Abstract
This article discusses several strategies for the use steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence methods to monitor unfolding transitions in proteins. The assumptions and limitations of several methods are discussed. Simulations are presented to show that certain fluorescence observables directly track the population of states in an unfolding transition, whereas other observables skew the transition toward the dominant fluorescing species. Several examples are given, involving the unfolding of Staphylococcal aureus nuclease A, in which thermodynamic information is obtained for the temperature and denaturant induced transitions in this protein.
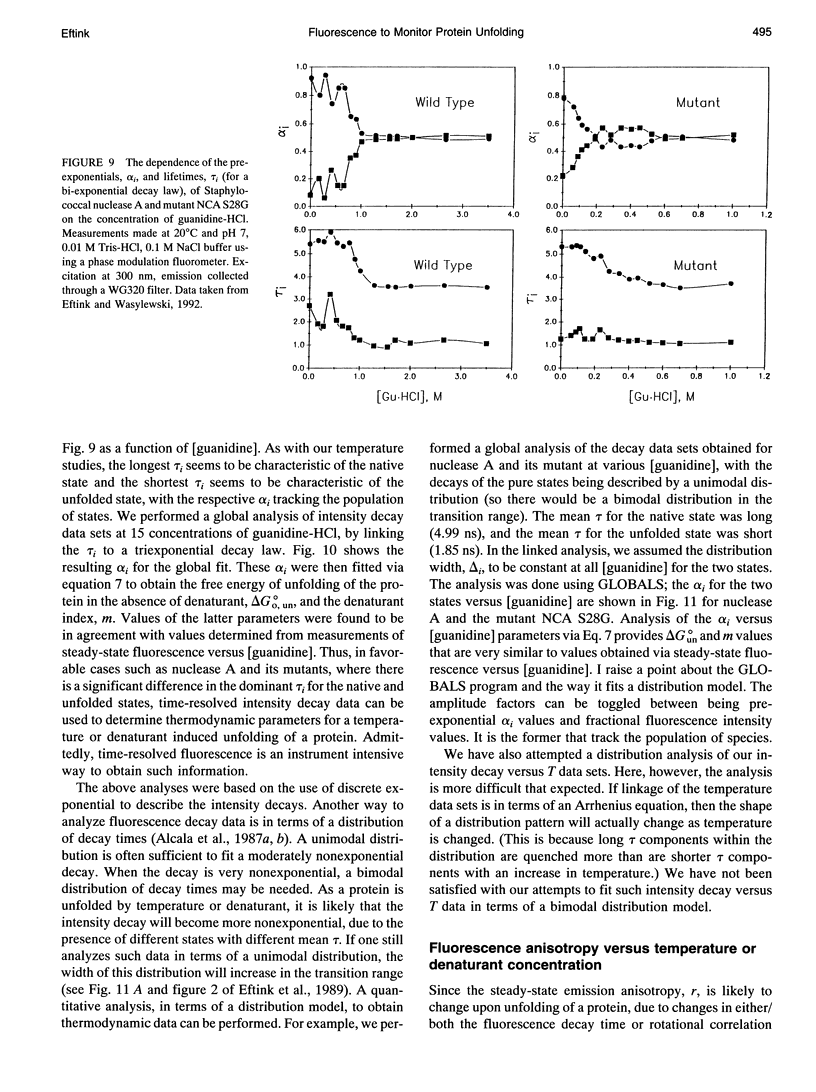
Full text
PDF


















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcala J. R., Gratton E., Prendergast F. G. Fluorescence lifetime distributions in proteins. Biophys J. 1987 Apr;51(4):597–604. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83384-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcala J. R., Gratton E., Prendergast F. G. Interpretation of fluorescence decays in proteins using continuous lifetime distributions. Biophys J. 1987 Jun;51(6):925–936. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83420-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amir D., Krausz S., Haas E. Detection of local structures in reduced unfolded bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Proteins. 1992 Apr;13(2):162–173. doi: 10.1002/prot.340130210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrick D., Baldwin R. L. Three-state analysis of sperm whale apomyoglobin folding. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 13;32(14):3790–3796. doi: 10.1021/bi00065a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becktel W. J., Schellman J. A. Protein stability curves. Biopolymers. 1987 Nov;26(11):1859–1877. doi: 10.1002/bip.360261104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beechem J. M., Brand L. Time-resolved fluorescence of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:43–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biltonen R. L., Freire E. Thermodynamic characterization of conformational states of biological macromolecules using differential scanning calorimetry. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1978;5(2):85–124. doi: 10.3109/10409237809177141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandts J. F., Hu C. Q., Lin L. N., Mos M. T. A simple model for proteins with interacting domains. Applications to scanning calorimetry data. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8588–8596. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandts J. F., Lin L. N. Study of strong to ultratight protein interactions using differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 24;29(29):6927–6940. doi: 10.1021/bi00481a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandts J. F., Oliveira R. J., Westort C. Thermodynamics of protein denaturation. Effect of pressu on the denaturation of ribonuclease A. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 17;9(4):1038–1047. doi: 10.1021/bi00806a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucci E., Malak H., Fronticelli C., Gryczynski I., Lakowicz J. R. Resolution of the lifetimes and correlation times of the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence of human hemoglobin solutions using 2 GHz frequency-domain fluorometry. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):6972–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauvin F., Toptygin D., Roseman S., Brand L. Time-resolved intrinsic fluorescence of Enzyme I. The monomer/dimer transition. Biophys Chem. 1992 Oct;44(3):163–173. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(92)80049-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F., Knutson J. R., Ziffer H., Porter D. Fluorescence of tryptophan dipeptides: correlations with the rotamer model. Biochemistry. 1991 May 28;30(21):5184–5195. doi: 10.1021/bi00235a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eftink M. R. Fluorescence techniques for studying protein structure. Methods Biochem Anal. 1991;35:127–205. doi: 10.1002/9780470110560.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eftink M. R., Ghiron C. A., Kautz R. A., Fox R. O. Fluorescence and conformational stability studies of Staphylococcus nuclease and its mutants, including the less stable nuclease-concanavalin A hybrids. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1193–1199. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eftink M. R., Gryczynski I., Wiczk W., Laczko G., Lakowicz J. R. Effects of temperature on the fluorescence intensity and anisotropy decays of staphylococcal nuclease and the less stable nuclease-conA-SG28 mutant. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 17;30(37):8945–8953. doi: 10.1021/bi00101a005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan D. A., Logan T. M., Liang H., Matayoshi E., Fesik S. W., Holzman T. F. Equilibrium denaturation of recombinant human FK binding protein in urea. