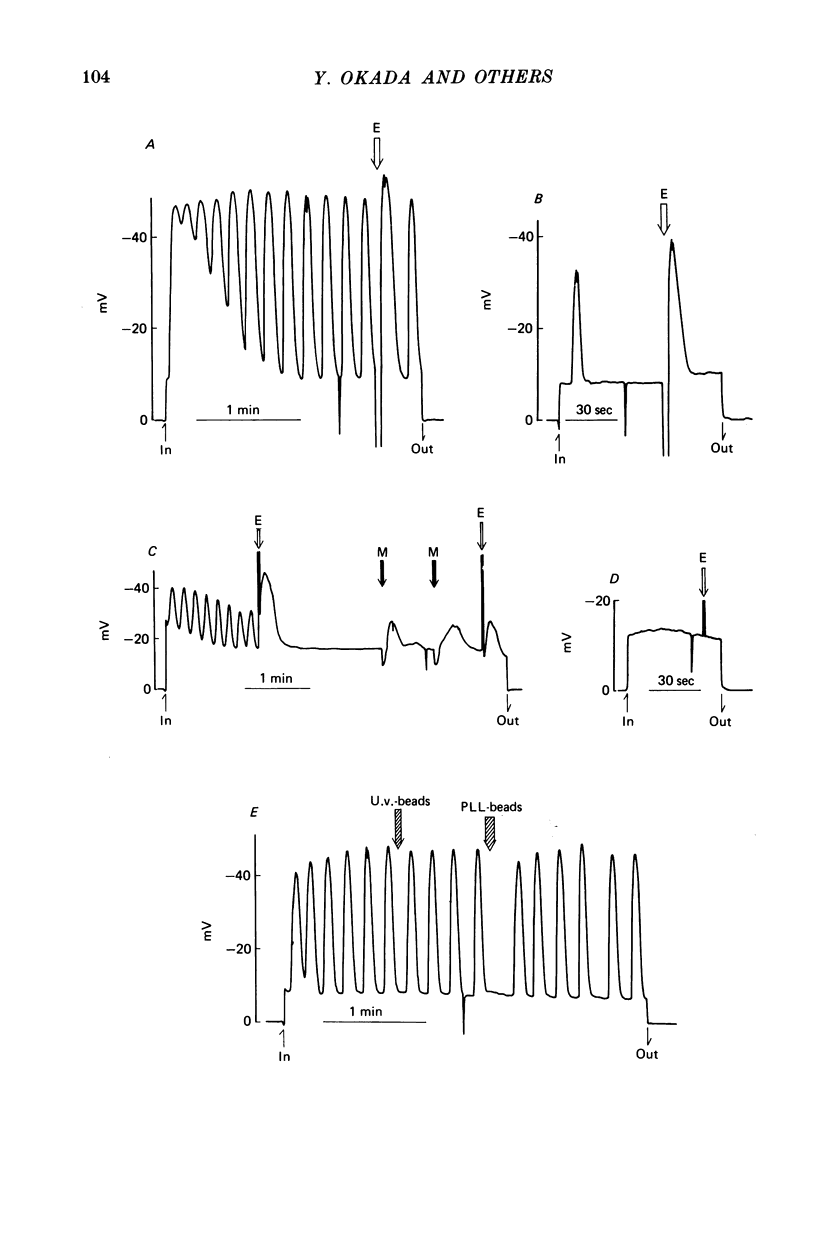
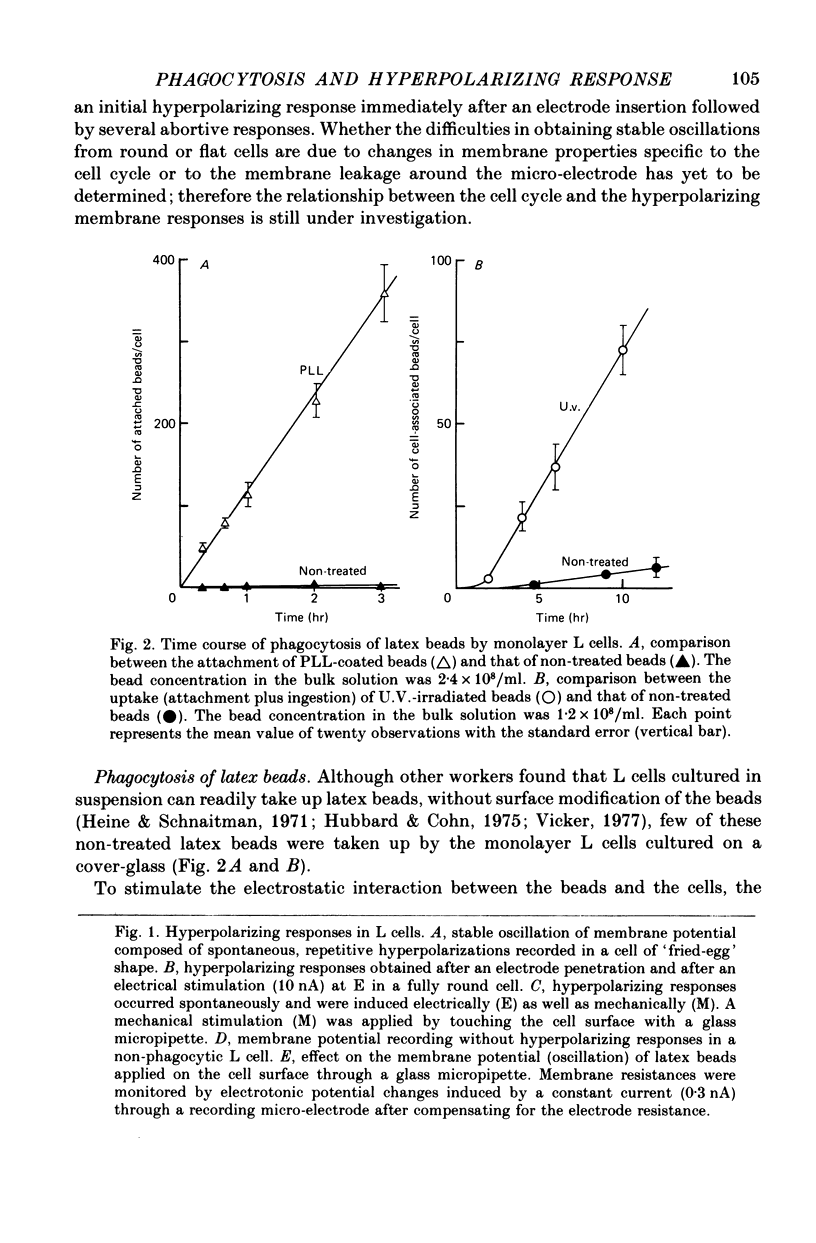
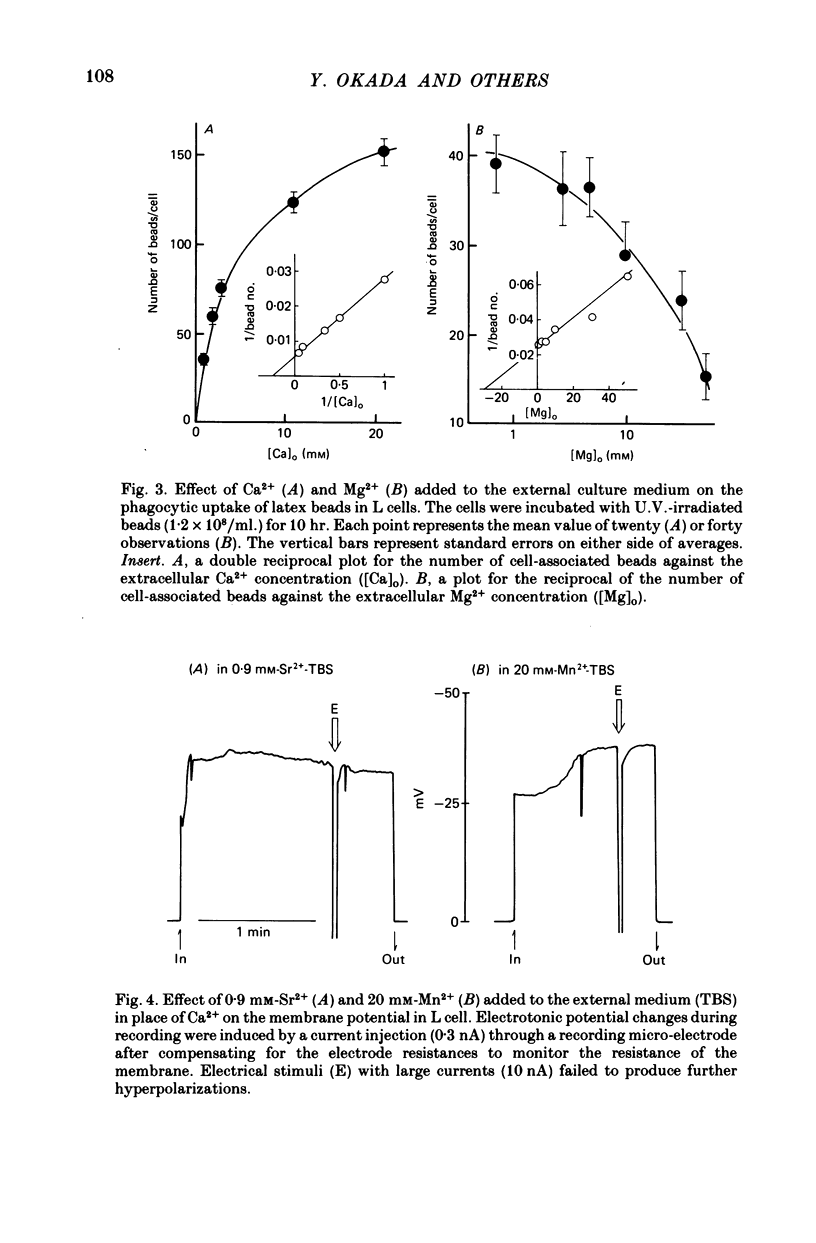
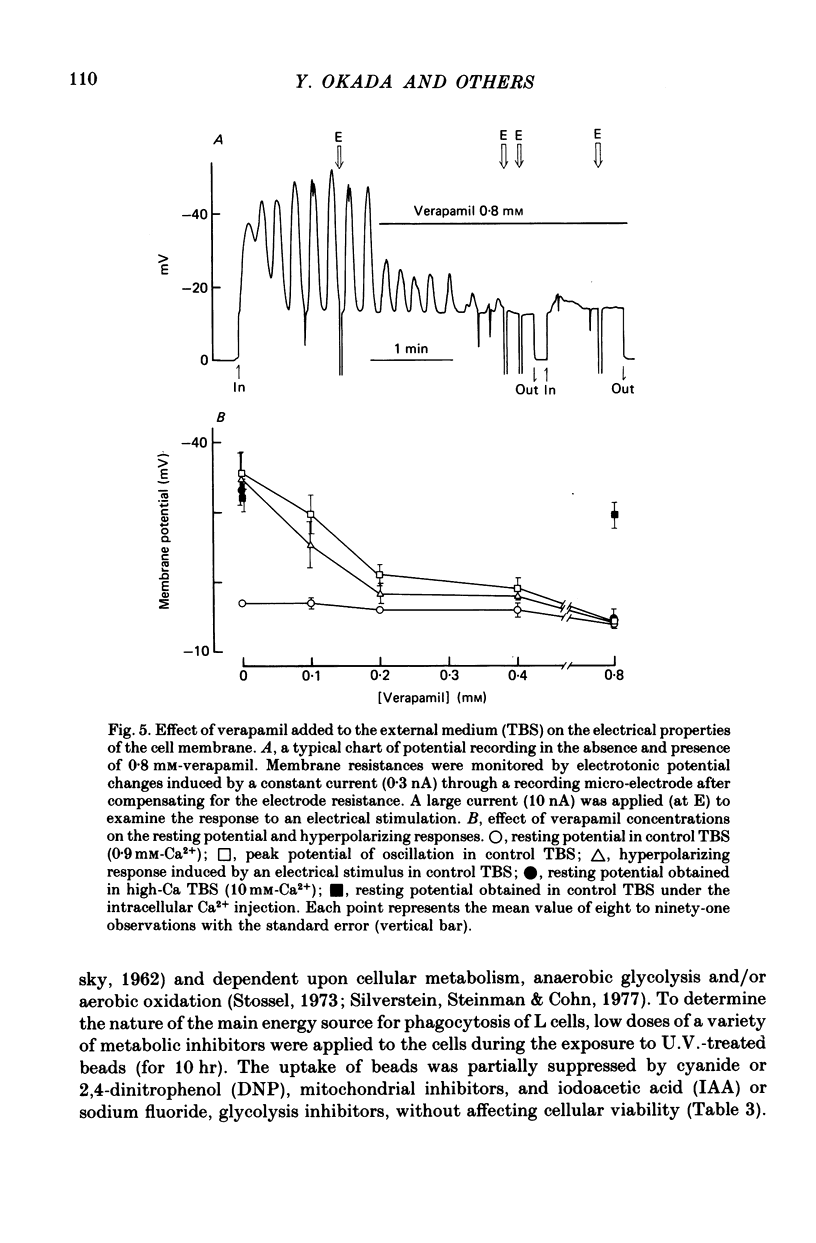
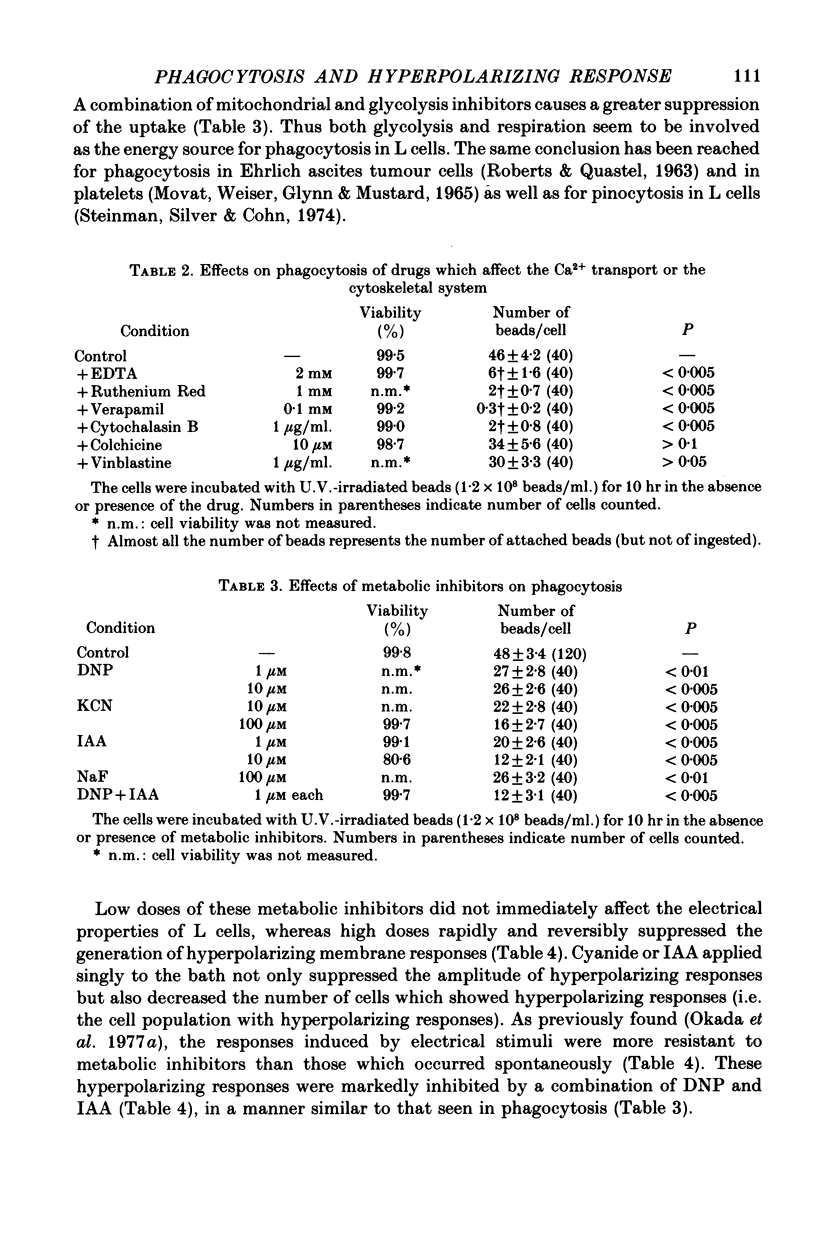
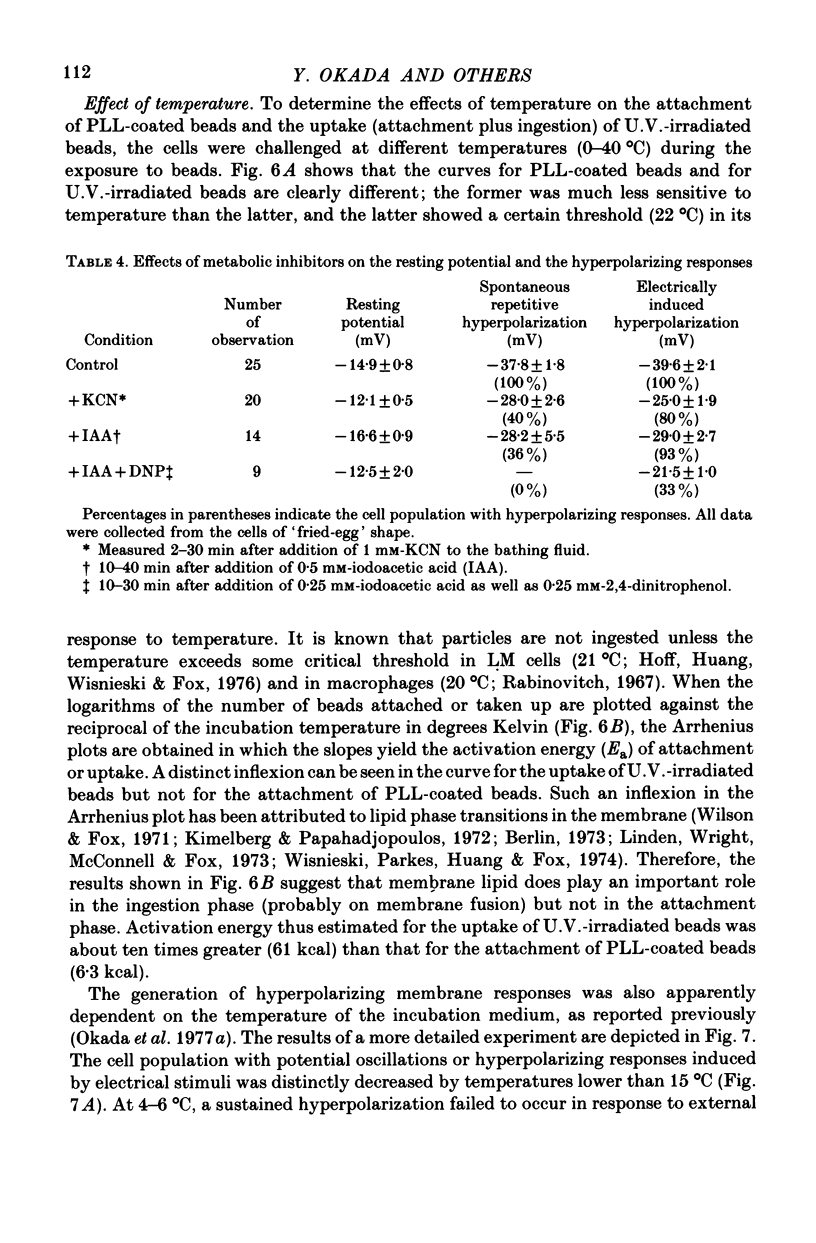
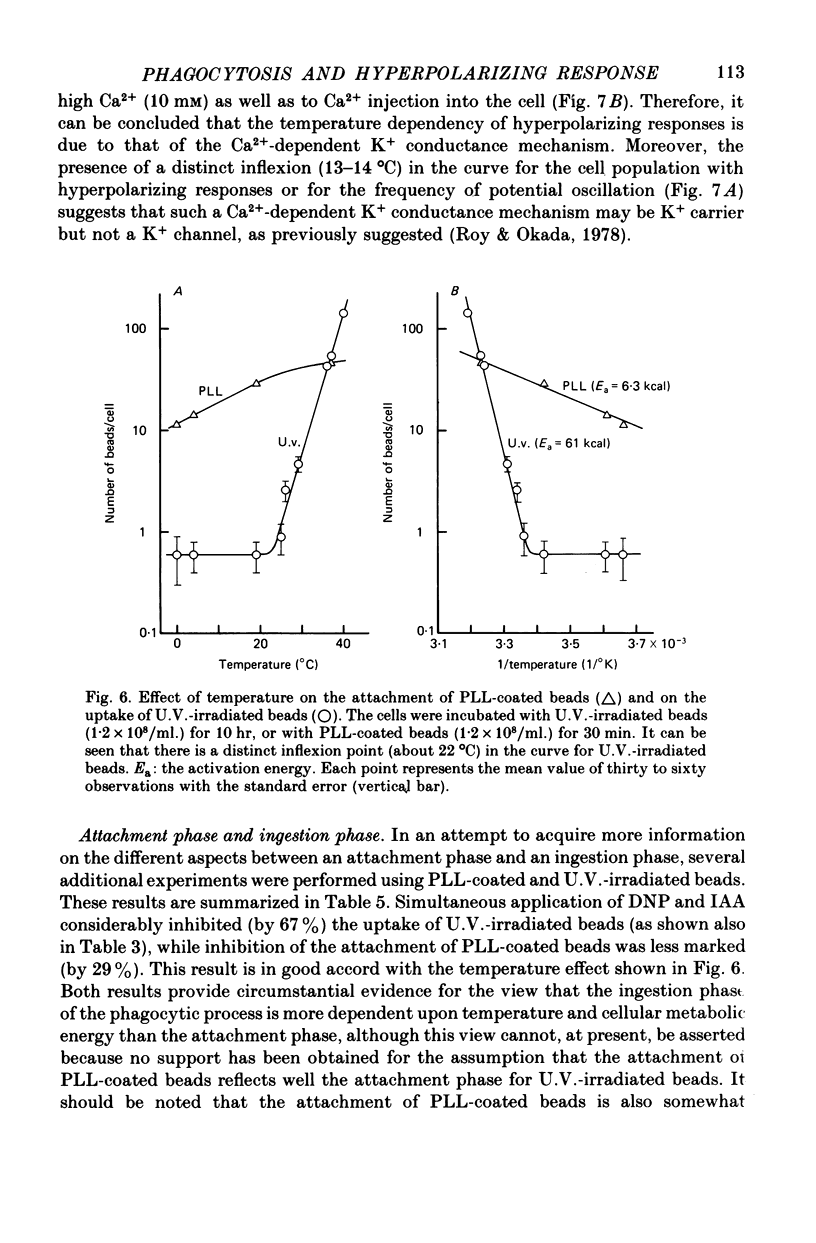
1. Fibroblastic L cells not only respond with a slow hyperpolarizing potential change to a mechanical or electrical stimulus but also show spontaneous, repetitive hyperpolarizations (i.e. membrane potential oscillation). 2. Almost all the cells can actively take up latex beads whose surfaces were treated by U.V. irradiation. 3. Non-phagocytic L cells hardly showed hyperpolarizing responses, while hyperpolarizing responses were obtained in all the phagocytic L cells. The exposure of the cell surface to beads, however, did not trigger the generation of hyperpolarizing responses. 4. Metabolic inhibitors, low temperature and cytochalasin B inhibited both the uptake of beads and the hyperpolarizing responses. 5. Increasing the external concentration of Ca2+ induced a remarkable stimulation of the phagocytosis of beads. Mg2+ and Ba2+, which inhibited hyperpolarizing responses due to competition for Ca2+ sites on the outer surface of the membrane, significantly suppressed the uptake of beads. 6. Verapamil, a Ca2+ channel blocker, inhibited not only hyperpolarizing membrane responses but also ingestion of beads. 7. It is concluded that the Ca2+ inflow on the hyperpolarizing membrane responses is closely associated with the phagocytic activity in L cells, probably through activation of the microfilament assembly.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Davies P., De Petris S. Role of contractile microfilaments in macrophage movement and endocytosis. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 4;232(31):153–155. doi: 10.1038/newbio232153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axline S. G., Reaven E. P. Inhibition of phagocytosis and plasma membrane mobility of the cultivated macrophage by cytochalasin B. Role of subplasmalemmal microfilaments. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):647–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin R. D. Temperature dependence of nucleoside membrane transport of rabbit alveolar macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4724–4730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Moulder J. W. Parasite-specified phagocytosis of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis by L and HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):598–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.598-606.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Fox R. I., Polyzonis M., Allison A. C., Haswell A. D. The inhibition of phagocytosis and facilitation of exocytosis in rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes by cytochalasin B. Lab Invest. 1973 Jan;28(1):16–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. T., Estensen R., Quie P. G. Cytochalasin B. 3. Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte phagocytosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):161–164. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dos Reis G. A., Oliveira-Castro G. M. Electrophysiology of phagocytic membranes. I. Potassium-dependent slow membrane hyperpolarizations in mice macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 19;469(3):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENDYKE R. M., BRIERTY R. E., SWISHER S. N. IN VITRO STUDIES ON ERYTHROPHAGOCYTOSIS. Blood. 1963 Sep;22:295–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K., Gallin J. I. Interaction of chemotactic factors with human macrophages. Induction of transmembrane potential changes. J Cell Biol. 1977 Oct;75(1):277–289. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K., Wiederhold M. L., Lipsky P. E., Rosenthal A. S. Spontaneous and induced membrane hyperpolarizations in macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Dec;86 (Suppl 2)(3 Pt 2):653–661. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040860510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S. Ca-dependent action potential. Membranes. 1975;3:359–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Schnaitman C. A. A method for the isolation of plasma membrane of animal cells. J Cell Biol. 1971 Mar;48(3):703–707. doi: 10.1083/jcb.48.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart M. P., Nelson P. G. Evidence for an intracellular calcium store releasable by surface stimuli ifibroblasts (L cells). J Gen Physiol. 1979 May;73(5):655–673. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.5.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. Externally disposed plasma membrane proteins. II. Metabolic fate of iodinated polypeptides of mouse L cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):461–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Hirsch J. G. The interaction in vitro of Mycoplasma pulmonis with mouse peritoneal macrophages and L-cells. J Exp Med. 1971 Feb 1;133(2):231–259. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. L. Metabolic basis of phagocytic activity. Physiol Rev. 1962 Jan;42:143–168. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1962.42.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno T. Calcium-dependent amylase release and electrophysiological measurements in cells of the pancreas. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(2):353–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Papahadjopoulos D. Phospholipid requirements for (Na + + K + )-ATPase activity: head-group specificity and fatty acid fluidity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 1;282(1):277–292. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G. Cytochalasin B. Dissociation of pinocytosis and phagocytosis by peritoneal macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Apr;79(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90490-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlhardt M., Bauer B., Krause H., Fleckenstein A. Differentiation of the transmembrane Na and Ca channels in mammalian cardiac fibres by the use of specific inhibitors. Pflugers Arch. 1972;335(4):309–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00586221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden C. D., Wright K. L., McConnell H. M., Fox C. F. Lateral phase separations in membrane lipids and the mechanism of sugar transport in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2271–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malawista S. E., Bodel P. T. The dissociation by colchicine of phagocytosis from increased oxygen consumption in human leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):786–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI105579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Stossel T. P., Vaughan M. Quantitative studies of phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 28;304(3):864–870. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Petersen O. H. Pancreatic acinar cells: ionic dependence of the membrane potential and acetycholine-induced depolarization. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(2):283–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Sheridan J. D., White J. G. Electrical responses by guinea pig megakaryocytes. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):643–645. doi: 10.1038/272643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Weiser W. J., Glynn M. F., Mustard J. F. Platelet phagocytosis and aggregation. J Cell Biol. 1965 Dec;27(3):531–543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe-Kaas A. C. Phagocytosis in rat Kupffer cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90589-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Peacock J., Minna J. An active electrical response in fibroblasts. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jul;60(1):58–71. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Doida Y., Roy G., Tsuchiya W., Inouye K., Inouye A. Oscillations of membrane potential in L cells. I. Basic characteristics. J Membr Biol. 1977 Aug 4;35(4):319–335. doi: 10.1007/BF01869957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Roy G., Tsuchiya W., Doida Y., Inouye A. Oscillations of membrane potential in L cells. II. Effect of monovalent ion concentrations and conductance changes associated with oscillations. J Membr Biol. 1977 Aug 4;35(4):337–350. doi: 10.1007/BF01869958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Tsuchiya W., Inouye A. Oscillations