Abstract
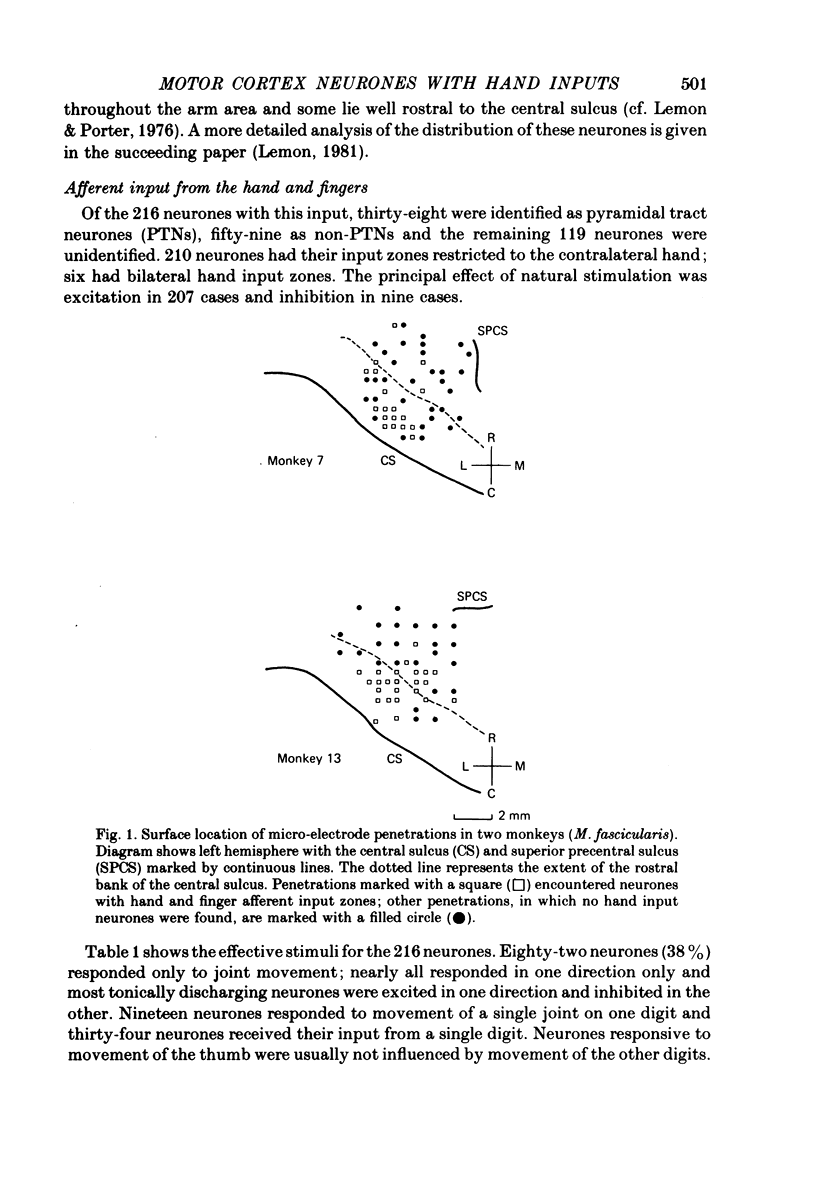
1. Records have been made from area 4 of the cerebral cortex in five conscious monkeys. The properties of 216 neurones responsive to natural stimulation of the hand and fingers have been investigated.
2. 46% of these neurones responded only to cutaneous stimulation (especially light brushing across the glabrous skin) and a further 38% responded only to movement of the digits. 4% responded to brief prods of the hand. 12% of the sample responded to more than one stimulus modality.
