Abstract
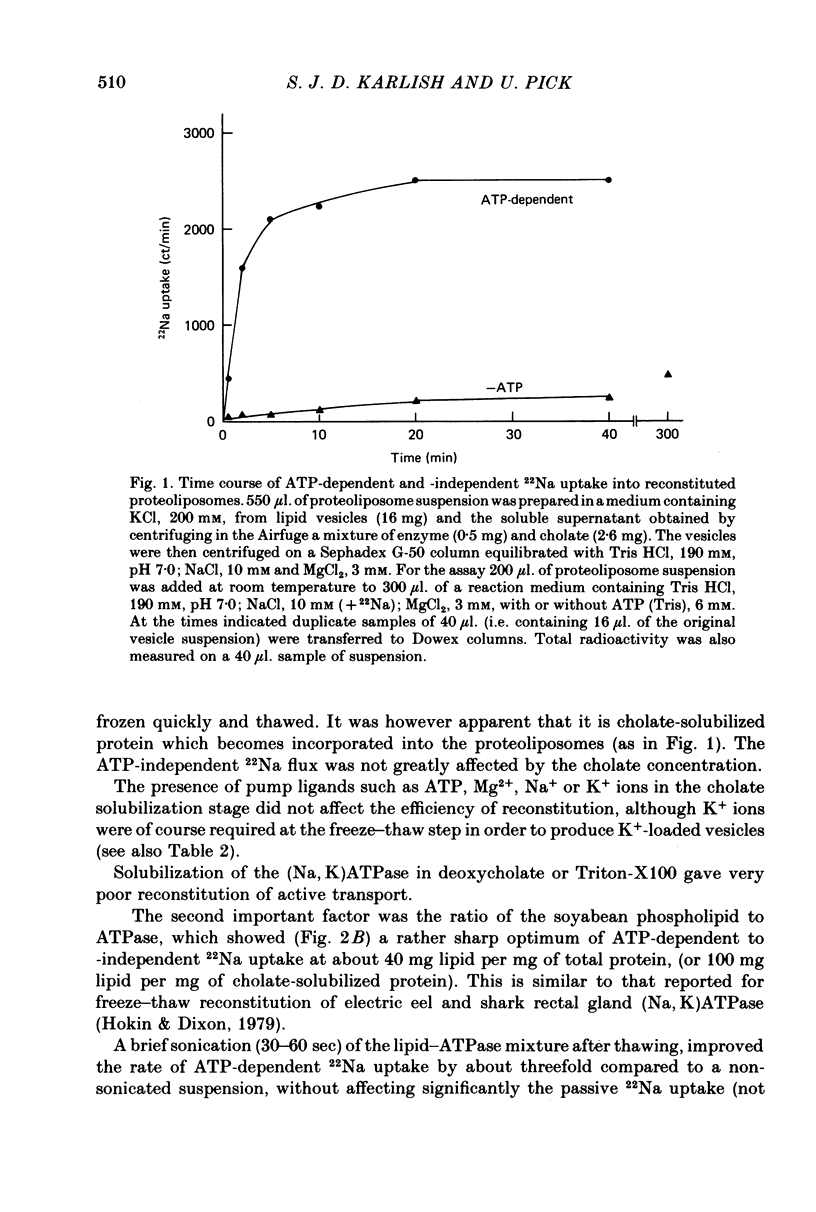
1. (Na,K)ATPase from kidney membranes has been reconstituted into proteoliposomes following solubilization in cholate, by the freeze—thaw sonication procedure described by Kasahara & Hinkle (1977). The method is rapid and convenient.
