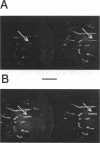
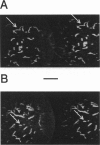
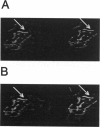
Abstract
Rhodamine-phalloidin was added to F-actin, and the orientation of transition dipoles of the dye was measured in single actin filaments by polarization of fluorescence. Rhodamine-phalloidin was well immobilized on the surface of actin, indicating that changes in orientation of the dye reported changes in orientation of actin monomers. In stationary filaments the dipoles were inclined at 49.3 degrees with respect to the filament axis. The disorganization of dipoles in stationary filaments was insignificant. When the filaments were made to translate, the average orientation of the dye did not change, but disorganization slightly increased. Disorganization increased significantly when filaments were free in solution. We concluded that, within the accuracy of our measurements (approximately 18%), actin monomers did not undergo major reorientations during motion, but that binding of myosin heads deformed the structure of filaments.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreev O. A., Andreeva A. L., Borejdo J. Polarization of fluorescently labeled myosin subfragment-1 fully or partially decorating muscle fibers and myofibrils. Biophys J. 1993 Sep;65(3):1027–1038. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81161-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod D. Carbocyanine dye orientation in red cell membrane studied by microscopic fluorescence polarization. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):557–573. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85271-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett V. A., Fajer P., Polnaszek C. F., Thomas D. D. High-Resolution Detection of muscle Crossbridge Orientation by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):144–147. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83628-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of actin-bound myosin heads in active myofibrils. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 13;32(14):3812–3821. doi: 10.1021/bi00065a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borejdo J., Assulin O., Ando T., Putnam S. Cross-bridge orientation in skeletal muscle measured by linear dichroism of an extrinsic chromophore. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):391–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borejdo J., Burlacu S. Distribution of actin filament lengths and their orientation measured by gel electrophoresis in capillaries. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1991 Aug;12(4):394–407. doi: 10.1007/BF01738594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borejdo J., Burlacu S. Measuring orientation of actin filaments within a cell: orientation of actin in intestinal microvilli. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):300–309. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81060-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borejdo J., Putnam S., Morales M. F. Fluctuations in polarized fluorescence: evidence that muscle cross bridges rotate repetitively during contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6346–6350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borejdo J., Putnam S. Polarization of fluorescence from single skinned glycerinated rabbit psoas fibers in rigor and relaxation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 11;459(3):578–595. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlacu S., Janmey P. A., Borejdo J. Distribution of actin filament lengths measured by fluorescence microscopy. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):C569–C577. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.3.C569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Walker S. B., Pollard T. D. Pyrene actin: documentation of the validity of a sensitive assay for actin polymerization. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Apr;4(2):253–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00712034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix J. A., Verkman A. S. Mapping of fluorescence anisotropy in living cells by ratio imaging. Application to cytoplasmic viscosity. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82526-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelman E. H., DeRosier D. J. Image analysis shows that variations in actin crossover spacings are random, not compensatory. Biophys J. 1992 Nov;63(5):1299–1305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81716-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L. Muscle contraction and free energy transduction in biological systems. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):999–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.3156404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englander S. W., Calhoun D. B., Englander J. J. Biochemistry without oxygen. Anal Biochem. 1987 Mar;161(2):300–306. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90454-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujime S., Ishiwata S. Dynamic study of F-actin by quasielastic scattering of laser light. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 28;62(1):251–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fushimi K., Dix J. A., Verkman A. S. Cell membrane fluidity in the intact kidney proximal tubule measured by orientation-independent fluorescence anisotropy imaging. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82527-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough A. H., Taylor D. L. Fluorescence anisotropy imaging microscopy maps calmodulin binding during cellular contraction and locomotion. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(5):1095–1107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.5.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1356–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Itoh H., Ishiwata S., Hirano K., Nishizaka T., Hayakawa T. Dual-view microscopy with a single camera: real-time imaging of molecular orientations and calcium. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):67–73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Mihashi K. Pulse-fluorometry study on actin and heavy meromyosin using F-actin labelled with N-(1-pyrene)maleimide. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(2):279–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kron S. J., Spudich J. A. Fluorescent actin filaments move on myosin fixed to a glass surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6272–6276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki M., Barden J. A., dos Remedios C. G., Phillips L., Hambly B. D. Interaction of phalloidin with chemically modified actin. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 15;165(1):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki M., Onuma H., Mihashi K. Interaction of actin water epsilon-ATP. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 15;46(1):17–19. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80324-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki M., dos Remedios C. G., Barden J. A. Spatial relationship between the nucleotide-binding site, Lys-61 and Cys-374 in actin and a conformational change induced by myosin subfragment-1 binding. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):339–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nihel T., Mendelson R. A., Botts J. The site of force generation in muscle contraction as deduced from fluorescence polarization studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):274–277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizaka T., Yagi T., Tanaka Y., Ishiwata S. Right-handed rotation of an actin filament in an in vitro motile system. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):269–271. doi: 10.1038/361269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostap E. M., Yanagida T., Thomas D. D. Orientational distribution of spin-labeled actin oriented by flow. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):966–975. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81684-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochniewicz-Nakayama E., Yanagida T., Oosawa F. Studies on conformation of F-actin in muscle fibers in the relaxed state, rigor, and during contraction using fluorescent phalloidin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1663–1667. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochniewicz E., Yanagida T. Inhibition of sliding movement of F-actin by crosslinking emphasizes the role of actin structure in the mechanism of motility. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):761–772. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90397-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutt C. E., Lindberg U. Actin as the generator of tension during muscle contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):319–323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyter D. H., Kron S. J., Toyoshima Y. Y., Spudich J. A., Reisler E. Subtilisin cleavage of actin inhibits in vitro sliding movement of actin filaments over myosin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):465–470. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. A., Ludescher R. D., Dahlberg P. S., Fajer P. G., Bennett R. L., Thomas D. D. Time-resolved rotational dynamics of phosphorescent-labeled myosin heads in contracting muscle fibers. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 30;29(43):10023–10031. doi: 10.1021/bi00495a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K., Ando M., Sutoh K., Toyoshima Y. Y. Site-directed mutations of Dictyostelium actin: disruption of a negative charge cluster at the N terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7711–7714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait J. F., Frieden C. Polymerization-induced changes in the fluorescence of actin labeled with iodoacetamidotetramethylrhodamine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jun;216(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawada K. Physicochemical studies of F-actin-heavy meromyosin solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 25;172(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Cooke R. Orientation of spin-labeled myosin heads in glycerinated muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1980 Dec;32(3):891–906. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85024-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Seidel J. C., Gergely J. Rotational dynamics of spin-labeled F-actin in the sub-millisecond time range. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):257–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonomura Y., Appel P., Morales M. On the molecular weight of myosin. II. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):515–521. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tregear R. T., Mendelson R. A. Polarization from a helix of fluorophores and its relation to that obtained from muscle. Biophys J. 2009 Jan 1;15(5):455–467. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85830-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda T. Q., Kron S. J., Spudich J. A. Myosin step size. Estimation from slow sliding movement of actin over low densities of heavy meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):699–710. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90287-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. L., Taylor D. L. Preparation and characterization of a new molecular cytochemical probe: 5-iodoacetamidofluorescein-labeled actin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Nov;28(11):1198–1206. doi: 10.1177/28.11.6107318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Pope B. Studies on the chymotryptic digestion of myosin. Effects of divalent cations on proteolytic susceptibility. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr;111(2):129–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. G., Mendelson R. A. A comparison of order and orientation of crossbridges in rigor and relaxed muscle fibres using fluorescence polarization. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Dec;4(6):671–693. doi: 10.1007/BF00712160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida T., Nakase M., Nishiyama K., Oosawa F. Direct observation of motion of single F-actin filaments in the presence of myosin. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):58–60. doi: 10.1038/307058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida T., Oosawa F. Polarized fluorescence from epsilon-ADP incorporated into F-actin in a myosin-free single fiber: conformation of F-actin and changes induced in it by heavy meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):507–524. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]