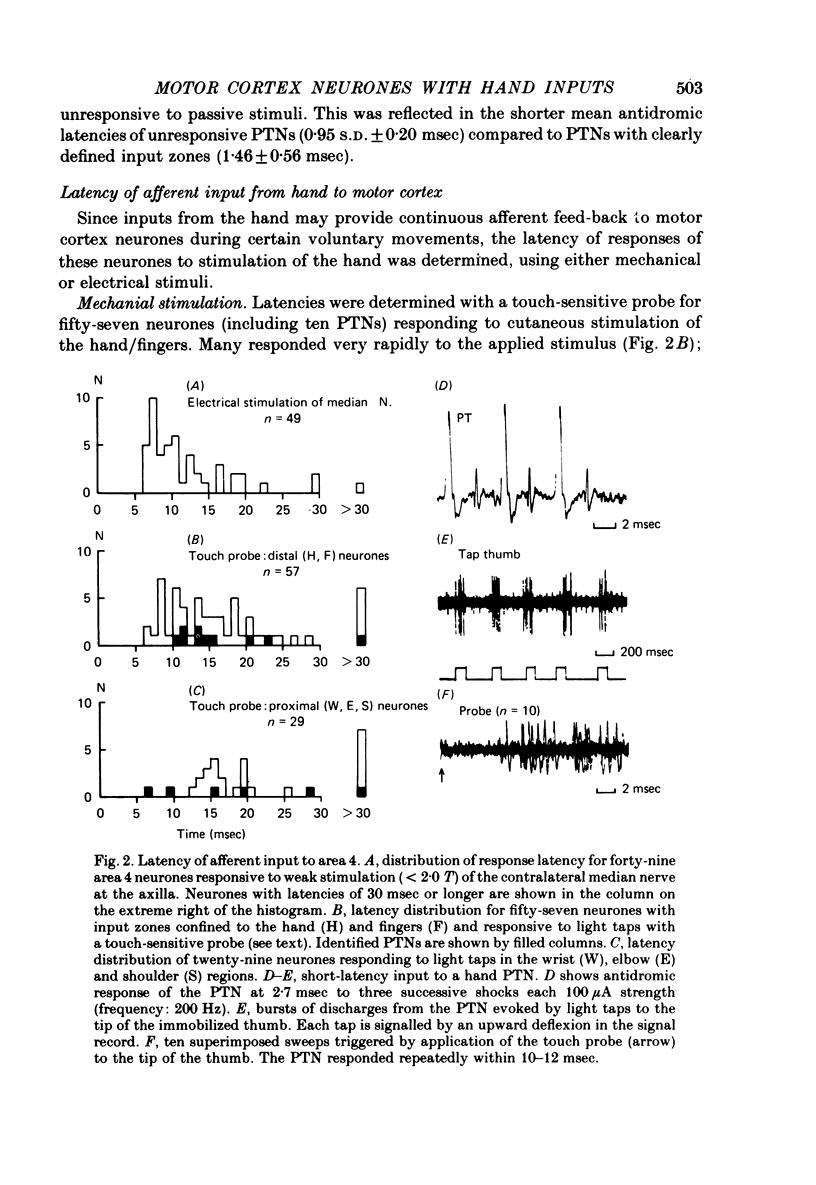
3. Many hand-input neurones, including pyramidal tract neurones, responded at short-latency (8-15 msec) to light mechanical stimulation of the hand and to weak electrical stimulation of the median nerve.
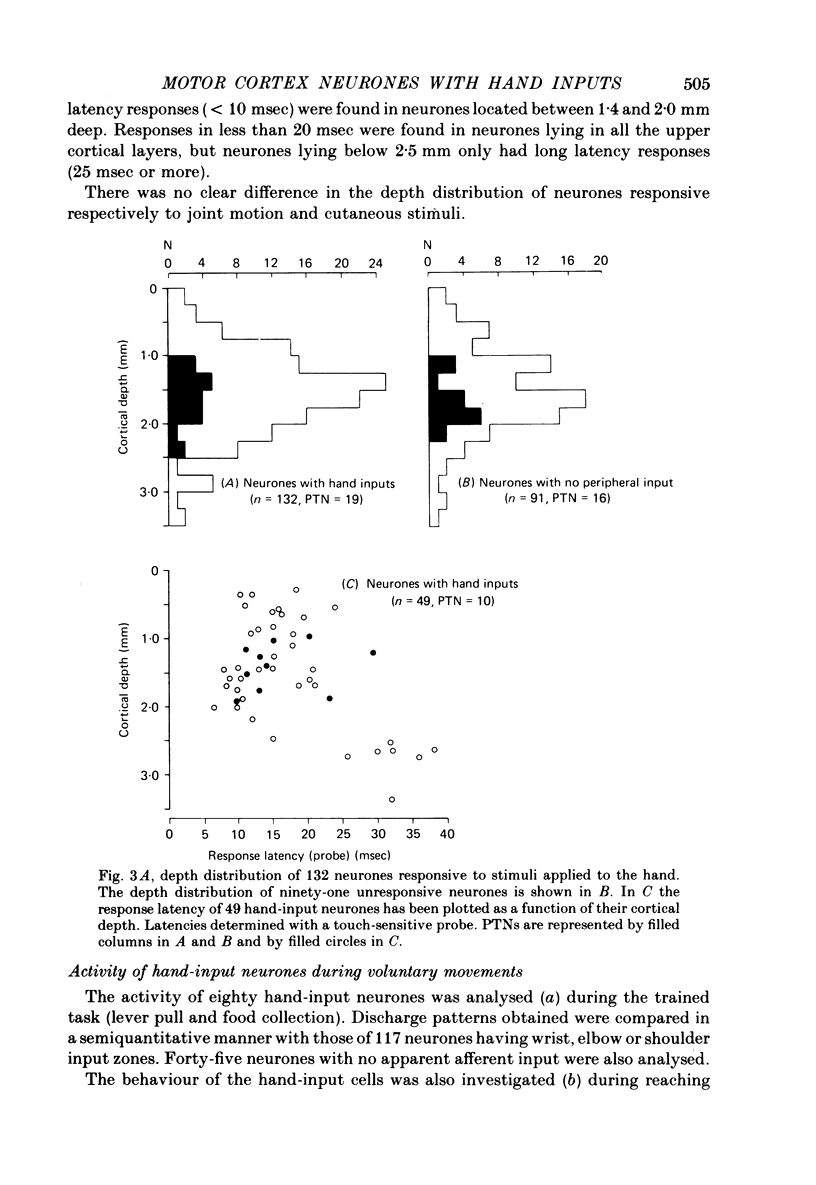
4. Responsive neurones were found at all depths of the cortical grey matter. Responses of shortest latency were encountered in neurones probably located in layers IV and V.
