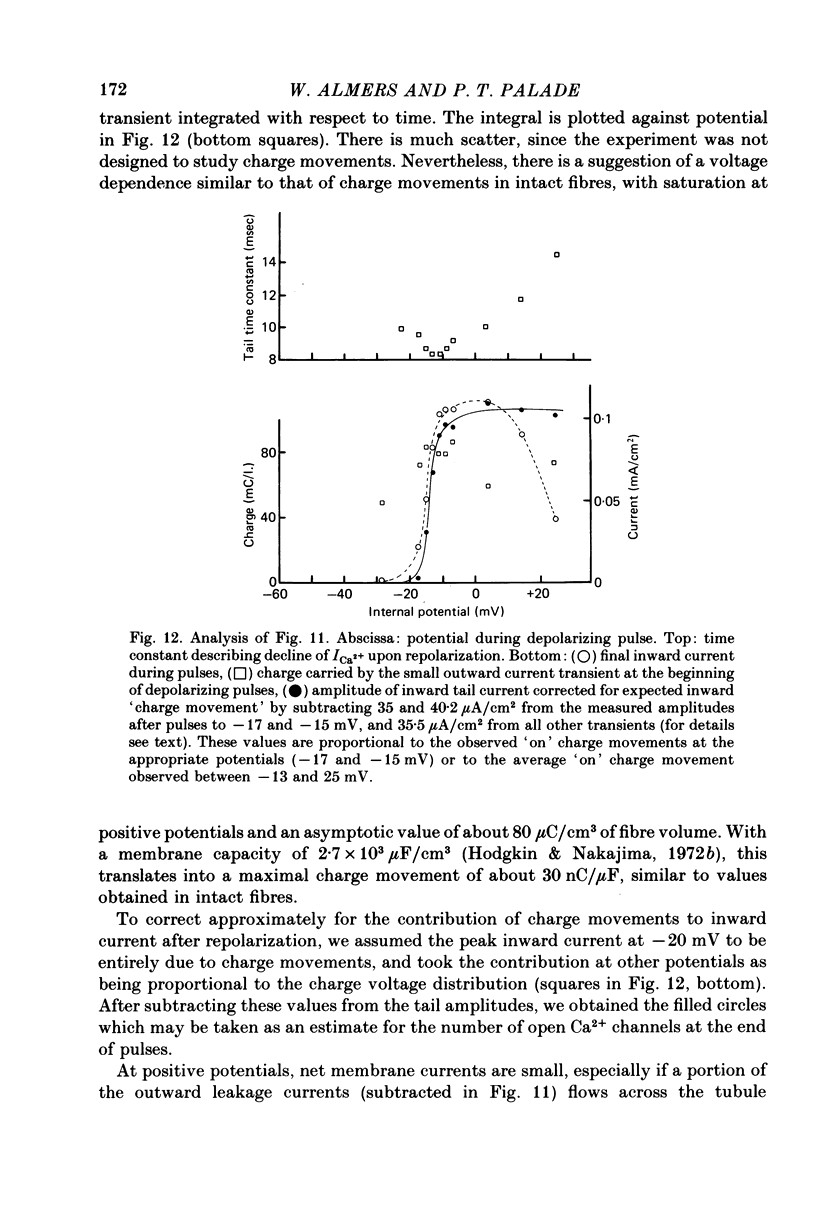
Abstract
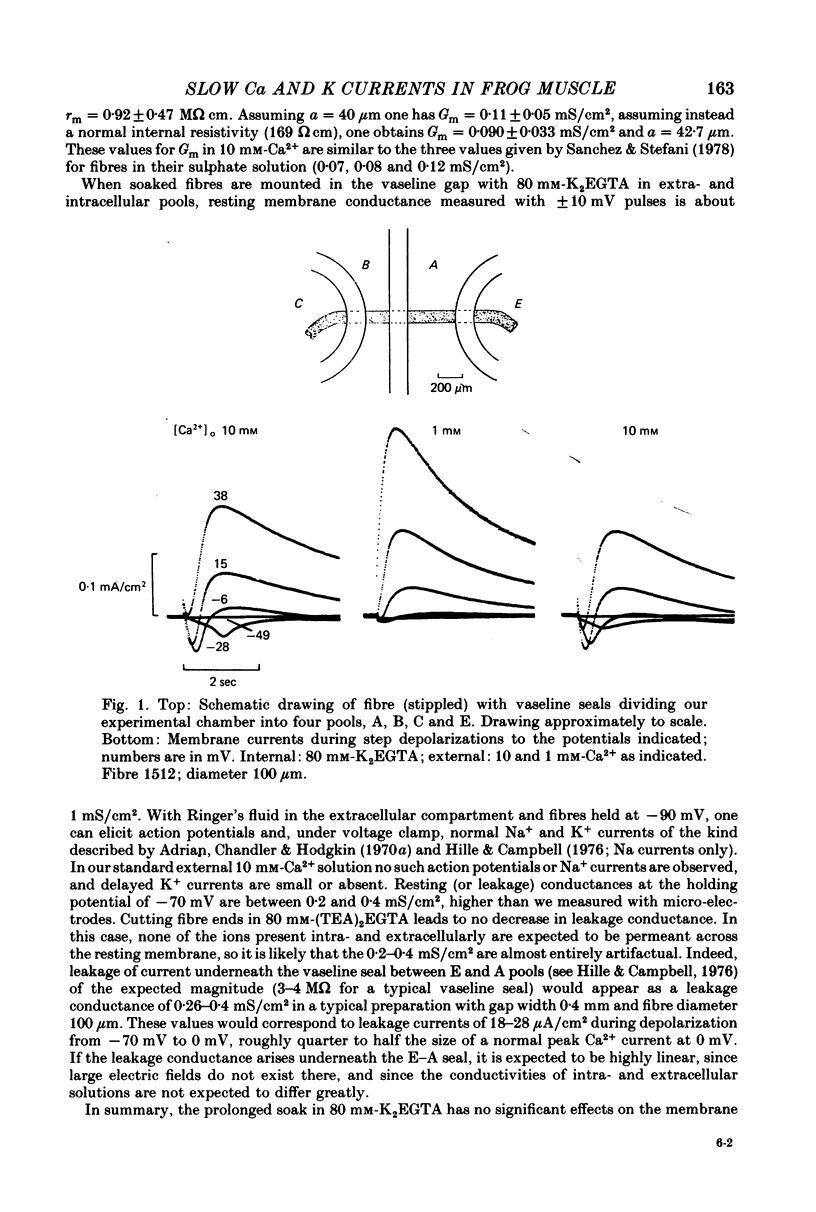
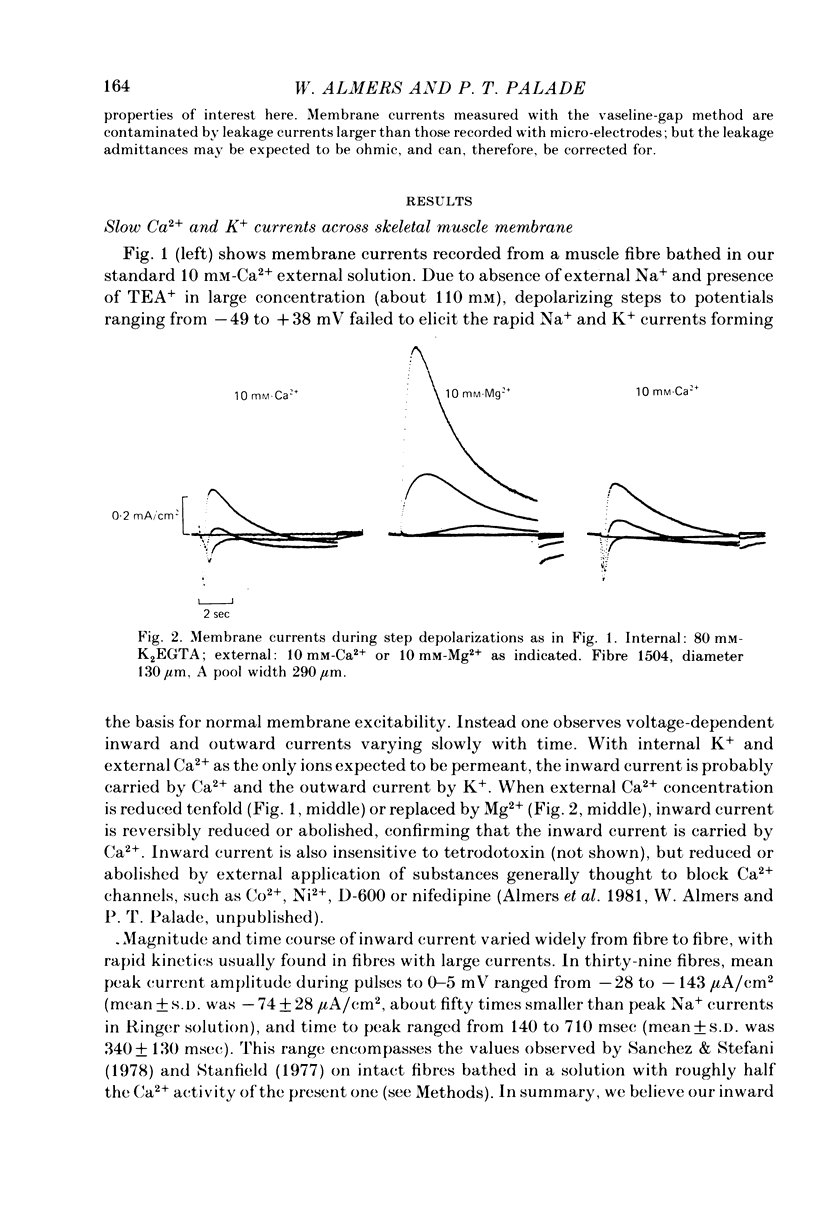
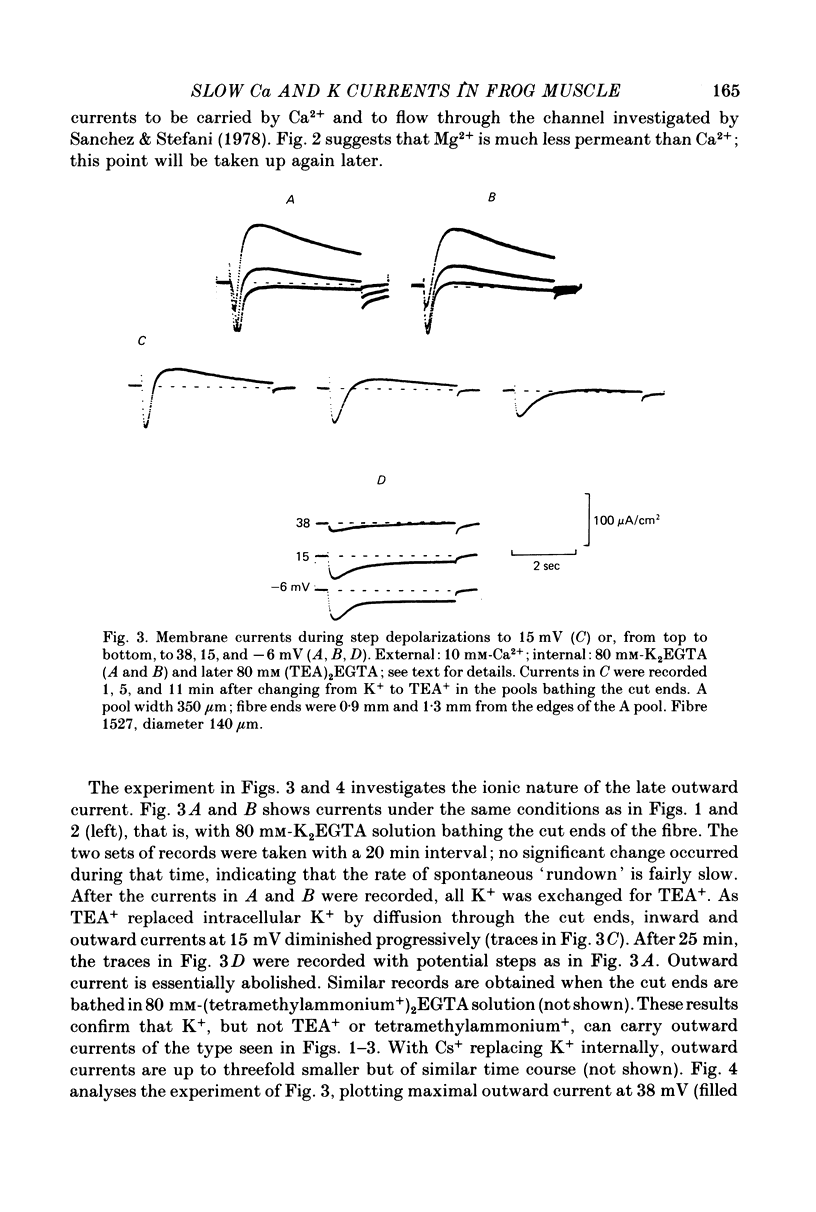
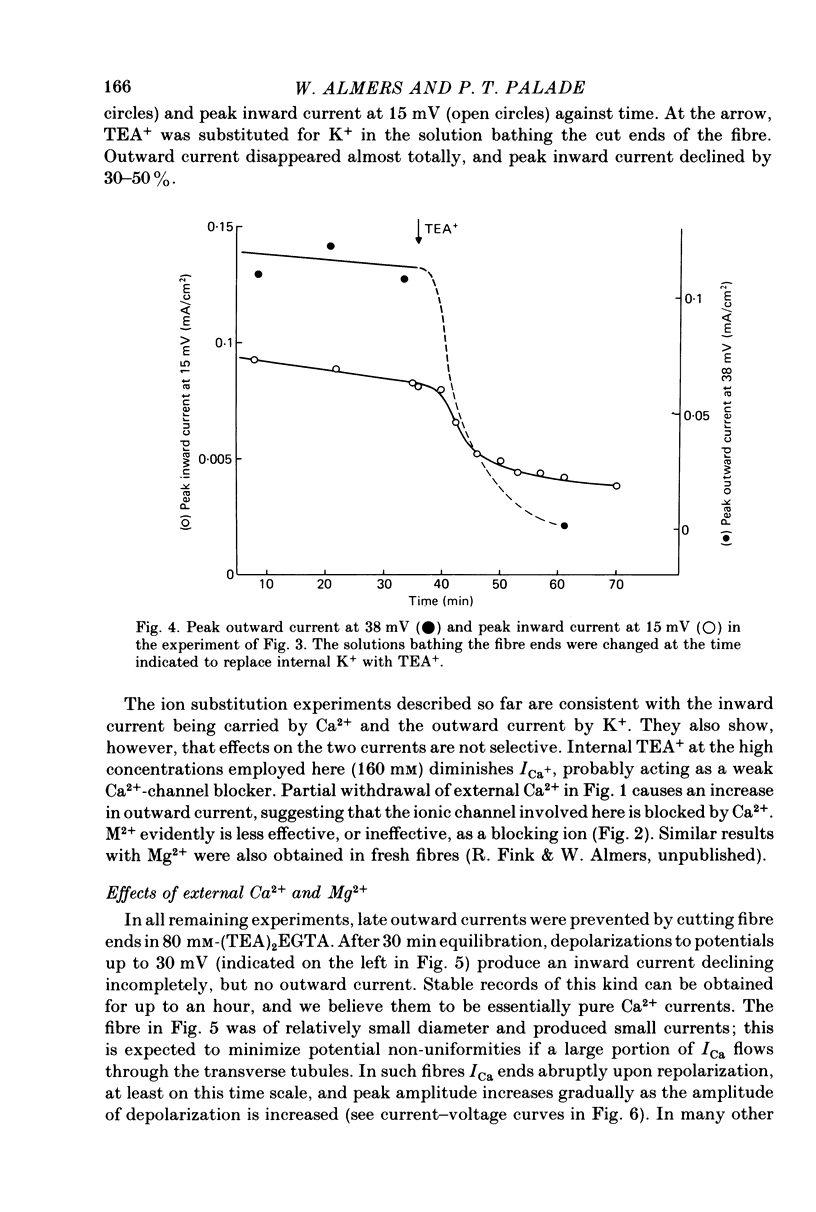
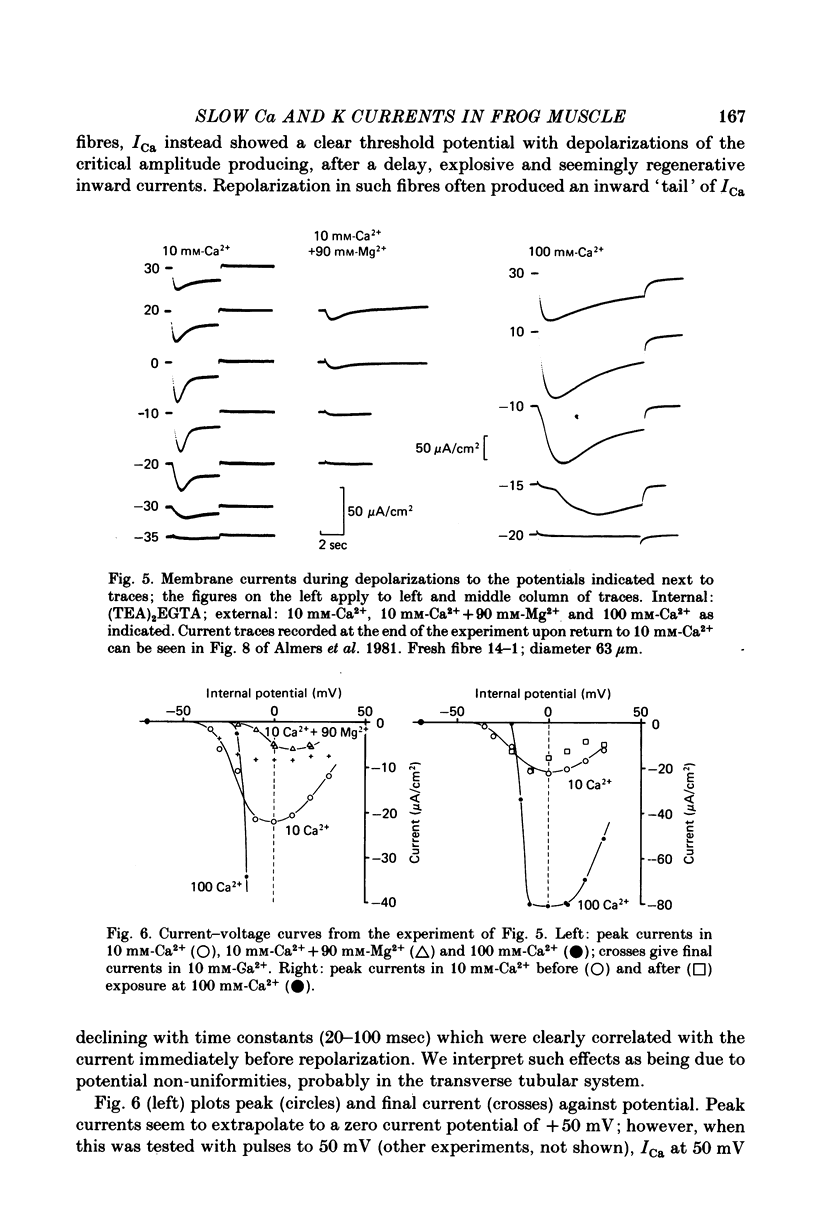
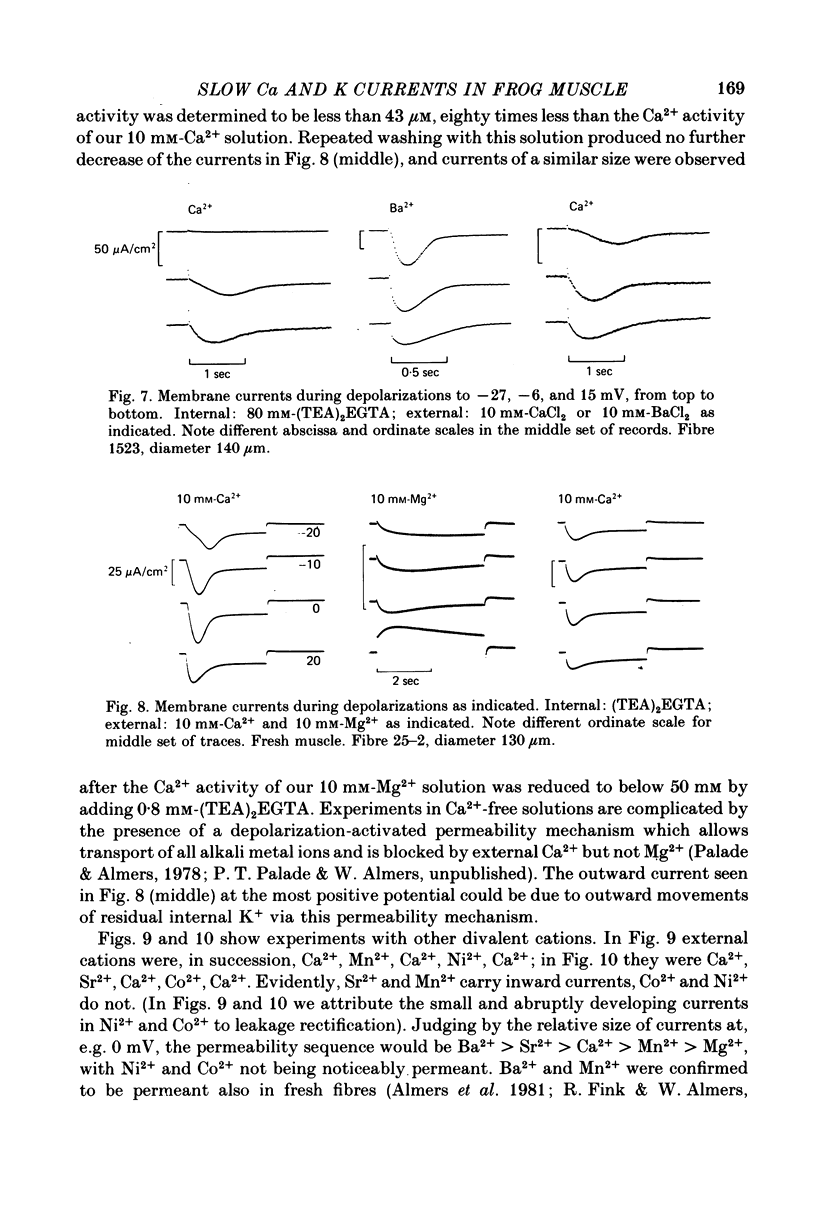
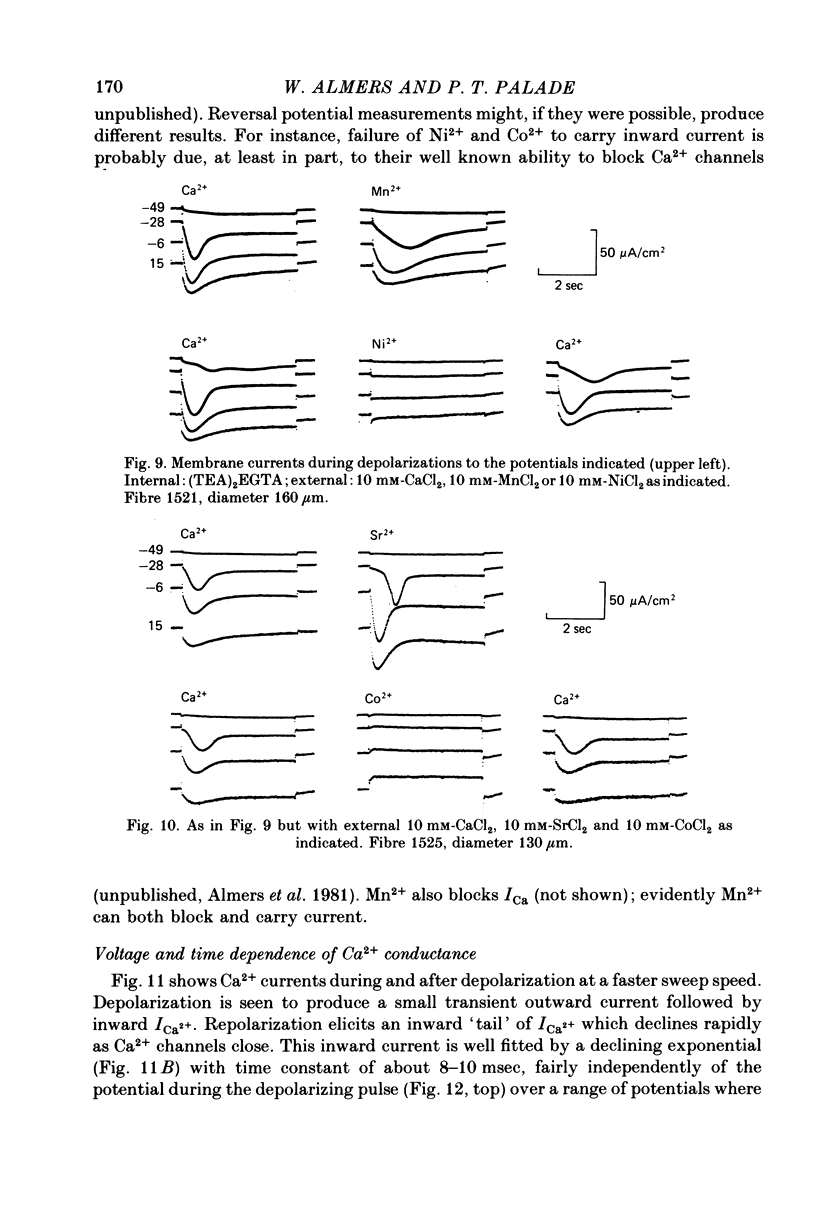
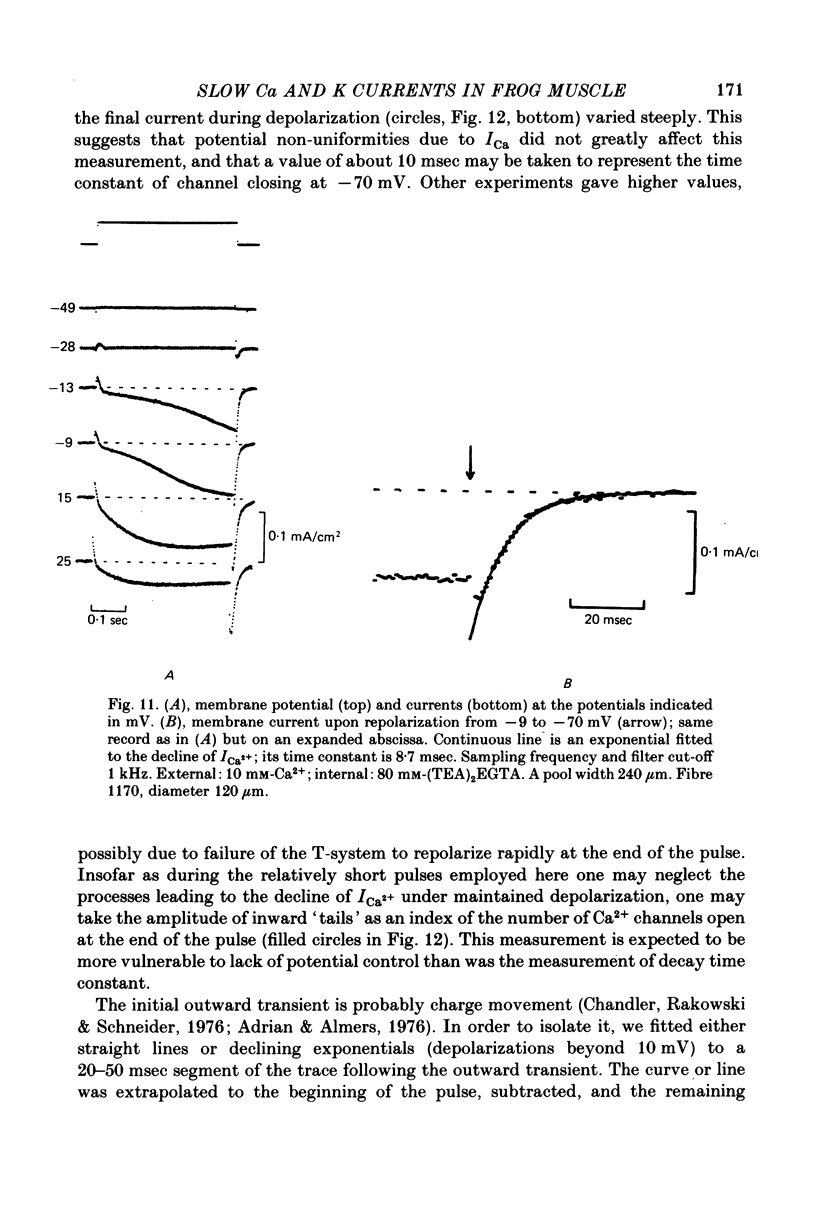
1. A vaseline-gap voltage-clamp technique was used to record slow Ca2+ and K+ currents from frog skeletal muscle fibres loaded with the Ca2+ chelator EGTA. 2. K+ currents were increased when Mg2+ replaced external Ca2+, and they were abolished when internal K+ was replaced by tetraethylammonium (TEA+). Ca2+ currents could be studied in isolation in fibres loaded with (TEA)2EGTA. 3. Under