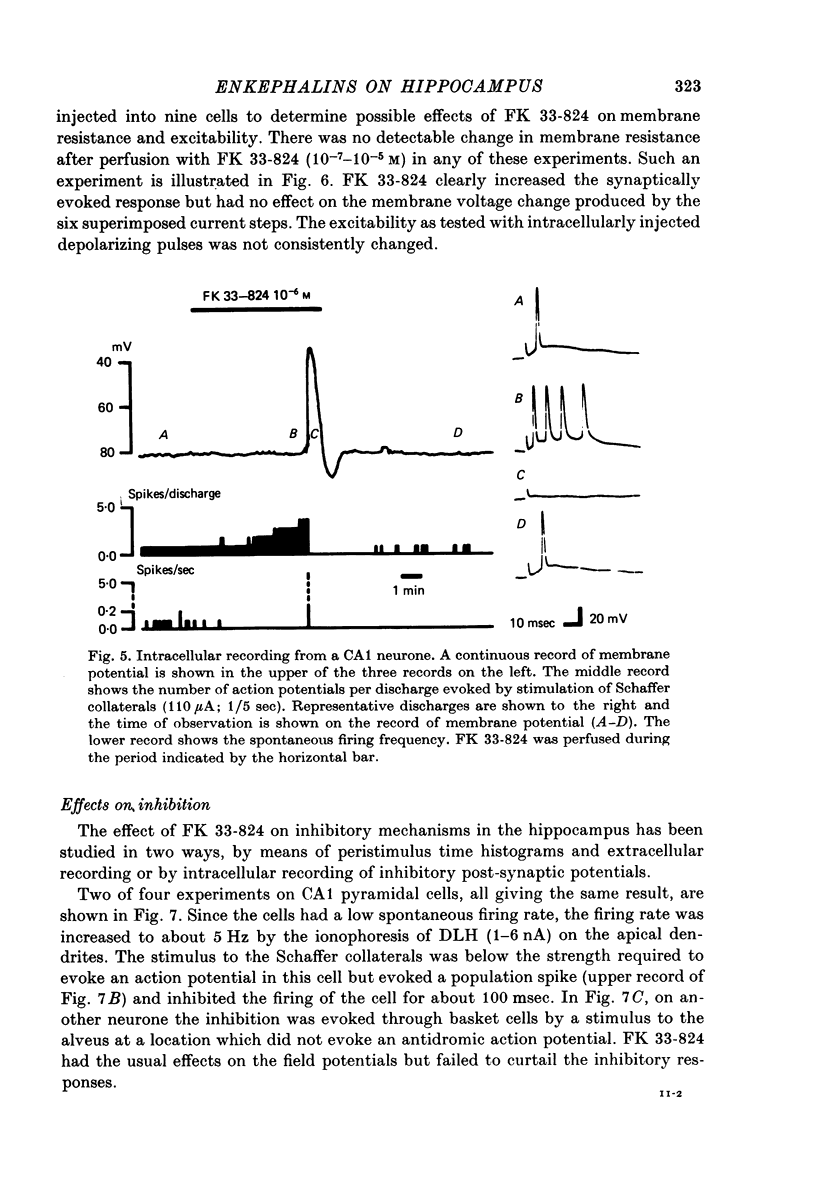
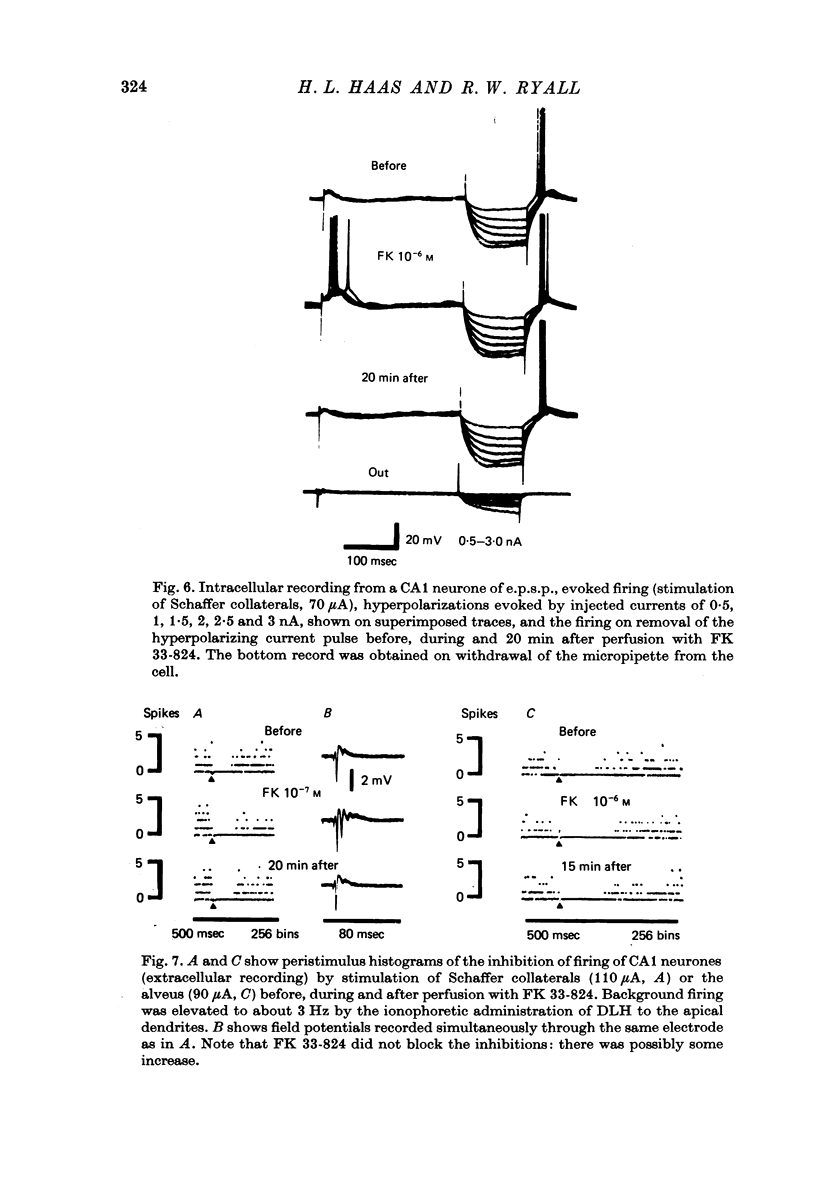
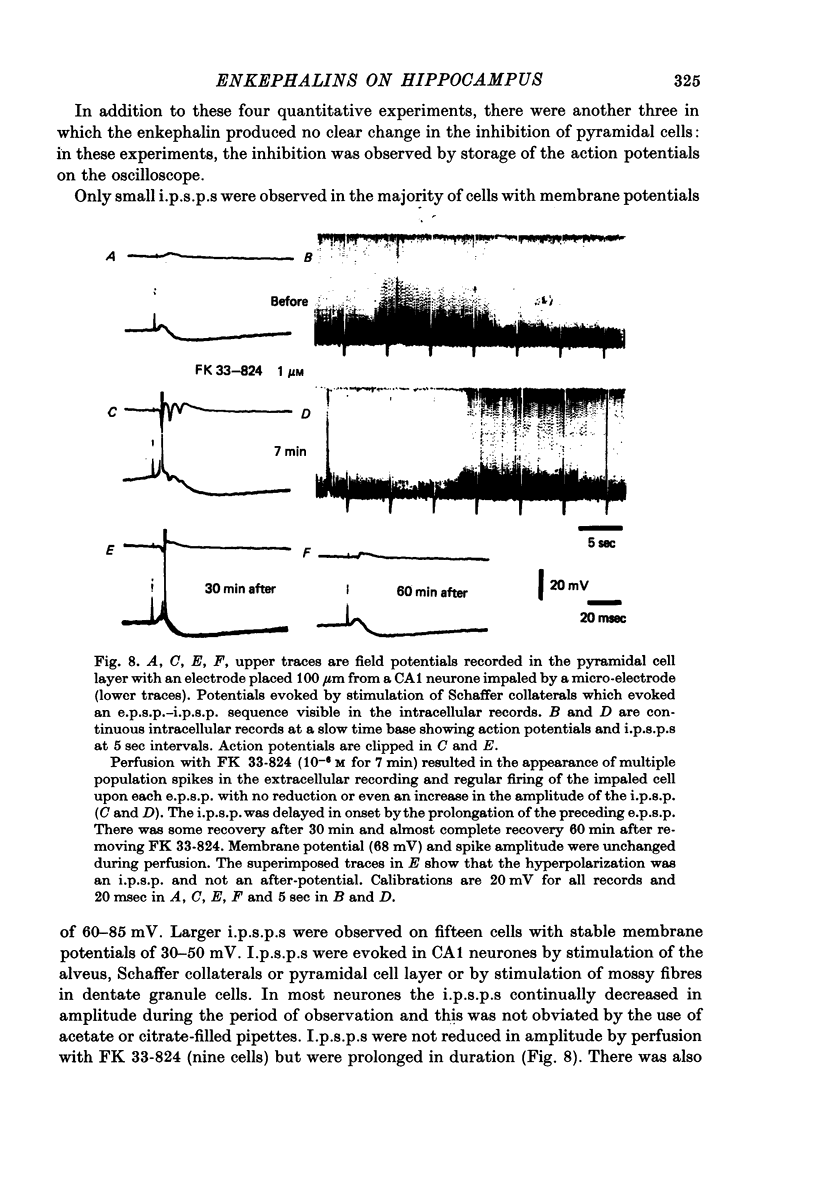
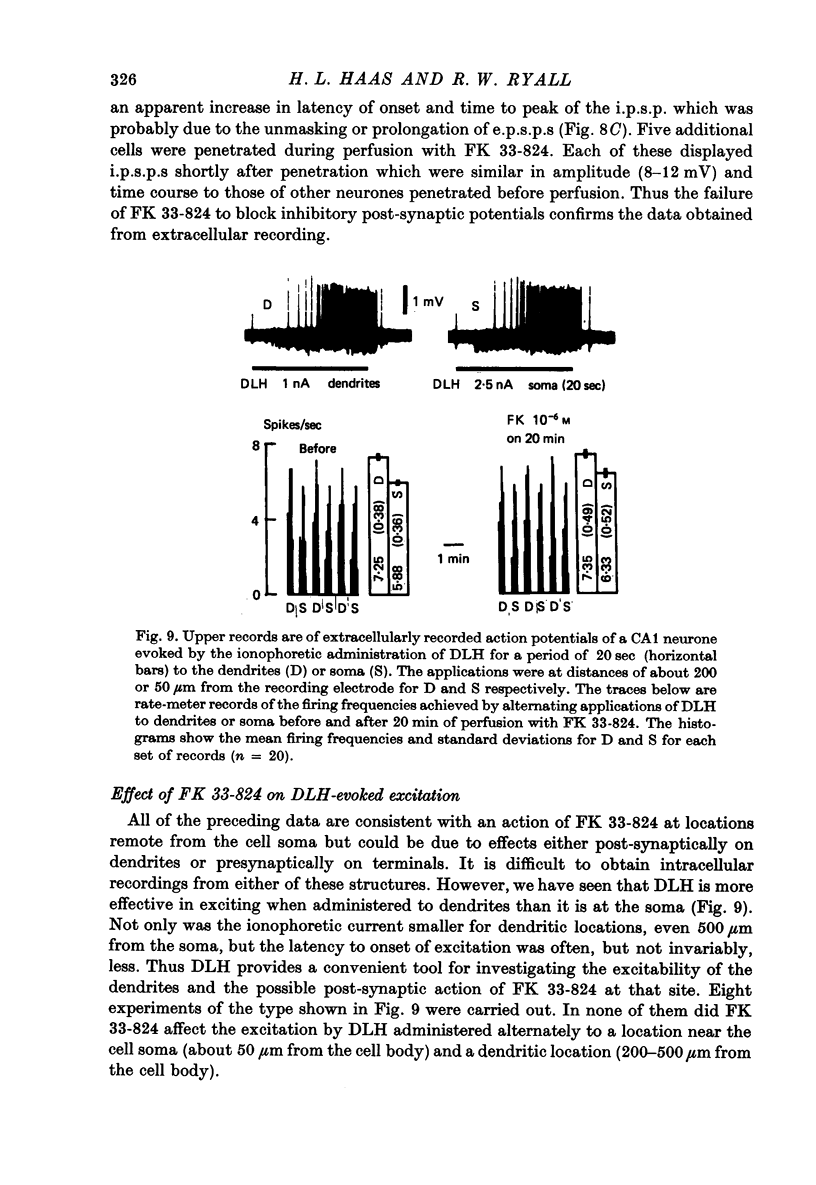
Abstract
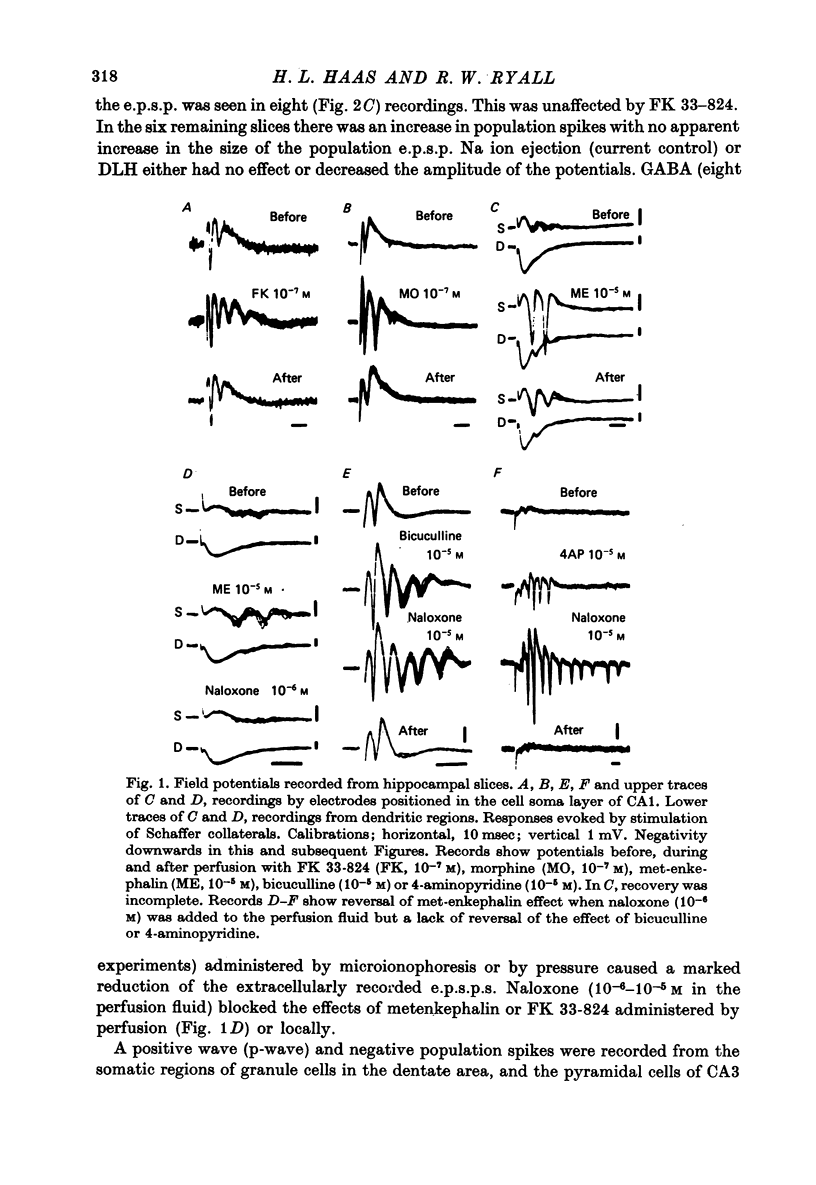
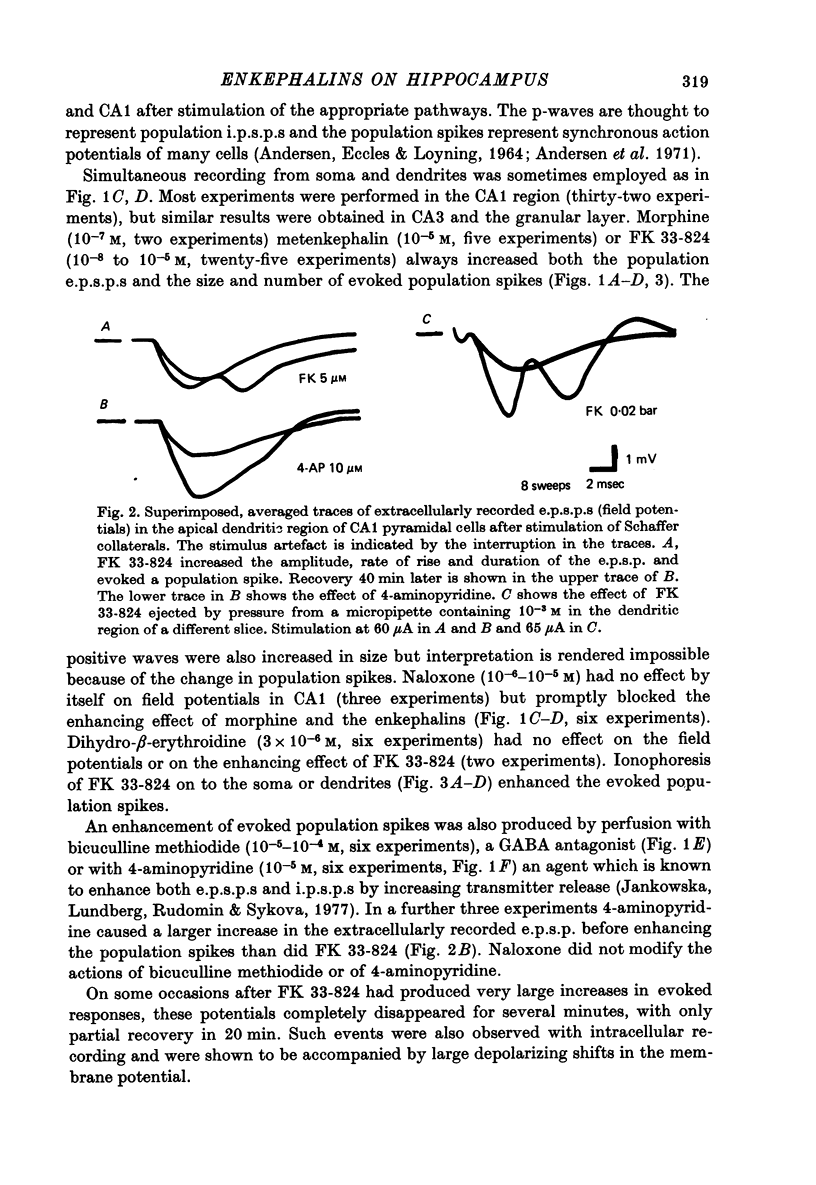
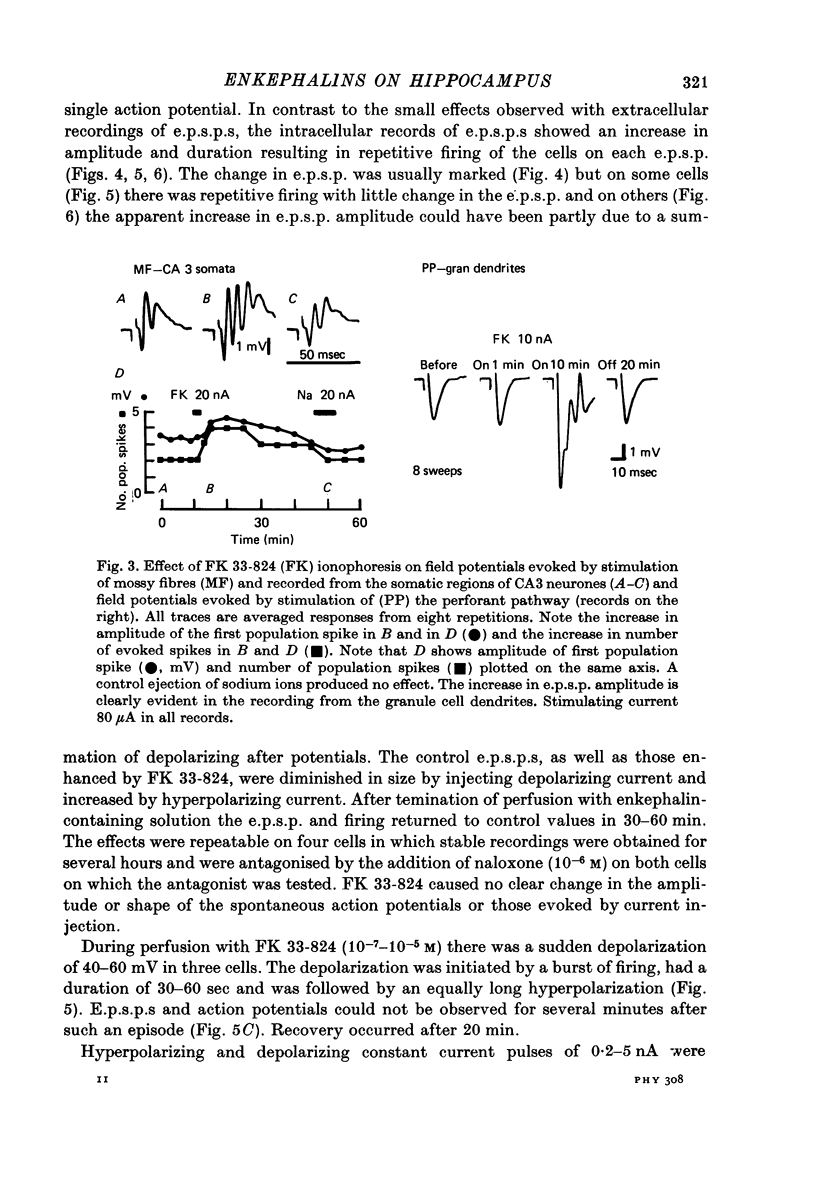
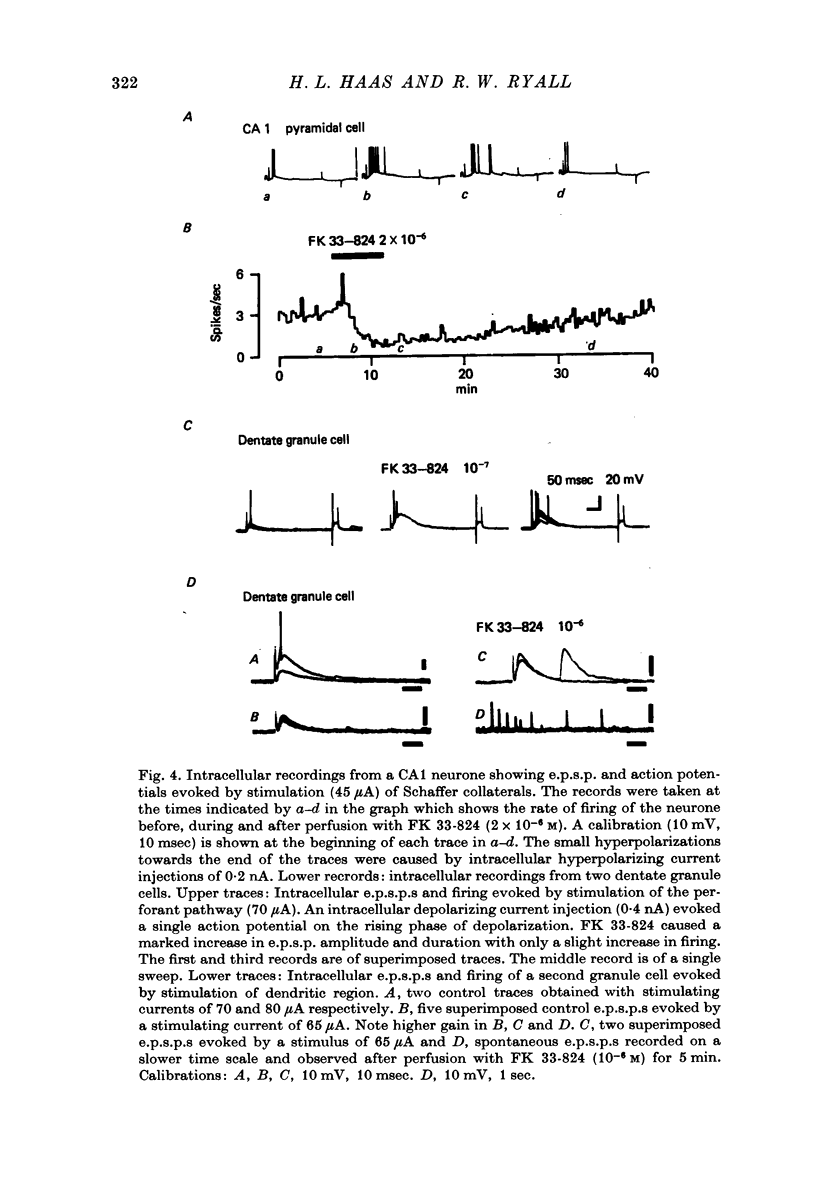
1. Extracellular recordings of postsynaptic potentials (field potentials), population spikes or unitary action potentials and intracellular records of excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials were obtained from neurons in superfused slices of rat hippocampus, to study the mechanism of the excitatory effect of enkephalins. 2. Most experiments were carried out with a synthetic, stable enkephalin analogue (FK 33-824) administered either by perfusion or by local administration (ionophoresis or pressure application from micropipettes). Comparisons were made when appropriate with metenkephalin, morphine, 4-aminopyridine and bicuculline. 