Abstract
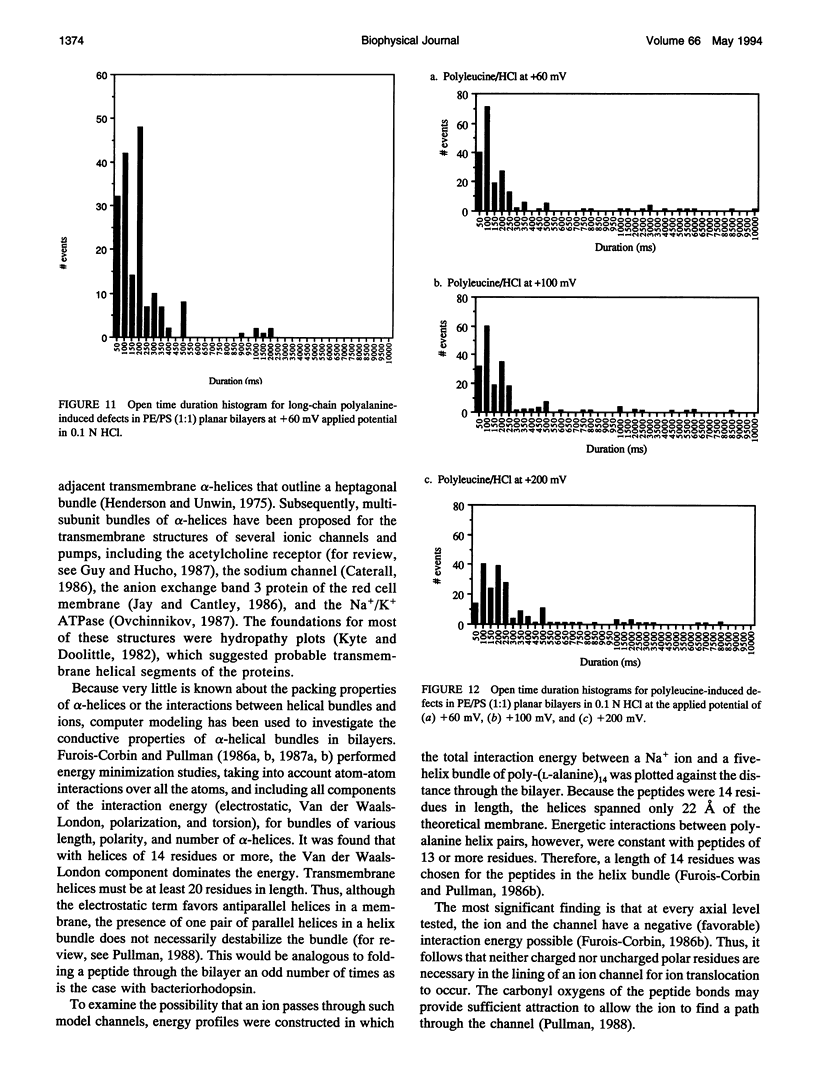
Proton translocation is important in membrane-mediated processes such as ATP-dependent proton pumps, ATP synthesis, bacteriorhodopsin, and cytochrome oxidase function. The fundamental mechanism, however, is poorly understood. To test the theoretical possibility that bundles of hydrophobic alpha-helices could provide a low energy pathway for ion translocation through the lipid bilayer, polyamino acids were incorporated into extruded liposomes and planar lipid membranes, and proton translocation was measured. Liposomes with incorporated long-chain poly-L-alanine or poly-L-leucine were found to have proton permeability coefficients 5 to 7 times greater than control liposomes, whereas short-chain polyamino acids had relatively little effect. Potassium permeability was not increased markedly by any of the polyamino acids tested. Analytical thin layer chromatography measurements of lipid content and a fluorescamine assay for amino acids showed that there were approximately 135 polyleucine or 65 polyalanine molecules associated with each liposome. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy indicated that a major fraction of the long-chain hydrophobic peptides existed in an alpha-helical conformation. Single-channel recording in both 0.1 N HCl and 0.1 M KCl was also used to determine whether proton-conducting channels formed in planar lipid membranes (phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylethanolamine, 1:1). Poly-L-leucine and poly-L-alanine in HCl caused a 10- to 30-fold increase in frequency of conductive events compared to that seen in KCl or by the other polyamino acids in either solution. This finding correlates well with the liposome observations in which these two polyamino acids caused the largest increase in membrane proton permeability but had little effect on potassium permeability. Poly-L-leucine was considerably more conductive than poly-L-alanine due primarily to larger event amplitudes and, to a lesser extent, a higher event frequency. Poly-L-leucine caused two populations of conductive events, one in the 0.1-0.5 pA range, and one in the 1.0-5.0 pA range, whereas nearly all events caused by poly-L-alanine were in the 0.1-0.5 pA range at an applied voltage of +60 mV. The channel-like activity appeared to switch between conductive and nonconductive states, with most open-times in the range of 50-200 ms. We conclude that hydrophobic polyamino acids produce proton-conducting defects in lipid bilayers that may be used to model functional proton channels in biological membranes.
