Abstract
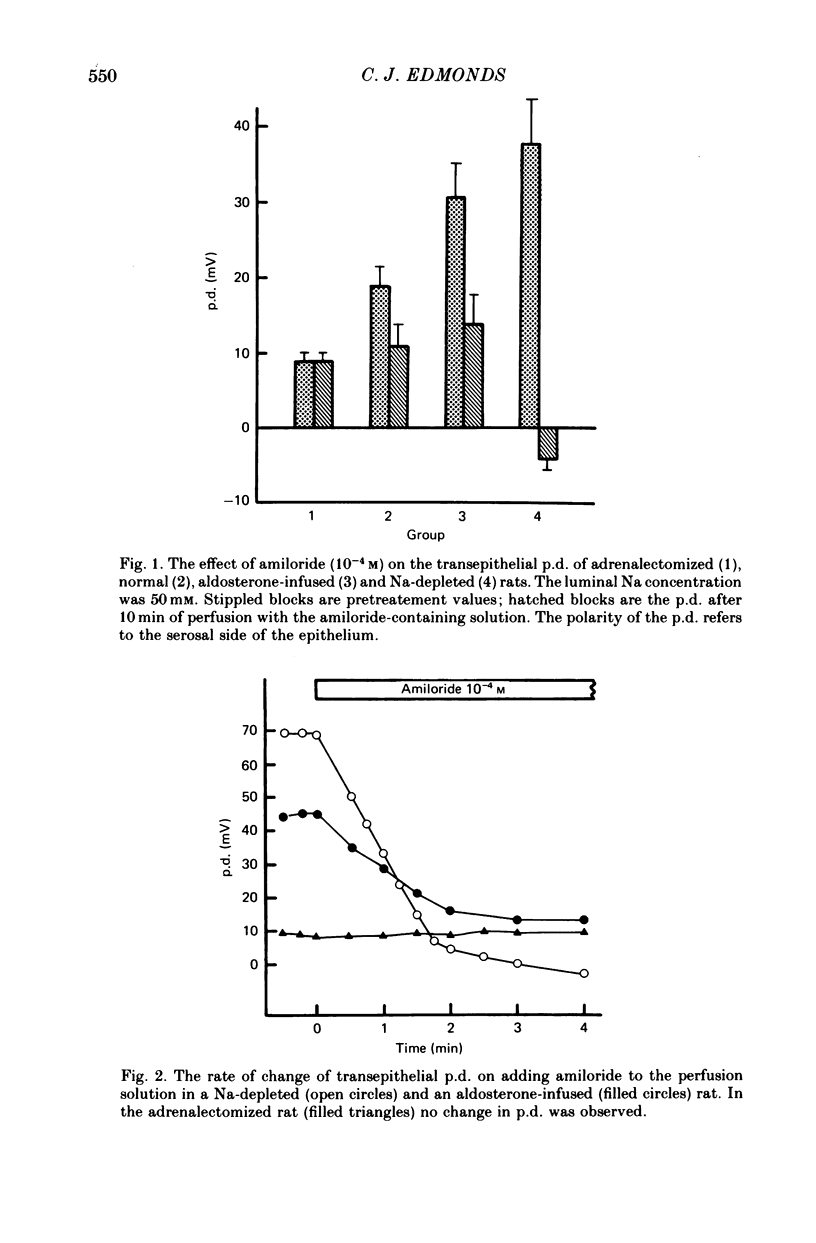
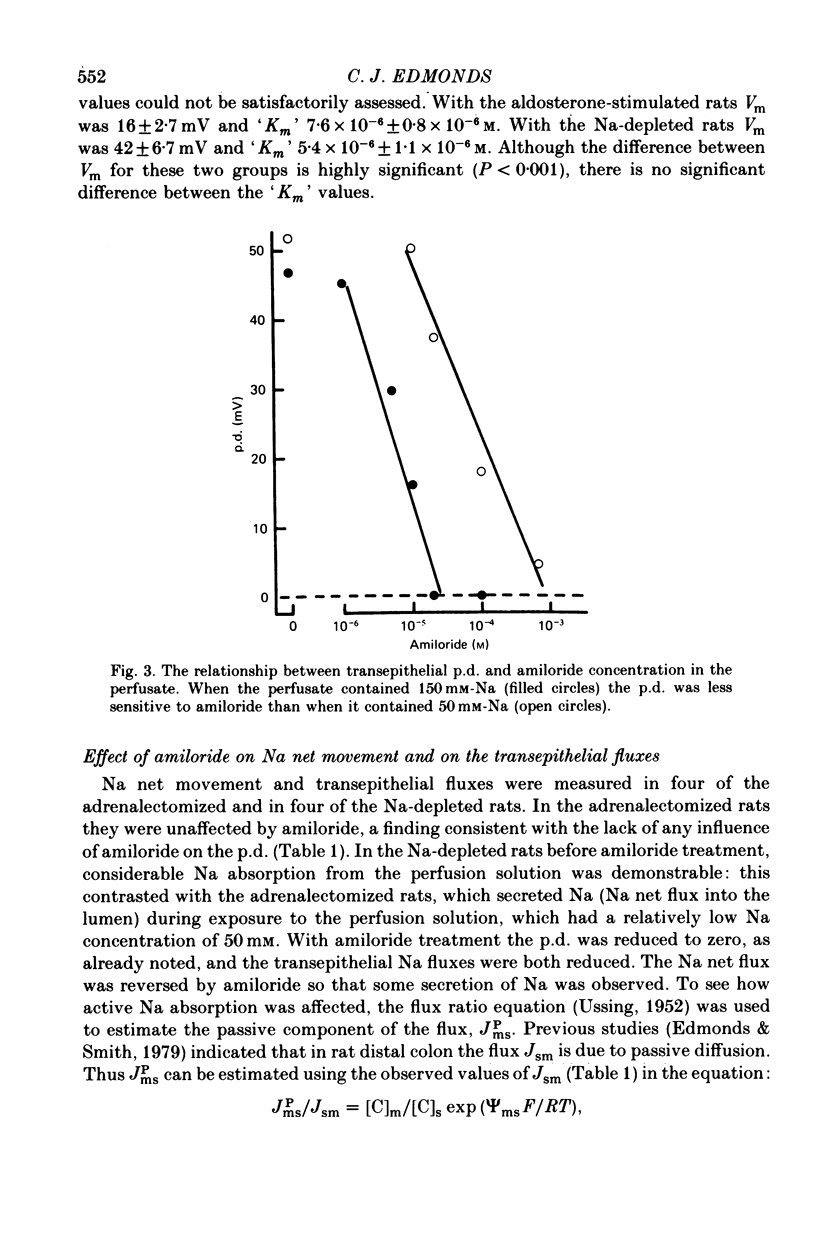
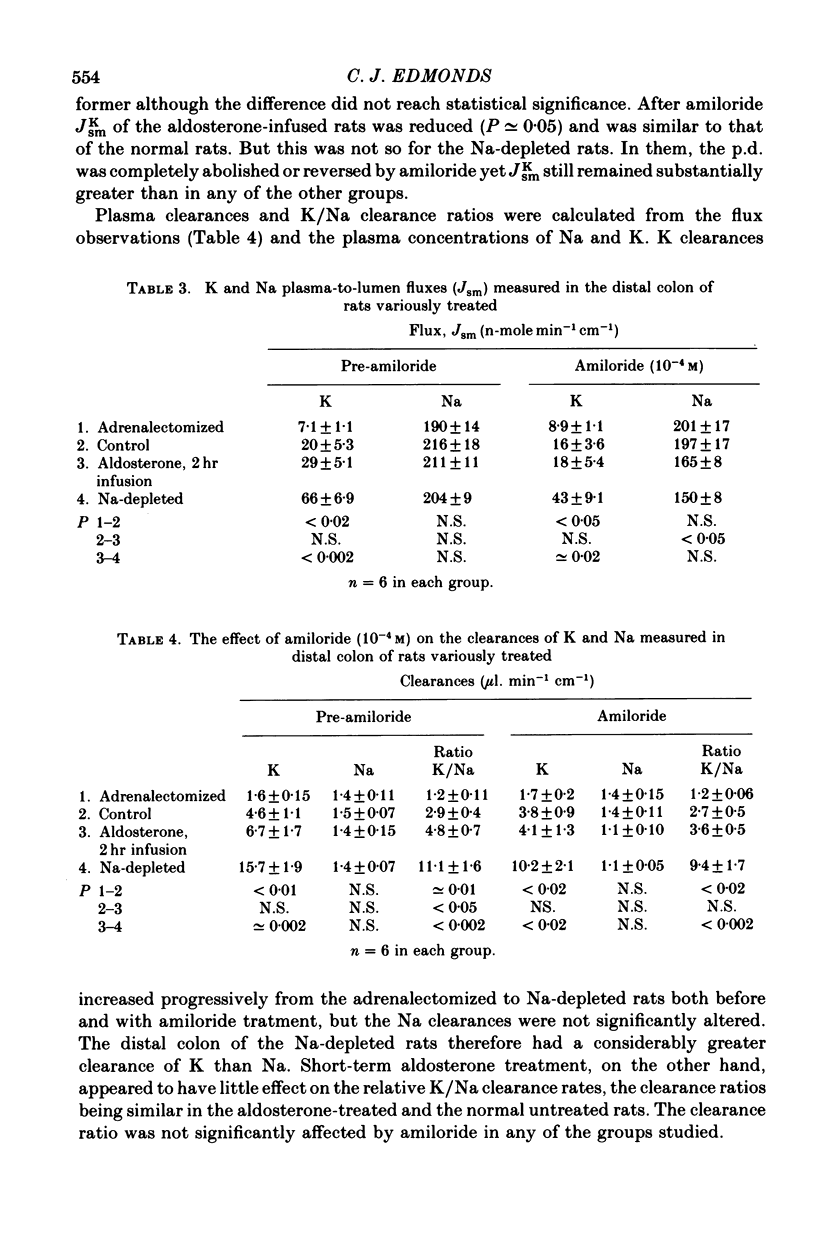
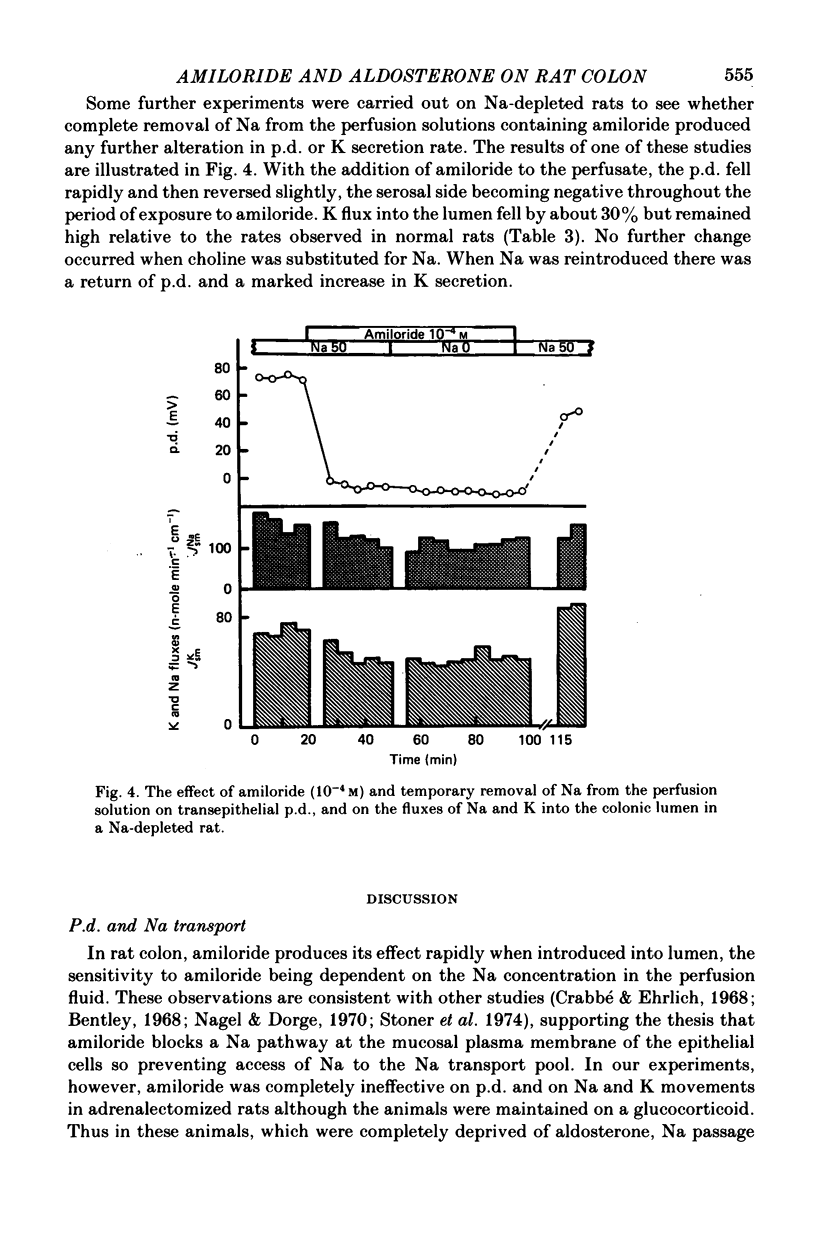
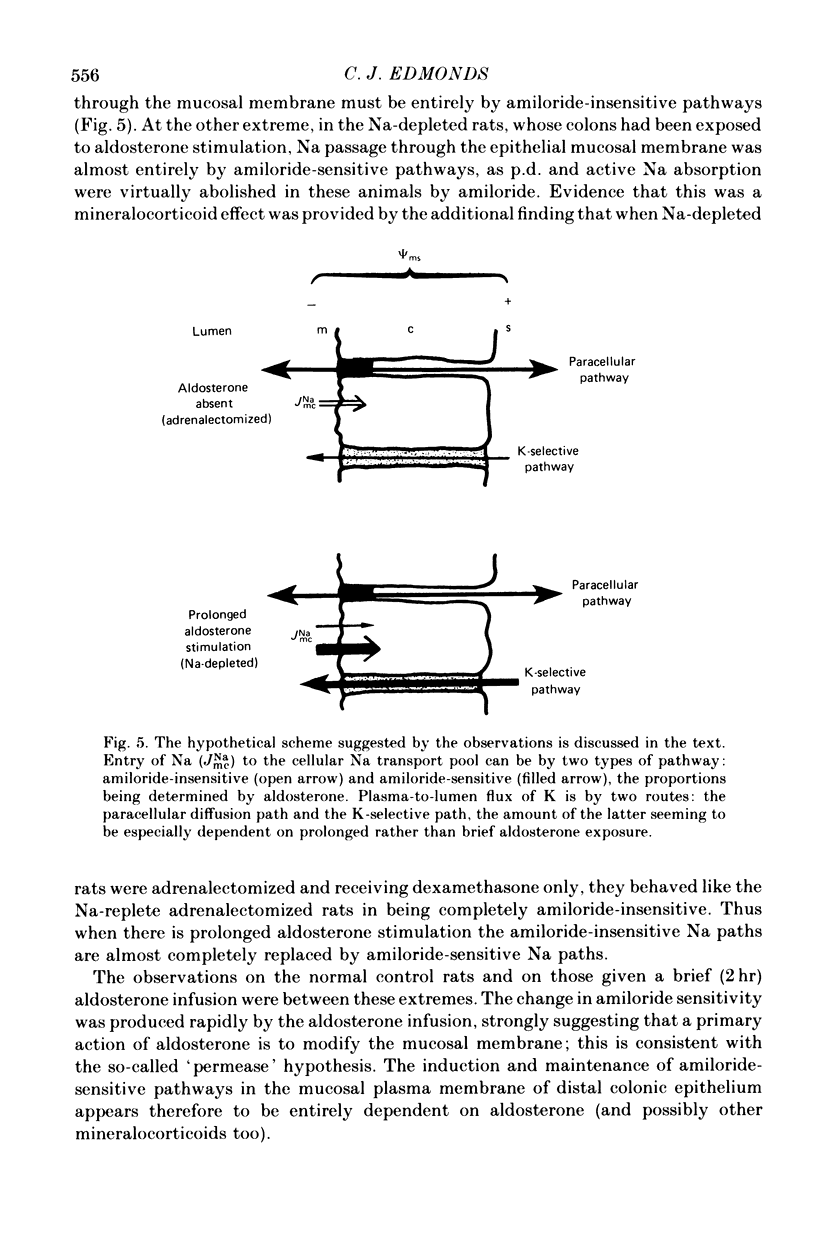
1. The effect of amiloride within the gut lumen on the transepithelial electrical potential difference (p.d.) and Na and K transport by the distal colon of adrenalectomized (dexamethasone-maintained), normal, aldosterone-infused and Na-depleted groups of rats was examined. 2. Amiloride had no effect in adrenalectomized rats; in normal rats, only the p.d. was significantly reduced. 3. In the group given a short (2 hr) aldosterone infusion, amiloride reduced the elevated p.d. and K secretion rate to normal levels. There was no change in apparent K permeability of the epithelium. 4. In the Na-depleted group, p.d. and Na absorption were virtually abolished by amiloride but although K secretion was reduced it still remained much above normal levels. Adrenalectomy prevented the effects of Na depletion. 