Abstract
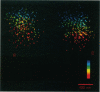
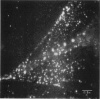
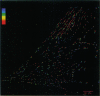
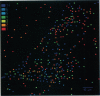
We have developed a technique to detect, recognize, and track each individual low density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) molecule and small receptor clusters on the surface of human skin fibroblasts. Molecular recognition and high precision (30 nm) simultaneous automatic tracking of all of the individual receptors in the cell surface population utilize quantitative time-lapse low light level digital video fluorescence microscopy analyzed by purpose-designed algorithms executed on an image processing work station. The LDL-Rs are labeled with the biologically active, fluorescent LDL derivative dil-LDL. Individual LDL-Rs and unresolved small clusters are identified by measuring the fluorescence power radiated by the sub-resolution fluorescent spots in the image; identification of single particles is ascertained by four independent techniques. An automated tracking routine was developed to track simultaneously, and without user intervention, a multitude of fluorescent particles through a sequence of hundreds of time-lapse image frames. The limitations on tracking precision were found to depend on the signal-to-noise ratio of the tracked particle image and mechanical drift of the microscope system. We describe the methods involved in (i) time-lapse acquisition of the low-light level images, (ii) simultaneous automated tracking of the fluorescent diffraction limited punctate images, (iii) localizing particles with high precision and limitations, and (iv) detecting and identifying single and clustered LDL-Rs. These methods are generally applicable and provide a powerful tool to visualize and measure dynamics and interactions of individual integral membrane proteins on living cell surfaces.
Full text
PDF




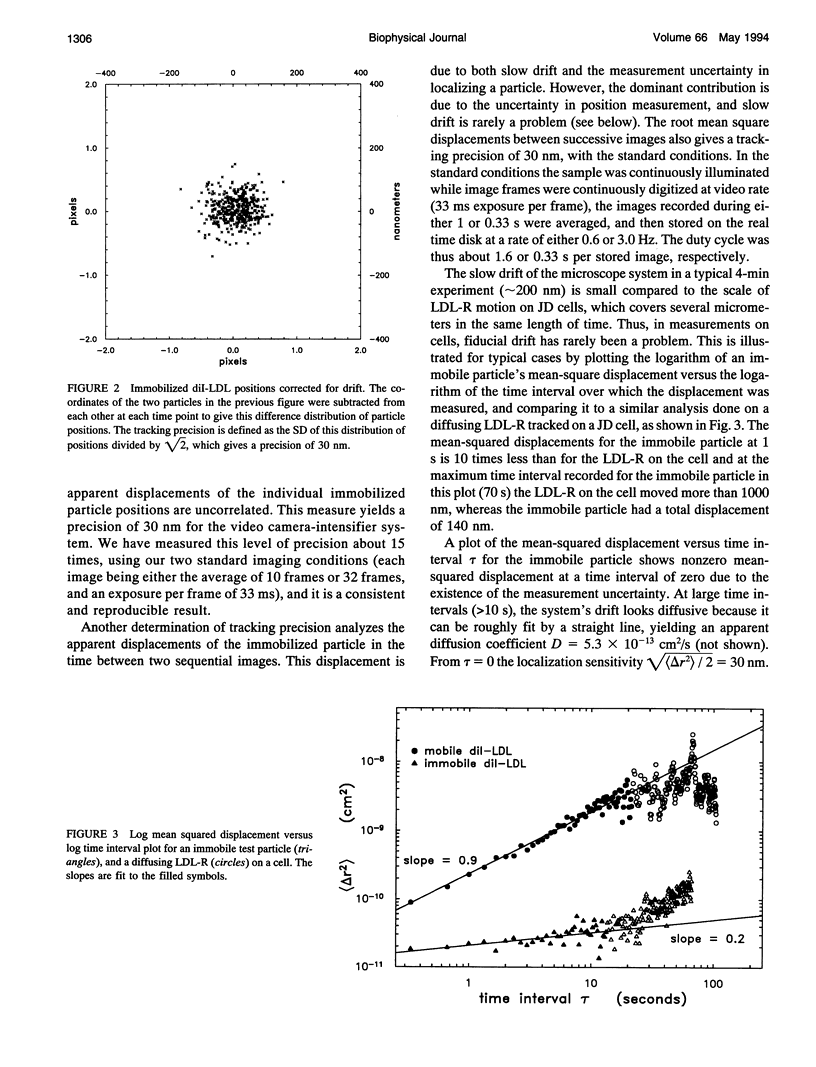
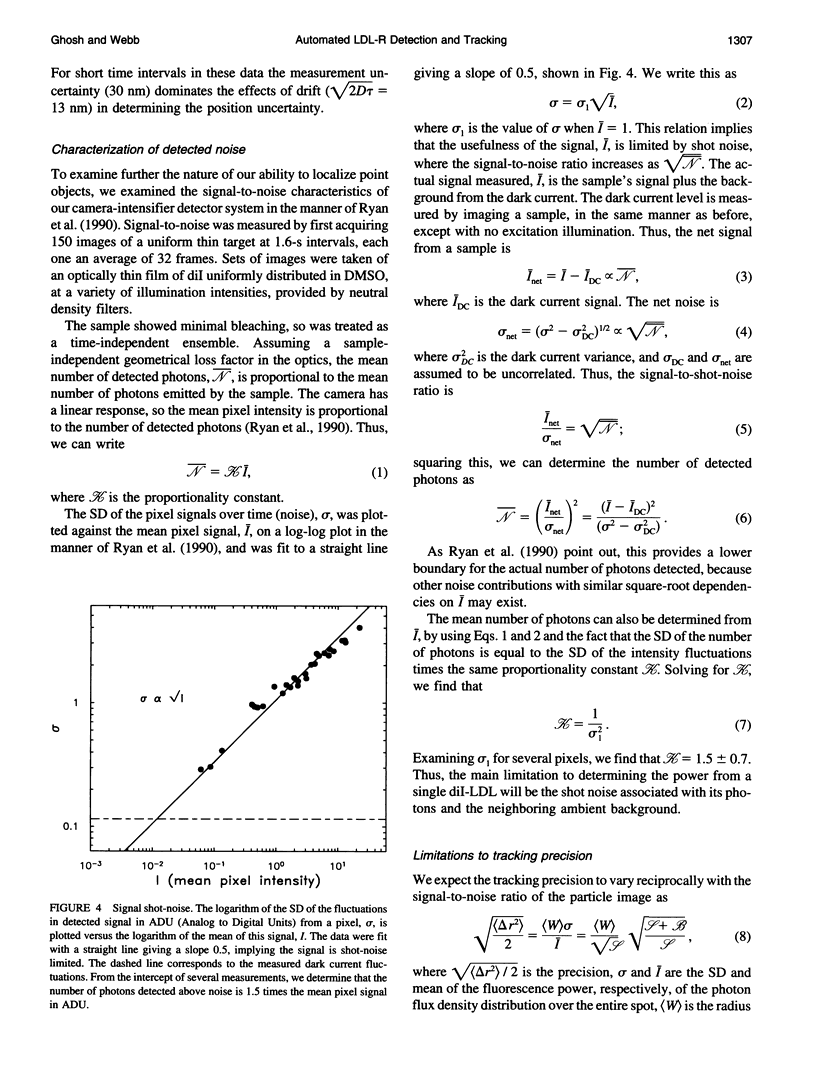






Images in this article
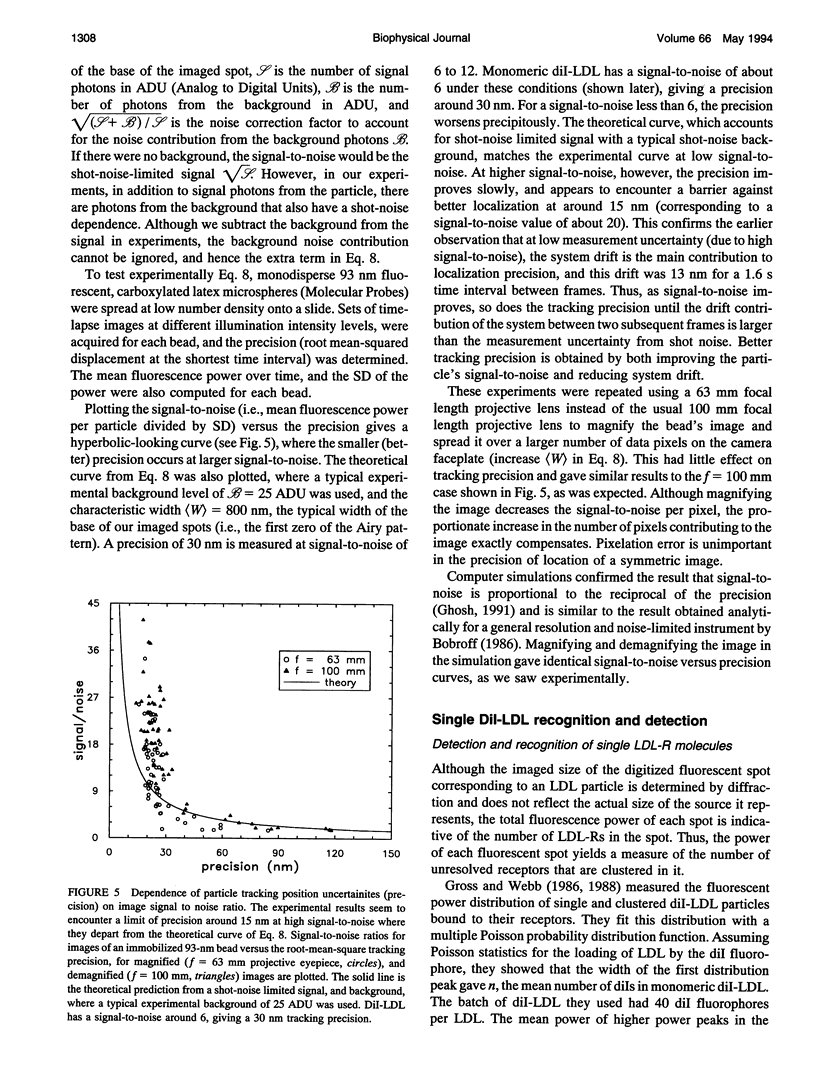
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
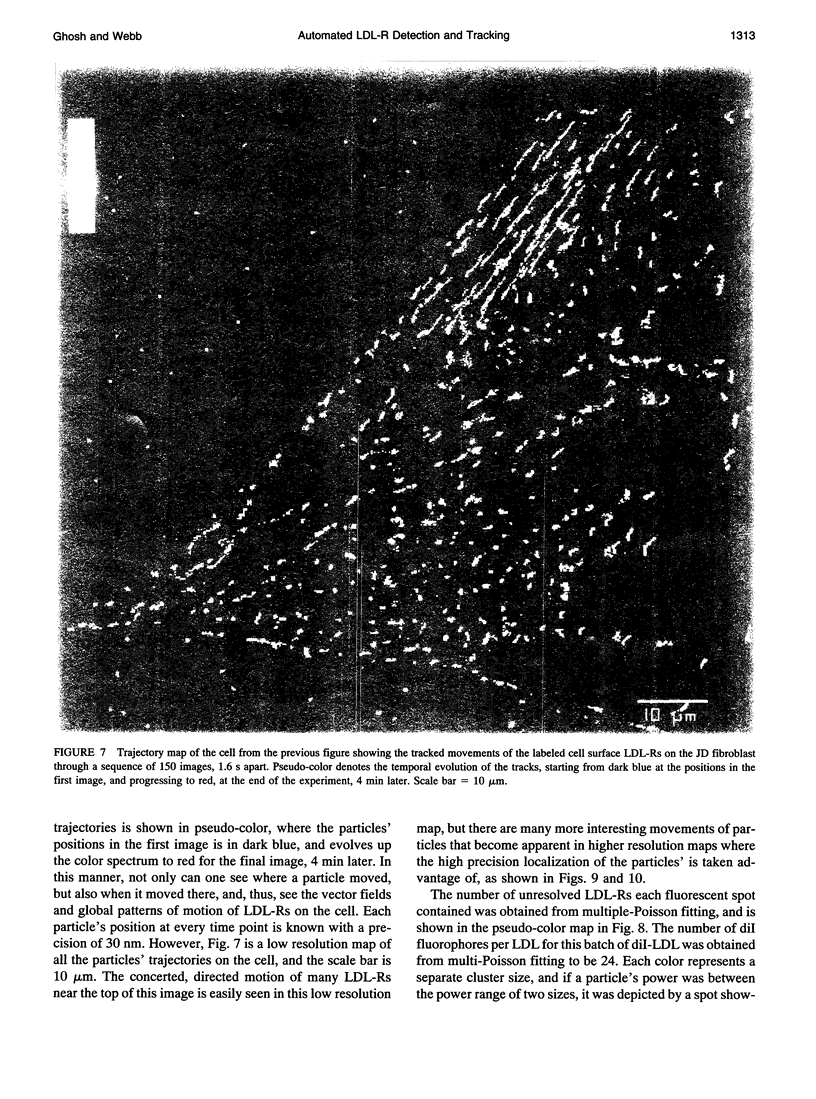
- Anderson C. M., Georgiou G. N., Morrison I. E., Stevenson G. V., Cherry R. J. Tracking of cell surface receptors by fluorescence digital imaging microscopy using a charge-coupled device camera. Low-density lipoprotein and influenza virus receptor mobility at 4 degrees C. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):415–425. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
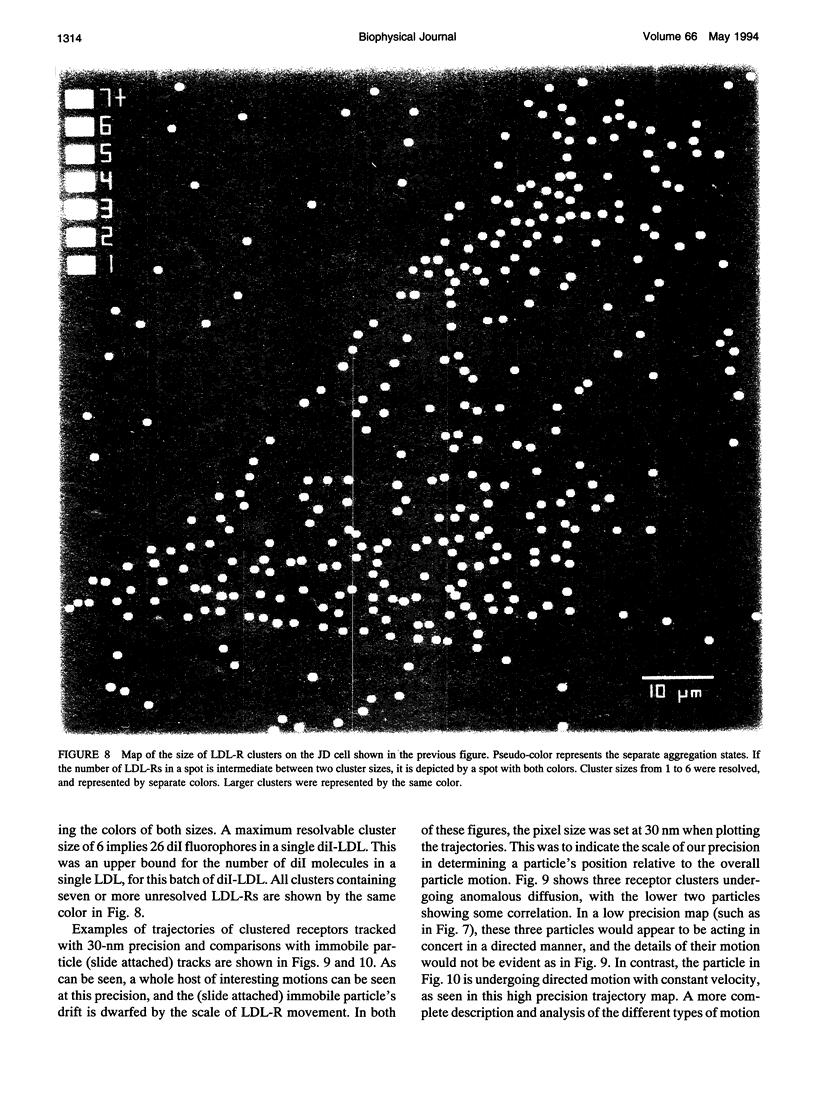
- Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Elson E., Webb W. W. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1055–1069. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85755-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
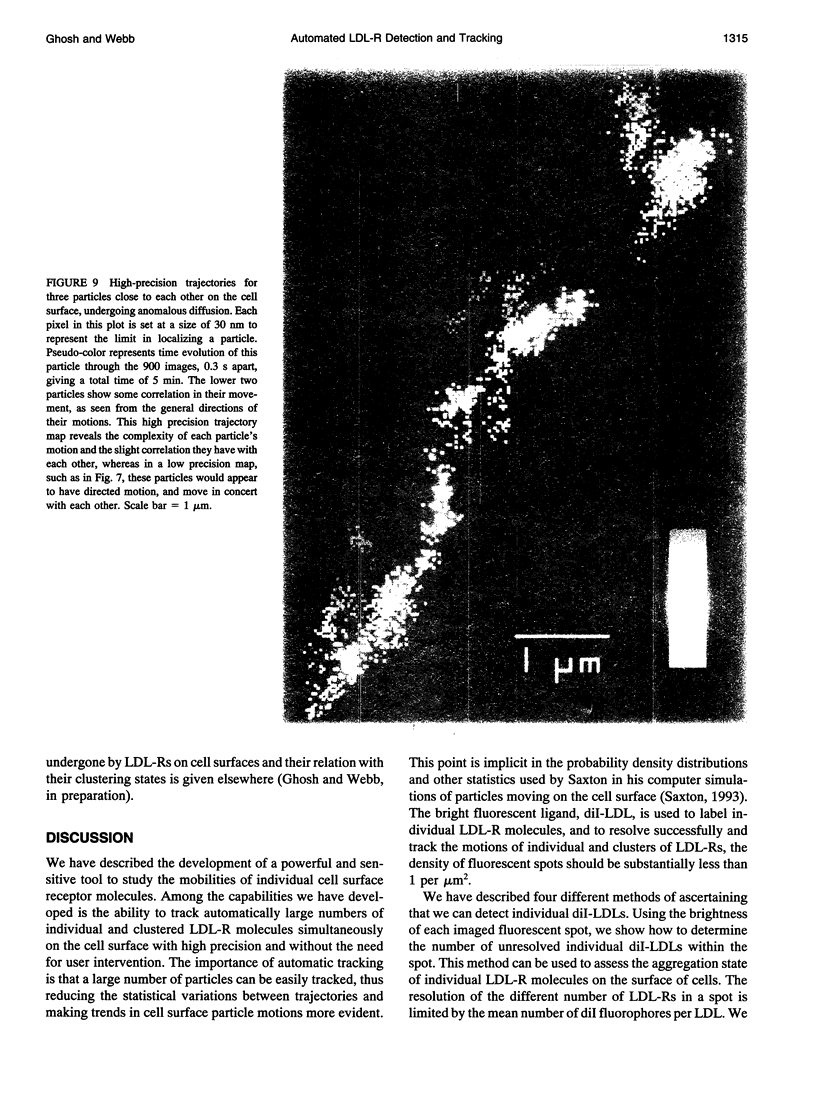