Full text
PDF


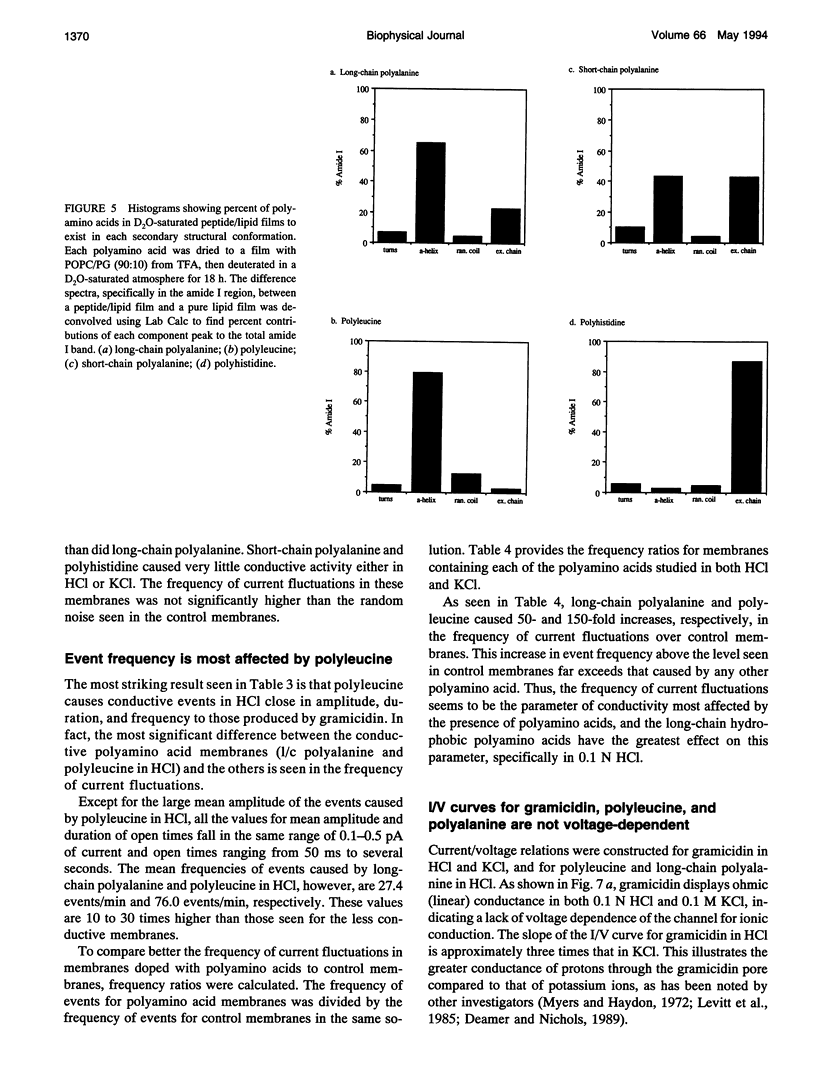
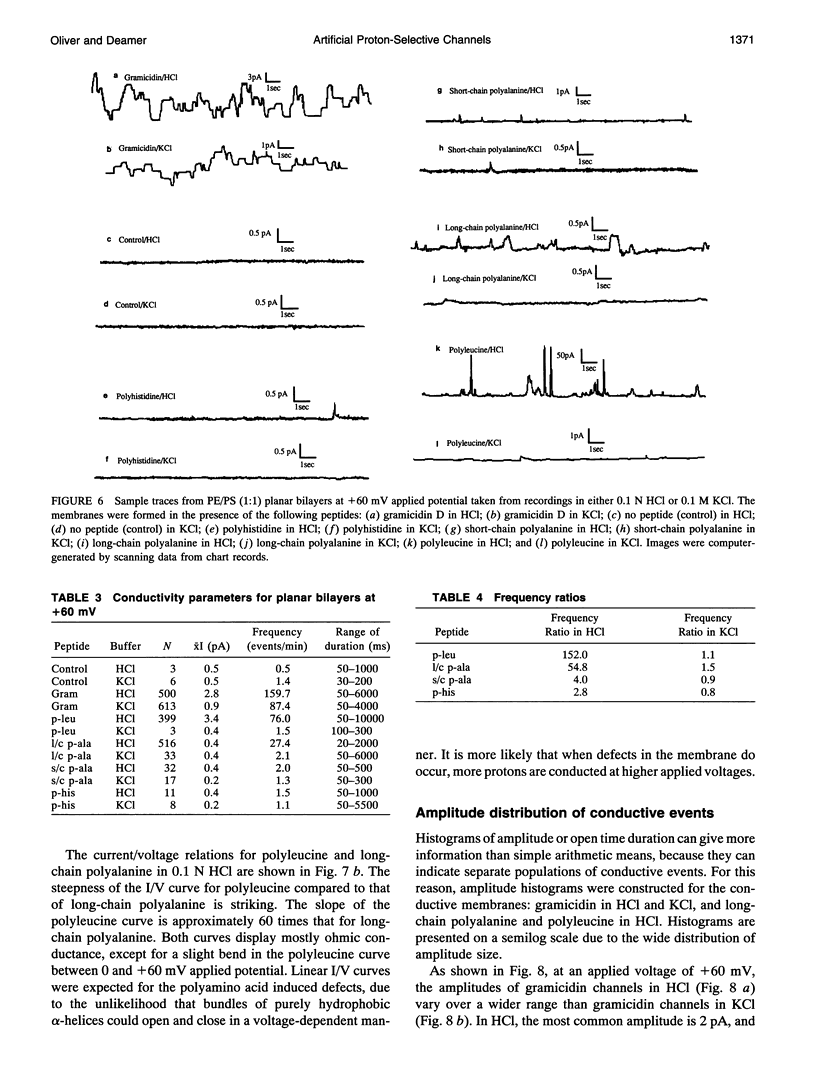
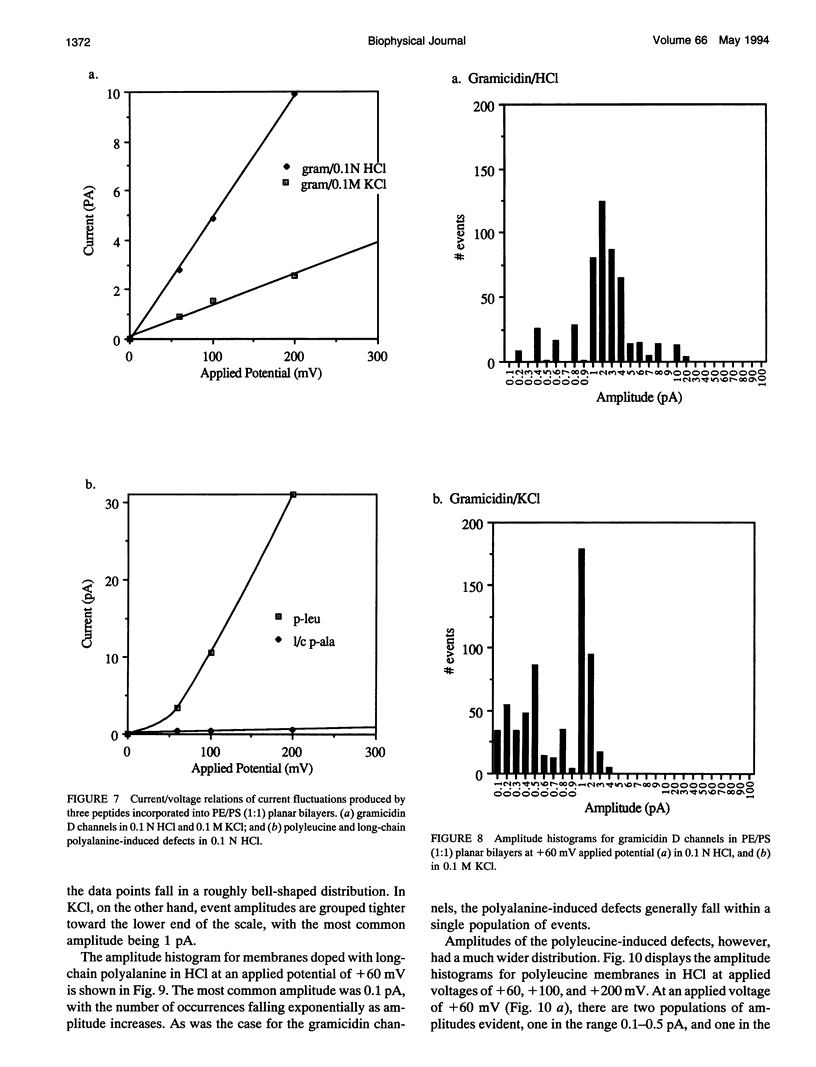
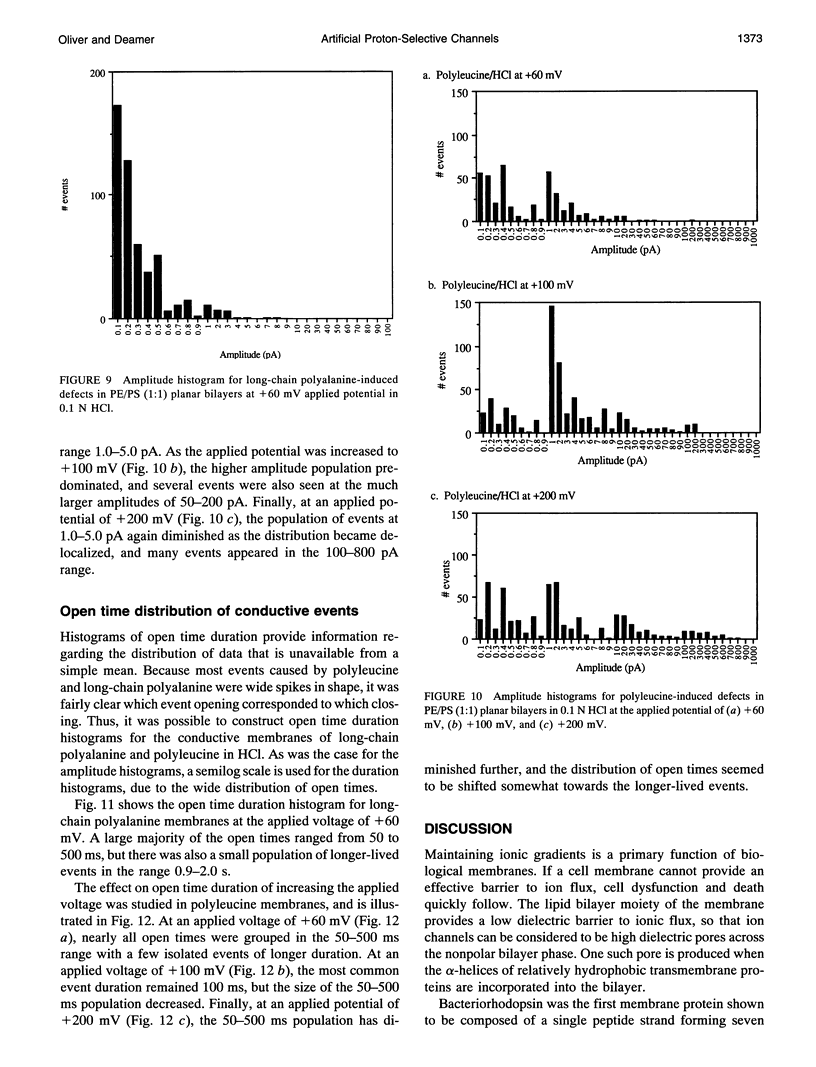




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akeson M., Deamer D. W. Proton conductance by the gramicidin water wire. Model for proton conductance in the F1F0 ATPases? Biophys J. 1991 Jul;60(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82034-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegel C. M., Gould J. M. Kinetics of hydrogen ion diffusion across phospholipid vesicle membranes. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 9;20(12):3474–3479. doi: 10.1021/bi00515a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. D. Bioenergetic coupling to protonmotive force: should we be considering hydronium ion coordination and not group protonation? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Jan;13(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Rothschild K. J. Fourier transform infrared techniques for probing membrane protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:541–570. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byler D. M., Susi H. Examination of the secondary structure of proteins by deconvolved FTIR spectra. Biopolymers. 1986 Mar;25(3):469–487. doi: 10.1002/bip.360250307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Molecular properties of voltage-sensitive sodium channels. