Abstract
To evaluate the contributions of cross-linker dynamics and polymer deformation to the frequency-dependent stiffness of actin filament gels, we compared the rheological properties of actin gels with three types of cross-linkers: a weak one, Acanthamoeba alpha-actinin (dissociation rate constant 5.2 s-1, association rate constant 1.1 x 10(6) M-1 s-1); a strong one, chicken smooth muscle alpha-actinin (dissociation rate constant 0.66 s-1, association rate constant 1.20 x 10(6) M-1 s-1); and an extremely strong one, biotin/avidin (dissociation rate constant approximately zero). The biotin/avidin cross-linked gel, whose behavior is determined by polymer bending alone, behaves like a solid and shows no frequency dependence. The amoeba alpha-actinin cross-linked gel behaves like a viscoelastic fluid, and the frequency dependence of the stiffness can be explained by a mathematical model for dynamically cross-linked gels. The stiffness of the chicken alpha-actinin cross-linked gel is independent of frequency, and has viscoelastic properties intermediate between the two. The two alpha-actinins have similar association rate constants for binding to actin filaments, consistent with a diffusion-limited reaction. Rigid cross-links make the gel stiff, but make it elastic without the ability to deform permanently. Dynamically cross-linked actin filaments should allow the cell to react passively to various outside forces without any sort of signaling. Slower, signal-mediated pathways, such as severing filaments or changing the affinity of cross-linkers, could alter the nature of these passive reactions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-controlled macromolecular interactions. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:131–160. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard A., Ohanian V., Critchley D. The structure and function of alpha-actinin. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989 Aug;10(4):280–289. doi: 10.1007/BF01758424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., Heath J., Moss D. The membrane-associated 'cortex' of animal cells: its structure and mechanical properties. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1986;4:71–88. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_4.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., White J. G. Cortical flow in animal cells. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):883–888. doi: 10.1126/science.3277283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. Rapid dissociation and reassociation of actomyosin cross-bridges during force generation: a newly observed facet of cross-bridge action in muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10490–10494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlacu S., Janmey P. A., Borejdo J. Distribution of actin filament lengths measured by fluorescence microscopy. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):C569–C577. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.3.C569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Walker S. B., Pollard T. D. Pyrene actin: documentation of the validity of a sensitive assay for actin polymerization. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Apr;4(2):253–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00712034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese J. D., Frieden C. Effect of filamin and controlled linear shear on the microheterogeneity of F-actin/gelsolin gels. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1990;17(3):236–249. doi: 10.1002/cm.970170310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig S. W., Lancashire C. L., Cooper J. A. Preparation of smooth muscle alpha-actinin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):316–321. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham C. C., Gorlin J. B., Kwiatkowski D. J., Hartwig J. H., Janmey P. A., Byers H. R., Stossel T. P. Actin-binding protein requirement for cortical stability and efficient locomotion. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):325–327. doi: 10.1126/science.1549777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson E. L. Cellular mechanics as an indicator of cytoskeletal structure and function. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:397–430. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. Cytoskeleton-associated cell contacts. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;1(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorlin J. B., Yamin R., Egan S., Stewart M., Stossel T. P., Kwiatkowski D. J., Hartwig J. H. Human endothelial actin-binding protein (ABP-280, nonmuscle filamin): a molecular leaf spring. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1089–1105. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
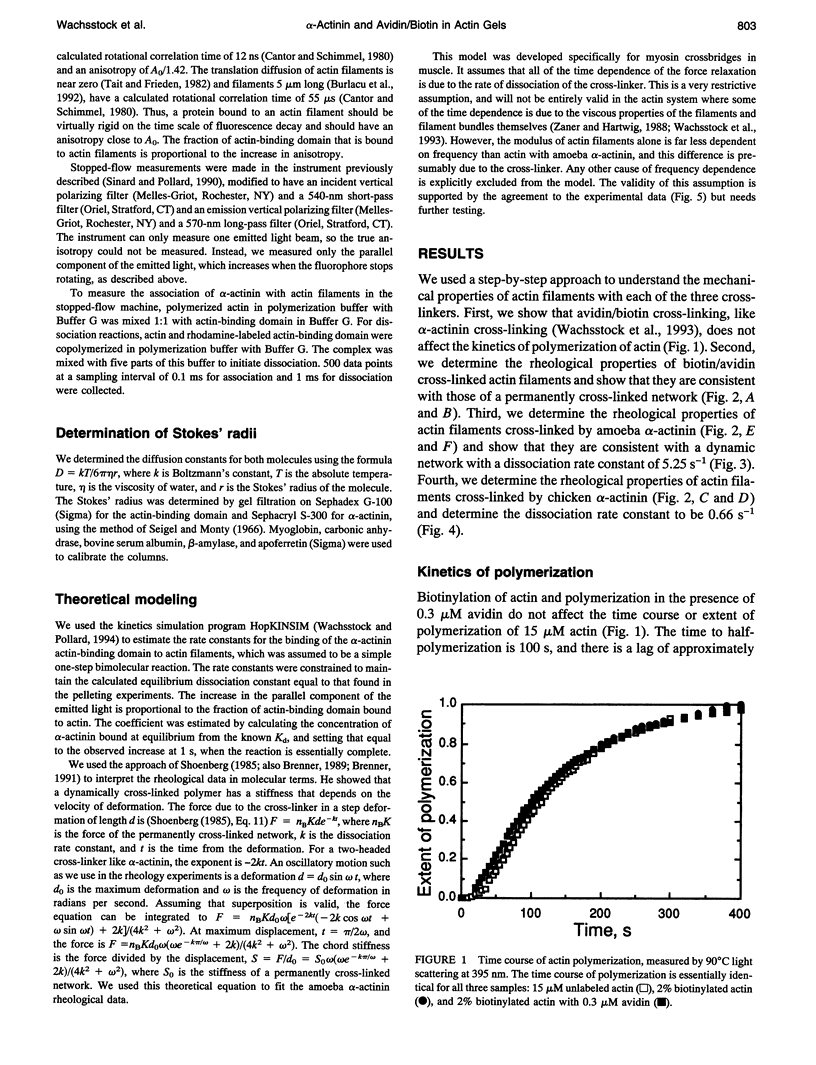
- Green N. M. Avidin and streptavidin. Methods Enzymol. 1990;184:51–67. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)84259-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Shevlin P. The architecture of actin filaments and the ultrastructural location of actin-binding protein in the periphery of lung macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):1007–1020. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Hvidt S., Lamb J., Stossel T. P. Resemblance of actin-binding protein/actin gels to covalently crosslinked networks. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):89–92. doi: 10.1038/345089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