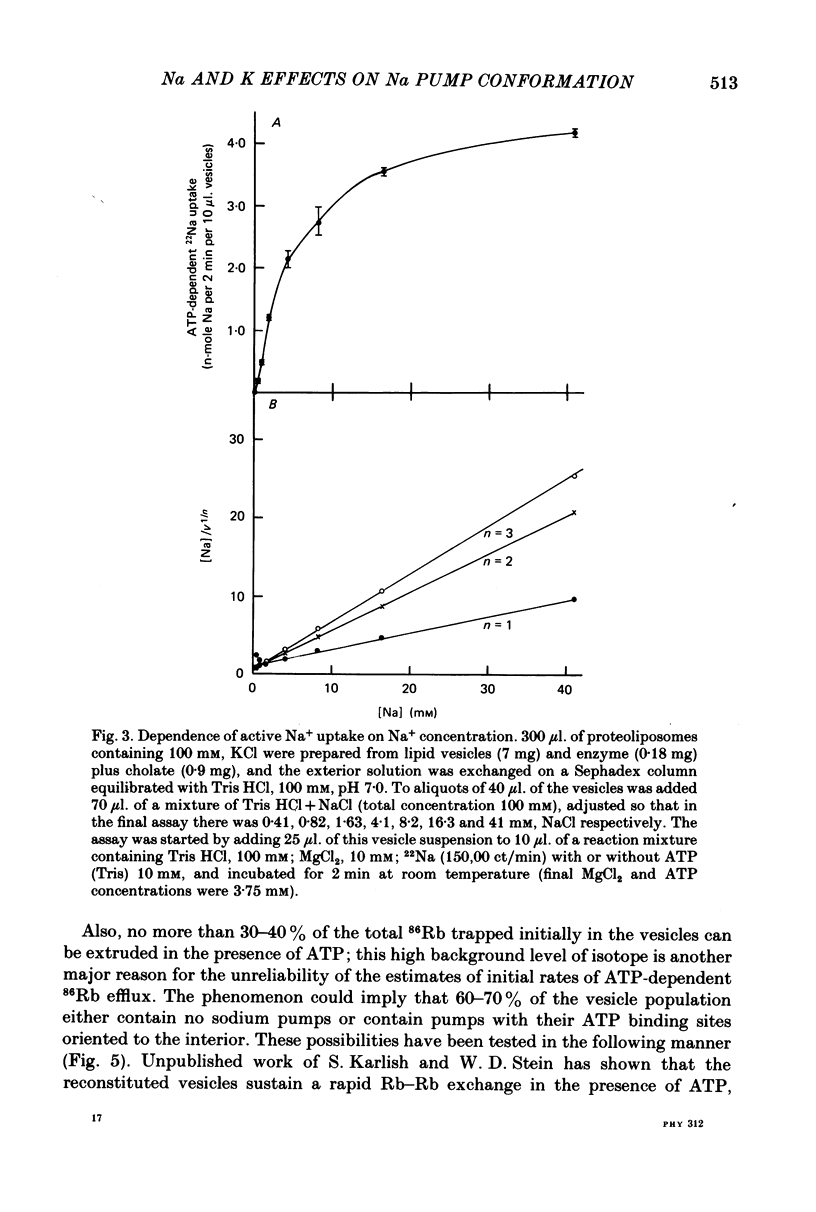
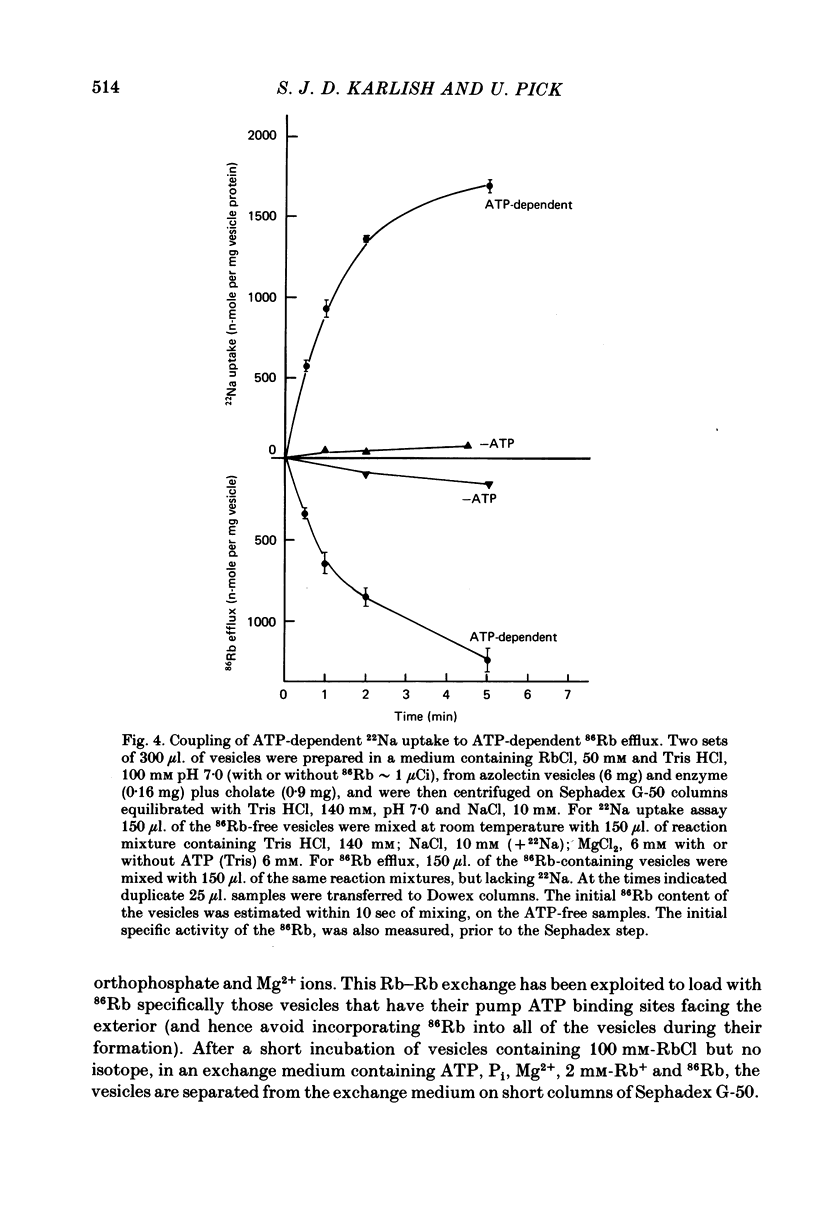
2. Upon addition of ATP to the exterior medium the reconstituted vesicles sustain high rates of active 22Na uptake and 86Rb efflux with many properties similar to those of the Na/K pump in well characterized cells such as erythrocytes.
