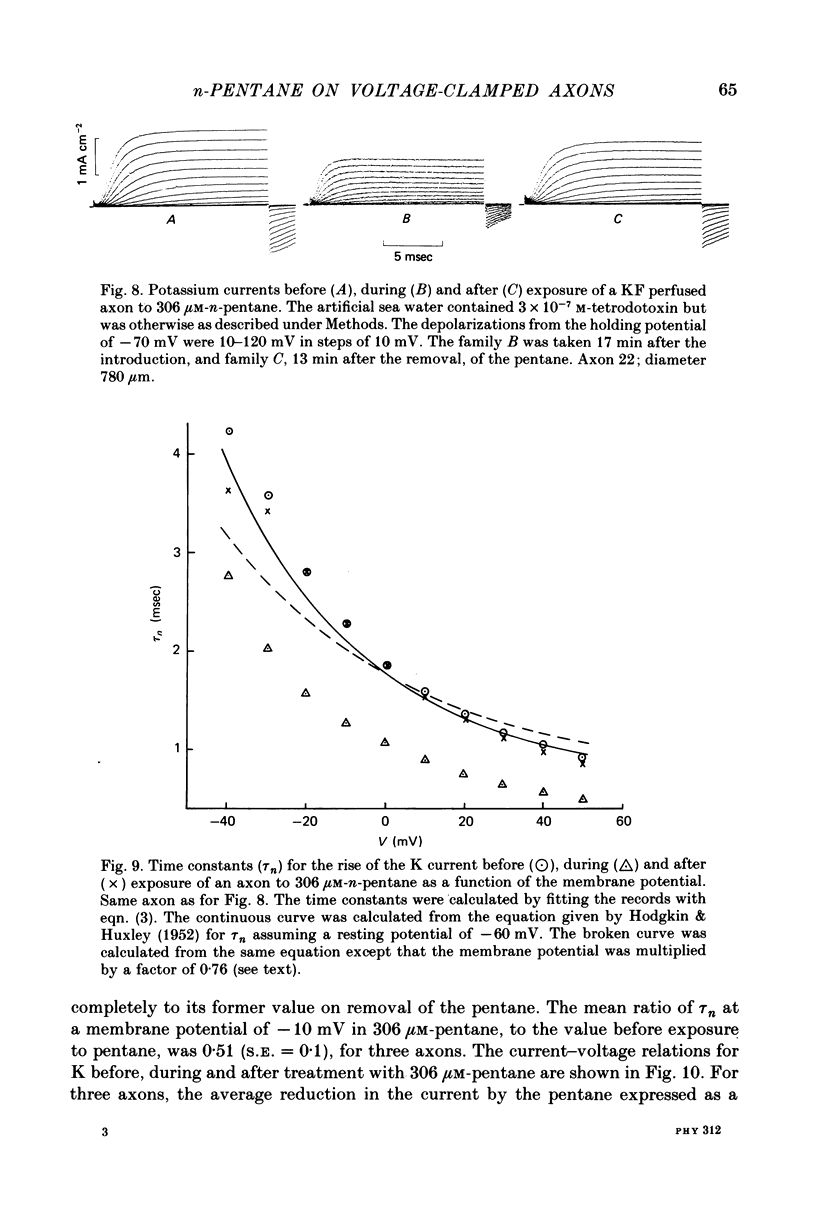
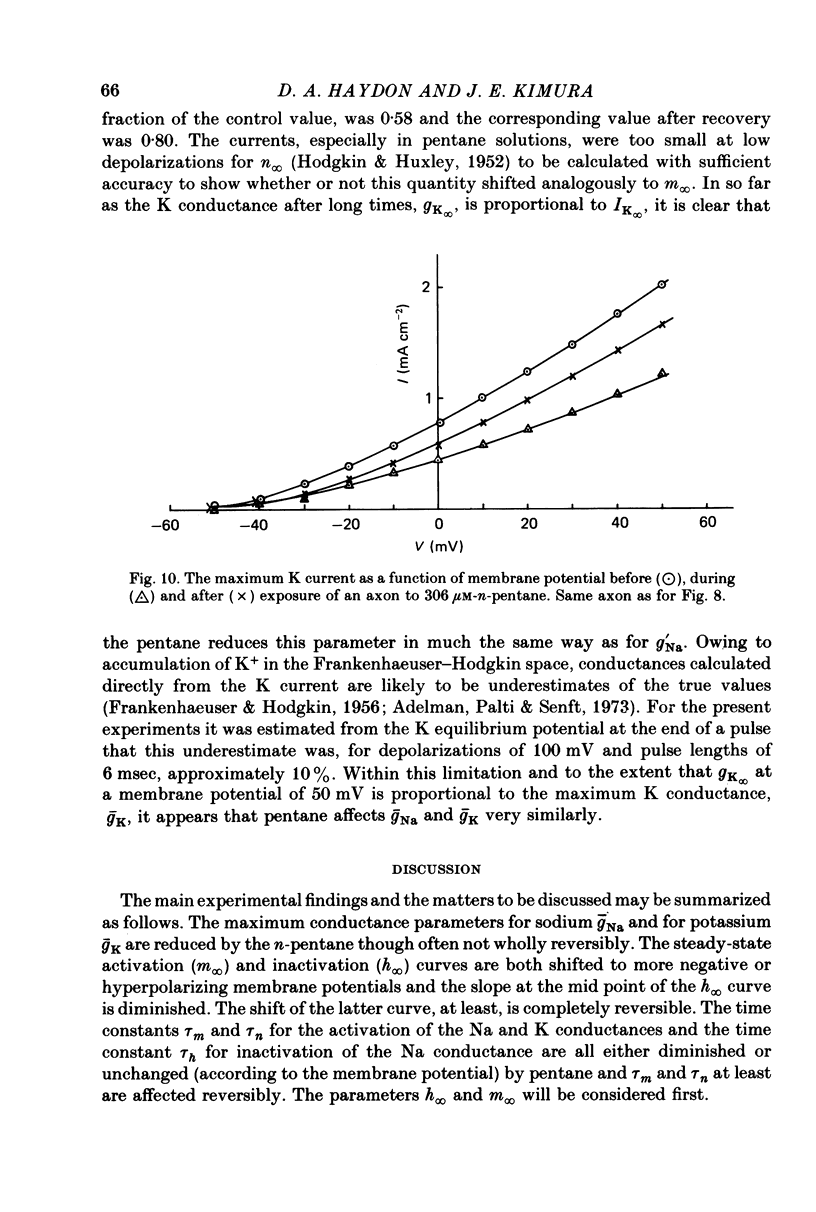
Abstract
1. Sodium and potassium currents have been recorded in intracellularly perfused squid giant axons before, during and after exposure to solutions of n-pentane in artificial sea water. 2. The currents were fitted with equations similar to those proposed by Hodgkin & Huxley (1952) and the changes in the parameters of these equations in the presence of pentane were calculated. 3. In the range of membrane potential -40 to 40 mV, the time constants for activation (tau m) and inactivation (tau h) of the Na current, and for activation (tau n) of the K current were all reduced by the pentane. 4. The curve of the steady-state inactivation parameter (h infinity) for the Na current against membrane potential was shifted by the pentane in a hyperpolarizing direction (at h infinity = 0.5 this shift was approx. -15 mV in 275 microM-pentane) and the slope at all potentials was reduced. 5. The curve of the steady-state activation parameter (m infinity) for the Na current against membrane potential was also shifted by the pentane in a hyperpolarizing direction (in 153 microM-pentane, 10 mV at m infinity = 0.5). 6. The maximum Na and K conductances gNa and gK were lowered by the pentane, though not usually completely reversibly. 7. The changes in position and slope of the steady-state inactivation curve have been tentatively accounted for in terms of an increase in membrane thickness.