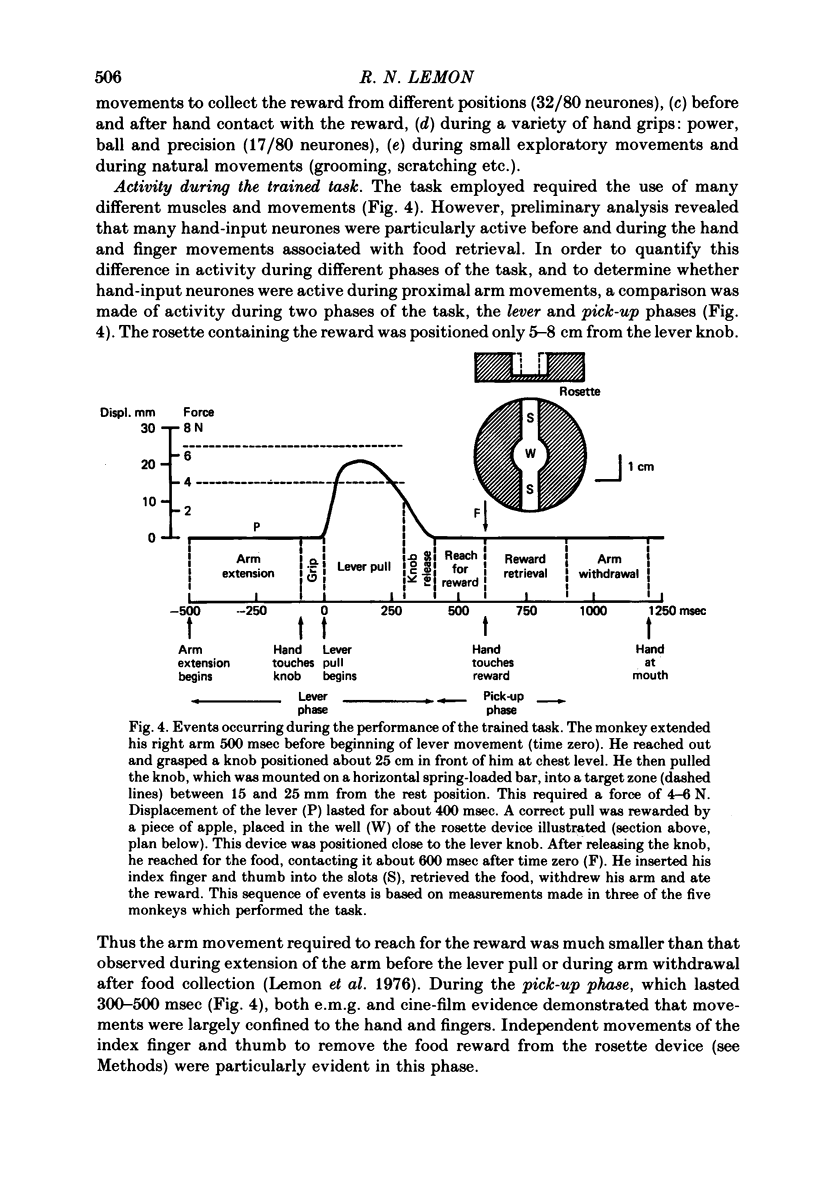
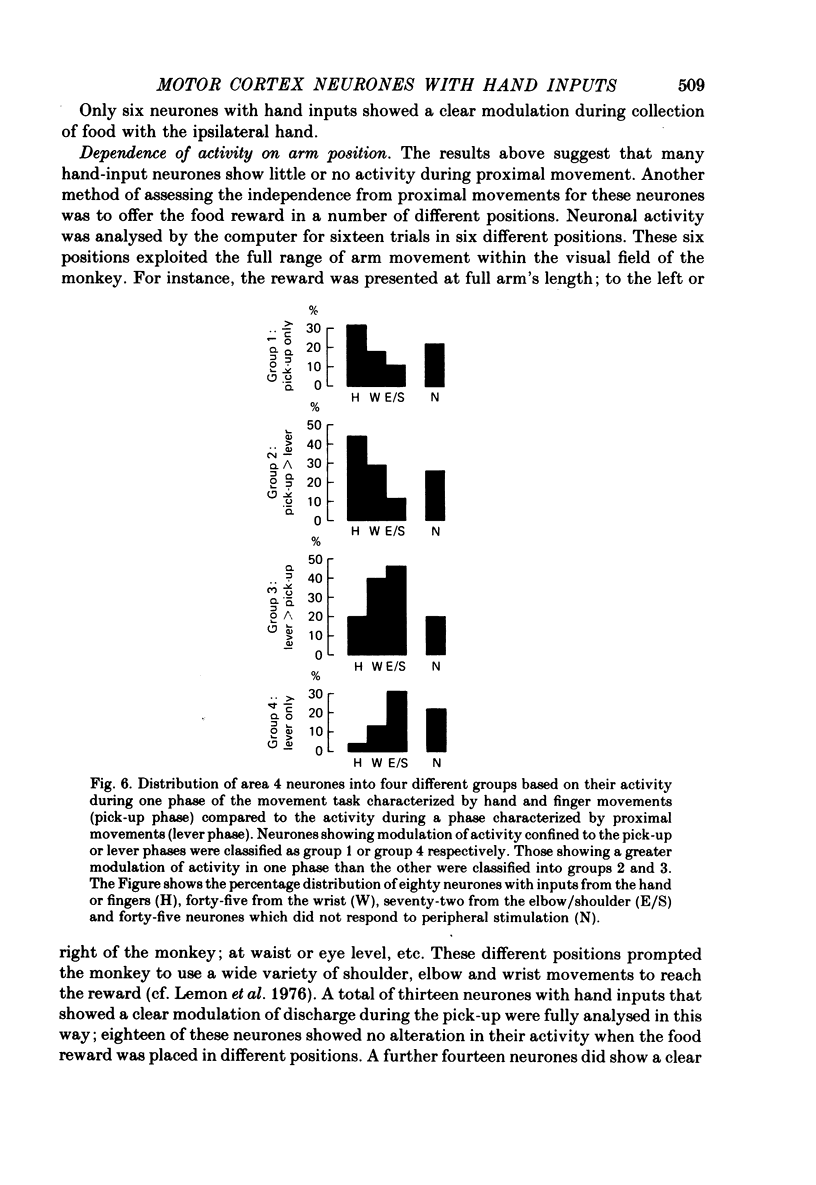
5. The behaviour of eighty hand-input neurones was analysed during a simple, stereotyped task which involved pulling a lever and collecting a food reward from a small well. For comparison, the activity of 117 neurones with inputs from the wrist, elbow or shoulder was also analysed.
