Abstract
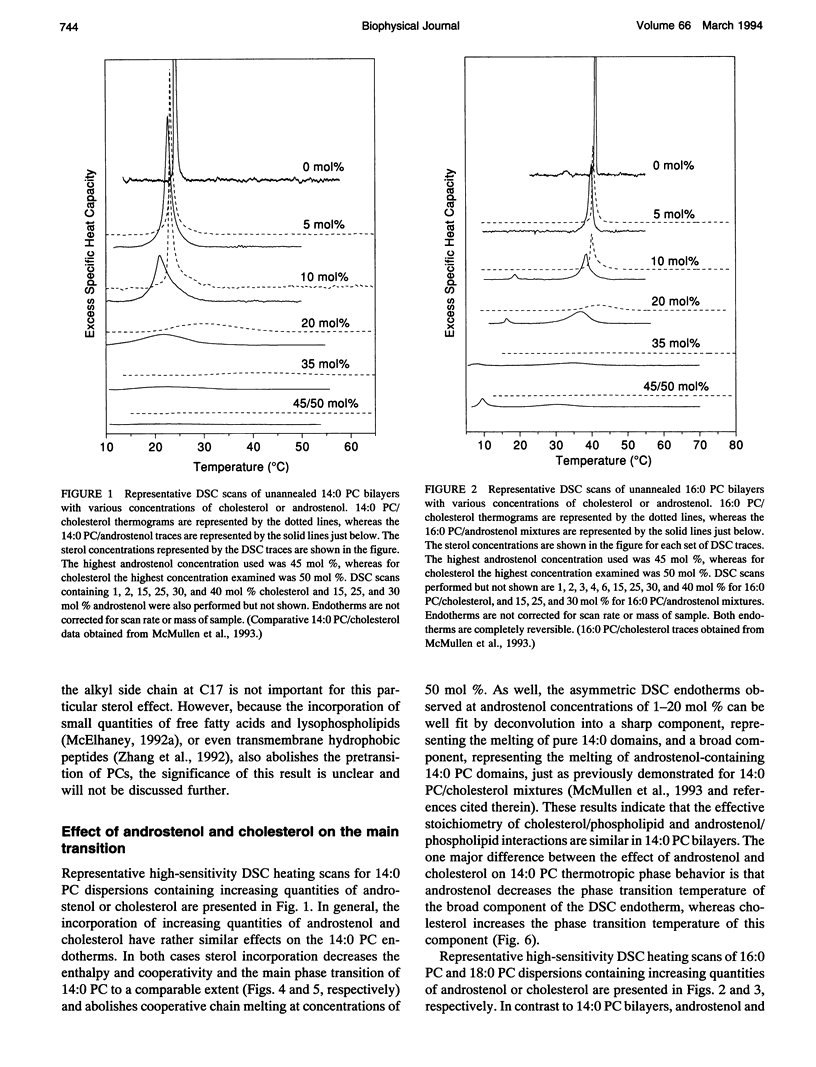
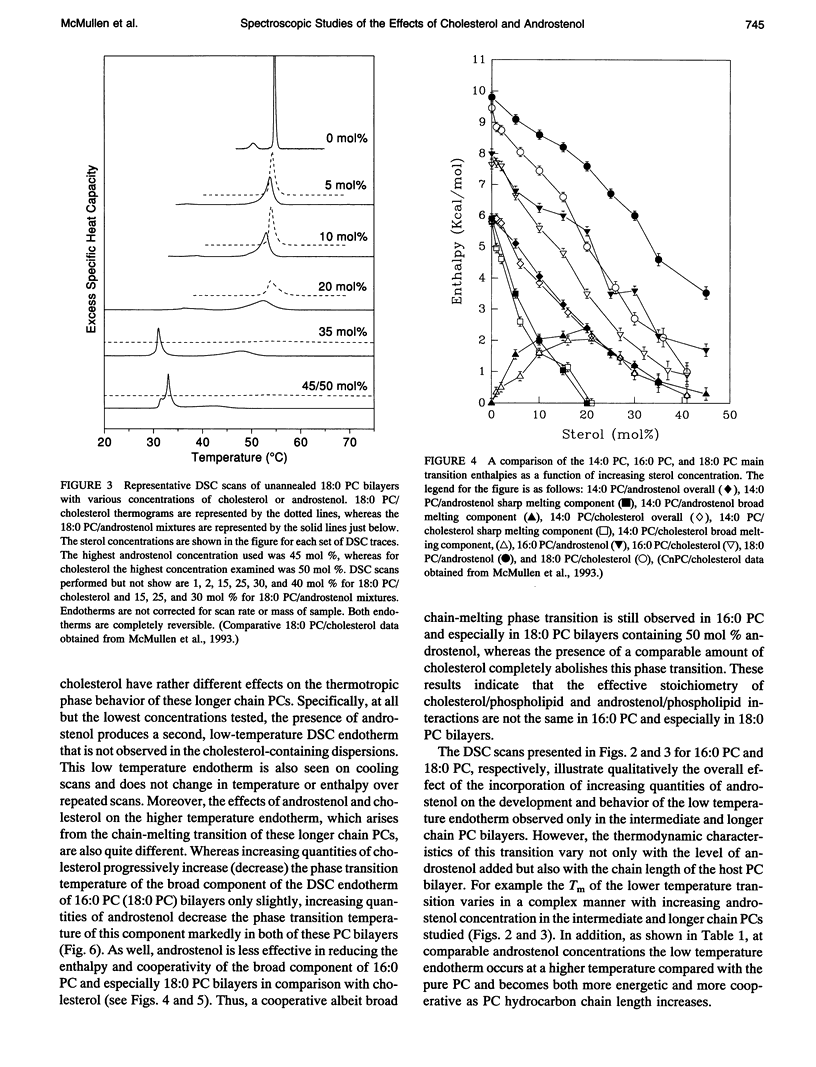
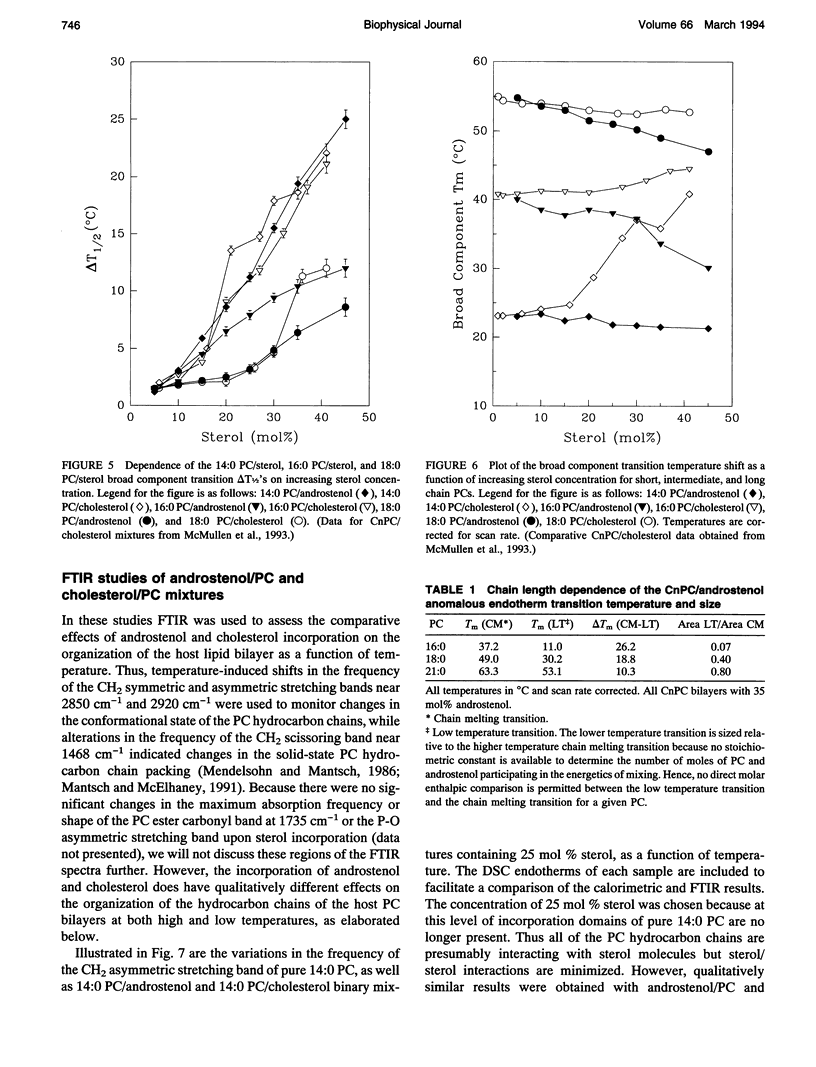
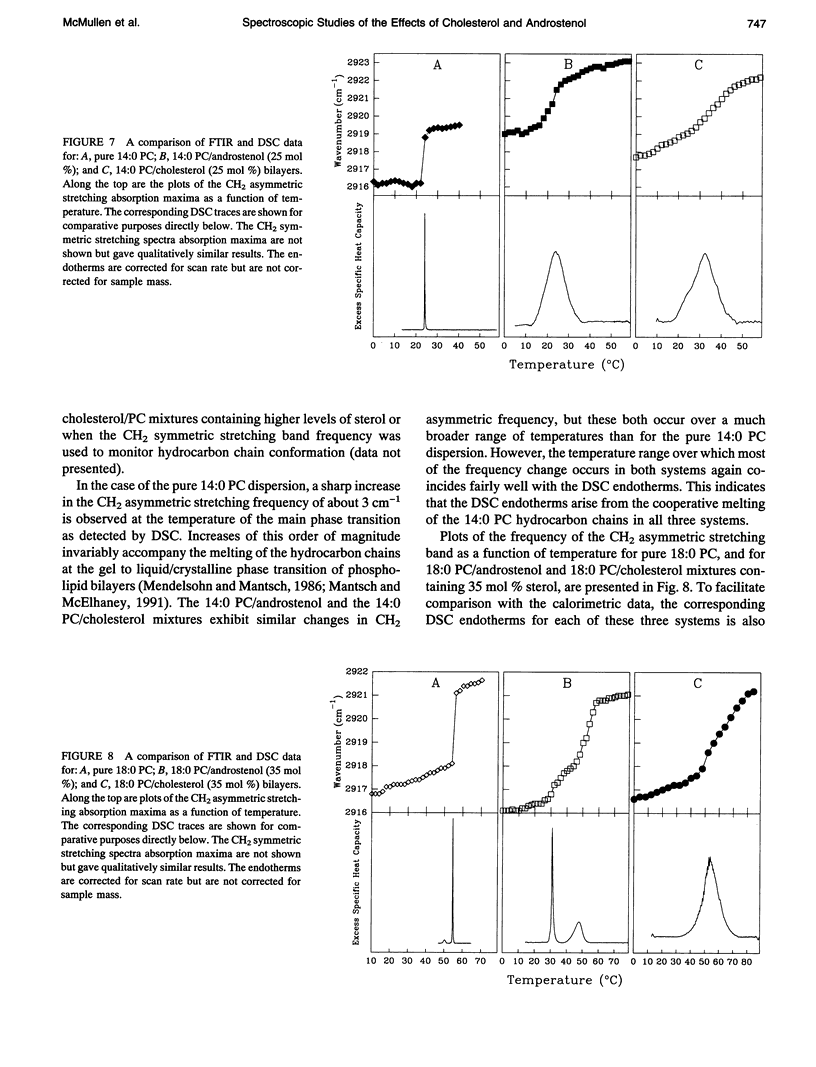
We have investigated the comparative effects of the incorporation of increasing quantities of androstenol and cholesterol on the thermotropic phase behavior of aqueous dispersions of members of a homologous series of linear saturated diacyl PCs1 using high sensitivity DSC. We have also employed FTIR and 31P-NMR spectroscopy to study the comparative effects of androstenol and cholesterol incorporation on the organization of the host PC bilayer in both the gel and liquid-crystalline states. The effects of androstenol and cholesterol incorporation on the thermotropic phase behavior of shorter chain PCs like 14:0 PC are generally similar but not identical. The incorporation of either sterol progressively decreases the temperature and enthalpy, but not the cooperativity, of the pretransition and completely abolishes it at sterol concentrations above 5 mol%. Moreover, at sterol concentrations of 1 to 20-25 mol%, both androstenol and cholesterol incorporation produce DSC endotherms consisting of superimposed sharp and broad components, the former due to the hydrocarbon chain melting of sterol-poor and the latter to the melting of sterol-rich 14:0 PC domains. The temperature and cooperativity of the sharp component are reduced slightly with increasing concentration of androstenol or cholesterol, and the enthalpy of the sharp component decreases progressively and becomes zero at 20-25 mol% sterol. As well, at cholesterol or androstenol concentrations above 20-25 mol%, the enthalpy of the broad component also decreases linearly with increasing sterol incorporation and becomes zero at sterol levels of about 50 mol%. However, whereas cholesterol incorporation progressively increases the temperature of the broad component of the DSC endotherm, androstenol incorporation decreases the temperature of this component. In contrast, the effects of androstenol and cholesterol incorporation on the thermotropic phase behavior of the intermediate and longer chain PCs studied here are considerably different. Although the incorporation of cholesterol increases the main phase transition temperature of 16:0 PC slightly and decreases the phase transition of 18:0 PC and 21:0 PC, androstenol