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):1920–1927. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando T., Royer C. A. Unfolding of trp repressor studied using fluorescence spectroscopic techniques. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 28;31(29):6683–6691. doi: 10.1021/bi00144a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL S. J., GLOGOVSKY R. L. INFLUENCE OF PRESSURE ON THE REVERSIBLE UNFOLDING OR RIBONUCLEASE AND POLY-GAMMA-L-GLUTAMATE. J Phys Chem. 1965 May;69:1515–1519. doi: 10.1021/j100889a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittelman M. S., Matthews C. R. Folding and stability of trp aporepressor from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 31;29(30):7011–7020. doi: 10.1021/bi00482a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S. K., Deckman I. C., Culp J. S., Minnich M. D., Brooks I. S., Hensley P., Debouck C., Meek T. D. Use of protein unfolding studies to determine the conformational and dimeric stabilities of HIV-1 and SIV proteases. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 6;31(39):9491–9501. doi: 10.1021/bi00154a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griko Y. V., Privalov P. L., Sturtevant J. M., Venyaminov SYu Cold denaturation of staphylococcal nuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3343–3347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczynski I., Eftink M., Lakowicz J. R. Conformation heterogeneity in proteins as an origin of heterogeneous fluorescence decays, illustrated by native and denatured ribonuclease T1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 13;954(3):244–252. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J., Baldwin R. L. A quantitative treatment of the kinetics of the folding transition of ribonuclease A. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 6;15(7):1462–1473. doi: 10.1021/bi00652a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser R. M., Negus D. K. Picosecond fluorescence decay of tryptophans in myoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4399–4403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes T. R., Kautz R. A., Goodman M. A., Gill J. F., Fox R. O. Transfer of a beta-turn structure to a new protein context. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):73–76. doi: 10.1038/339073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James E., Wu P. G., Stites W., Brand L. Compact denatured state of a staphylococcal nuclease mutant by guanidinium as determined by resonance energy transfer. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 27;31(42):10217–10225. doi: 10.1021/bi00157a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. R., Davenport L., Brand L. Anisotropy decay associated fluorescence spectra and analysis of rotational heterogeneity. 1. Theory and applications. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1805–1810. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Gryczynski I., Cheung H. C., Wang C. K., Johnson M. L., Joshi N. Distance distributions in proteins recovered by using frequency-domain fluorometry. Applications to troponin I and its complex with troponin C. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9149–9160. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepock J. R., Ritchie K. P., Kolios M. C., Rodahl A. M., Heinz K. A., Kruuv J. Influence of transition rates and scan rate on kinetic simulations of differential scanning calorimetry profiles of reversible and irreversible protein denaturation. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 22;31(50):12706–12712. doi: 10.1021/bi00165a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez Mayorga O., Freire E. Dynamic analysis of differential scanning calorimetry data. Biophys Chem. 1987 Jul;27(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(87)80049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumry R., Biltonen R. Validity of the "two-state" hypothesis for conformational transitions of proteins. Biopolymers. 1966 Sep;4(8):917–944. doi: 10.1002/bip.1966.360040808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Genetic and structural analysis of the protein stability problem. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):6885–6888. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mei G., Rosato N., Silva N., Jr, Rusch R., Gratton E., Savini I., Finazzi-Agrò A. Denaturation of human Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase by guanidine hydrochloride: a dynamic fluorescence study. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 18;31(32):7224–7230. doi: 10.1021/bi00147a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. N. Determination and analysis of urea and guanidine hydrochloride denaturation curves. Methods Enzymol. 1986;131:266–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)31045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. N., Grimsley G. R. Ribonuclease T1 is stabilized by cation and anion binding. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3242–3246. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. N., Laurents D. V., Thomson J. A. pH dependence of the urea and guanidine hydrochloride denaturation of ribonuclease A and ribonuclease T1. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2564–2572. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paladini A. A., Jr, Weber G. Pressure-induced reversible dissociation of enolase. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2587–2593. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palleros D. R., Shi L., Reid K. L., Fink A. L. Three-state denaturation of DnaK induced by guanidine hydrochloride. Evidence for an expandable intermediate. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 27;32(16):4314–4321. doi: 10.1021/bi00067a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L. Cold denaturation of proteins. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(4):281–305. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L. Thermodynamic problems of protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:47–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. B., Wyssbrod H. R., Porter R. A., Schwartz G. P., Michaels C. A., Laws W. R. Correlation of tryptophan fluorescence intensity decay parameters with 1H NMR-determined rotamer conformations: [tryptophan2]oxytocin. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1585–1594. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer C. A., Hinck A. P., Loh S. N., Prehoda K. E., Peng X., Jonas J., Markley J. L. Effects of amino acid substitutions on the pressure denaturation of staphylococcal nuclease as monitored by fluorescence and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1993 May 18;32(19):5222–5232. doi: 10.1021/bi00070a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer C. A., Weber G., Daly T. J., Matthews K. S. Dissociation of the lactose repressor protein tetramer using high hydrostatic pressure. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8308–8315. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Wada A. Comparative study of GuHCl denaturation of globular proteins. I. Spectroscopic and chromatographic analysis of the denaturation curves of ribonuclease A, cytochrome c, and pepsinogen. Biopolymers. 1983 Sep;22(9):2105–2122. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro M. M., Bolen D. W. Unfolding free energy changes determined by the linear extrapolation method. 1. Unfolding of phenylmethanesulfonyl alpha-chymotrypsin using different denaturants. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8063–8068. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellman J. A. The thermodynamic stability of proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:115–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Meeker A. K., Freire E. Stability mutants of staphylococcal nuclease: large compensating enthalpy-entropy changes for the reversible denaturation reaction. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4761–4768. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Meeker A. K. Mutant forms of staphylococcal nuclease with altered patterns of guanidine hydrochloride and urea denaturation. Proteins. 1986 Sep;1(1):81–89. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara T., Kuwajima K., Sugai S. Folding of staphylococcal nuclease A studied by equilibrium and kinetic circular dichroism spectra. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 12;30(10):2698–2706. doi: 10.1021/bi00224a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Flanagan J., Sturtevant J. M. Thermal unfolding of staphylococcal nuclease and several mutant forms thereof studied by differential scanning calorimetry. Protein Sci. 1993 Apr;2(4):567–576. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson J. A., Shirley B. A., Grimsley G. R., Pace C. N. Conformational stability and mechanism of folding of ribonuclease T1. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11614–11620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timm D. E., Neet K. E. Equilibrium denaturation studies of mouse beta-nerve growth factor. Protein Sci. 1992 Feb;1(2):236–244. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., Brochon J. C., Merola F., Jordi W., Gallay J. Nanosecond dynamics of horse heart apocytochrome c in aqueous solution as studied by time-resolved fluorescence of the single tryptophan residue (Trp-59). Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8752–8761. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Drickamer H. G. The effect of high pressure upon proteins and other biomolecules. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 Feb;16(1):89–112. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipp A., Kauzmann W. Pressure denaturation of metmyoglobin. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 9;12(21):4217–4228. doi: 10.1021/bi00745a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