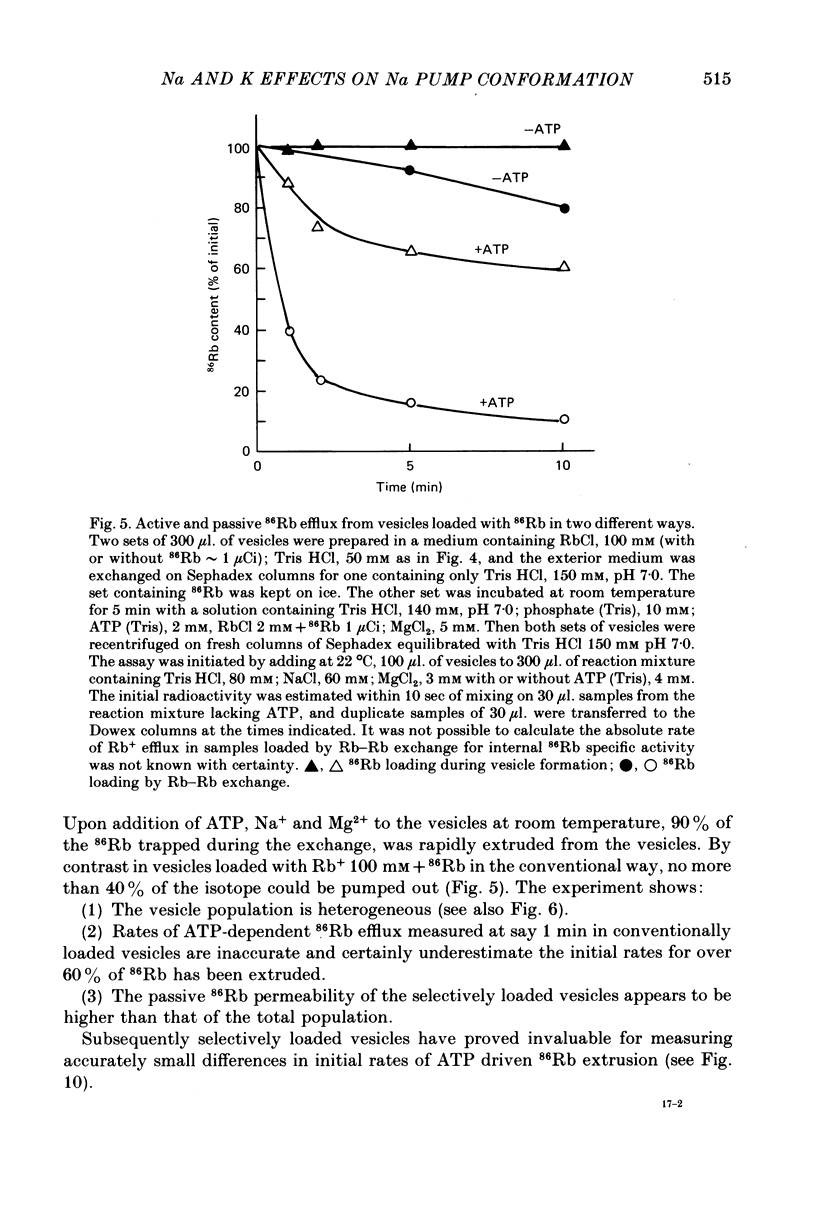
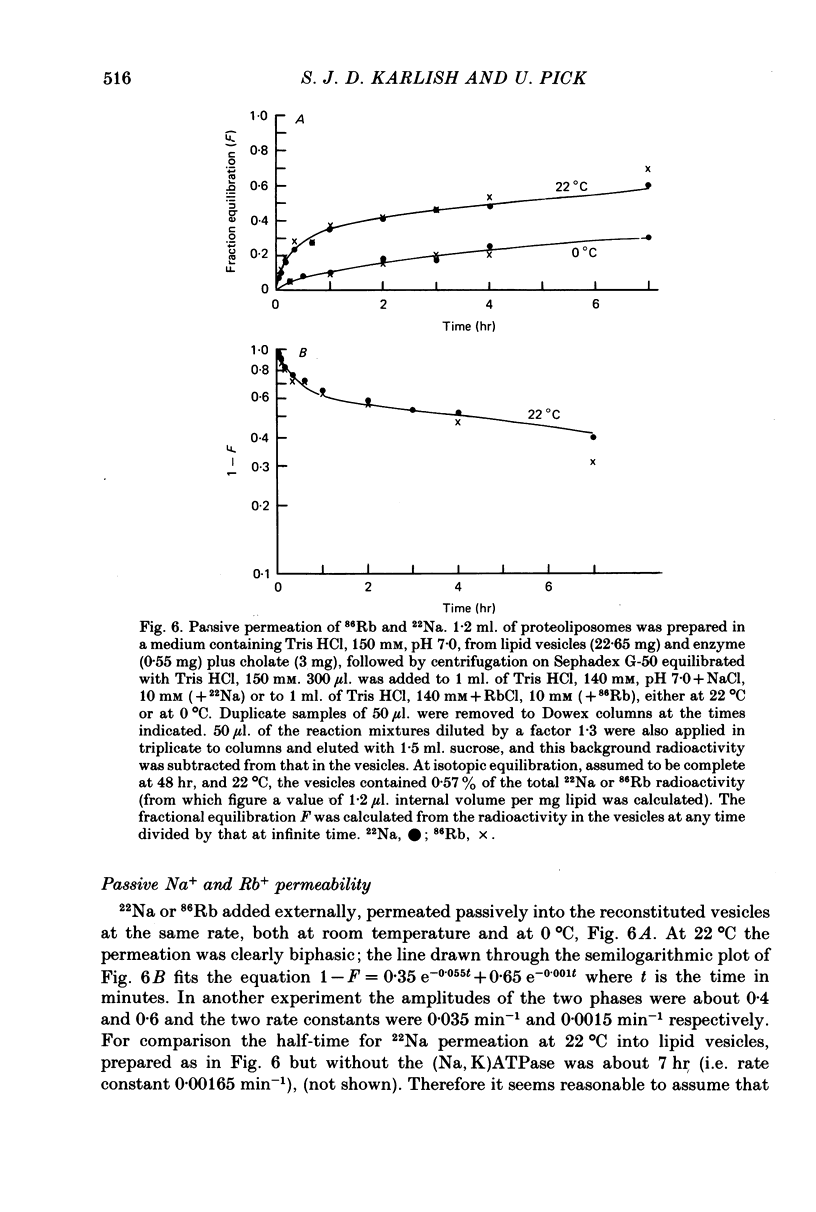
3. Observations on both active and passive transport of 22 Na and 86Rb indicate that the vesicle population is heterogeneous; about 40 per cent contain Na/K pumps and the remainder seem to be plain lipid vesicles.