5. P.d. change occurred rapidly when amiloride was added to the perfusate. Increasing the Na concentration in the perfusate reduced the sensitivity to amiloride. Apparent 'Km' values estimated from p.d. changes (luminal Na, 50 mM) were similar for aldosterone-infused (7.6 X 10(-6) M) and Na-depleted (5.4 X 10(-6) M) rats. 6. Aldosterone appears to be essential for the induction of amiloride-sensitive Na paths in the mucosal plasma membrane of rat colonic epithelial cells. Prolonged aldosterone stimulation, as in the Na-depleted rats, increases the amiloride-sensitive Na paths while largely suppressing the amiloride-insensitive Na paths; in addition, the K/Na clearance rate ratio of the epithelium is increased. AMiloride interacts only with one set of Na paths and does not interact directly with K paths.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastl C. P., Binder H. J., Hayslett J. P. Role of glucocorticoids and aldosterone in maintenance of colonic cation transport. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):F181–F186. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.3.F181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley P. J. Amiloride: a potent inhibitor of sodium transport across the toad bladder. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):317–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremaschi D., Ferguson D. R., Hénin S., James P. S., Meyer G., Smith M. W. Post-natal development of amiloride sensitive sodium transport in pig distal colon. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:481–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Shum W. K. Effects of vasopressin and aldosterone on amiloride binding in toad bladder epithelial cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 17;189(1097):543–575. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1975.0072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duarte C. G., Chomety F., Giebisch G. Effect of amiloride, ouabain, and furosemide on distal tubular function in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Aug;221(2):632–640. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.2.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J., Marriott J. C. The effect of aldosterone and adrenalectomy on the electrical potential difference of rat colon and on the transport of sodium, potassium, chloride and bicarbonate. J Endocrinol. 1967 Dec;39(4):517–531. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0390517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J., Smith T. Epithelial transport pathways of rat colon determined in vivo by impulse response analysis. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:471–485. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J. Transport of potassium by the colon of normal and sodium-depleted rats. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):603–617. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman D., Funder J. W., Edelman I. S. Subcellular mechanisms in the action of adrenal steroids. Am J Med. 1972 Nov;53(5):545–560. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Turnheim K. Ion transport by rabbit colon: II. Unidirectional sodium influx and the effects of amphotericin B and amiloride. J Membr Biol. 1978 May 3;40(3):193–211. doi: 10.1007/BF02002968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange S., Veit C., Hegel U., Gutsche U. Die Wirkung von Amilorid auf den Elektrolyttransport des Rattencolon und ihre Abhängigkeit von Mineralocorticoiden. Endokrinologie. 1974 May;63(2):271–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel W., Dörge A. Effect of Amiloride on sodium transport of frog skin. I. Action on intracellular sodium content. Pflugers Arch. 1970;317(1):84–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00586701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rask-Madsen J., Hjelt K. Effect of amiloride on electrical activity and electrolyte transport in human colon. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read N. W., Holdsworth C. D., Levin R. J. Electrical measurement of intestinal absorption of glucose in man. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):624–627. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91946-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner L. C., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Ion transport in cortical collecting tubule; effect of amiloride. Am J Physiol. 1974 Aug;227(2):453–459. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USSING H. H. Some aspects of the application of tracers in permeability studies. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1952;13:21–65. doi: 10.1002/9780470122587.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


