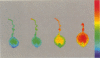Abstract
We used digital calcium imaging with Fura-2 in conjunction with the tight-seal whole-cell patch clamp technique to describe a novel cation conductance in olfactory neurons of the clawed toad Xenopus laevis. Substitution of extracellular Ca2+ and Na+ was used as a tool to change [Ca2+]i. When [Ca2+]i was increased to about 450 nM, a conductance gcat activated that was permeable for cations. Upon gcat activation, an increase in [Ca2+]i occurred in the dendritic knob. Once activated, gcat showed no further dependence upon [Ca2+]i. Icat is shown to be different from the current activated by a mixture of the odorants citralva and amyl acetate. We conclude that there are two different cation conductances in the peripheral compartments of olfactory neurons in X. laevis.
Full text
PDF


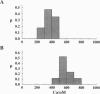
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide mediates glutamate-linked enhancement of cGMP levels in the cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):9030–9033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.9030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breer H., Klemm T., Boekhoff I. Nitric oxide mediated formation of cyclic GMP in the olfactory system. Neuroreport. 1992 Nov;3(11):1030–1032. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199211000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fadool D. A., Ache B. W. Plasma membrane inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-activated channels mediate signal transduction in lobster olfactory receptor neurons. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):907–918. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90243-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein S., Darrow B., Shepherd G. M. Activation of the sensory current in salamander olfactory receptor neurons depends on a G protein-mediated cAMP second messenger system. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):825–835. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein S., Werblin F. Odor-induced membrane currents in vertebrate-olfactory receptor neurons. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.2704991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frings S., Lynch J. W., Lindemann B. Properties of cyclic nucleotide-gated channels mediating olfactory transduction. Activation, selectivity, and blockage. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Jul;100(1):45–67. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frings S. Protein kinase C sensitizes olfactory adenylate cyclase. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Feb;101(2):183–205. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene S. J., Gesteland R. C. Calcium-activated chloride conductance in frog olfactory cilia. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3624–3629. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03624.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurahashi T. Activation by odorants of cation-selective conductance in the olfactory receptor cell isolated from the newt. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:177–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurahashi T., Yau K. W. Co-existence of cationic and chloride components in odorant-induced current of vertebrate olfactory receptor cells. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):71–74. doi: 10.1038/363071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischka F. W., Schild D. Effects of nitric oxide upon olfactory receptor neurones in Xenopus laevis. Neuroreport. 1993 May;4(5):582–584. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199305000-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischka F. W., Schild D. Standing calcium gradients in olfactory receptor neurons can be abolished by amiloride or ruthenium red. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Nov;102(5):817–831. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.5.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. W., Maxfield F. R. Preparation of solutions with free calcium concentration in the nanomolar range using 1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 15;193(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90044-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Augustine G. J. Calcium gradients and buffers in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo D., Miyamoto T., Bryant B. P., Teeter J. H. Odor stimuli trigger influx of calcium into olfactory neurons of the channel catfish. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1166–1168. doi: 10.1126/science.2168580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo D., Teeter J. H., Honda E., Boyle A. G., Marecek J. F., Prestwich G. D., Kalinoski D. L. Evidence for an InsP3-gated channel protein in isolated rat olfactory cilia. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 1):C667–C673. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.3.C667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo D., Teeter J. H. Olfactory neurons exhibit heterogeneity in depolarization-induced calcium changes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C1051–C1061. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronnett G. V., Snyder S. H. Molecular messengers of olfaction. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Dec;15(12):508–513. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90104-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild D., Bischofberger J. Ca2+ modulates an unspecific cation conductance in olfactory cilia of Xenopus laevis. Exp Brain Res. 1991;84(1):187–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00231774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild D. Whole-cell currents in olfactory receptor cells of Xenopus laevis. Exp Brain Res. 1989;78(2):223–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00228894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]