Abstract
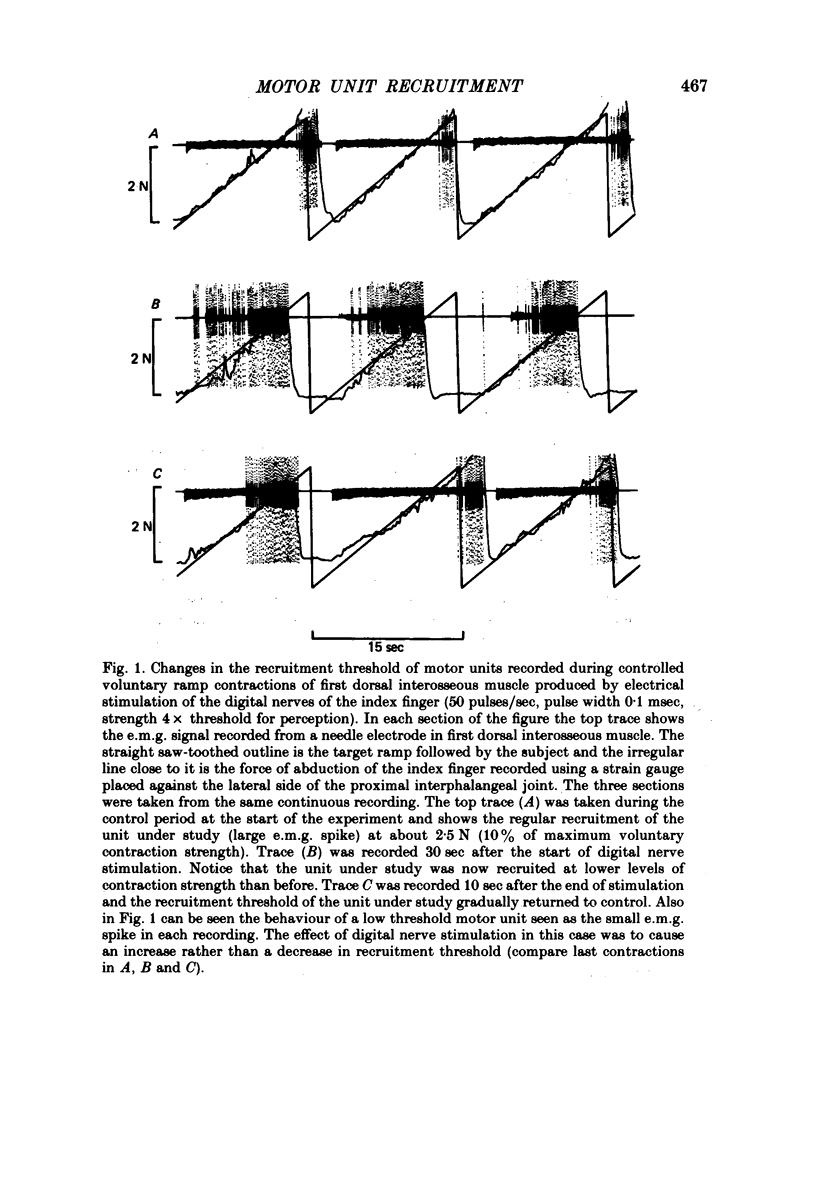
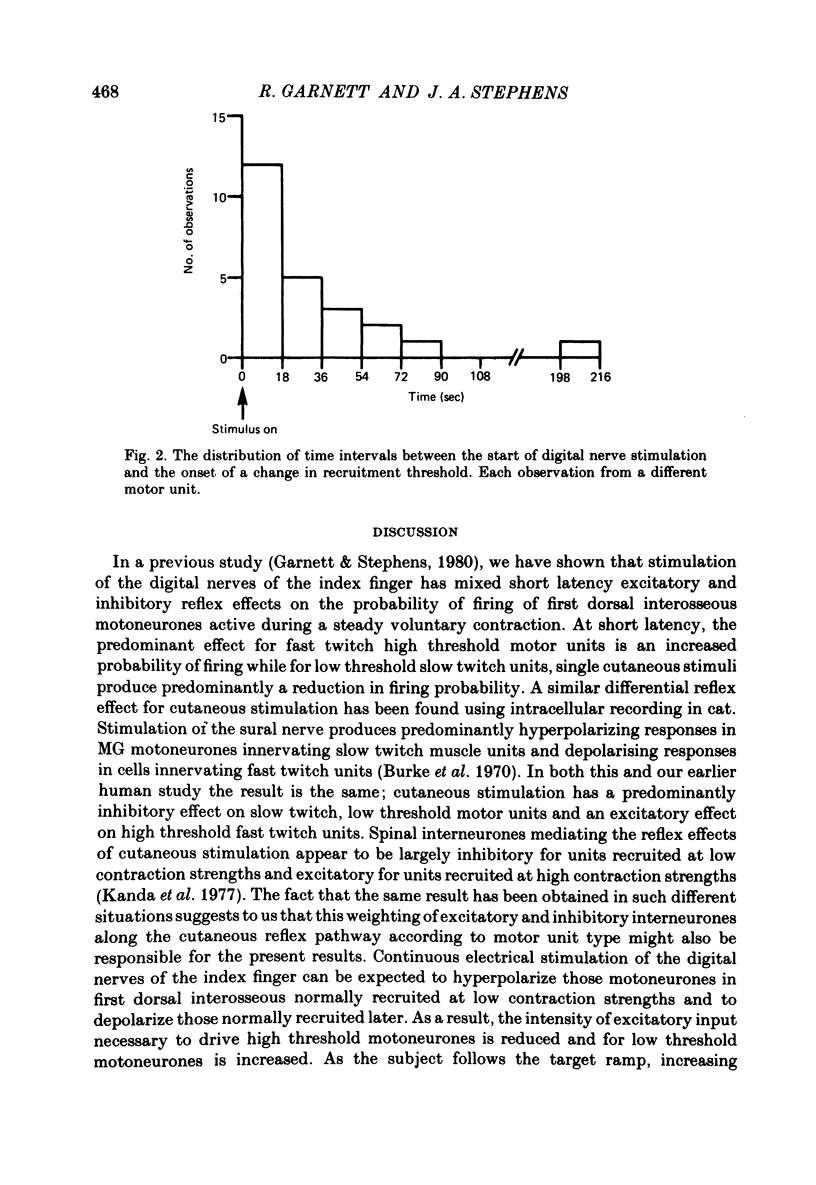
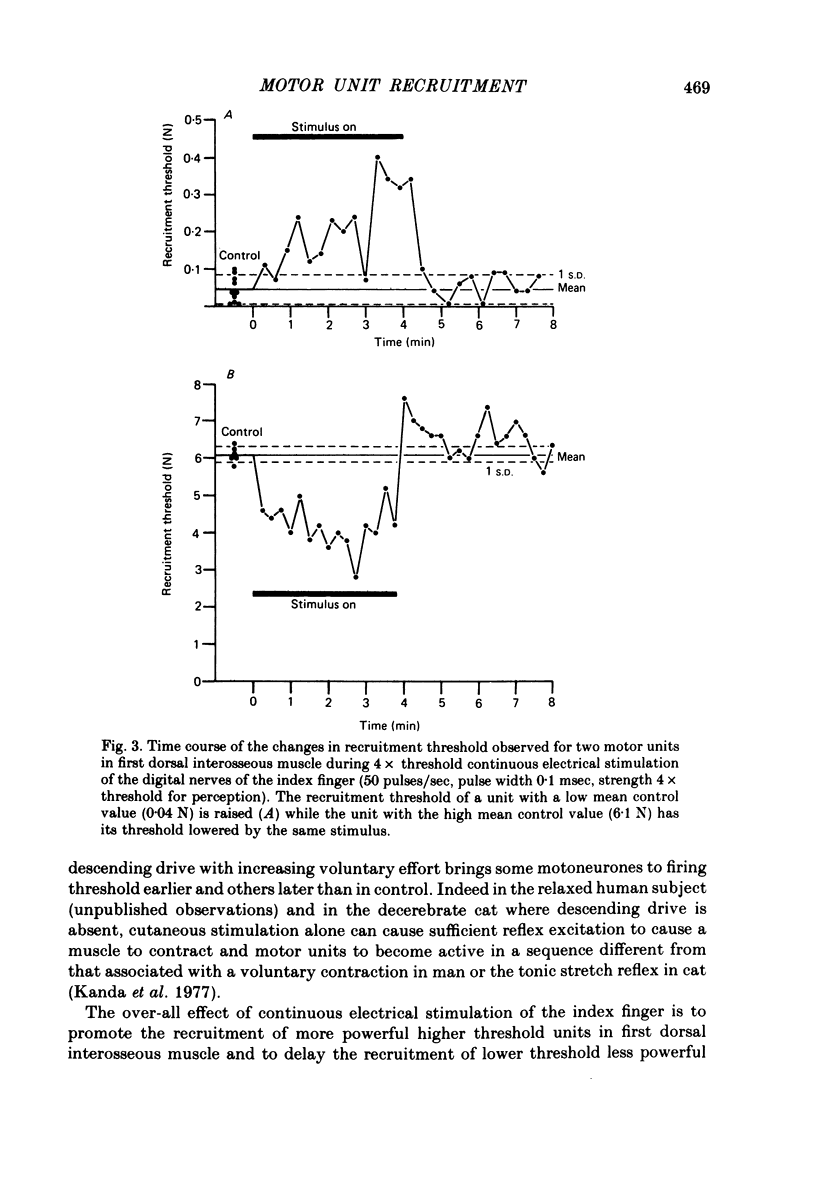
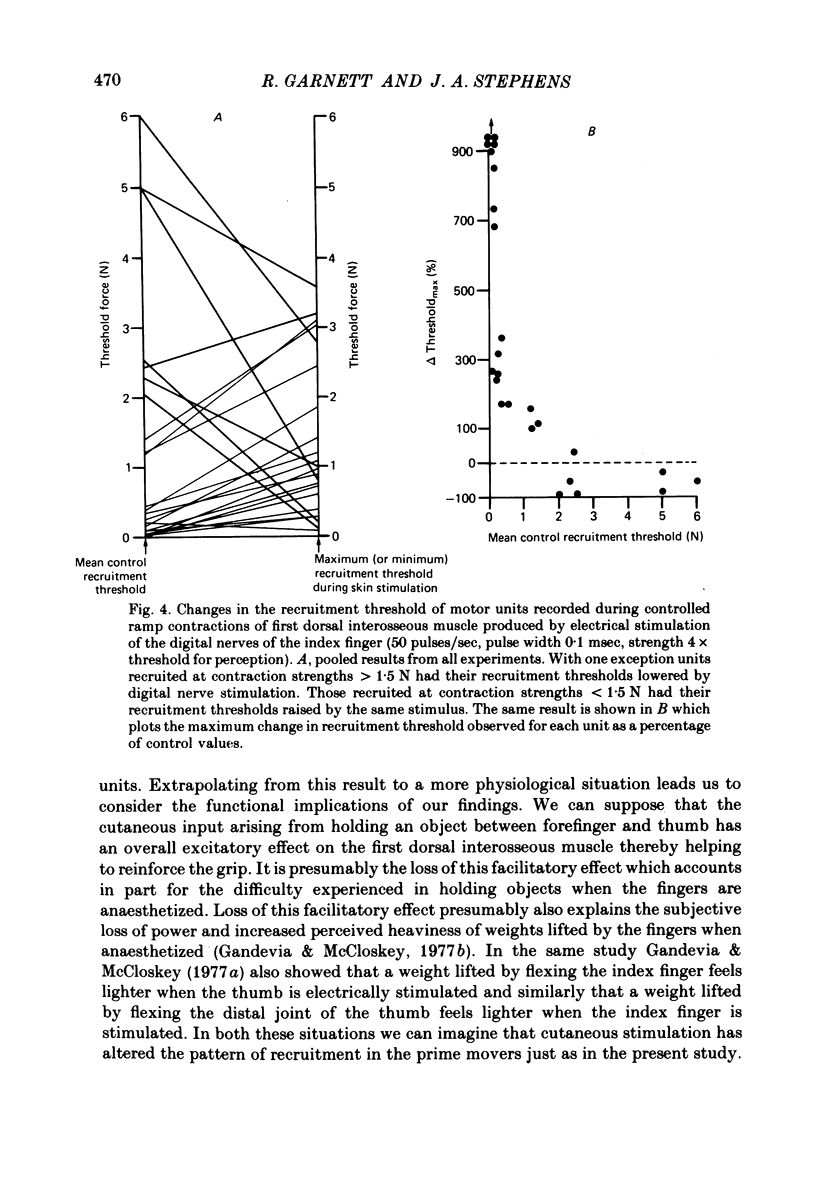
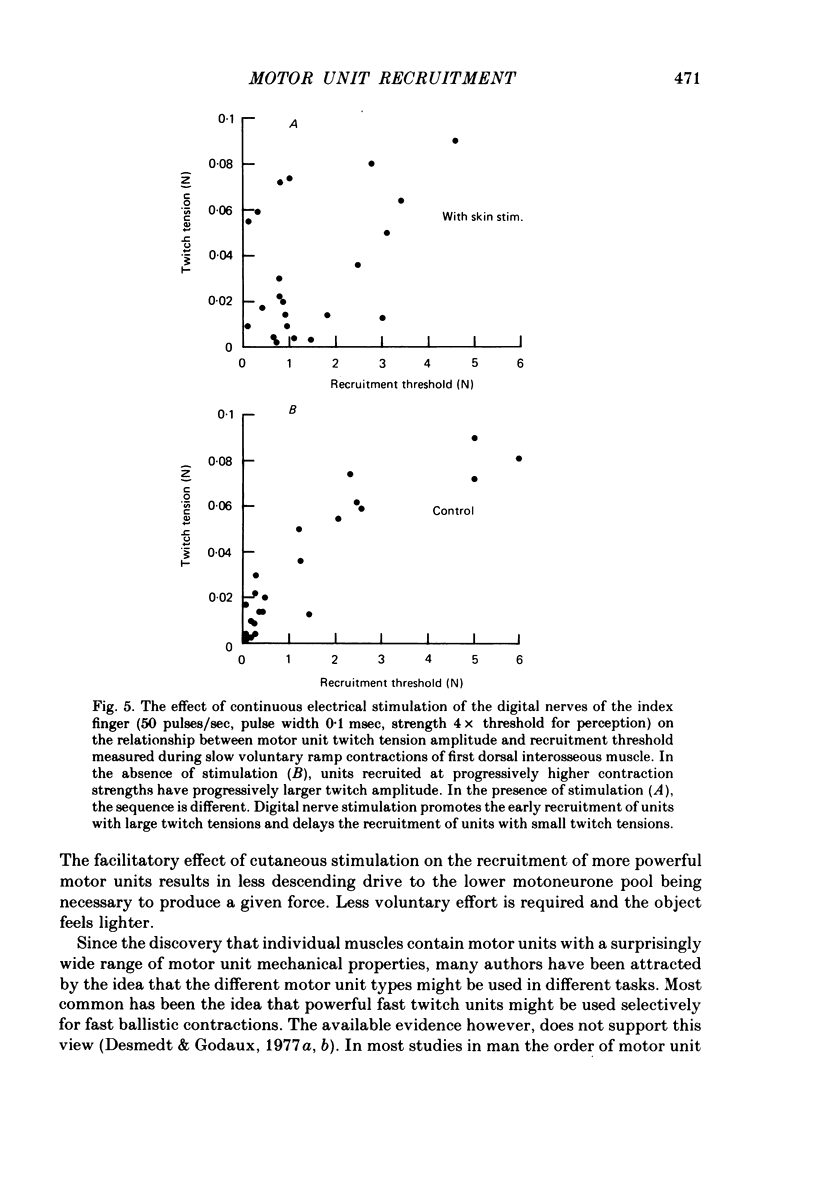
1. The effect of cutaneous stimulation on the recruitment of motor units has been studied during slowly increasing voluntary contractions of human first dorsal interosseous muscle. 2. Continuous electrical stimulation of the index finger at 4 x threshold for perception caused an increase in the recruitment threshold of units normally recruited at contraction strengths less than 1.5 N and a decrease in the recruitment threshold of units normally recruited at contraction strengths greater than 1.5 N. 3. It is concluded that the recruitment order of motor units during gradually increasing voluntary muscle contraction is not fixed but depends in part on cutaneous input.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buller N. P., Garnett R., Stephens J. A. The use of skin stimulation to produce reversal of motor unit recruitment order during voluntary muscle contraction in man [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:1P–2P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Jankowska E., ten Bruggencate G. A comparison of peripheral and rubrospinal synaptic input to slow and fast twitch motor units of triceps surae. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):709–732. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Rymer W. Z. Relative strength of synaptic input from short-latency pathways to motor units of defined type in cat medial gastrocnemius. J Neurophysiol. 1976 May;39(3):447–458. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büdingen H. J., Freund H. J. The relationship between the rate of rise of isometric tension and motor unit recruitment in a human forearm muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Mar 11;362(1):61–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00588682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamann H. P., Gillies J. D., Henneman E. Effects of inhibitory inputs on critical firing level and rank order of motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Nov;37(6):1350–1360. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.6.1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmedt J. E., Godaux E. Ballistic contractions in fast or slow human muscles: discharge patterns of single motor units. J Physiol. 1978 Dec;285:185–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmedt J. E., Godaux E. Ballistic contractions in man: characteristic recruitment pattern of single motor units of the tibialis anterior muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(3):673–693. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmedt J. E., Godaux E. Fast motor units are not preferentially activated in rapid voluntary contractions in man. Nature. 1977 Jun 23;267(5613):717–719. doi: 10.1038/267717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINSTEIN B., LINDEGARD B., NYMAN E., WOHLFART G. Morphologic studies of motor units in normal human muscles. Acta Anat (Basel) 1955;23(2):127–142. doi: 10.1159/000140989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund H. J., Büdingen H. J., Dietz V. Activity of single motor units from human forearm muscles during voluntary isometric contractions. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Jul;38(4):933–946. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.4.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McCloskey D. I. Changes in motor commands, as shown by changes in perceived heaviness, during partial curarization and peripheral anaesthesia in man. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):673–689. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McCloskey D. I. Effects of related sensory inputs on motor performances in man studied through changes in perceived heaviness. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):653–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett R., Stephens J. A. Changes in the recruitment threshold of motor units in human first dorsal interosseous muscle produced by skin stimulation [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:13P–14P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett R., Stephens J. A. The reflex responses of single motor units in human first dorsal interosseous muscle following cutaneous afferent stimulation. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:351–364. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimby L., Hannerz J. Firing rate and recruitment order of toe extensor motor units in different modes of voluntary conraction. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(3):865–879. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henneman E., Clamann H. P., Gillies J. D., Skinner R. D. Rank order of motoneurons within a pool: law of combination. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Nov;37(6):1338–1349. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.6.1338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henneman E., Somjen G., Carpenter D. O. Excitability and inhibitability of motoneurons of different sizes. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28(3):599–620. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda K., Burke R. E., Walmsley B. Differential control of fast and slow twitch motor units in the decerebrate cat. Exp Brain Res. 1977 Aug 8;29(1):57–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00236875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Henneman E. Terminals of single Ia fibers: location, density, and distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):171–187. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-Brown H. S., Stein R. B., Yemm R. The contractile properties of human motor units during voluntary isometric contractions. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):285–306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-Brown H. S., Stein R. B., Yemm R. The orderly recruitment of human motor units during voluntary isometric contractions. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):359–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somjen G., Carpenter D. O., Henneman E. Responses of motoneurons of different sizes to graded stimulation of supraspinal centers of the brain. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Sep;28(5):958–965. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.5.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. A., Garnett R., Buller N. P. Reversal of recruitment order of single motor units produced by cutaneous stimulation during voluntary muscle contraction in man. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):362–364. doi: 10.1038/272362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. A., Usherwood T. P. The mechanical properties of human motor units with special reference to their fatiguability and recruitment threshold. Brain Res. 1977 Apr 8;125(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90361-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