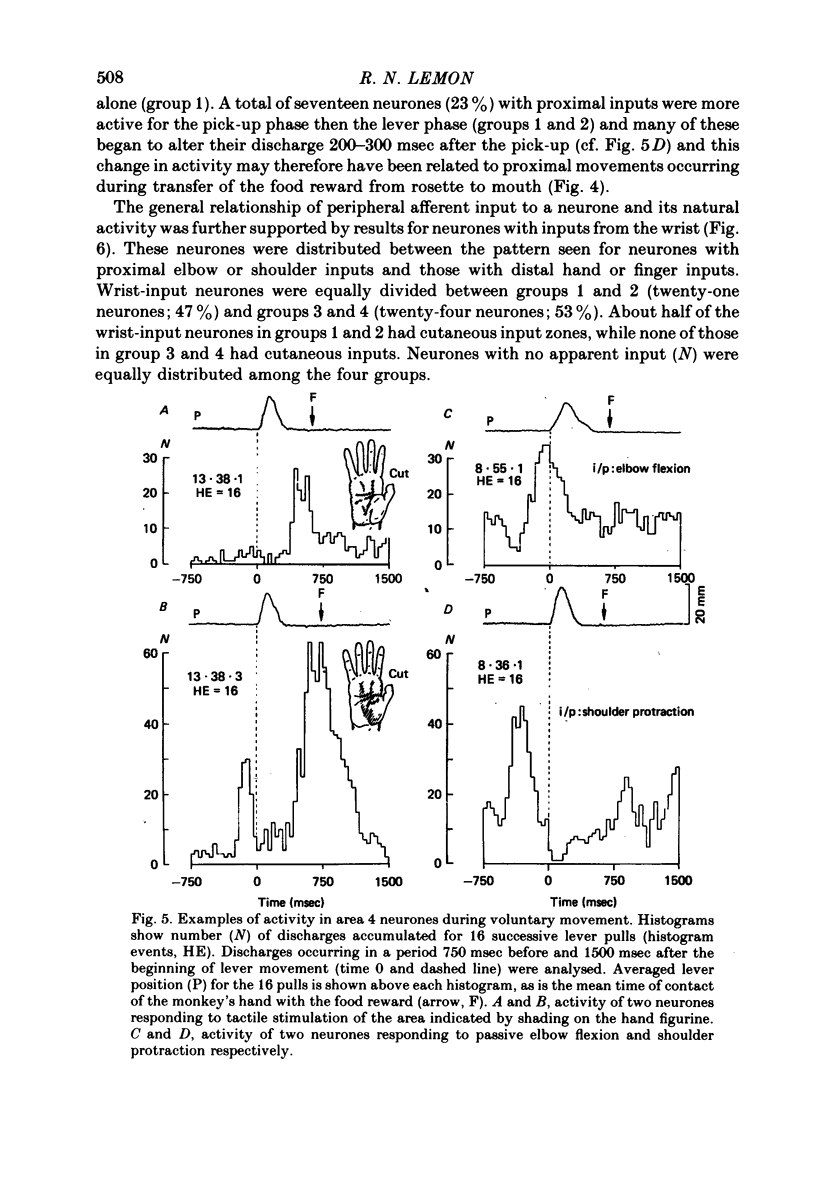
6. Nearly all hand-input neurones modulated their activity either before (48/80) or during (29/80) the retrieval of the reward which required precision grip between index finger and thumb. Many were silent during proximal arm movements and some displayed activity patterns independent of these movements.