maintained depolarization, Ca2+ currents slowly increase (half-time of 35 msec or more at 25 mV) and then decline to a steady value. Decline under repolarization is rapid (half-time of 6-7 msec) and complete. During an action potential, the Ca2+ influx through this system is probably less than the influx observed with tracers. 4. Ba2+, Sr2+, Ca2+, Mn2+ and Mg2+ can carry current across the membrane; Ni2+ and Co2+ cannot. Ca2+ currents are weakly blocked by external Mg2+.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W. Sodium and calcium gating currents in an Aplysia neurone. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:467–481. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Charge movement in the membrane of striated muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):339–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Slow changes in potassium permeability in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):645–668. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Peachey L. D. Reconstruction of the action potential of frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):103–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Fishman H. M., Lee K. S., Moore L. E., Brown A. M. The units of calcium conduction in Helix neurones. Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):379–382. doi: 10.1038/274379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Fink R., Palade P. T. Calcium depletion in frog muscle tubules: the decline of calcium current under maintained depolarization. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:177–207. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Currents associated with the ionic gating structures in nerve membrane. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:265–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIANCHI C. P., SHANES A. M. Calcium influx in skeletal muscle at rest, during activity, and during potassium contracture. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Mar 20;42(4):803–815. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaty G. N., Stefani E. Calcium dependent electrical activity in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Aug 27;194(1114):141–150. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. A non-linear voltage dependent charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):245–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. A. Ca fluxes in single twitch muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Nov;50(2):255–267. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink R., Lüttgau H. C. An evaluation of the membrane constants and the potassium conductance in metabolically exhausted muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(2):215–238. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Fukuda J., Eaton D. C. Membrane currents carried by Ca, Sr, and Ba in barnacle muscle fiber during voltage clamp. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):564–578. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Campbell D. T. An improved vaseline gap voltage clamp for skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):265–293. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. Analysis of the membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):121–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. The effect of diameter on the electrical constants of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):105–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostiuk P. G., Kryshtal' O. A., Pidoplichko V. I. Otsenka provodimosti odinochnogo kal'tsievogo kanala po fluktuatsiiam toka s ispol'zovaniem éffekta EGTA. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1978 Jan;238(2):478–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Shakhovalov Y. A. Separation of sodium and calcium currents in the somatic membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):545–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryshtal' O. A., Pidoplichko V. I. Toki smeshcheniia, sviazannye s aktivatsiei vorotnogo mekhanizma kal'tsievykh kanalov v membrane nervnoi kletki. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1976;231(5):1248–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. F., Trautwein W. Membrane currents in cat myocardium: separation of inward and outward components. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:193–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi R. Manganese-dependent propagated action potentials and their depression by electrical stimulation in guinea-pig myocardium perfused by sodium-free media. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(2):139–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:1–43. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. Inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:197–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. A calcium dependent inward current in frog skeletal muscle fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Apr 25;368(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00585206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The effect of the tetraethylammonium ion on the delayed currents of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):209–229. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


