Abstract
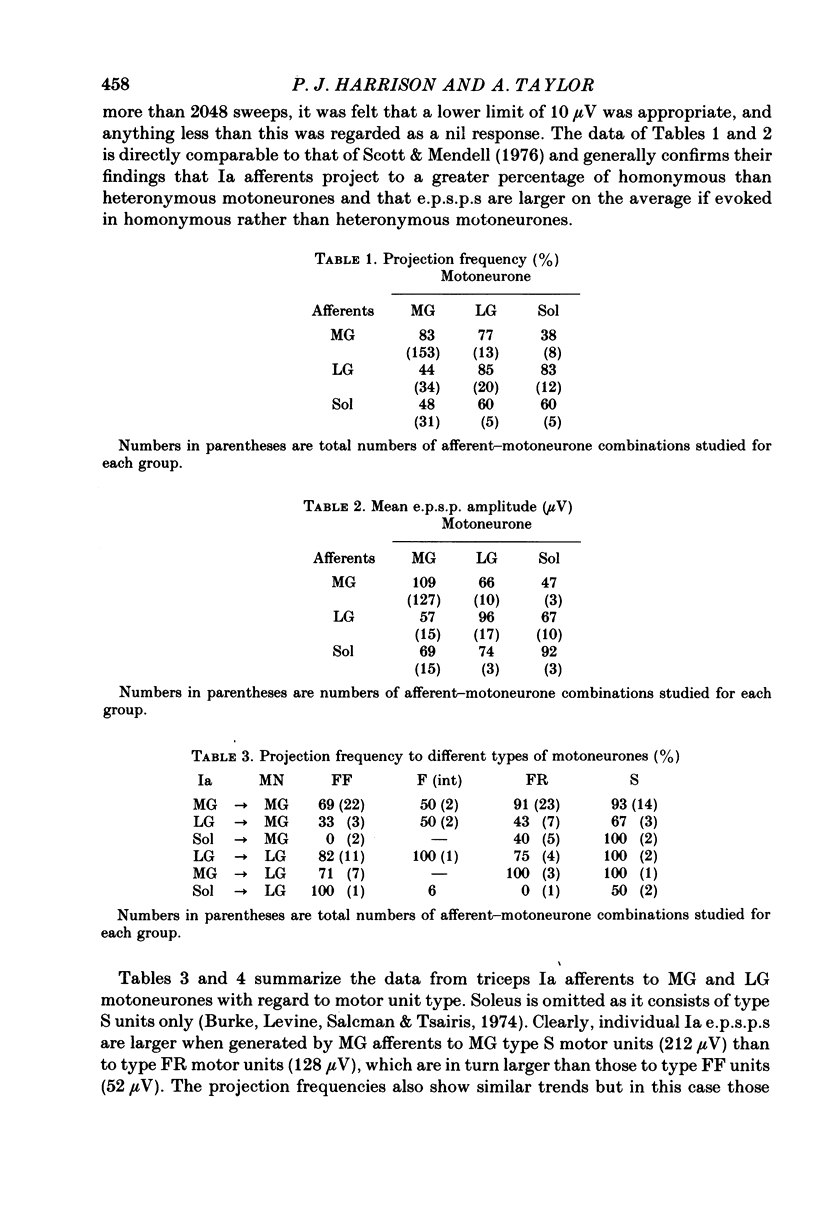
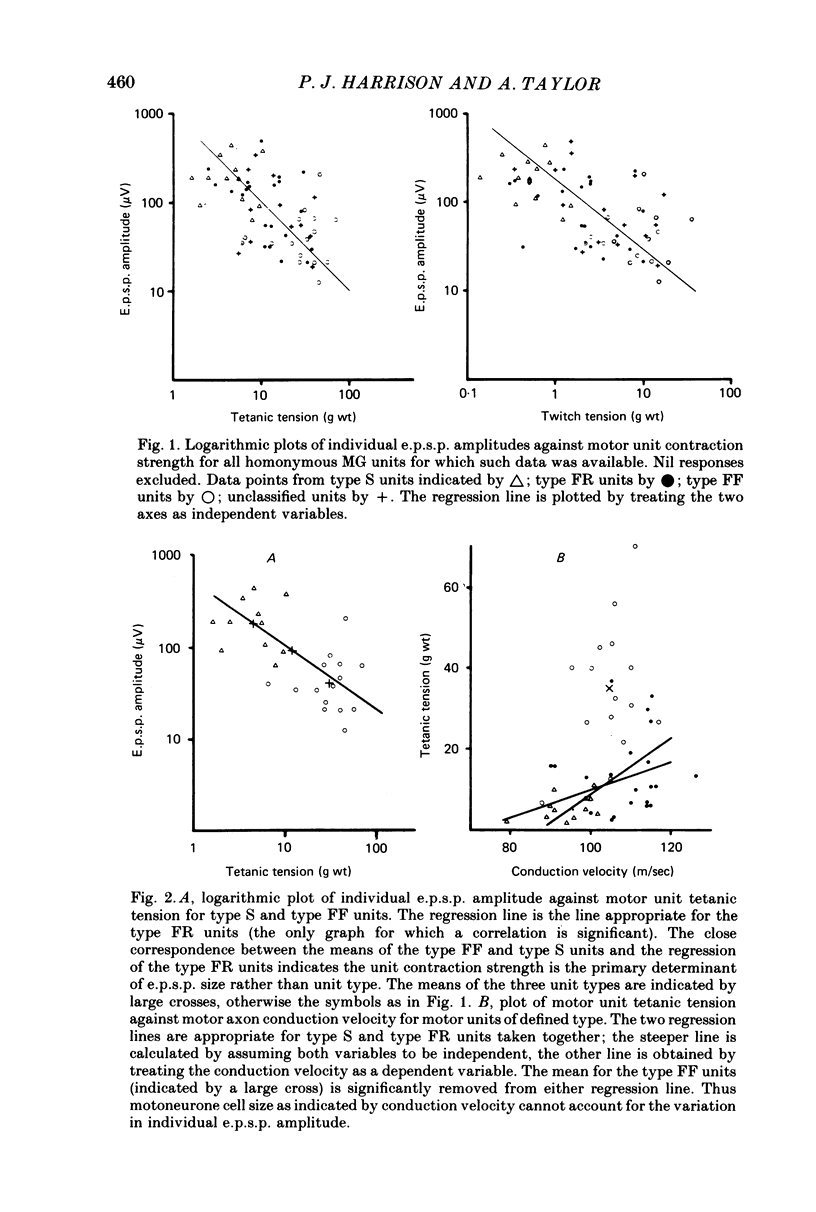
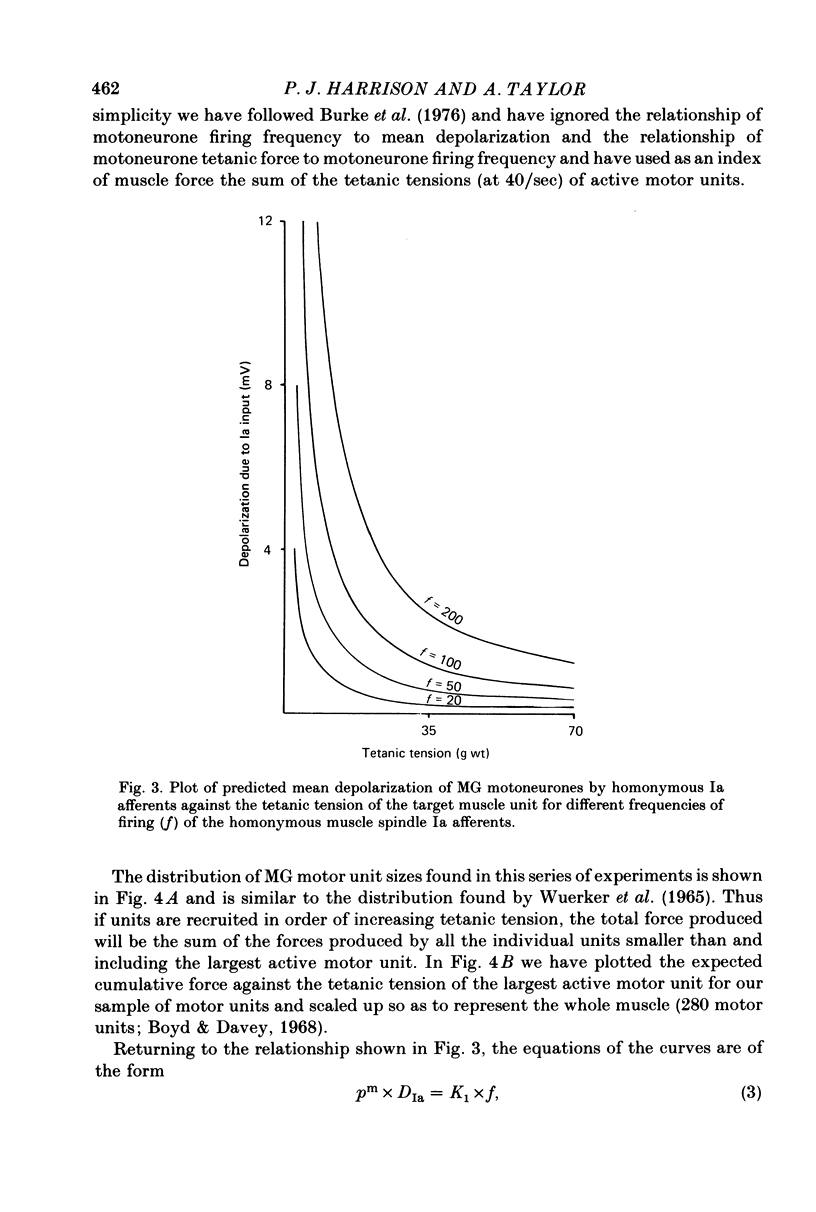
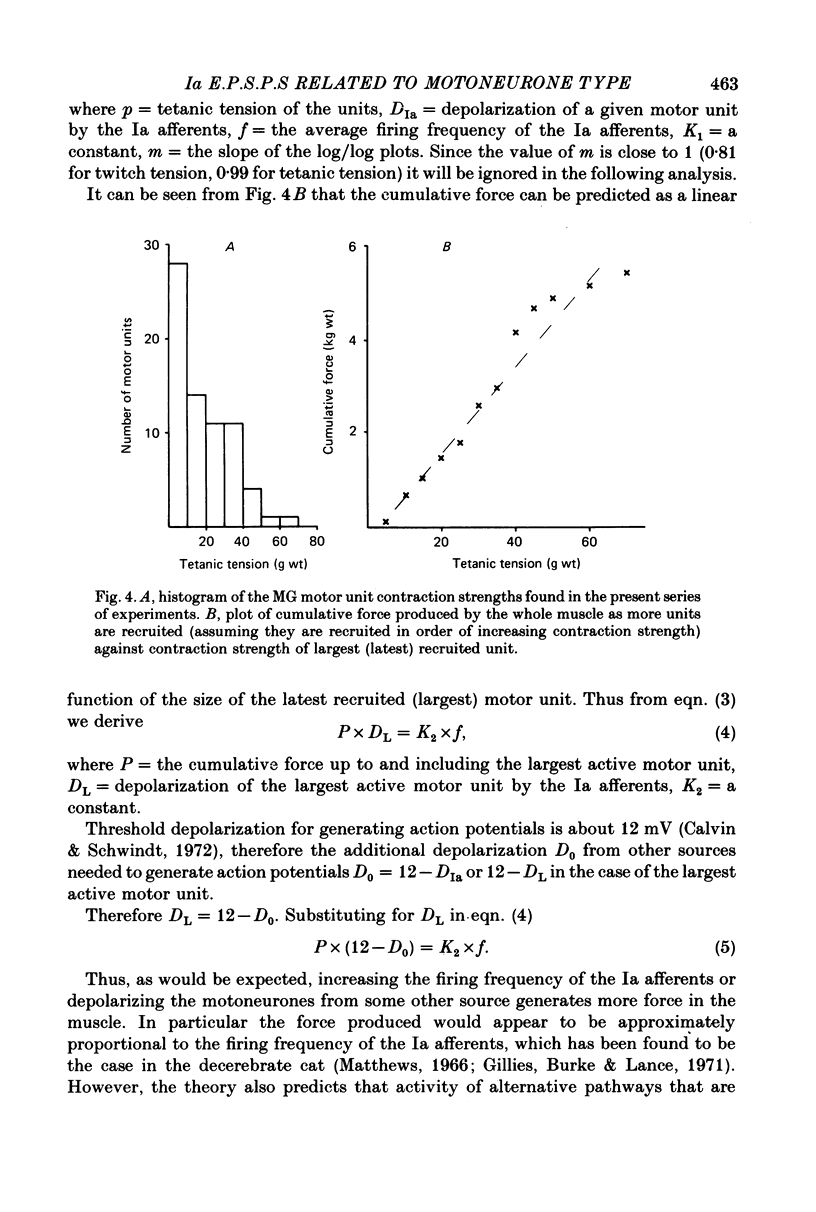
1. The monosynaptic projection of single Ia muscle spindle afferents to motoneurones of identified type has been examined by spike triggered averaging in barbiturate anaesthetized cats. 2. The amplitude of averaged individual monosynaptic e.p.s.p.s in medical gastrocnemius motoneurones from homonymous Ia afferents was clearly related to the motor unit mechanical properties. It was largest in type S units, intermediate in type FR and smallest in type FF. 3. The projection frequency of homonymous Ia afferents to medial gastrocnemius motoneurones followed the same order. 4. Similar trends were evident in both respects for the heteronymous projections of triceps surae. 5. The mechanical property of units which related most directly to e.p.s.p. size was muscle unit contraction strength, a single continuous relation existing throughout all three unit types. 6. On the basis of motor axon conduction velocity measurements, it appeared that motoneurone size could provide a simple explanation for e.p.s.p. size in type S and type FR units, but not in type FF. The latter had unduly small e.p.s.p.s relative to their axon conduction velocity, indicating a qualitatively different presynaptic organization for FF motoneurones from the others. 7. The data make it possible to predict that Ia afferent excitation alone would cause recruitment of units in order of increasing contraction strength and that this order would also obtain if a substantial part of the excitation came from other sources with uniform effect on all unit types. 8. It is shown that a consequence of the observed organization is that the gain of the Ia mediated stretch reflex would be approximately proportional to the developed force.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appenteng K., O'Donovan M. J., Somjen G., Stephens J. A., Taylor A. The projection of jaw elevator muscle spindle afferents to fifth nerve motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:409–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BASMAJIAN J. V. Control and training of individual motor units. Science. 1963 Aug 2;141(3579):440–441. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3579.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Crill W. E. Specific membrane properties of cat motoneurones. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):301–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Firing patterns of gastrocnemius motor units in the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1968 Jun;196(3):631–654. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Group Ia synaptic input to fast and slow twitch motor units of cat triceps surae. J Physiol. 1968 Jun;196(3):605–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Jankowska E., ten Bruggencate G. A comparison of peripheral and rubrospinal synaptic input to slow and fast twitch motor units of triceps surae. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):709–732. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Salcman M., Tsairis P. Motor units in cat soleus muscle: physiological, histochemical and morphological characteristics. J Physiol. 1974 May;238(3):503–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Tsairis P., Zajac F. E., 3rd Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):723–748. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Motor unit properties and selective involvement in movement. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1975;3:31–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Motor unit types of cat triceps surae muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):141–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Rymer W. Z. Relative strength of synaptic input from short-latency pathways to motor units of defined type in cat medial gastrocnemius. J Neurophysiol. 1976 May;39(3):447–458. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. The role of synaptic organization in the control of motor unit activity during movement. Prog Brain Res. 1979;50:61–67. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60807-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin W. H., Schwindt P. C. Steps in production of motoneuron spikes during rhythmic firing. J Neurophysiol. 1972 May;35(3):297–310. doi: 10.1152/jn.1972.35.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullheim S., Kellerth J. O. A morphological study of the axons and recurrent axon collaterals of cat alpha-motoneurones supplying different functional types of muscle unit. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:301–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullheim S., Kellerth J. O. A morphological study of the axons and recurrent axon collaterals of cat sciatic alpha-motoneurons after intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Apr 1;178(3):537–557. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEVANANDAN M. S., ECCLES R. M., WESTERMAN R. A. SINGLE MOTOR UNITS OF MAMMALIAN MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1965 May;178:359–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. N., Sears T. A. The proprioceptive reflex control of the intercostal muscles during their voluntary activation. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):711–738. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett R. A., O'Donovan M. J., Stephens J. A., Taylor A. Motor unit organization of human medial gastrocnemius. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:33–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett R., Stephens J. A. Changes in the recruitment threshold of motor units in human first dorsal interosseous muscle produced by skin stimulation [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:13P–14P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett R., Stephens J. A. The reflex responses of single motor units in human first dorsal interosseous muscle following cutaneous afferent stimulation. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:351–364. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies J. D., Burke D. J., Lance J. W. Tonic vibration reflex in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Mar;34(2):252–262. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.2.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb G. L., Agarwal G. C. Effects of initial conditions on the Hoffman reflex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Jun;34(3):226–230. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.3.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimby L., Hannerz J. Differences in recruitment order of motor units in phasic and tonic flexion reflex in "spinal man". J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Oct;33(5):562–570. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.5.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN E., SOMJEN G., CARPENTER D. O. FUNCTIONAL SIGNIFICANCE OF CELL SIZE IN SPINAL MOTONEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:560–580. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henneman E., Clamann H. P., Gillies J. D., Skinner R. D. Rank order of motoneurons within a pool: law of combination. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Nov;37(6):1338–1349. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.6.1338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce G. C., Rack P. M., Ross H. F. The forces generated at the human elbow joint in response to imposed sinusoidal movements of the forearm. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(2):351–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D. Input resistance, electrical excitability, and size of ventral horn cells in cat spinal cord. Science. 1966 Jun 17;152(3729):1637–1640. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3729.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. Monosynaptic excitation of motoneurones from muscle spindle secondary endings of intercostal and triceps surae muscles in the cat. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(2):64P–66P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. Monosynaptic excitation of motoneurones from secondary endings of muscle spindles. Nature. 1974 Nov 15;252(5480):243–244. doi: 10.1038/252243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. Spike triggered averaging for the measurement of single unit conduction velocities. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(2):58P–59P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Comments on reflex actions evoked by electrical stimulation of group II muscle afferents. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 25;122(3):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90466-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher H. R., Ruenzel P., Fetz E., Henneman E. Postsynatpic population potentials recorded from ventral roots perfused with isotonic sucrose: connections of groups Ia and II spindle afferent fibers with large populations of motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Jul;42(4):1146–1164. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.4.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCPHEDRAN A. M., WUERKER R. B., HENNEMAN E. PROPERTIES OF MOTOR UNITS IN A HETEROGENEOUS PALE MUSCLE (M. GASTROCNEMIUS) OF THE CAT. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Jan;28:85–99. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Servo action in human voluntary movement. Nature. 1972 Jul 21;238(5360):140–143. doi: 10.1038/238140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Servo action in the human thumb. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(1):1–44. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. B. The reflex excitation of the soleus muscle of the decerebrate cat caused by vibbration applied to its tendon. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):450–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Henneman E. Terminals of single Ia fibers: location, density, and distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):171–187. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill E. G., Ainsworth A. Glass-coated platinum-plated tungsten microelectrodes. Med Biol Eng. 1972 Sep;10(5):662–672. doi: 10.1007/BF02476084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-Brown H. S., Stein R. B., Yemm R. The orderly recruitment of human motor units during voluntary isometric contractions. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):359–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S. G., Mendell L. M. Projection of single knee flexor Ia fibers to homonymous and heteronymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1978 May;41(3):778–787. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.3.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proske U., Waite P. M. Properties of types of motor units in the medial gastrochemius muscle of the cat. Brain Res. 1974 Feb 15;67(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. G., Mendell L. M. Individual EPSPs produced by single triceps surae Ia afferent fibers in homonymous and heteronymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Jul;39(4):679–692. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.4.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer E. K., Watt D. G., Taylor A., Reinking R. M., Stuart D. G. Analysis of muscle receptor connections by spike-triggered averaging. 2. Spindle group II afferents. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1393–1402. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. B. Peripheral control of movement. Physiol Rev. 1974 Jan;54(1):215–243. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.1.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt D. G., Stauffer E. K., Taylor A., Reinking R. M., Stuart D. G. Analysis of muscle receptor connections by spike-triggered averaging. 1. Spindle primary and tendon organ afferents. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1375–1392. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yemm R. The orderly recruitment of motor units of the masseter and temporal muscles during voluntary isometric contraction in man. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):163–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Theoretical implications of the size principle of motoneurone recruitment. J Theor Biol. 1973 Mar;38(3):587–596. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(73)90259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