- Axelrod D. Lateral motion of membrane proteins and biological function. J Membr Biol. 1983;75(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01870794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak L. S., Webb W. W. Diffusion of low density lipoprotein-receptor complex on human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):846–852. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak L. S., Webb W. W. Fluorescent low density lipoprotein for observation of dynamics of individual receptor complexes on cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):595–604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J. Rotational and lateral diffusion of membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):289–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denk W., Webb W. W., Hudspeth A. J. Mechanical properties of sensory hair bundles are reflected in their Brownian motion measured with a laser differential interferometer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5371–5375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geerts H., De Brabander M., Nuydens R., Geuens S., Moeremans M., De Mey J., Hollenbeck P. Nanovid tracking: a new automatic method for the study of mobility in living cells based on colloidal gold and video microscopy. Biophys J. 1987 Nov;52(5):775–782. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83271-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelles J., Schnapp B. J., Sheetz M. P. Tracking kinesin-driven movements with nanometre-scale precision. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):450–453. doi: 10.1038/331450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein in cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:241–260. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D., Webb W. W. Molecular counting of low-density lipoprotein particles as individuals and small clusters on cell surfaces. Biophys J. 1986 Apr;49(4):901–911. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83718-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Mahley R. W. Receptor binding of cholesterol-induced high-density lipoproteins containing predominantly apoprotein E to cultured fibroblasts with mutations at the low-density lipoprotein receptor locus. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 2;19(18):4359–4365. doi: 10.1021/bi00559a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K., Elson E., Koppel D., Webb W. Fluorescence photobleaching in cell biology. Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):283–284. doi: 10.1038/295283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusumi A., Sako Y., Yamamoto M. Confined lateral diffusion of membrane receptors as studied by single particle tracking (nanovid microscopy). Effects of calcium-induced differentiation in cultured epithelial cells. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):2021–2040. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81253-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey M., Poo M. M. Protein diffusion in cell membranes: some biological implications. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;87:19–81. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Arnold K. S., Mahley R. W. Rate and equilibrium constants for binding of apo-E HDLc (a cholesterol-induced lipoprotein) and low density lipoproteins to human fibroblasts: evidence for multiple receptor binding of apo-E HDLc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2311–2315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Weinstein J. N., Mahley R. W. Acetoacetylated lipoproteins used to distinguish fibroblasts from macrophages in vitro by fluorescence microscopy. Arteriosclerosis. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):177–185. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.1.3.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. A., Millard P. J., Webb W. W. Imaging [Ca2+]i dynamics during signal transduction. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton M. J. Lateral diffusion in an archipelago. Single-particle diffusion. Biophys J. 1993 Jun;64(6):1766–1780. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81548-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Waggoner A. S., Wang C. H., Hoffman J. F. Studies on the mechanism by which cyanine dyes measure membrane potential in red blood cells and phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3315–3330. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb W. W., Barak L. S., Tank D. W., Wu E. S. Molecular mobility on the cell surface. Biochem Soc Symp. 1981;(46):191–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yechiel E., Edidin M. Micrometer-scale domains in fibroblast plasma membranes. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):755–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]