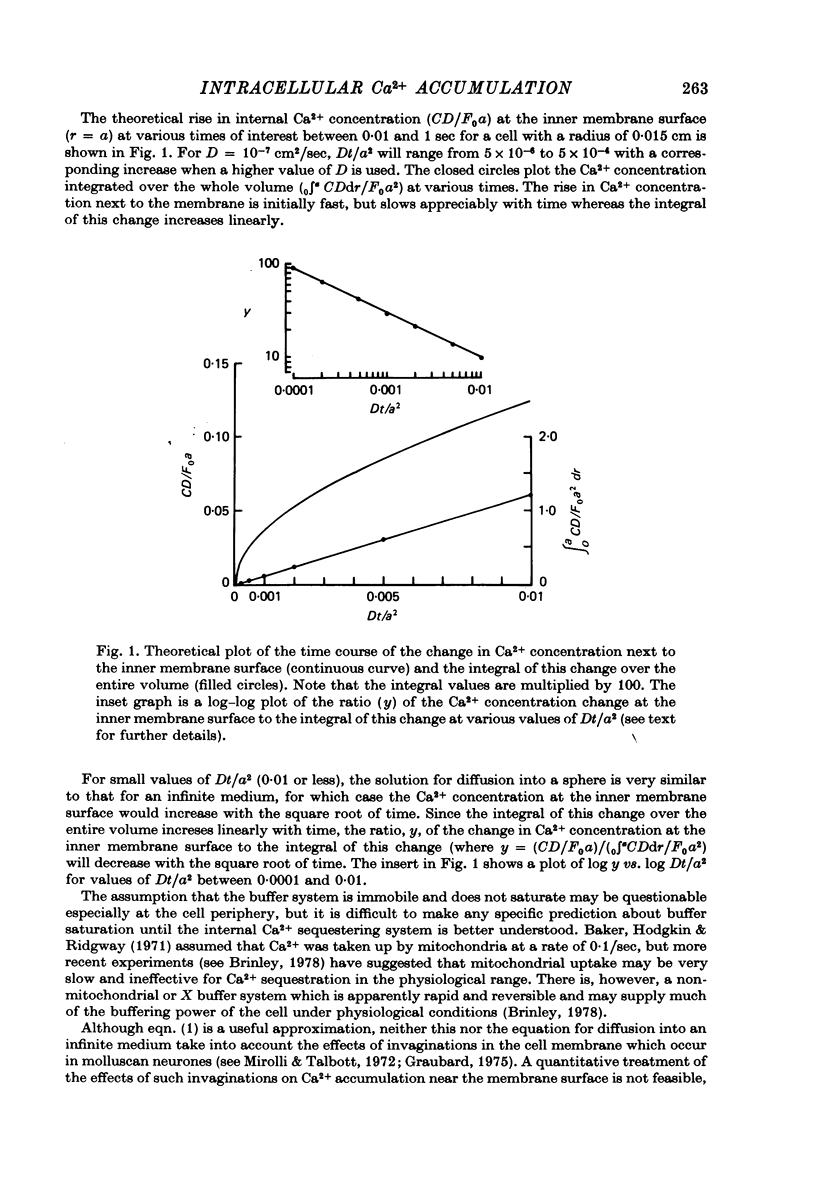
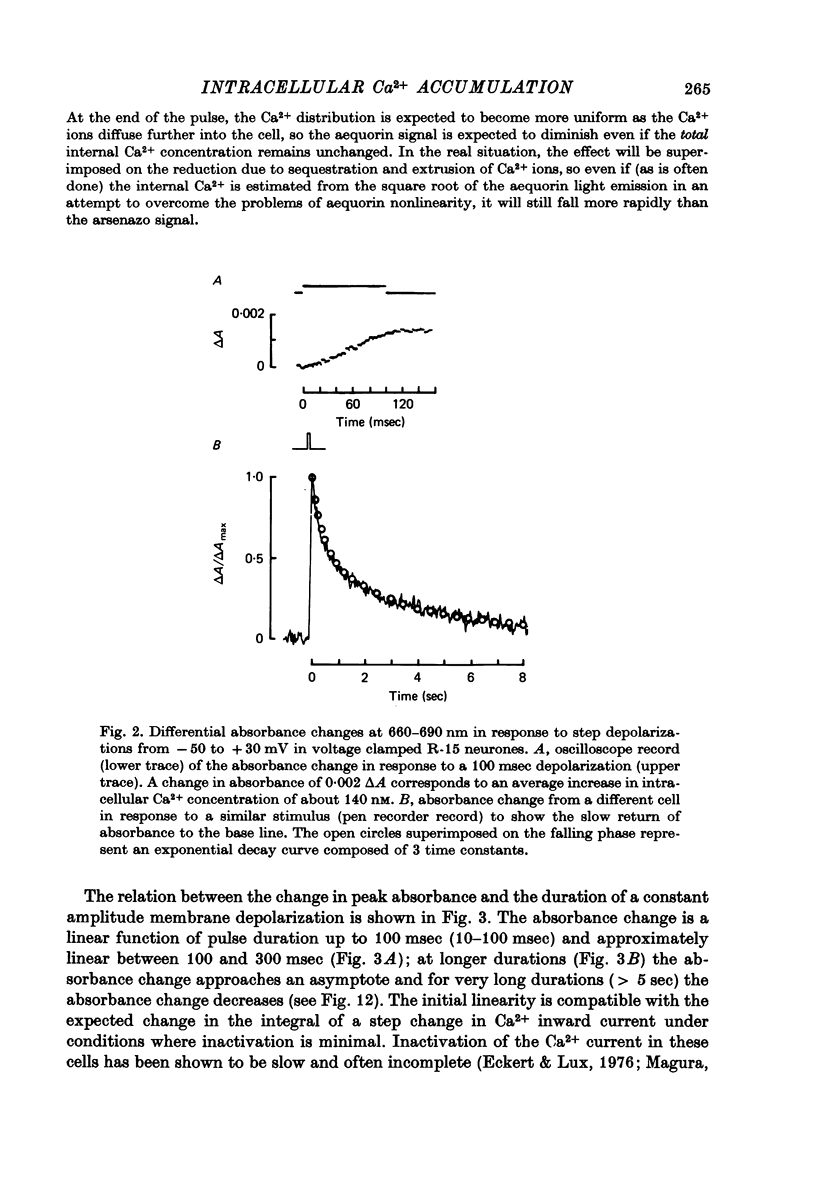
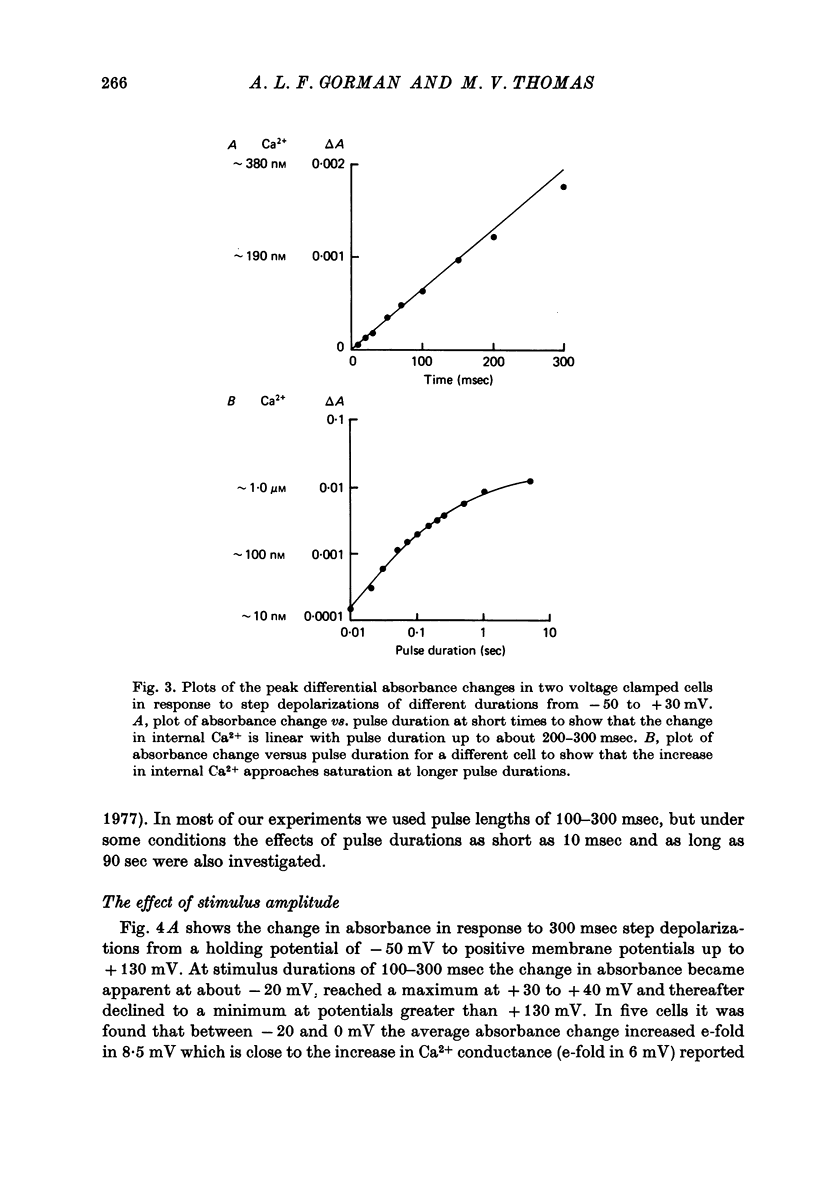
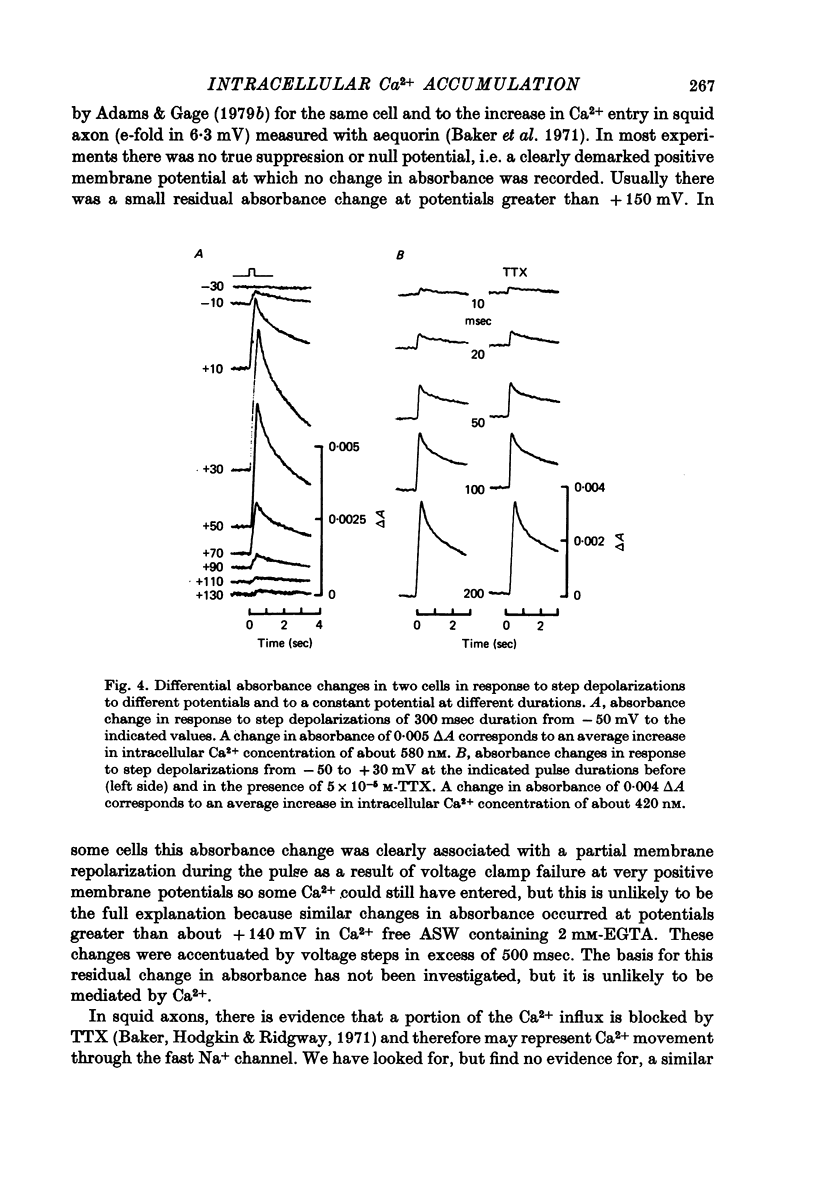
Abstract
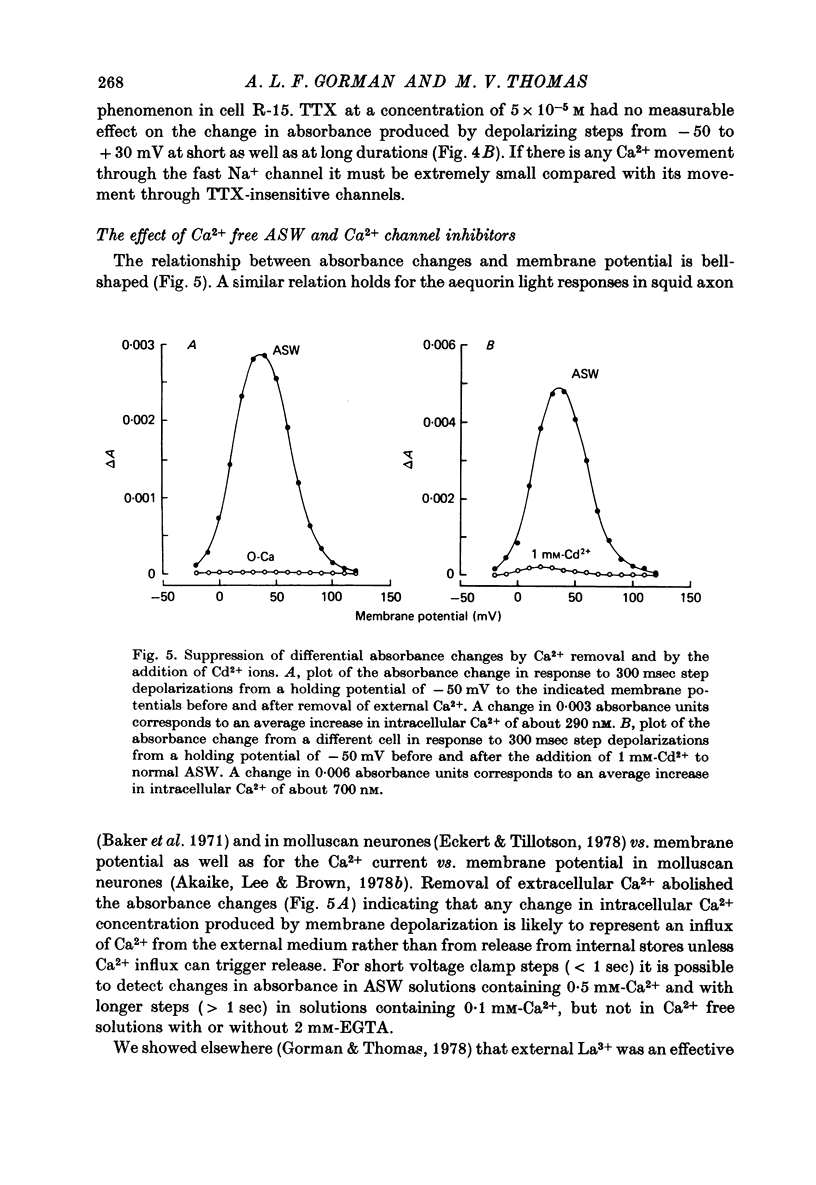
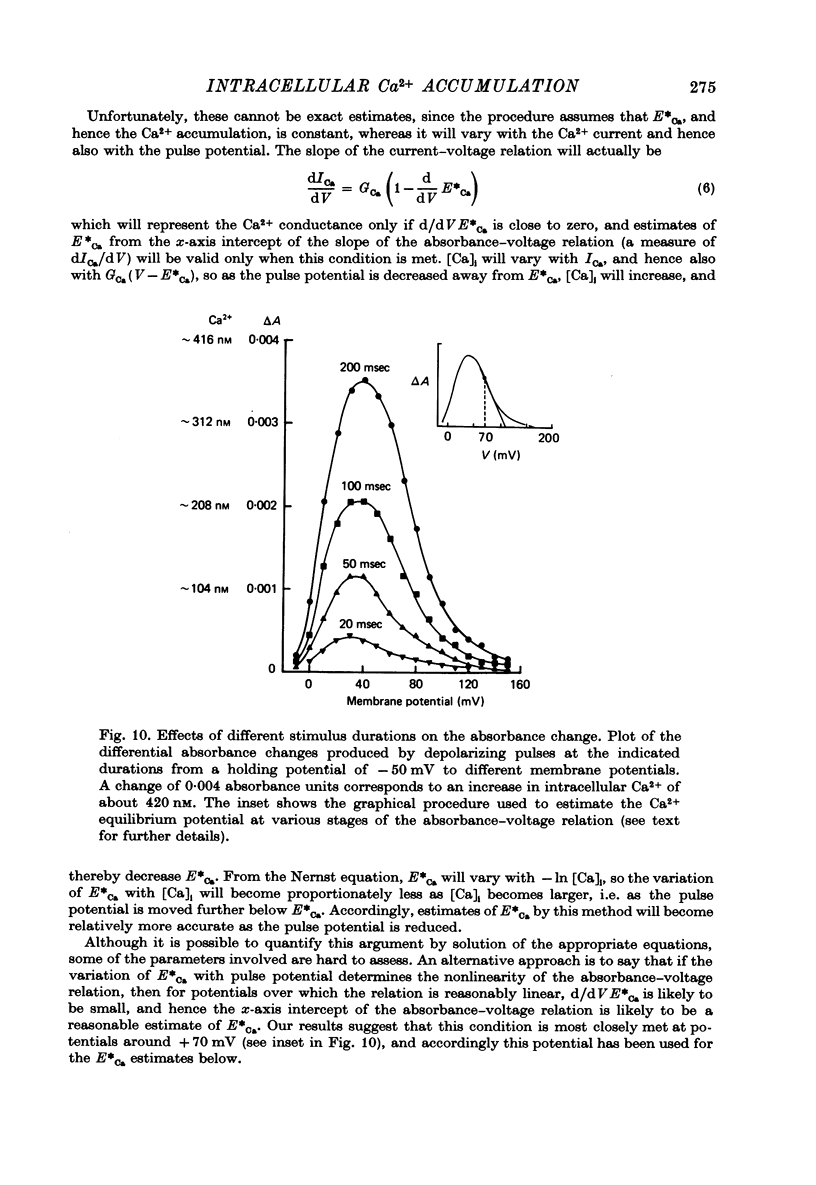
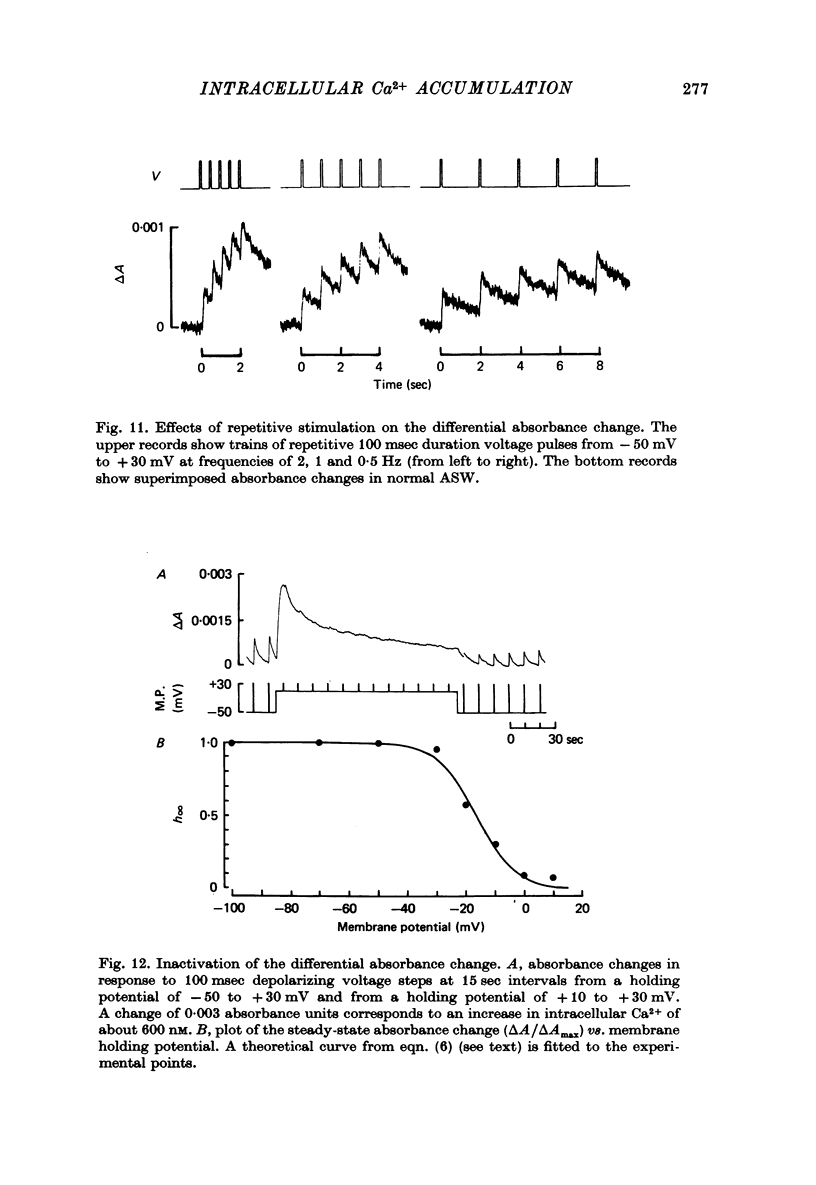
1. The bursting pacemaker neurone R-15 of Aplysia was injected with the Ca2+ sensitive dye arsenzo III. Changes in absorbance were measured with a differential spectrophotometer to monitor changes in free intracellular Ca2+ during membrane depolarization under voltage clamp conditions. 