Full text
PDF
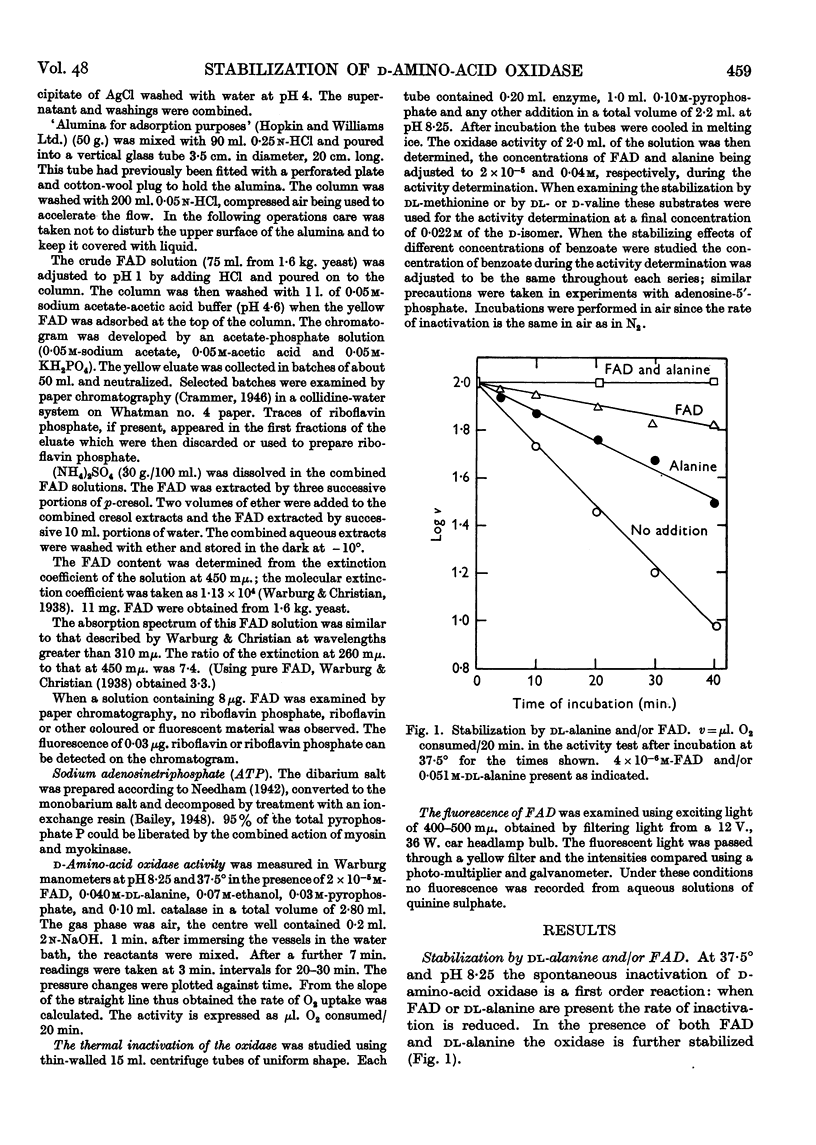
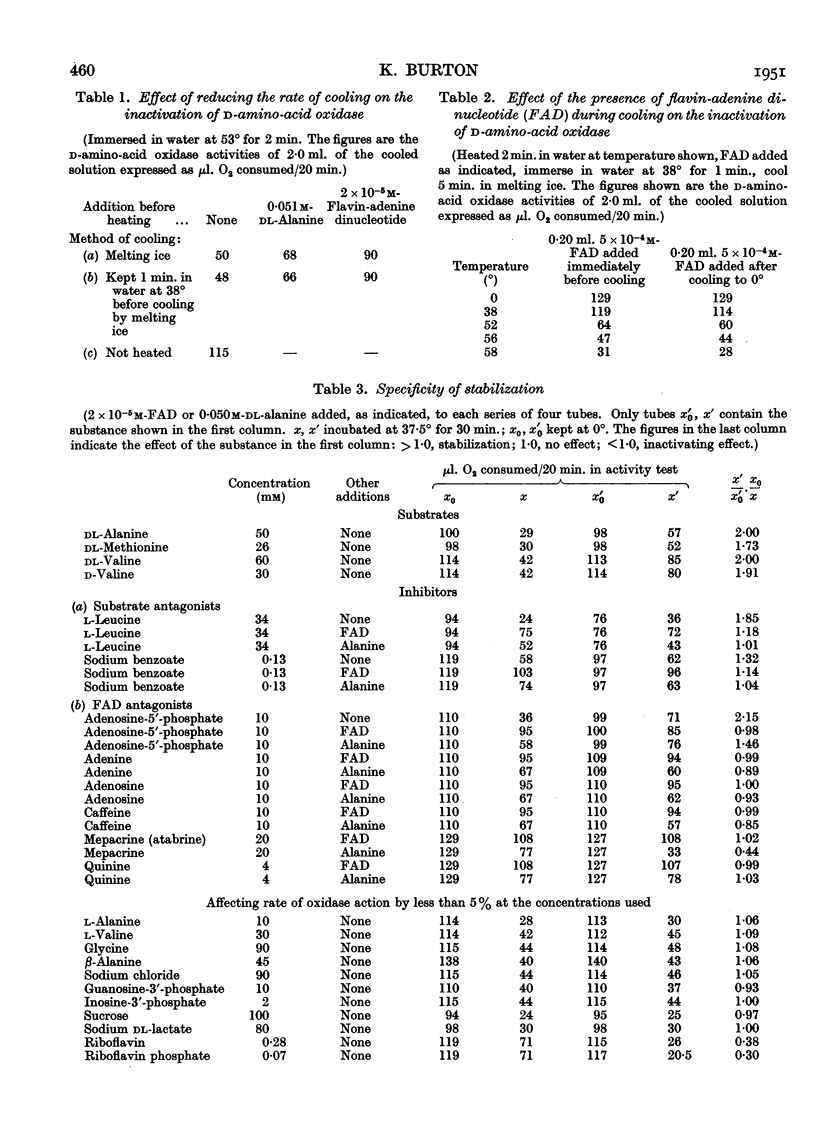
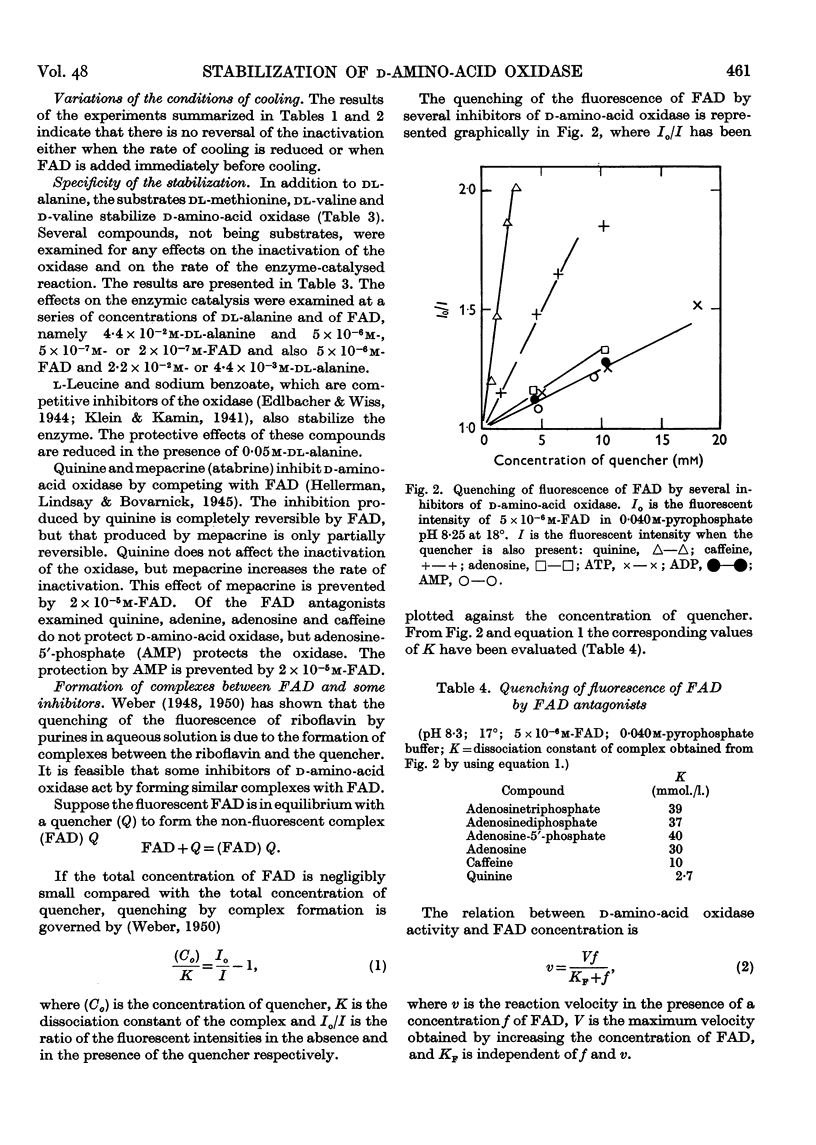
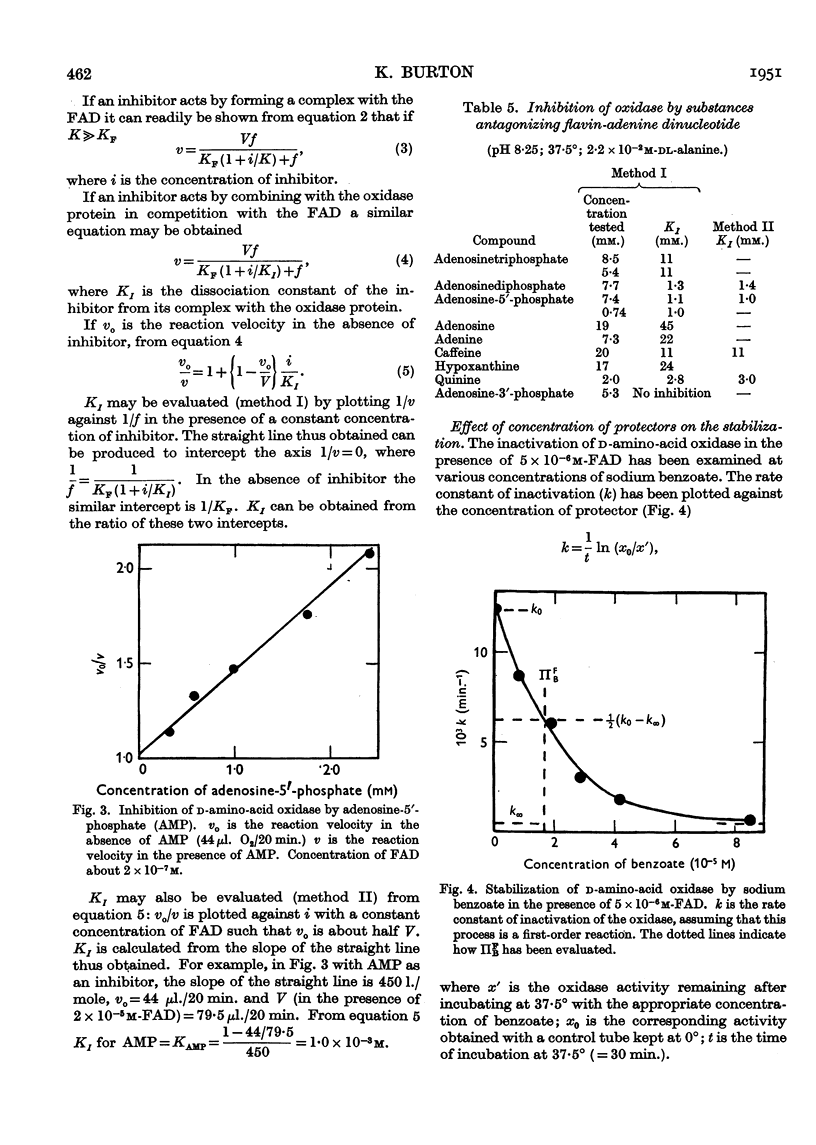


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Delory G. E., King E. J. The rate of enzymic hydrolysis of phosphoric esters: 2. Relation of structure to dissociation constant, Michaelis constant, and rate of hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1943;37(5):547–550. doi: 10.1042/bj0370547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keilin D., Hartree E. F. Properties of azide-catalase. Biochem J. 1945;39(2):148–157. doi: 10.1042/bj0390148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham D. M. The adenosinetriphosphatase activity of myosin preparations. Biochem J. 1942 Feb;36(1-2):113–120. doi: 10.1042/bj0360113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proceedings of the Biochemical Society. Biochem J. 1948;42(1):i.1–i.x. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G. Fluorescence of riboflavin and flavin-adenine dinucleotide. Biochem J. 1950 Jun-Jul;47(1):114–121. doi: 10.1042/bj0470114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