4. The major Na+- or K+-stabilized non-phosphorylated conformational forms of the (Na, K)ATPase, E1. Na and E2. (K) respectively, have been investigated in the proteoliposomes, with particular regard to sidedness of the actions of Na+ and K+.
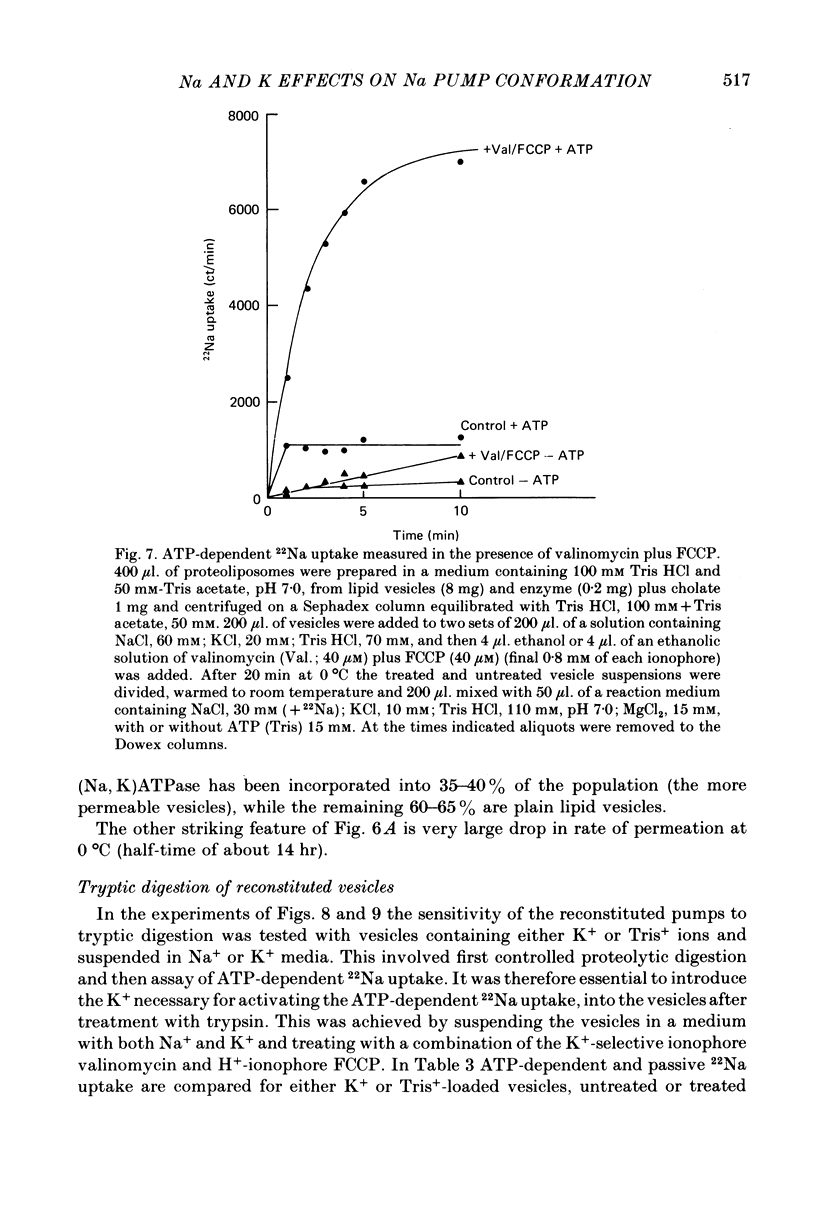
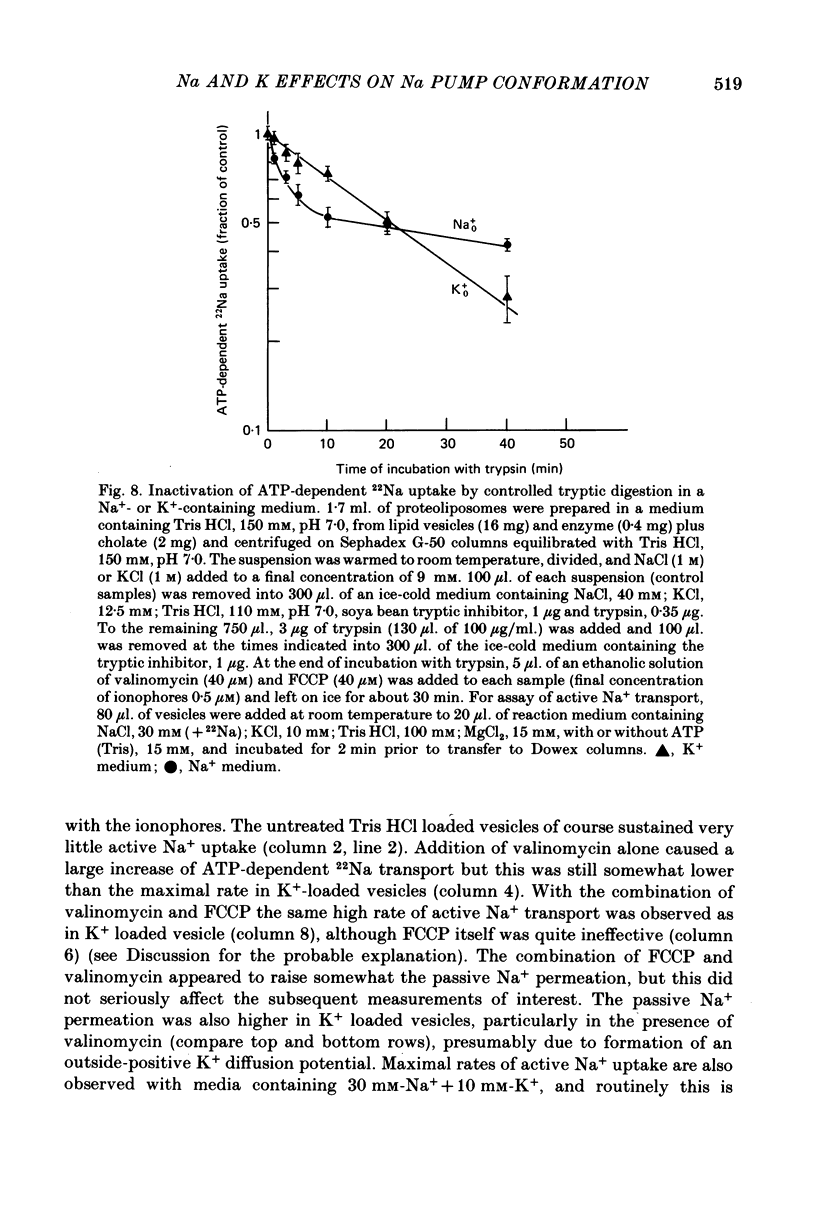
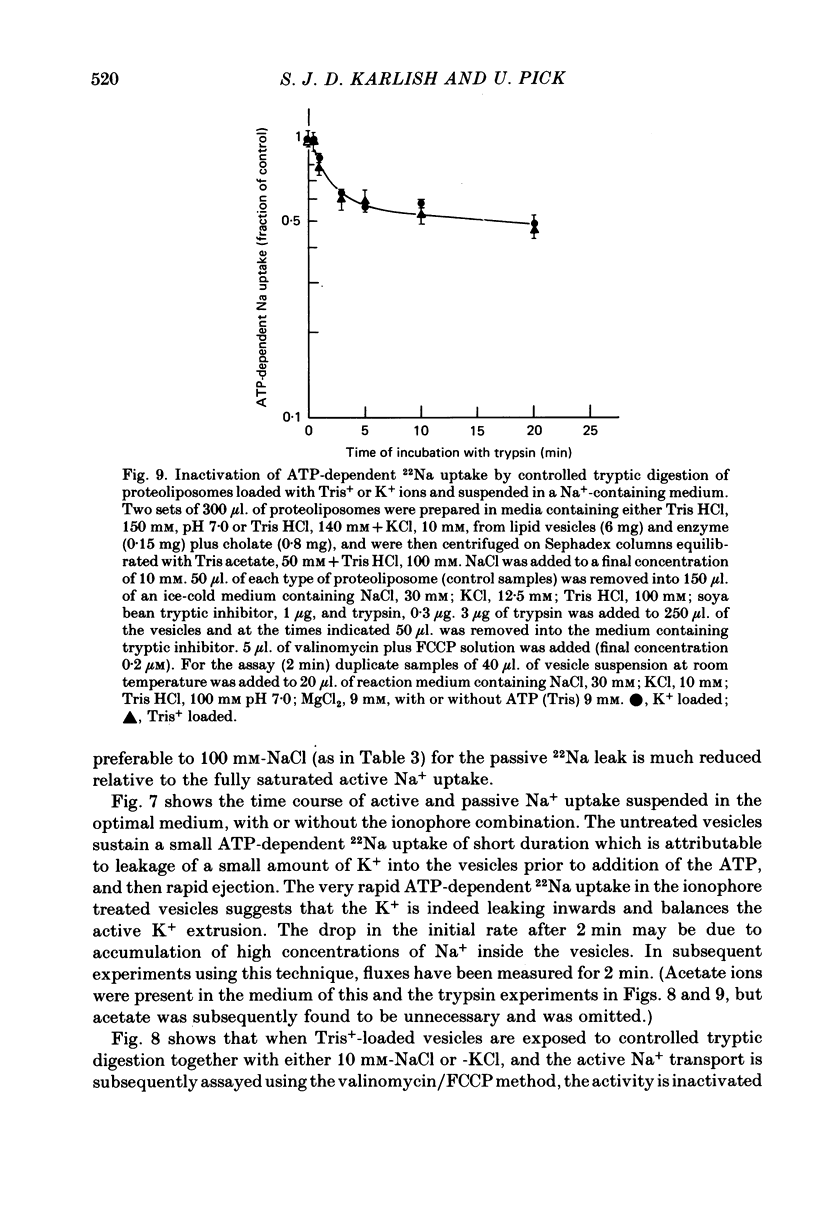