7. By contrast, the activity of many neurones with proximal arm (elbow, shoulder) inputs was unrelated to food retrieval and manipulation, but well related to arm movements.
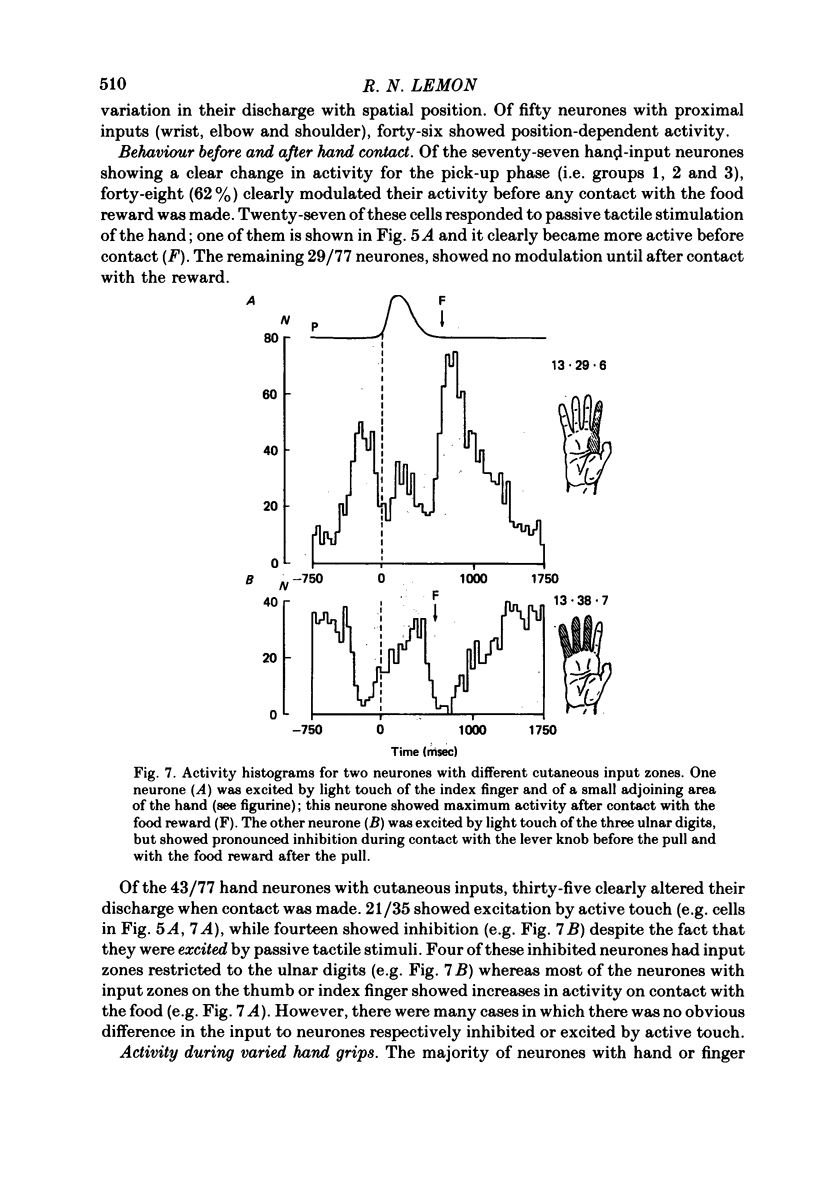
8. Forty-three of the eighty neurones had cutaneous input from the hand. Twenty-seven were active before hand contact. Thirty-five modulated their discharge when contact was made (twenty-one excitation, fourteen inhibition).
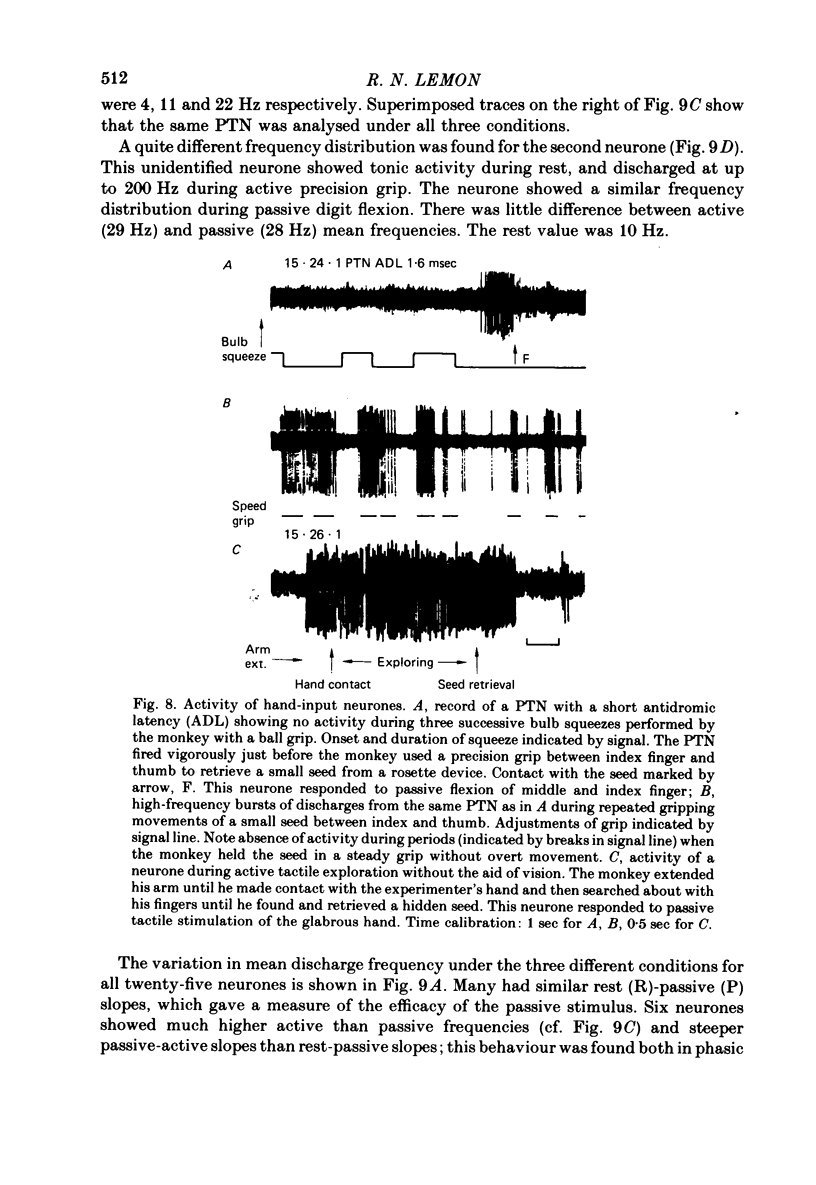
9. Most hand-input neurones were more active during fractionated movements of the hand or fingers than during power or ball grips requiring simultaneous flexion of all digits. Neurones with glabrous inputs often showed intense activity during small, precise finger movements and during active tactile exploration without the aid of vision.
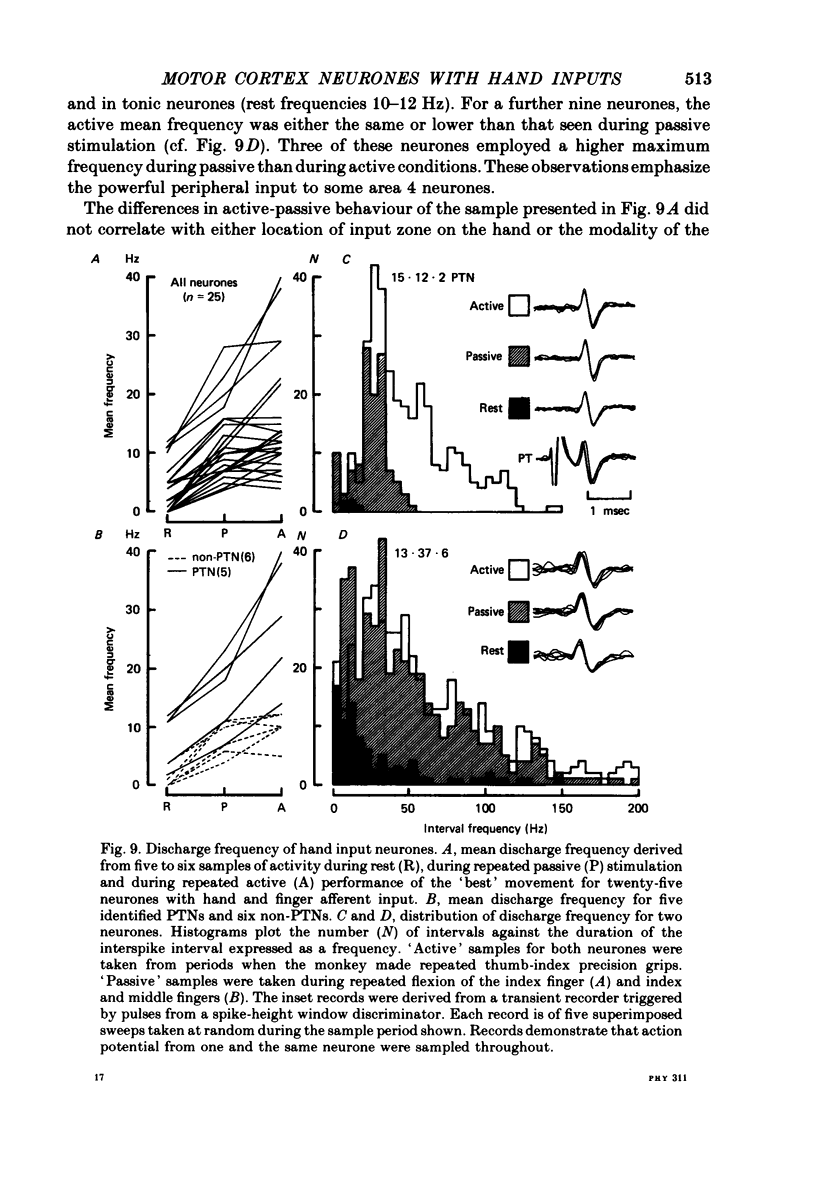
10. Analysis of the discharge frequency of twenty-five hand-input neurones revealed that some (mainly non-pyramidal tract neurones) had a similar mean frequency and range of modulation during both active movement and passive stimulation. Others (mainly pyramidal tract neurones) had a greater frequency range and higher mean frequency during active than during passive movements.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asanuma H., Larsen K. D., Yumiya H. Receptive fields of thalamic neurons projecting to the motor cortex in the cat. Brain Res. 1979 Aug 24;172(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90534-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asanuma H., Zarzecki P., Jankowska E., Hongo T., Marcus S. Projection of individual pyramidal tract neurons to lumbar motor nuclei of the monkey. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Jan 2;34(1):73–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00238342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP P. O., BURKE W., DAVIS R. The identification of single units in central visual pathways. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:409–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman J., Bush B. M., Porter R. Deficient influence of peripheral stimuli on precentral neurones in monkeys with dorsal column lesions. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:27–48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman J., Kuypers H. G. Cerebral control of contralateral and ipsilateral arm, hand and finger movements in the split-brain rhesus monkey. Brain. 1973 Dec;96(4):653–674. doi: 10.1093/brain/96.4.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catman-Berrevoets C. E., Kuypers H. G., Lemon R. N. Cells of origin of the frontal projections to magnocellular and parvocellular red nucleus and superior colliculus in cynomolgus monkey. An HRP study. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Apr;12(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)91477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catsman-Berrevoets C. E., Kuypers H. G. Differential laminar distribution of corticothalamic neurons projecting to the VL and the center median. An HRP study in the cynomolgus monkey. Brain Res. 1978 Oct 13;154(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90706-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough J. F., Kernell D., Phillips C. G. The distribution of monosynaptic excitation from the pyramidal tract and from primary spindle afferents to motoneurones of the baboon's hand and forearm. J Physiol. 1968 Sep;198(1):145–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad B., Matsunami K., Meyer-Lohmann J., Wiesendanger M., Brooks V. B. Cortical load compensation during voluntary elbow movements. Brain Res. 1974 May 17;71(2-3):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90994-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVARTS E. V. RELATION OF DISCHARGE FREQUENCY TO CONDUCTION VELOCITY IN PYRAMIDAL TRACT NEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Mar;28:216–228. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.2.