of membrane potential in L cells. IV. Role of intracellular Ca2+ in hyperpolarizing excitability. J Membr Biol. 1979 Jun 7;47(4):357–376. doi: 10.1007/BF01869744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Ishibashi S., Takano T. Evidence for bactericidal activity of polymorphonuclear leukocytes without phagocytosis. J Biochem. 1979 Aug;86(2):469–475. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS H. J., TERRYBERRY J. E. Counting actively metabolizing tissue cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1957 Oct;13(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(57)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penny R., Galton D. A., Scott J. T., Eisen V. Studies on neutrophil function. 1. Physiological and pharmacological aspects. Br J Haematol. 1966 Sep;12(5):623–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb00145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesanti E. L., Axline S. G. Phagolysosome formation in normal and colchicine-treated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):903–913. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Saito S. The influence of natural and synthetic cationic substances on phagocytic activity of human polymorphonuclear cells. An alternative pathway of phagocytic enhancement. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Nov;117(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90421-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS J., QUASTEL J. H. PARTICLE UPTAKE BY POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUCOCYTES AND EHRLICH ASCITES-CARCINOMA CELLS. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:150–156. doi: 10.1042/bj0890150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. The dissociation of the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis by macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Apr;46(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90405-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. Uptake of aldehyde-treated erythrocytes by L2 cells: inhibition by anti-red cell antibody or by coating the erythrocytes with purified proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Feb;54(2):210–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90235-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E. P., Axline S. G. Subplasmalemmal microfilaments and microtubules in resting and phagocytizing cultivated macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1973 Oct;59(1):12–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy G., Okada Y. Oscillation of membrane potential in L cells: III K + current-voltage curves. J Membr Biol. 1978 Feb 3;38(4):347–357. doi: 10.1007/BF01870151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., SHIRLEY W., BAUMSTARK J. S. Effect of osmolarity on phagocytosis. J Bacteriol. 1963 Feb;85:306–313. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.2.306-313.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Silver J. M., Cohn Z. A. Pinocytosis in fibroblasts. Quantitative studies in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):949–969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Serum-dependent phagocytosis of paraffin oil emulsified with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):690–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Mason R. J., Hartwig J., Vaughan M. Quantitative studies of phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes: use of emulsions to measure the initial rate of phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):615–624. doi: 10.1172/JCI106851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Phagocytosis: recognition and ingestion. Semin Hematol. 1975 Jan;12(1):83–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Quantitative studies of phagocytosis. Kinetic effects of cations and heat-labile opsonin. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):346–356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama H., Katsumoto T., Takagi A. Ultrastructural studies on the phagocytosis of the cultured mouse macrophages and the effects of cytochalasin B, colchicine and pH conditions on their morphology. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1975;24(3):145–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicker M. G. On the origin of the phagocytic membrane. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Oct 1;109(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G., Fox C. F. Biogenesis of microbial transport systems: evidnce for coupled incorporation of newly synthesized lipids and proteins into membrane. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jan 14;55(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisnieski B. J., Parkes J. G., Huang Y. O., Fox C. F. Physical and physiological evidence for two phase transitions in cytoplasmic membranes of animal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Effects of cytochalasin B on polymorphonuclear leucocyte locomotion, phagocytosis and glycolysis. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Aug;73(2):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]