2. Dye absorbance increased linearly for depolarizing pulse durations up to 100 msec and approximately linearly between 100 and 300 msec, but for longer durations the absorbance change decreased. 3. The absorbance change vs. voltage relation increased steeply between -20 and 0 mV (e-fold per 8.5 mV), peaked at +36 mV and declined non-linearly to an estimated null or suppression potential of about +139 mV. 4. TTX (5 x 10(-5 M) had no effect on the change in dye absorbance produced by brief or long duration stimuli whereas Ca2+ free ASW abolished all changes in dye absorbance. 5. The absorbance change saturated with increasing external Ca2+ concentrations. The relation between dye absorbance and external Ca2+ concentration was hyperbolic and for a small range of external Ca2+ concentration and membrane potentials could be fitted by a Michaelis--Menten expression where the dissociation constant and the maximum absorbance change are voltage dependent. 6. The absorbance change was reduced by external divalent ions which block the Ca2+ channel (e.g. Cd2+ and Ni2+). The suppression of dye absorbance was increased by membrane depolarization and suggests that there is a voltage dependent site within the Ca2+ channel which binds divalent ions. 7. The decline of the absorbance--voltage relation from its peak to the suppression potential showed a greater nonlinearity when longer duration voltage clamp pulses were used. The non-linearity can be explained if the accumulation of Ca2+ ions next to the inner surface of the membrane during depolarization reduces the driving force on Ca2+ ions and thus decreases Ca2+ ion influx. 8. The suppression potential estimated from the absorbance--voltage relation increased 29 mV per tenfold change in the external Ca2+ concentration and thus can be used to estimate the Ca2+ equilibrium potential. 9. The change in dye absorbance produced by brief depolarizing voltage clamp steps was inactivated at positive holding potentials (50% inactivation at about -14 mV). Our results suggest that the slow decrease in dye absorbance during prolonged depolarization is caused by inactivation of the Ca2+ channel.