incorporation decreases the main phase transition temperatures of all three PCs rather markedly. Moreover, androstenol is less effective in reducing the enthalpy and cooperativity of the broad component of the DSC endotherm of 16:0 PC and especially 18:0 PC bilayers in comparison to cholesterol. Androstenol incorporation (> 5 mol%) also results in the appearance of a second, low temperature endotherm in the DSC traces of the intermediate and longer chain PC dispersions that is not observed in similar cholesterol/PC dispersions. FTIR and 31P-NMR results suggest that this endotherm arises from a temperature-induced dissolution of androstenol in the gel phase PC bilayers. This second endotherm occurs at lower androstenol concentrations and increases in area at a given androstenol level as the chain length of the host PC bilayer increases. We ascribe the increasing immiscibility of androstenol in both the gel and liquid-crystalline states of PC bilayers of increasing thickness to an increasing degree of hydrophobic mismatch between the androstenol molecule and the host phospholipid bilayer.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alecio M. R., Golan D. E., Veatch W. R., Rando R. R. Use of a fluorescent cholesterol derivative to measure lateral mobility of cholesterol in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5171–5174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckdorfer K. R., Demel R. A., De Gier J., van Deenen L. L. The effect of partial replacements of membrane cholesterol by other steroids on the osmotic fragility and glycerol permeability of erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 15;183(2):334–345. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Bruckdorfer K. R., van Deenen L. L. Structural requirements of sterols for the interaction with lecithin at the air water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Bruckdorfer K. R., van Deenen L. L. The effect of sterol structure on the permeability of lipomes to glucose, glycerol and Rb + . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., De Kruyff B. The function of sterols in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):109–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estep T. N., Mountcastle D. B., Biltonen R. L., Thompson T. E. Studies on the anomalous thermotropic behavior of aqueous dispersions of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine-cholesterol mixtures. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1984–1989. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Mouritsen O. G., Bloom M. Relationships between lipid membrane area, hydrophobic thickness, and acyl-chain orientational order. The effects of cholesterol. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):405–412. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82557-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo A. L., Wade C. G. Lipid lateral diffusion by pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2300–2308. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. A., Engelman D. M. Bacteriorhodopsin remains dispersed in fluid phospholipid bilayers over a wide range of bilayer thicknesses. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. N., Mak N., McElhaney R. N. A differential scanning calorimetric study of the thermotropic phase behavior of model membranes composed of phosphatidylcholines containing linear saturated fatty acyl chains. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6118–6126. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. N., McElhaney R. N. Subgel phases of n-saturated diacylphosphatidylcholines: a Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopic study. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7946–7953. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. N., McElhaney R. N. Thermotropic phase behavior of model membranes composed of phosphatidylcholines containing iso-branched fatty acids. 1. Differential scanning calorimetric studies. Biochemistry. 1985 May 7;24(10):2431–2439. doi: 10.1021/bi00331a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. N., Sykes B. D., McElhaney R. N. Thermotropic phase behavior of model membranes composed of phosphatidylcholines containing cis-monounsaturated acyl chain homologues of oleic acid: differential scanning calorimetric and 31P NMR spectroscopic studies. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 9;27(3):880–887. doi: 10.1021/bi00403a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblom G., Johansson L. B., Arvidson G. Effect of cholesterol in membranes. Pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance measurements of lipid lateral diffusion. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2204–2207. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Mateo P. L., Sturtevant J. M. High-sensitivity scanning calorimetric study of mixtures of cholesterol with dimyristoyl- and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2464–2468. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantsch H. H., McElhaney R. N. Phospholipid phase transitions in model and biological membranes as studied by infrared spectroscopy. Chem Phys Lipids. 1991 Mar;57(2-3):213–226. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(91)90077-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen T. P., Lewis R. N., McElhaney R. N. Differential scanning calorimetric study of the effect of cholesterol on the thermotropic phase behavior of a homologous series of linear saturated phosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):516–522. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen O. G., Bloom M. Mattress model of lipid-protein interactions in membranes. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):141–153. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84007-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham D., McIntosh T. J., Evans E. Thermomechanical and transition properties of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine/cholesterol bilayers. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4668–4673. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nezil F. A., Bloom M. Combined influence of cholesterol and synthetic amphiphillic peptides upon bilayer thickness in model membranes. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1176–1183. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81926-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegler J., Möhwald H. Elastic interactions of photosynthetic reaction center proteins affecting phase transitions and protein distributions. Biophys J. 1986 Jun;49(6):1111–1118. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83740-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein J. L., Smith B. A., McConnell H. M. Lateral diffusion in binary mixtures of cholesterol and phosphatidylcholines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):15–18. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaram M. B., Thompson T. E. Interaction of cholesterol with various glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelin. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10670–10675. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance and the head group structure of phospholipids in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 31;515(2):105–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. A., Finegold L. Cholesterol interacts with all of the lipid in bilayer membranes. Implications for models. Biophys J. 1990 Jan;57(1):153–156. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82516-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. A., Finegold L. Interaction of cholesterol with saturated phospholipids: role of the C(17) side chain. Chem Phys Lipids. 1990 Dec;56(2-3):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(90)90105-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., Gallay J. Steroid-lipid interactions in sonicated dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl choline vesicles: a steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence anisotropy study with all trans-1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene as probe. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 29;113(3):799–810. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vist M. R., Davis J. H. Phase equilibria of cholesterol/dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures: 2H nuclear magnetic resonance and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):451–464. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L. Cholesterol and the cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 9;822(3-4):267–287. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. P., Lewis R. N., Hodges R. S., McElhaney R. N. Interaction of a peptide model of a hydrophobic transmembrane alpha-helical segment of a membrane protein with phosphatidylcholine bilayers: differential scanning calorimetric and FTIR spectroscopic studies. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 24;31(46):11579–11588. doi: 10.1021/bi00161a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruyff B., Demel R. A., van Deenen L. L. The effect of cholesterol and epicholesterol incorporation on the permeability and on the phase transition of intact Acholeplasma laidlawii cell membranes and derived liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):331–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