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evarts E. V. Relation of pyramidal tract activity to force exerted during voluntary movement. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jan;31(1):14–27. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Cheney P. D., German D. C. Corticomotoneuronal connections of precentral cells detected by postspike averages of EMG activity in behaving monkeys. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 24;114(3):505–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90973-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Finocchio D. V. Correlations between activity of motor cortex cells and arm muscles during operantly conditioned response patterns. Exp Brain Res. 1975 Sep 29;23(3):217–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00239736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McCloskey D. I. Changes in motor commands, as shown by changes in perceived heaviness, during partial curarization and peripheral anaesthesia in man. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):673–689. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghez C., Pisa M. Inhibition of afferent transmission in cuneate nucleus during voluntary movement in the cat. Brain Res. 1972 May 12;40(1):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaxma R., Kuypers H. G. Intrahemispheric cortical connexions and visual guidance of hand and finger movements in the rhusus monkey. Brain. 1975 Jun;98(2):239–260. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallett M., Marsden C. D. Ballistic flexion movements of the human thumb. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:33–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallett M., Shahani B. T., Young R. R. EMG analysis of stereotyped voluntary movements in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Dec;38(12):1154–1162. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.12.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepp-Reymond M. C., Wyss U. R., Anner R. Neuronal coding of static force in the primate motor cortex. J Physiol (Paris) 1978;74(3):287–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne M. K., Porter R. The discharges during movement of cells in the ventrolateral thalamus of the conscious monkey. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:349–372. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne M. K., Tracey D. J. The afferents and projections of the ventroposterolateral thalamus in the monkey. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Jun 1;36(1):129–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00238473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey D. R., Corrie W. S. Properties of pyramidal tract neuron system within a functionally defined subregion of primate motor cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Jan;41(1):216–243. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.1.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey D. R., Schmidt E. M., Thompson W. D. Predicting measures of motor performance from multiple cortical spike trains. Science. 1970 Nov 13;170(3959):758–762. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3959.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., Wise S. P. Size, laminar and columnar distribution of efferent cells in the sensory-motor cortex of monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1977 Oct 15;175(4):391–438. doi: 10.1002/cne.901750403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUYPERS H. G. Central cortical projections to motor and somato-sensory cell groups. An experimental study in the rhesus monkey. Brain. 1960 Mar;83:161–184. doi: 10.1093/brain/83.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kievit J., Kuypers H. G. Organization of the thalamo-cortical connexions to the frontal lobe in the rhesus monkey. Exp Brain Res. 1977 Sep 28;29(3-4):299–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00236173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamarre Y., Bioulac B., Jacks B. Activity of pre-entral neurones in conscious monkeys: effects of deafferentation and cerebellar ablation. J Physiol (Paris) 1978;74(3):253–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. G., Hopkins D. A. The development of motor control in the rhesus monkey: evidence concerning the role of corticomotoneuronal connections. Brain. 