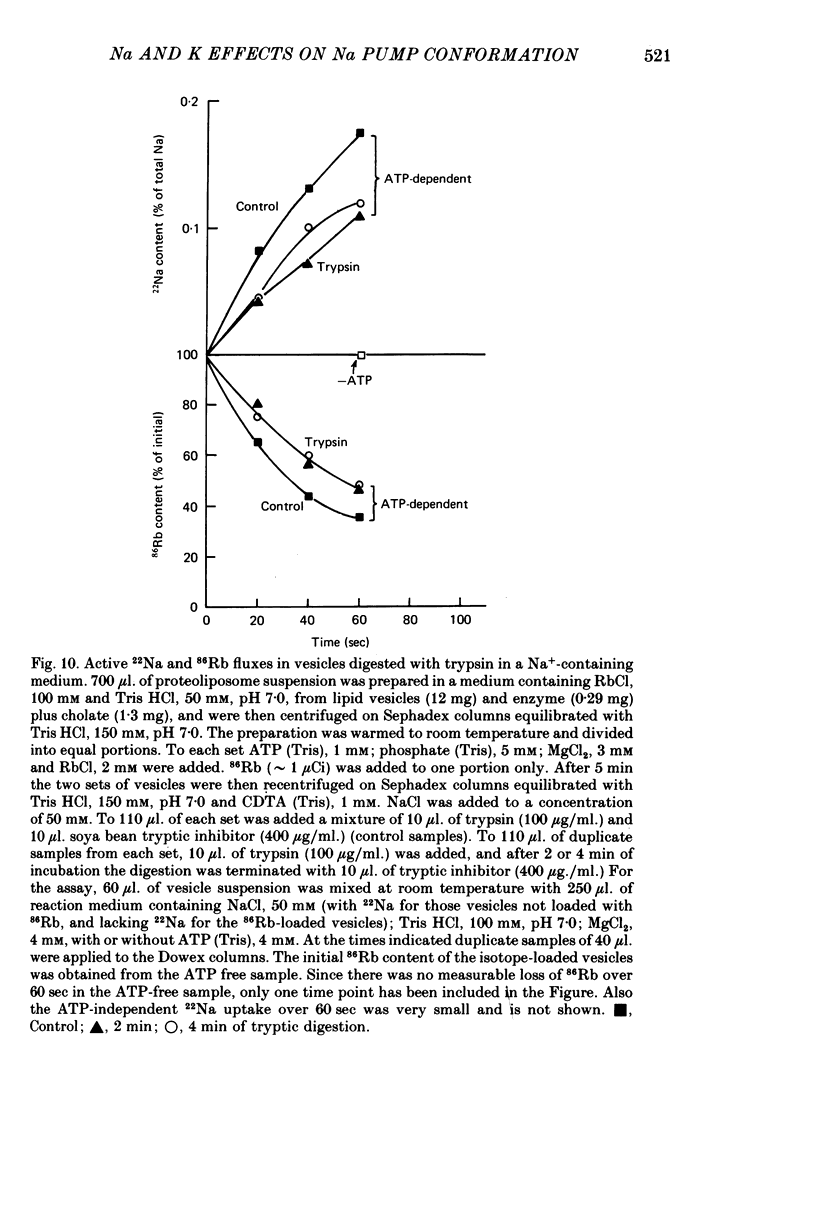
5. Tryptic digestion of the vesicles reveals the Na+- and K+-stabilized conformations E1. Na and E2. (K) as characterized originally for purified (Na, K)ATPase (Jørgensen, 1975). Controlled trypsinolysis of Tris+-loaded vesicles in a Na+-or K+-containing medium leads to typical biphasic (Na+) or simple exponential (K+) time courses respectively, for loss of ATP-dependent 22Na uptake (assayed subsequent to the tryptic digestion in the presence of inophores valinomycin plus FCCP). Tryptic digestion of K+- or Rb+- or Tris+-loaded vesicles suspended in a Na+ medium results only in the biphasic (E1. Na) pattern of loss of ATP-dependent 22Na uptake.