3. The enkephalins caused a small increase in extracellular recordings of e.p.s.p.s and a more marked increase in the amplitude and frequency of population spikes. The effect of 4-aminopyridine on the extracellular e.p.s.p. was more marked than that of enkephalins, indicating that the enkephalins may have an additional effect upon regenerative spike mechanisms in the dendrites, which is not possessed by 4-aminopyridine. The actions of the enkephalins and morphine were blocked by naloxone, which did not block the action of bicuculline or 4-aminopyridine. 4. The increase in extracellularly recorded e.p.s.p. was shown to be due to a marked increase in the e.p.s.p. amplitude recorded intracellularly in CA1 and CA3 neurones and dentate granule cells. The augmented e.p.s.p.s evoked more action potentials. 5. The increase in e.p.s.p. amplitude was not accompanied by any marked change in membrane potential or resistance. 6. The inhibition of background firing by appropriate stimulation and recorded as peristimulus histograms was not reduced by FK 33-824. There was a slight prolongation. 7. Intracellularly recorded i.p.s.p.s were not blocked by FK 33-824. There was a prolongation of the i.p.s.p.s and an apparent increase in latency due to the unmasking and prolongation of e.p.s.p.s. 8. Dendritic excitability, as tested with ionophoresis of DL-homocysteic acid locally to the dendrites was unaffected by FK 33-824. 9. It is concluded that the increase in e.p.s.p.s produced by enkephalins can be explained by an increased release of excitatory transmitter, as occurs with 4-aminopyridine.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P., ECCLES J. C., LOYNING Y. PATHWAY OF POSTSYNAPTIC INHIBITION IN THE HIPPOCAMPUS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jul;27:608–619. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.4.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Bliss T. V., Skrede K. K. Unit analysis of hippocampal polulation spikes. Exp Brain Res. 