1976 Jun;99(2):235–254. doi: 10.1093/brain/99.2.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. G., Kuypers H. G. The functional organization of the motor system in the monkey. I. The effects of bilateral pyramidal lesions. Brain. 1968 Mar;91(1):1–14. doi: 10.1093/brain/91.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon R. N., Hanby J. A., Porter R. Relationship between the activity of precentral neurones during active and passive movements in conscious monkeys. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Oct 29;194(1116):341–373. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon R. N., Porter R. Afferent input to movement-related precentral neurones in conscious monkeys. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Oct 29;194(1116):313–339. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon R. N. Short-latency peripheral inputs to the motor cortex in conscious monkeys. Brain Res. 1979 Jan 26;161(1):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon R. N. Variety of functional organization within the monkey motor cortex. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:521–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon R. N., van der Burg J. Short-latency peripheral inputs to thalamic neurones projecting to the motor cortex in the monkey. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Aug 1;36(3):445–462. doi: 10.1007/BF00238515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. M., Porter R. Pyramidal tract discharge in relation to movement performance in monkeys with partial anaesthesia of the movind hand. Brain Res. 1974 May 17;71(2-3):345–351. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90977-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. The sensory mechanism of servo action in human muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):521–535. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. T., Kwan H. C., MacKay W. A., Wong Y. C. Spatial organization of precentral cortex in awake primates. III. Input-output coupling. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Sep;41(5):1132–1139. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.5.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAPIER J. R. The prehensile movements of the human hand. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1956 Nov;38-B(4):902–913. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.38B4.902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. THE PYRAMIDAL PROJECTION TO MOTONEURONES OF SOME MUSCLE GROUPS OF THE BABOON'S FORELIMB. Prog Brain Res. 1964;12:222–245. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60625-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passingham R., Perry H., Wilkinson F. Failure to develop a precision grip in monkeys with unilateral neocortical lesions made in infancy. Brain Res. 1978 Apr 28;145(2):410–414. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90878-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. Early facilitation at corticomotoneuronal synapses. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):733–745. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R., Lewis M. M., Linklater G. F. A headpiece for recording discharges of neurons in unrestrained monkeys. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;30(1):91–93. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(71)90210-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R., Lewis M. M. Relationship of neuronal discharges in the precentral gyrus of monkeys to the performance of arm movements. Brain Res. 1975 Nov 7;98(1):21–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R., Rack P. M. Timing of the responses in the motor cortex of monkeys to an unexpected disturbance of finger position. Brain Res. 1976 Feb 20;103(2):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90794-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosén I., Asanuma H. Peripheral afferent inputs to the forelimb area of the monkey motor cortex: input-output relations. Exp Brain Res. 1972;14(3):257–273. doi: 10.1007/BF00816162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda Y., Zarzecki P., Asanuma H. Spinal branching of pyramidal tract neurons in the monkey. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Jan 2;34(1):59–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00238341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloper J. J. An electron microscope study of the termination of afferent connections to the primate motor cortex. J Neurocytol. 1973 Dec;2(4):361–368. doi: 10.1007/BF01103794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloper J. J., Hiorns R. W., Powell T. P. A qualitative and quantitative electron microscopic study of the neurons in the primate motor and somatic sensory cortices. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Mar 23;285(1006):141–171. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1979.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloper J. J., Powell T. P. An experimental electron microscopic study of afferent connections to the primate motor and somatic sensory cortices. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Mar 23;285(1006):199–226. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1979.0005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. M., Hepp-Reymond M. C., Wyss U. R. Relation of activity in precentral cortical neurons to force and rate of force change during isometric contractions of finger muscles. Exp Brain Res. 1975 Sep 29;23(3):315–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00239743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strick P. L., Sterling P. Synaptic termination of afferents from the ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus in the cat motor cortex. A light and electron microscopy study. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Jan 1;153(1):77–106. doi: 10.1002/cne.901530107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thach W. T. Correlation of neural discharge with pattern and force of muscular activity, joint position, and direction of intended next movement in motor cortex and cerebellum. J Neurophysiol. 1978 May;41(3):654–676. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.3.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsumoto T., Nakamura S., Iwama K. Pyramidal tract control over cutaneous and kinesthetic sensory transmission in the cat thalamus. Exp Brain Res. 1975 Mar 27;22(3):281–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00234770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesendanger M. Input from muscle and cutaneous nerves of the hand and forearm to neurones of the precentral gyrus of baboons and monkeys. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(1):203–219. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. C., Kwan H. C., MacKay W. A., Murphy J. T. Spatial organization of precentral cortex in awake primates. I. Somatosensory inputs. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Sep;41(5):1107–1119. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.5.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler A. R., Burchiel K. J. Factors influencing accuracy of operant control of pyramidal tract neurons in monkey. Brain Res. 1978 Aug 25;152(2):418–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler A. R., Burchiel K. J. Operant control of pyramidal tract neurons: the role of spinal dorsal columns. Brain Res. 1978 Nov 24;157(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler A. R., Finch C. A. Operant conditioning of tonic firing patterns from precentral neurons in monkey neocortex. Brain Res. 1978 May 5;146(1):51–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