6. ATP-dependent 22Na uptake and 86Rb efflux are reduced by about the same extent following a short tryptic digestion in a Na+-containing medium.
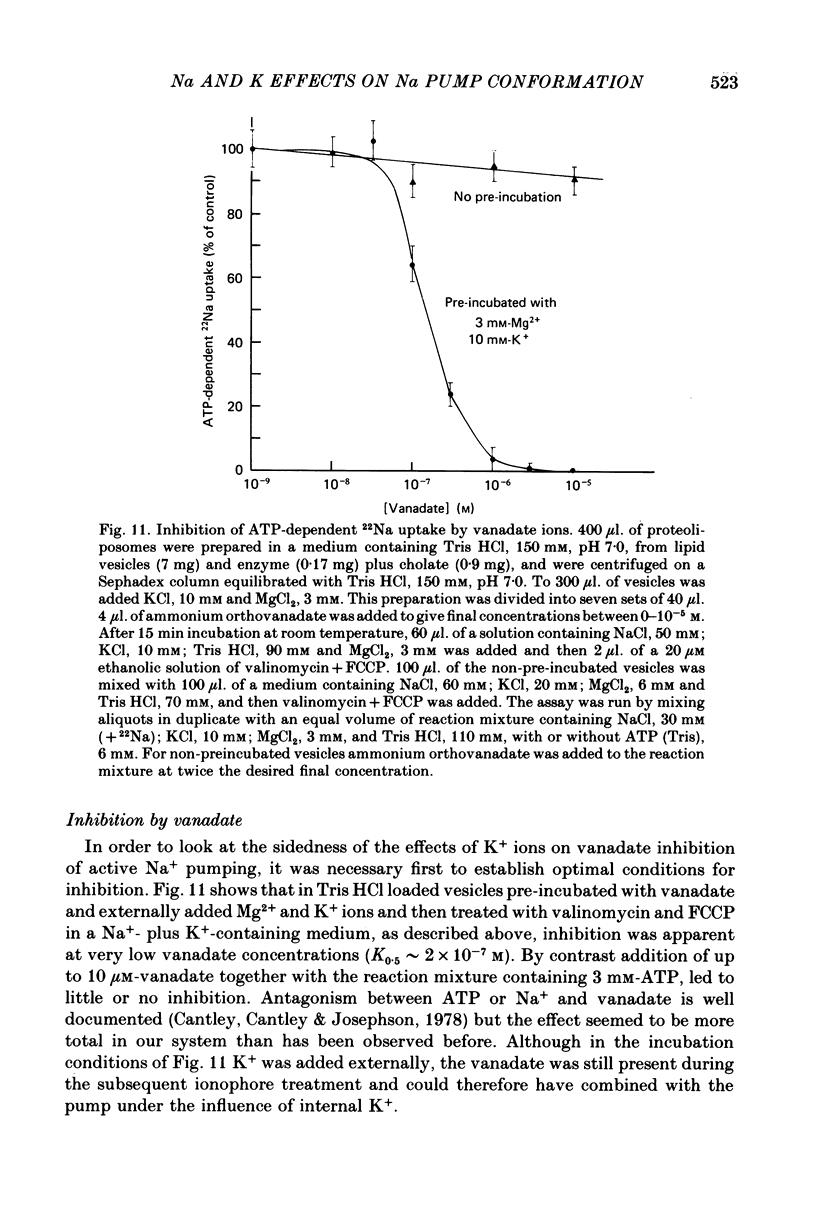
7. Vanadate ions inhibit ATP-dependent 22Na uptake into the vesicles, at low concentrations (K0·5 ∼ 2 × 10-7 m), following pre-incubation together with Mg2+ and K+ ions. K+ ions in the medium are effective, K+ ions within the vesicle are not. Na+ ions in the medium prevent inhibition by vanadate+Mg2+ but do not reverse inhibition in vesicles pre-incubated with vanadate, Mg2+ and K+ ions.