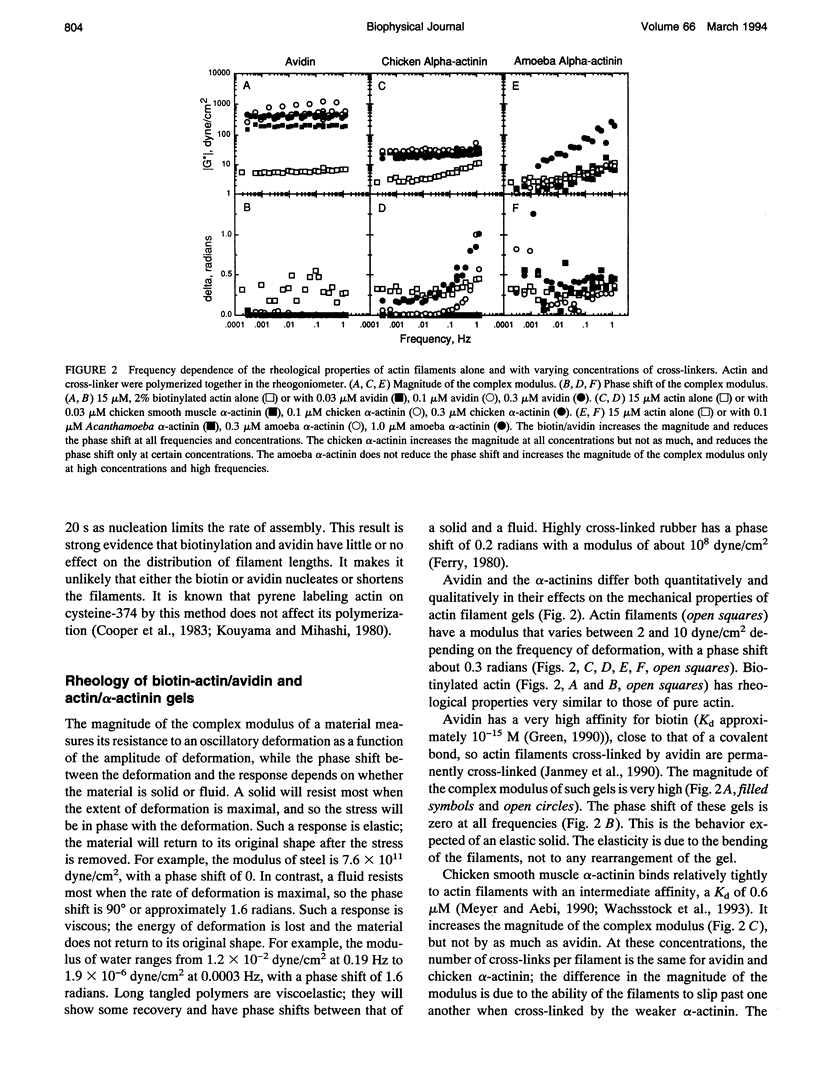
- Janmey P. A., Hvidt S., Peetermans J., Lamb J., Ferry J. D., Stossel T. P. Viscoelasticity of F-actin and F-actin/gelsolin complexes. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8218–8227. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson L. W., Sellers J. R., Taylor D. L. Actin-binding proteins regulate the work performed by myosin II motors on single actin filaments. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;22(4):274–280. doi: 10.1002/cm.970220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jockusch B. M., Isenberg G. Interaction of alpha-actinin and vinculin with actin: opposite effects on filament network formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3005–3009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Mihashi K. Pulse-fluorometry study on actin and heavy meromyosin using F-actin labelled with N-(1-pyrene)maleimide. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(2):279–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciver S. K., Wachsstock D. H., Schwarz W. H., Pollard T. D. The actin filament severing protein actophorin promotes the formation of rigid bundles of actin filaments crosslinked with alpha-actinin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1621–1628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. K., Aebi U. Bundling of actin filaments by alpha-actinin depends on its molecular length. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2013–2024. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal B., Sanger J. M., Sanger J. W. Binding and distribution of fluorescently labeled filamin in permeabilized and living cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;8(4):345–359. doi: 10.1002/cm.970080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J., Gukelberger G., Schick K. L., Zaner K. S. Probe diffusion in solutions of filamentous actin formed in the presence of gelsolin. Biopolymers. 1991 Oct;31(11):1265–1271. doi: 10.1002/bip.360311104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrup S. H., Erickson H. P. Kinetics of protein-protein association explained by Brownian dynamics computer simulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3338–3342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavalko F. M., Burridge K. Disruption of the actin cytoskeleton after microinjection of proteolytic fragments of alpha-actinin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):481–491. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. Cell division: direct measurement of maximum tension exerted by furrow of echinoderm eggs. Science. 1967 Jun 2;156(3779):1241–1243. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3779.1241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
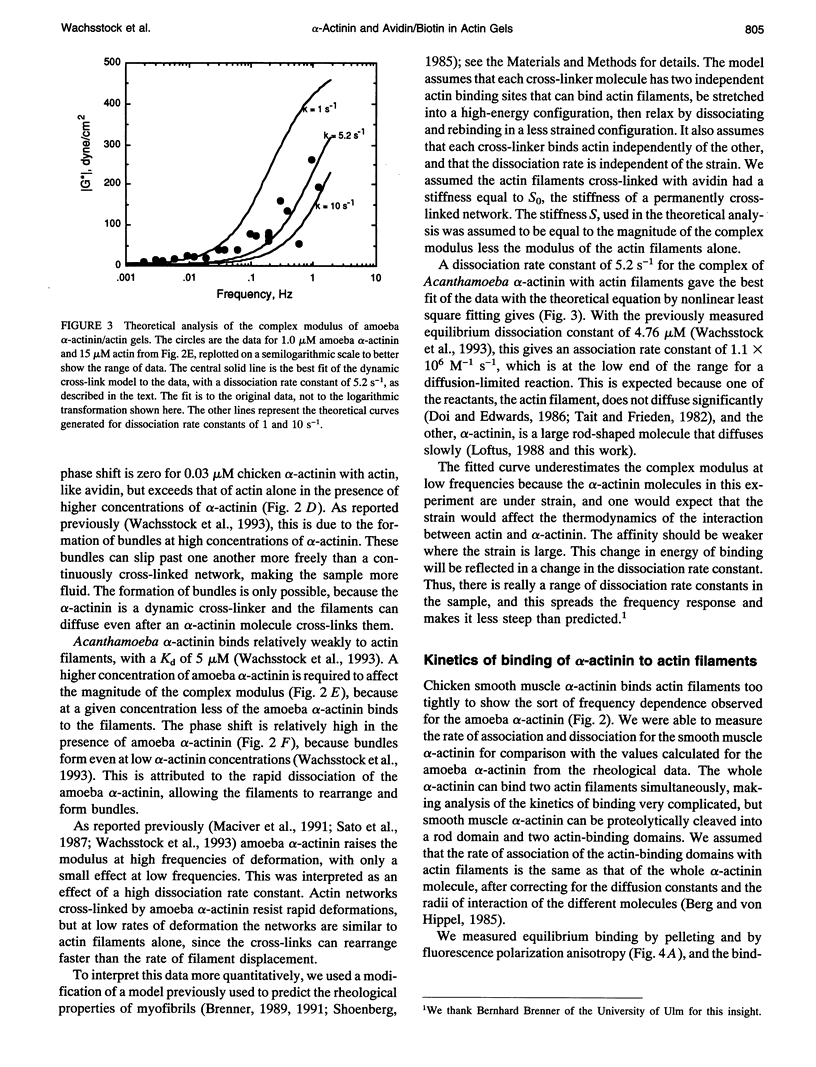
- Sato M., Leimbach G., Schwarz W. H., Pollard T. D. Mechanical properties of actin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8585–8592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Schwarz W. H., Pollard T. D. Dependence of the mechanical properties of actin/alpha-actinin gels on deformation rate. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):828–830. doi: 10.1038/325828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M. Equilibrium muscle cross-bridge behavior. Theoretical considerations. Biophys J. 1985 Sep;48(3):467–475. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83802-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinard J. H., Pollard T. D. Acanthamoeba myosin-II minifilaments assemble on a millisecond time scale with rate constants greater than those expected for a diffusion limited reaction. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3654–3660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
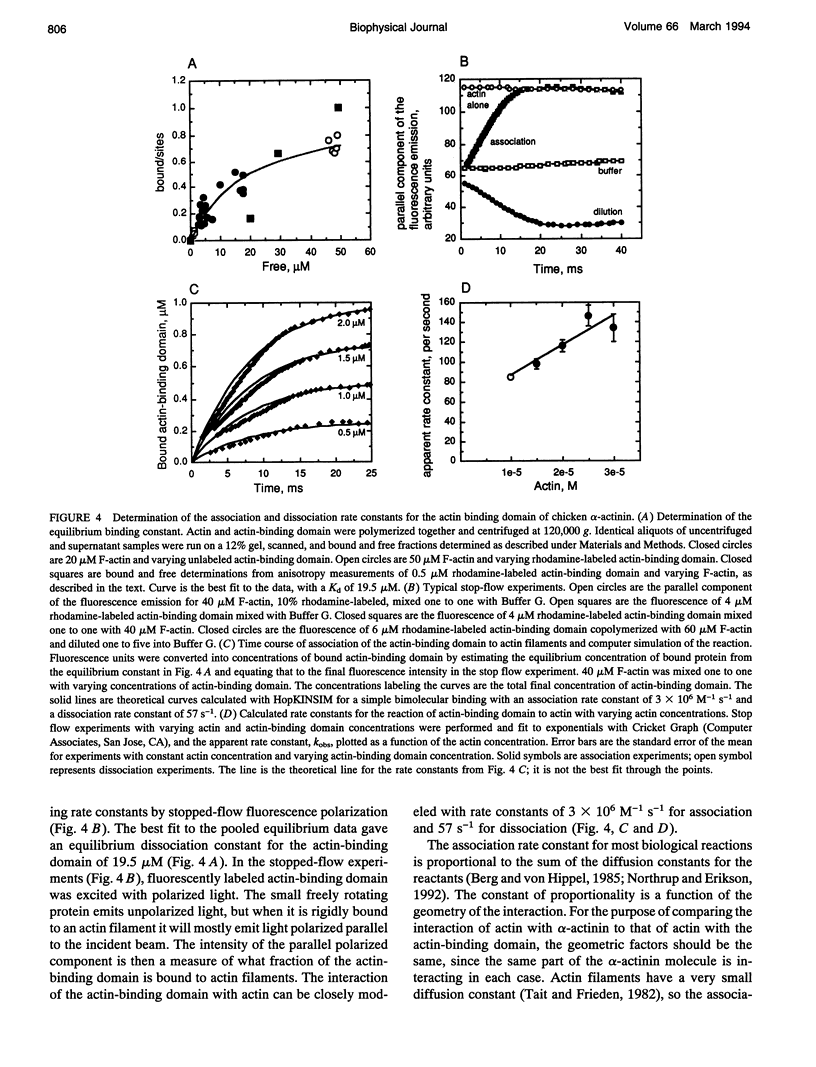
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Contribution of actin to the structure of the cytoplasmic matrix. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 2):15s–21s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.15s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait J. F., Frieden C. Polymerization and gelation of actin studied by fluorescence photobleaching recovery. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 20;21(15):3666–3674. doi: 10.1021/bi00258a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsstock D. H., Schwartz W. H., Pollard T. D. Affinity of alpha-actinin for actin determines the structure and mechanical properties of actin filament gels. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81059-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A., Maciver S. F-actin capping proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;5(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaner K. S., Hartwig J. H. The effect of filament shortening on the mechanical properties of gel-filtered actin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4532–4536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