Full text
PDF
















Selected References
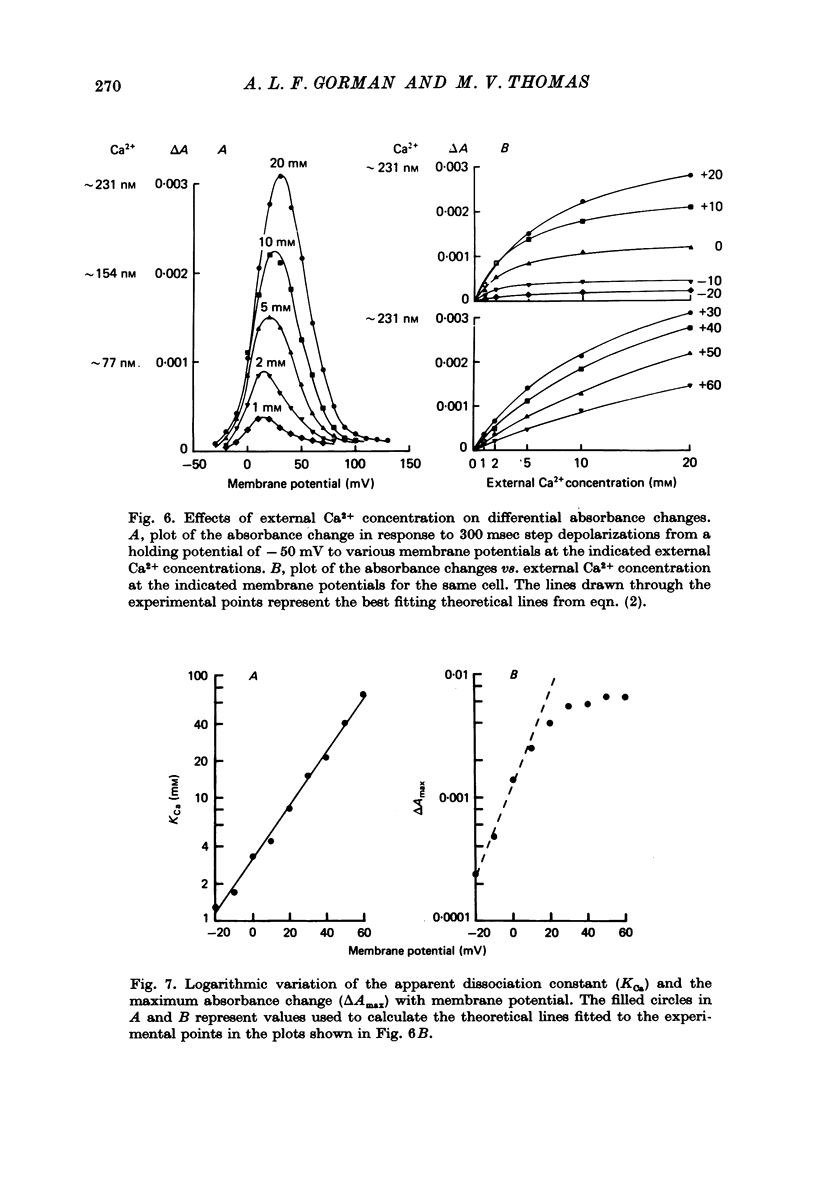
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
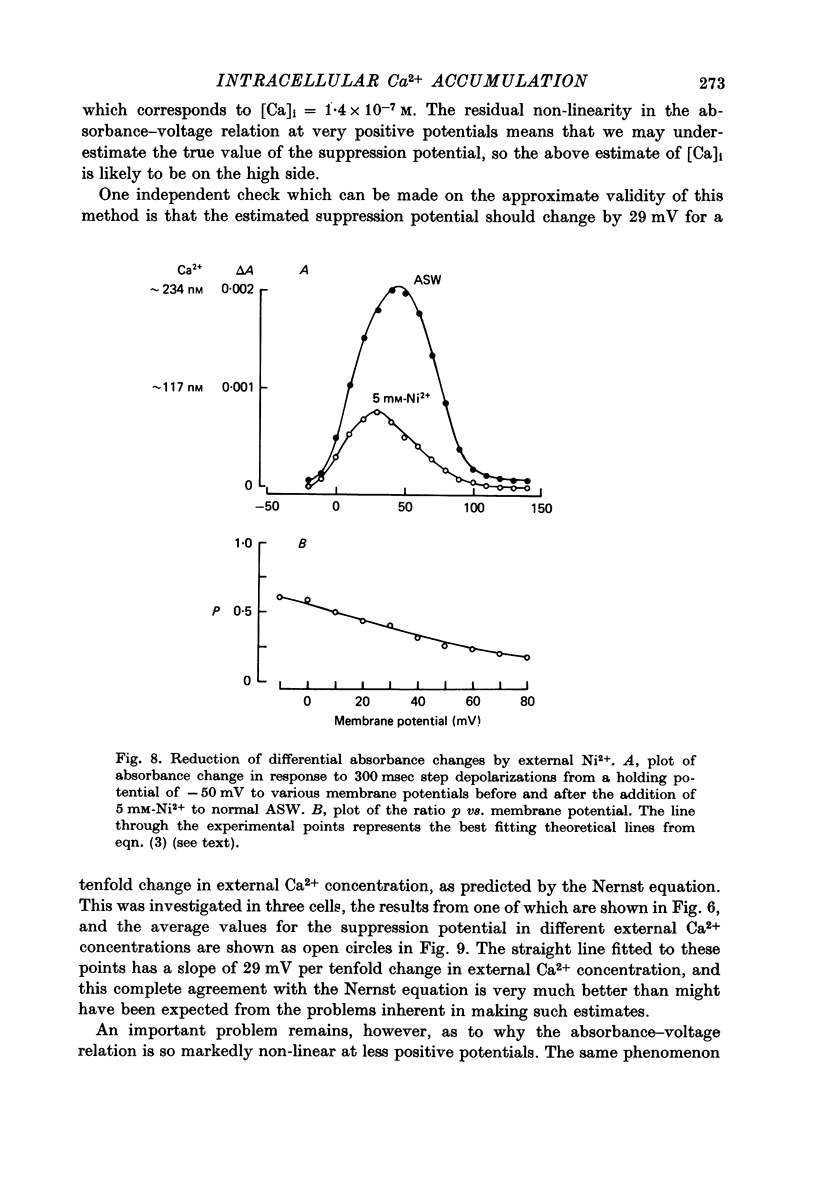
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W. Characteristics of sodium and calcium conductance changes produced by membrane depolarization in an Aplysia neurone. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:143–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
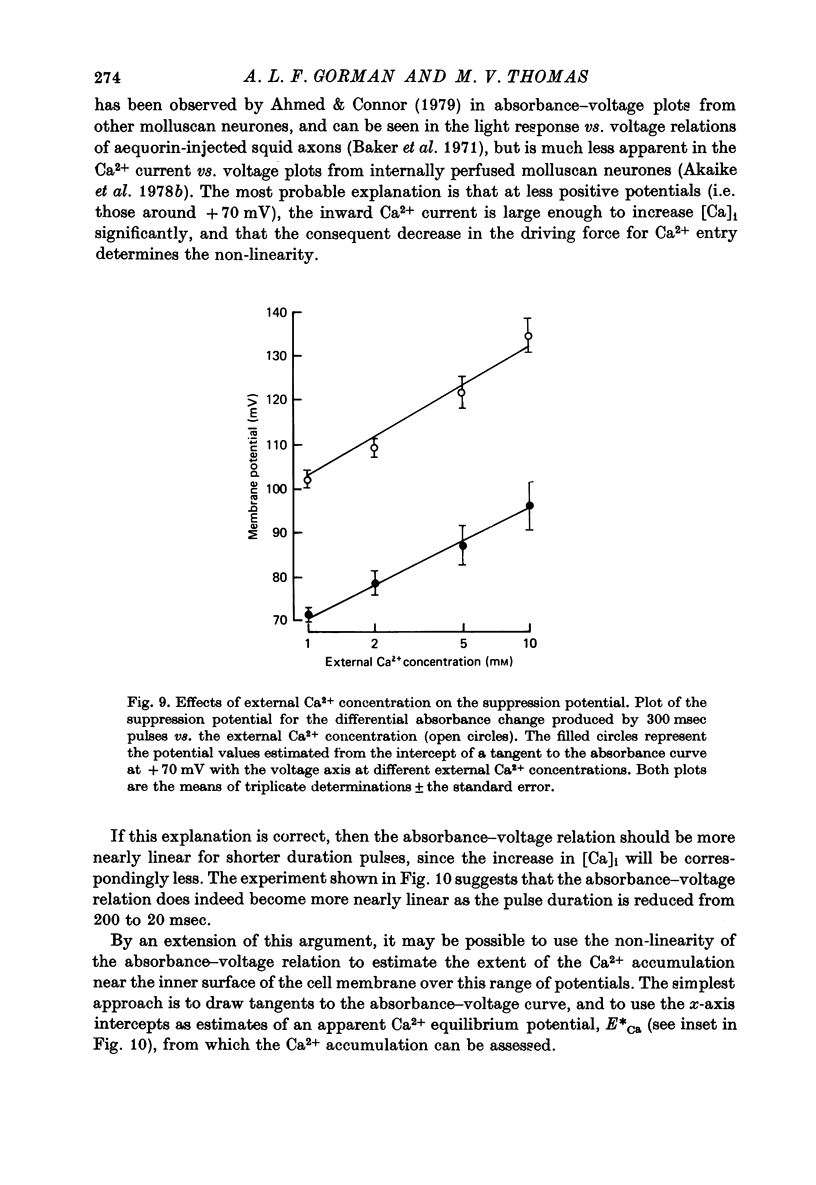
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W. Ionic currents in response to membrane depolarization in an Aplysia neurone. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:115–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed Z., Connor J. A. Measurement of calcium influx under voltage clamp in molluscan neurones using the metallochromic dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:61–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Fishman H. M., Lee K. S., Moore L. E., Brown A. M. The units of calcium conduction in Helix neurones. Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):379–382. doi: 10.1038/274379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Lee K. S., Brown A. M. The calcium current of Helix neuron. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):509–531. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen D. G., Blinks J. R., Prendergast F. G. Aequorin luminescence: relation of light emission to calcium concentration--a calcium-independent component. Science. 1977 Mar 11;195(4282):996–998. doi: 10.1126/science.841325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Effects of manganese and other agents on the calcium uptake that follows depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):511–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler G. W., Jr, Reuter H. Membrane calcium current in ventricular myocardial fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):191–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L. The effect of cyanide on the efflux of calcium from squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):497–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Eckert R. Calcium entry leads to inactivation of calcium channel in Paramecium. Science. 1978 Dec 15;202(4373):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.103199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr Calcium buffering in squid axons. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:363–392. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Scarpa A. Ionized magnesium concentration in axoplasm of dialyzed squid axons. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 15;50(1):82–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Brodwick M. S., Eaton D. C. Intracellular calcium and extra-retinal photoreception of Aplysia Giant neurons. J Neurobiol. 1977 Jan;8(1):1–18. doi: 10.1002/neu.480080102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Brown P. K., Pinto L. H. Detection of light-induced changes of intracellular ionized calcium concentration in Limulus ventral photoreceptors using arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):299–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Cohen L. B., De Weer P., Pinto L. H., Ross W. N., Salzberg B. M. Rapid changes in intracellular free calcium concentration. Detection by metallochromic indicator dyes in squid giant axon. Biophys J. 1975 Nov;15(11):1155–1160. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85891-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A. Calcium current in molluscan neurones: measurement under conditions which maximize its visibility. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:41–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipolo R., Requena J., Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J., Scarpa A., Tiffert T. Ionized calcium concentrations in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Apr;67(4):433–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M., Bergman C. The steady-state potassium conductance of the Ranvier node at various external K-concentrations. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Aug 29;370(2):185–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00581693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Lux H. D. A voltage-sensitive persistent calcium conductance in neuronal somata of Helix. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(1):129–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D. Potassium activation associated with intraneuronal free calcium. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):437–439. doi: 10.1126/science.644308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D., Ridgway E. B. Voltage-dependent facilitation of Ca2+ entry in voltage-clamped, aequorin-injected molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1748–1752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geduldig D., Gruener R. Voltage clamp of the Aplysia giant neurone: early sodium and calcium currents. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;211(1):217–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Changes in the intracellular concentration of free calcium ions in a pace-maker neurone, measured with the metallochromic indicator dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:357–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Potassium conductance and internal calcium accumulation in a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:287–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graubard K. Voltage attenuation within Aplysia neurons: the effect of branching pattern. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90394-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S. Ca-dependent action potential. Membranes. 1975;3:359–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. Surface density of calcium ions and calcium spikes in the barnacle muscle fiber membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jan;50(3):583–601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Properties of a facilitating calcium current in pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):319–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Doroshenko P. A. Calcium currents in snail neurones. I. Identification of calcium current. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Apr 11;348(2):83–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00586471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Shakhovalov Y. A. Separation of sodium and calcium currents in the somatic membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):545–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K. Influence of ionic environment on the relationship between pre- and postsynaptic potentials. J Neurobiol. 1970;1(4):435–437. doi: 10.1002/neu.480010407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Podolsky R. J. Ionic mobility in muscle cells. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1297–1298. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents and their relation to synaptic transmission: voltage clamp study in squid giant synapse and theoretical model for the calcium gate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Heyer C. B. An aequorin study of a facilitating calcium current in bursting pacemaker neurons of Helix. Neuroscience. 1977;2(4):585–592. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magura I. S. Long-lasting inward current in snail neurons in barium solutions in voltage-clamp conditions. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jul 14;35(3):239–256. doi: 10.1007/BF01869952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirolli M., Talbott S. R. The geometrical factors determining the electrotonic properties of a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):19–34. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jul;58(1):36–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. D. The determination of the stability constant for calcium-EGTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 18;451(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B. Voltage-clamp studies of the calcium inward current in an identified snail neurone: comparison with the sodium inward current. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):253–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. V. Arsenazo III forms 2:1 complexes with Ca and 1:1 complexes with Mg under physiological conditions. Estimates of the apparent dissociation constants. Biophys J. 1979 Mar;25(3):541–548. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85322-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. V., Gorman A. L. Internal calcium changes in a bursting pacemaker neuron measured with arsenazo III. Science. 1977 Apr 29;196(4289):531–533. doi: 10.1126/science.850795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. V. Microelectrode amplifier with improved method of input-capacitance neutralisation. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1977 Jul;15(4):450–454. doi: 10.1007/BF02458001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D., Horn R. Inactivation without facilitation of calcium conductance in caesium-loaded neurones of Aplysia. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):312–314. doi: 10.1038/273312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D. Inactivation of Ca conductance dependent on entry of Ca ions in molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