8. The results show that the conformational forms E1. Na and E2. (K) are stabilized by Na+ or K+ ions respectively, bound to sites on the Na/K pump normally facing the cytoplasm. The significance of this finding is discussed in relation to the cation transport function of the pump.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anner B. M., Lane L. K., Schwartz A., Pitts B. J. A reconstituted Na+ + K+ pump in liposomes containing purified (Na+ + K+)-ATPase from kidney medulla. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 16;467(3):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., Cavieres J. J., Glynn, Grantham J. J. The effects of vanadate on the fluxes of sodium and potassium ions through the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:7–23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., DiPolo R. Sidedness of the ATP-Na+-K+ interactions with the Na+ pump in squid axons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 2;553(3):495–500. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., Glynn I. M. Commercial ATP containing traces of vanadate alters the response of (Na+ + K+) ATPase to external potassium. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):551–552. doi: 10.1038/272551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., Glynn I. M. Occlusion of K ions in the unphosphorylated sodium pump. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):510–512. doi: 10.1038/280510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L., Dipolo R. Vanadate selectively inhibits the Ko+-activated Na+ efflux in squid axons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 20;551(1):220–223. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90367-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blostein R., Chu L. Sidedness of (sodium, potassium)-adenosine triphosphate of inside-out red cell membrane vesicles. Interactions with potassium. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):3035–3043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blostein R. Side-specific effects of sodium on (Na,K)-ATPase. Studies with inside-out red cell membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6673–6677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Cantley L. G., Josephson L. A characterization of vanadate interactions with the (Na,K)-ATPase. Mechanistic and regulatory implications. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7361–7368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Josephson L., Warner R., Yanagisawa M., Lechene C., Guidotti G. Vanadate is a potent (Na,K)-ATPase inhibitor found in ATP derived from muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7421–7423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Resh M. D., Guidotti G. Vanadate inhibits the red cell (Na+, K+) ATPase from the cytoplasmic side. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):552–554. doi: 10.1038/272552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasko O. D., Knowles A. F., Shertzer H. G., Suolinna E. M., Racker E. The use of ion-exchange resins for studying ion transport in biological systems. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:57–65. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90506-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giotta G. J. Native (Na-+ + K-+)-dependent adenosine triphosphatase has two trypsin-sensitive sites. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5159–5164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Hoffman J. F., Lew V. L. Some "partial reactions" of the sodium pump. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Aug 20;262(842):91–102. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Karlish S. J. ATP hydrolysis associated with an uncoupled sodium flux through the sodium pump: evidence for allosteric effects of intracellular ATP and extracellular sodium. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(2):465–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Karlish S. J. The sodium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1975;37:13–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.37.030175.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Lew V. L., Lüthi U. Reversal of the potassium entry mechanism in red cells, with and without reversal of the entire pump cycle. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):371–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin S. M. Active transport of sodium and potassium ions by the sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase from renal medulla. Reconstitution of the purified enzyme into a well defined in vitro transport system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5630–5642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. J., Pressman B. C. Obligate cation exchanges in red cells. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):918–920. doi: 10.1038/216918a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilden S., Hokin L. E. Active potassium transport coupled to active sodium transport in vesicles reconstituted from purified sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase from the rectal gland of Squalus acanthias. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6296–6303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. VI. Differential tryptic modification of catalytic functions of the purified enzyme in presence of NaCl and KCl. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 1;466(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90211-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ plus K+ )-ATPase. 3. Purification from the outer medulla of mammalian kidney after selective removal of membrane components by sodium dodecylsulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):36–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+, K+)-ATPase. V. Conformational changes in the enzyme Transitions between the Na-form and the K-form studied with tryptic digestion as a tool. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 2;401(3):399–415. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90239-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L., Anner B. M. Purification and characterization of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. VIII. Altered Na+ : K+ transport ratio in vesicles reconstituted with purified (Na+ + K+)-ATPase that has been selectively modified with trypsin in presence of NaCl. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 23;555(3):485–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90401-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L., Karlish S. J. Defective conformational response in a selectively trypsinized (Na+ + K+)-ATPase studied with tryptophan fluorescence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 10;597(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L., Klodos I. Purification and characterization of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. VII. Tryptic degradation of the Na-form of the enzyme protein resulting in selective modification of dephosphorylation reactions of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 2;507(1):8–16. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90369-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Beaugé L. A., Glynn I. M. Vanadate inhibits (Na+ + K+)ATPase by blocking a conformational change of the unphosphorylated form. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):333–335. doi: 10.1038/282333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Yates D. W., Glynn I. M. Conformational transitions between Na+-bound and K+-bound forms of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase, studied with formycin nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 7;525(1):252–264. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Yates D. W., Glynn I. M. Elementary steps of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase mechanism, studied with formycin nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 7;525(1):230–251. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Yates D. W. Tryptophan fluorescence of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase as a tool for study of the enzyme mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 10;527(1):115–130. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara M., Hinkle P. C. Reconstitution and purification of the D-glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7384–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. L., Hegyvary C., Kume S. Activation by adenosine triphosphate in the phosphorylation kinetics of sodium and potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6530–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Fisher L. W. Reconstitution of an ATP-dependent sodium pump with an ATPase from electric eel and pure phospholipids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):1144–1150. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90793-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E. Reconstitution of a calcium pump with phospholipids and a purified Ca ++ - adenosine triphosphatase from sacroplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8198–8200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons T. J. Potassium: potassium exchange catalysed by the sodium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;237(1):123–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