1971;13(2):208–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00234086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Sundberg S. H., Sveen O., Wigström H. Specific long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):736–737. doi: 10.1038/266736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belcher G., Ryall R. W. Differential excitatory and inhibitory effects of opiates on non-nociceptive and nociceptive neurones in the spinal cord of the cat. Brain Res. 1978 Apr 28;145(2):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90864-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belcher G., Ryall R. W. Substance P and Renshaw cells: a new concept of inhibitory synaptic interactions. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;272(1):105–119. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Dray A. Morphine and neurotransmitter substances: Microiontophoretic study in the rat brain stem. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;50(1):47–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Felix D., Johnston G. A., McLennan H. Antagonism between bicuculline and GABA in the cat brain. Brain Res. 1971 Oct 8;33(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. Effects of morphine and naloxone on Renshaw cells and spinal interneurones in morphine dependent and non-dependent rats. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 27;113(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90943-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Gjerstad L. Penicillin blocks hippocampal IPSPs, unmasking prolonged EPSPs. Brain Res. 1979 May 18;168(1):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Schaerer B., Vosmansky M. A simple perfusion chamber for the study of nervous tissue slices in vitro. J Neurosci Methods. 1979 Dec;1(4):323–325. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(79)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Lundberg A., Rudomin P., Sykova E. Effects of 4-aminopyridine on transmission in excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the spinal cord. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 11;136(2):387–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90816-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Siggins G. R., Ling N., Bloom F. E., Guillemin R. Neuronal actions of endorphins and enkephalins among brain regions: a comparative microiontophoretic study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2584–2588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistri A. Morphine-induced changes in the spontaneous and electrically evoked acetylcholine release from the isolated spinal cord. Brain Res. 1976 Jul 9;110(2):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. Opiates, opioid peptides and single neurones. Life Sci. 1979 Apr 23;24(17):1527–1545. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roemer D., Buescher H. H., Hill R. C., Pless J., Bauer W., Cardinaux F., Closse A., Hauser D., Huguenin R. A synthetic enkephalin analogue with prolonged parenteral and oral analgesic activity. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):547–549. doi: 10.1038/268547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roemer D., Pless J. Structure activity relationship of orally active enkephalin analogues as analgesics. Life Sci. 1979 Feb 12;24(7):621–624. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh M., Akaike A., Takagi H. Excitation by morphine and enkephalin of single neurons of nucleus reticularis paragigantocellularis in the rat: a probable mechanism of analgesic action of opioids. Brain Res. 1979 Jun 22;169(2):406–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)91043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Andersen P. Glutamic acid sensitivity of dendrites in hippocampal slices in vitro. Adv Neurol. 1975;12:45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Slawsky M. Probable calcium spikes in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 21;135(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinacker A. Calcium-dependent presynaptic action of substance P at the frog neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):268–270. doi: 10.1038/267268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Dendritic mechanisms underlying penicillin-induced epileptiform activity. Science. 1979 Jun 15;204(4398):1228–1231. doi: 10.1126/science.451569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto C. Activation of hippocampal neurons by mossy fiber stimulation in thin brain sections in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1972;14(4):423–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00235037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., French E. D., Siggins G. R., Bloom F. E. Opioid peptides may excite hippocampal pyramidal neurons by inhibiting adjacent inhibitory interneurons. Science. 1979 Jul 27;205(4404):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.451610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


