Abstract
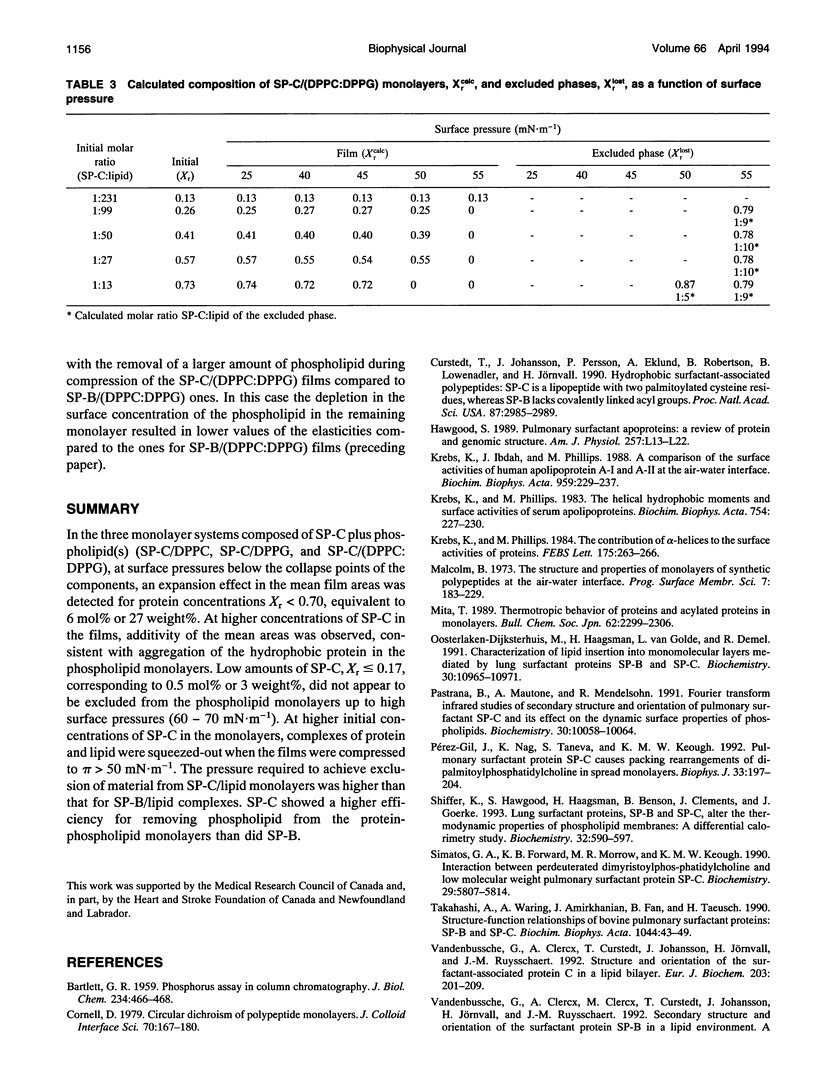
The interaction of the hydrophobic pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), dipalmitoylphosphatidylglycerol (DPPG) and DPPC:DPPG (7:3, mol:mol) in spread monolayers at the air-water interface has been studied. At low concentrations of SP-C (about 0.5 mol% or 3 weight%protein) the protein-lipid films collapsed at surface pressures of about 70 mN.m-1, comparable to those of the lipids alone. At initial protein concentrations higher than 0.8 mol%, or 4 weight%, the isotherms displayed kinks at surface pressures of about 50 mN.m-1 in addition to the collapse plateaux at the higher pressures. The presence of less than 6 mol%, or 27 weight%, of SP-C in the protein-lipid monolayers gave a positive deviation from ideal behavior of the mean areas in the films. Analyses of the mean areas in the protein-lipid films as functions of the monolayer composition and surface pressure showed that SP-C, associated with some phospholipid (about 8-10 lipid molecules per molecule of SP-C), was squeezed out from the monolayers at surface pressures of about 55 mN.m-1. The results suggest a potential role for SP-C to modify the composition of the monolayer at the air-water interface in the alveoli.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curstedt T., Johansson J., Persson P., Eklund A., Robertson B., Löwenadler B., Jörnvall H. Hydrophobic surfactant-associated polypeptides: SP-C is a lipopeptide with two palmitoylated cysteine residues, whereas SP-B lacks covalently linked fatty acyl groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S. Pulmonary surfactant apoproteins: a review of protein and genomic structure. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):L13–L22. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.2.L13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs K. E., Ibdah J. A., Phillips M. C. A comparison of the surface activities of human apolipoproteins A-I and A-II at the air/water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 15;959(3):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs K. E., Phillips M. C. The contribution of alpha-helices to the surface activities of proteins. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 1;175(2):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80748-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs K. E., Phillips M. C. The helical hydrophobic moments and surface activities of serum apolipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Nov 29;754(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90165-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterlaken-Dijksterhuis M. A., Haagsman H. P., van Golde L. M., Demel R. A. Characterization of lipid insertion into monomolecular layers mediated by lung surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 12;30(45):10965–10971. doi: 10.1021/bi00109a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastrana B., Mautone A. J., Mendelsohn R. Fourier transform infrared studies of secondary structure and orientation of pulmonary surfactant SP-C and its effect on the dynamic surface properties of phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 15;30(41):10058–10064. doi: 10.1021/bi00105a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Gil J., Nag K., Taneva S., Keough K. M. Pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C causes packing rearrangements of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine in spread monolayers. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):197–204. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81582-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiffer K., Hawgood S., Haagsman H. P., Benson B., Clements J. A., Goerke J. Lung surfactant proteins, SP-B and SP-C, alter the thermodynamic properties of phospholipid membranes: a differential calorimetry study. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):590–597. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simatos G. A., Forward K. B., Morrow M. R., Keough K. M. Interaction between perdeuterated dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine and low molecular weight pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5807–5814. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi A., Waring A. J., Amirkhanian J., Fan B., Taeusch H. W. Structure-function relationships of bovine pulmonary surfactant proteins: SP-B and SP-C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 1;1044(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90216-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbussche G., Clercx A., Clercx M., Curstedt T., Johansson J., Jörnvall H., Ruysschaert J. M. Secondary structure and orientation of the surfactant protein SP-B in a lipid environment. A Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy study. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 29;31(38):9169–9176. doi: 10.1021/bi00153a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbussche G., Clercx A., Curstedt T., Johansson J., Jörnvall H., Ruysschaert J. M. Structure and orientation of the surfactant-associated protein C in a lipid bilayer. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jan 15;203(1-2):201–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb19848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Pullman A. Do helices in membranes prefer to form bundles or stay dispersed in the lipid phase? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 9;1070(2):493–496. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90091-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C. The surface properties of pure phospholipids in relation to those of lung extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 4;152(2):293–306. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. C., Hawgood S., Hamilton R. L. Changes in lipid structure produced by surfactant proteins SP-A, SP-B, and SP-C. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;5(1):41–50. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita T. Conformation of synthetic polypeptide monolayers. Nature. 1971 Jun 18;231(5303):445–446. doi: 10.1038/231445b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. H., Possmayer F. Comparative studies on the biophysical activities of the low-molecular-weight hydrophobic proteins purified from bovine pulmonary surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 12;961(3):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