Full text
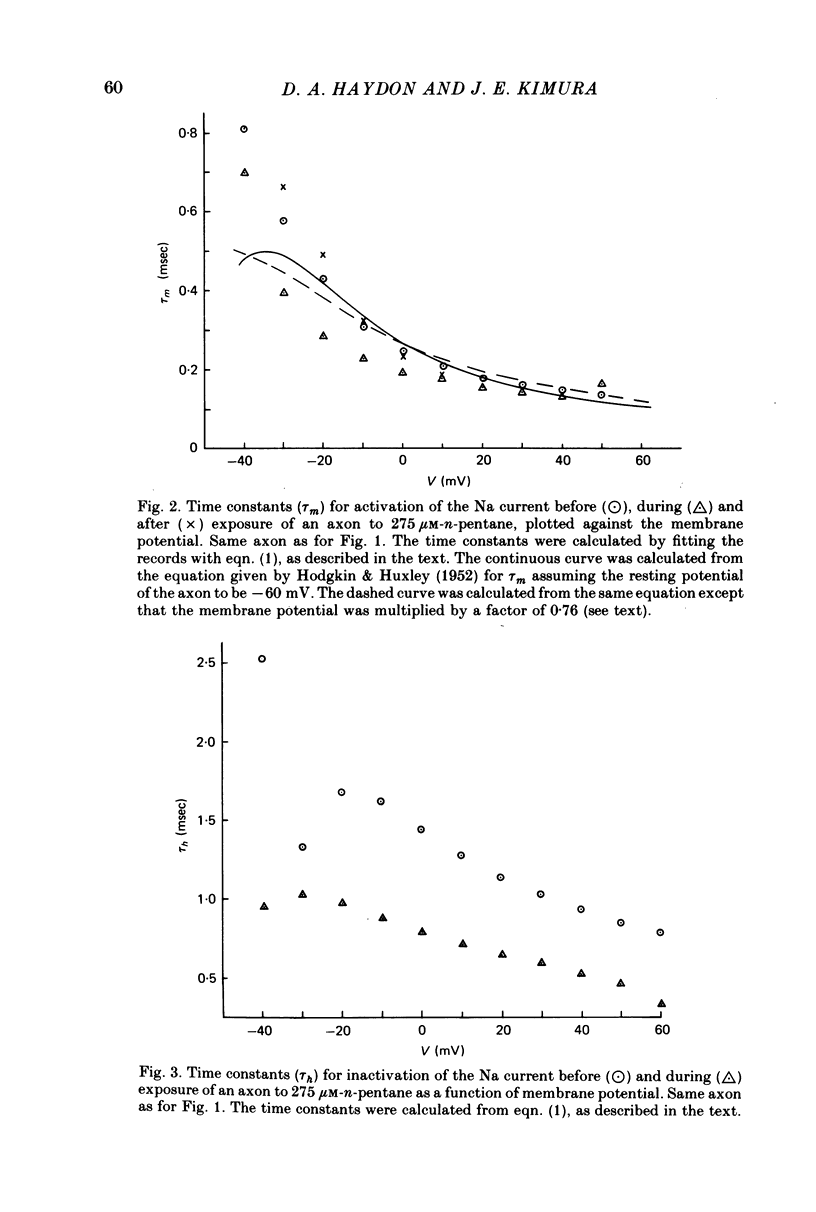
PDF


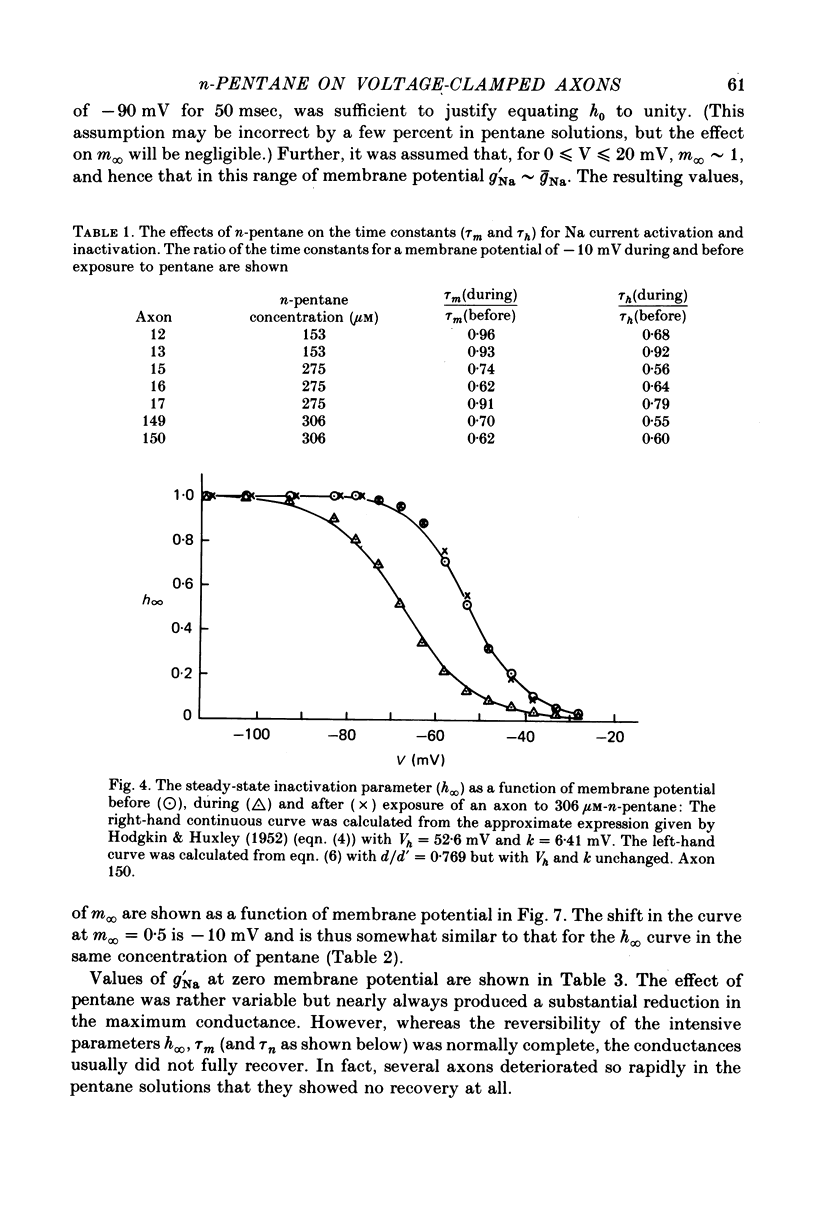




Selected References
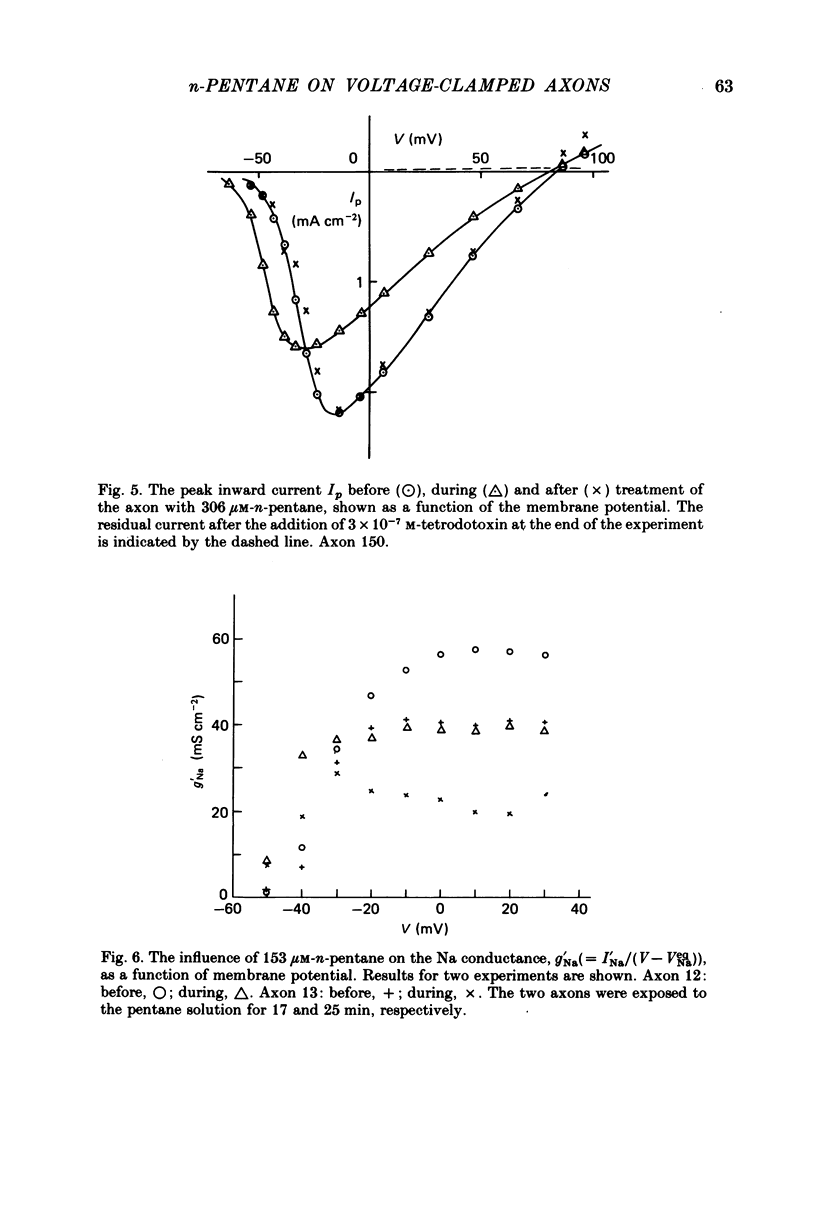
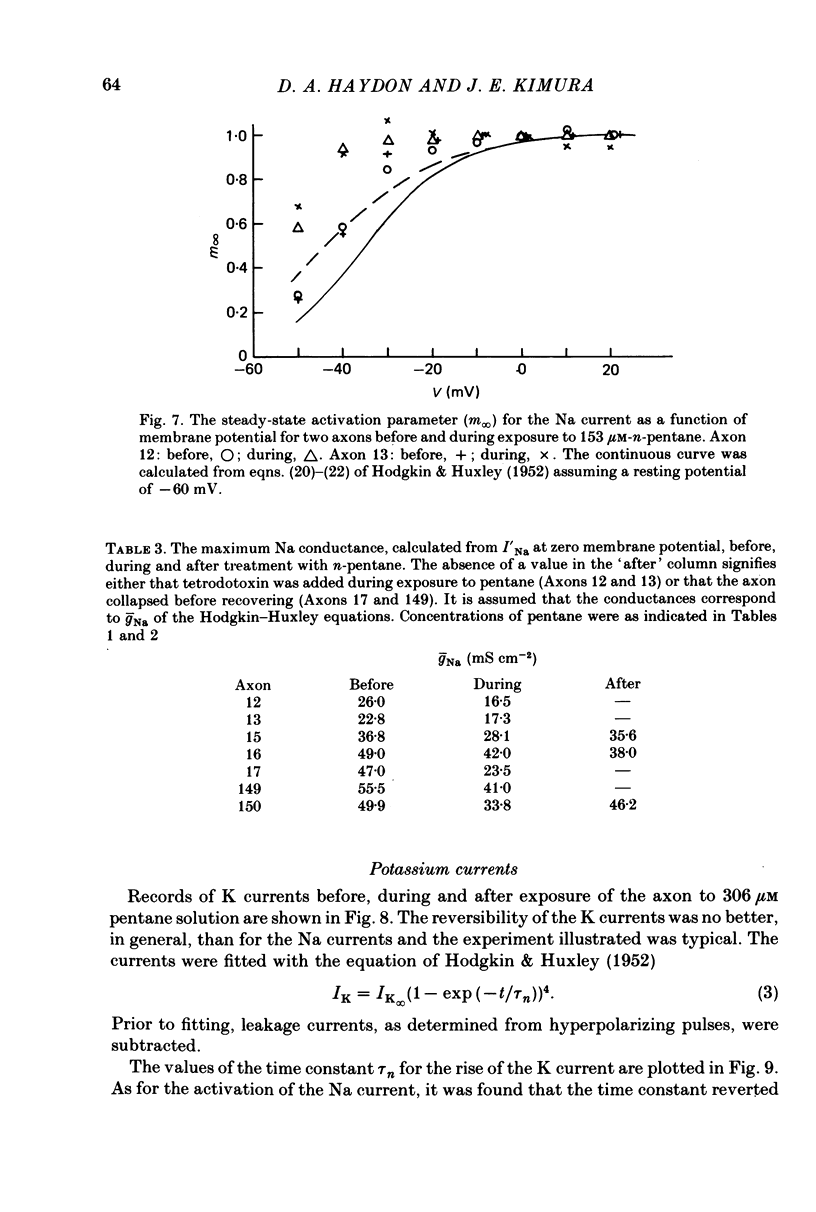
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman W. J., Jr, Palti Y., Senft J. P. Potassium ion accumulation in a periaxonal space and its effect on the measurement of membrane potassium ion conductance. J Membr Biol. 1973 Nov 8;13(4):387–410. doi: 10.1007/BF01868237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzi A. The application of fluorescent probes in membrane studies. Q Rev Biophys. 1975 May;8(2):237–316. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. B., Hille B., Keynes R. D. Light scattering and birefringence changes during activity in the electric organ of electrophorus electricus. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):489–509. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The after-effects of impulses in the giant nerve fibres of Loligo. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):341–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A. Functions of the lipid in bilayer ion permeability. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:2–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Hendry B. M., Levinson S. R., Requena J. Anaesthesia by the n-alkanes. A comparative study of nerve impulse blockage and the properties of black lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 3;470(1):17–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Requena J., Urban B. W. Some effects of aliphatic hydrocarbons on the electrical capacity and ionic currents of the squid giant axon membrane. J Physiol. 1980 Dec;309:229–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry B. M., Urban B. W., Haydon D. A. The blockage of the electrical conductance in a pore-containing membrane by the n-alkanes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 19;513(1):106–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. E., Meves H. The effect of temperature on the asymmetrical charge movement in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:479–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