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:953–985. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement N. R., Gould J. M. Pyranine (8-hydroxy-1,3,6-pyrenetrisulfonate) as a probe of internal aqueous hydrogen ion concentration in phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1534–1538. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell B. A., Separovic F., Thomas D. E., Atkins A. R., Smith R. Effect of acyl chain length on the structure and motion of gramicidin A in lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Oct 16;985(2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell B. Gramicidin A--phospholipid model systems. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1987 Dec;19(6):655–676. doi: 10.1007/BF00762301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Santis P., Palleschi A., Savino M., Scipioni A., Sesta B., Verdini A. Poly(DL-proline), a synthetic polypeptide behaving as an ion channel across bilayer membranes. Biophys Chem. 1985 Mar;21(3-4):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(85)80008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGrado W. F., Wasserman Z. R., Lear J. D. Protein design, a minimalist approach. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):622–628. doi: 10.1126/science.2464850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Nichols J. W. Proton flux mechanisms in model and biological membranes. J Membr Biol. 1989 Feb;107(2):91–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01871715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Nichols J. W. Proton-hydroxide permeability of liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):165–168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W. Proton permeation of lipid bilayers. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1987 Oct;19(5):457–479. doi: 10.1007/BF00770030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds D. T. The alpha-helix dipole in membranes: a new gating mechanism for ion channels. Eur Biophys J. 1985;13(1):31–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00266307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg M., Hall J. E., Mead C. A. The nature of the voltage-dependent conductance induced by alamethicin in black lipid membranes. J Membr Biol. 1973 Dec 31;14(2):143–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01868075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epand R. M., Surewicz W. K., Hughes D. W., Mantsch H., Segrest J. P., Allen T. M., Anantharamaiah G. M. Properties of lipid complexes with amphipathic helix-forming peptides. Role of distribution of peptide charges. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4628–4635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernster L., Schatz G. Mitochondria: a historical review. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):227s–255s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.227s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillingame R. H. The proton-translocating pumps of oxidative phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1079–1113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
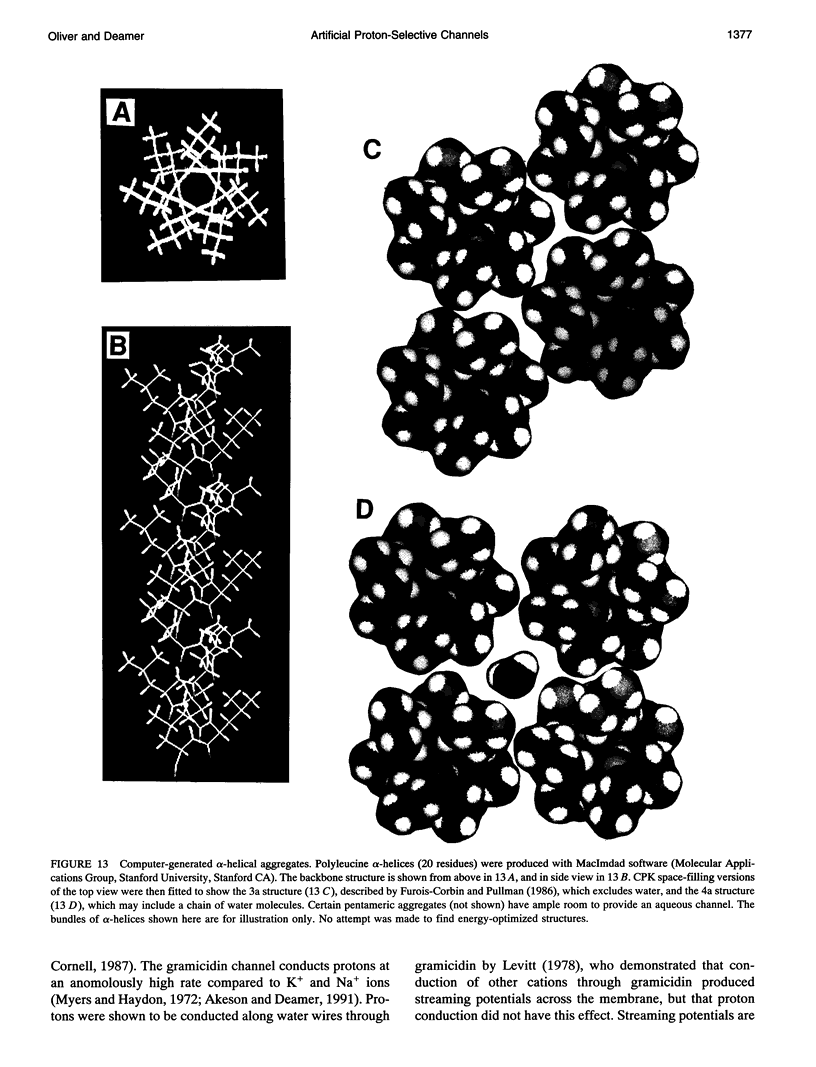
- Furois-Corbin S., Pullman A. Theoretical study of potential ion-channels formed by a bundle of alpha-helices: effect of the presence of polar residues along the channel inner wall. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Feb;4(4):589–597. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10507663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furois-Corbin S., Pullman A. Theoretical study of the packing of alpha-helices into possible transmembrane bundles. Sequences including alanines, leucines and serines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 7;902(1):31–45. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall M. C. Thickness dependence in the action of gramicidin A on lipid bilayers. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Nov;147(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E., Vodyanoy I., Balasubramanian T. M., Marshall G. R. Alamethicin. A rich model for channel behavior. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):233–247. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84151-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Oldani D., Phillips M. C. Mechanism of ion escape from phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine single bilayer vesicles. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4507–4517. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitz F., Spach G., Seta P., Gavach C. Ion conducting pores induced by oligo-L-alanine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 30;107(2):481–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91516-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of purple membrane obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):28–32. doi: 10.1038/257028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. I. Studies of the unit conductance channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):294–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe J., Sebald W. The proton conducting F0-part of bacterial ATP synthases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 9;768(1):1–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(84)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs R. E., White S. H. The nature of the hydrophobic binding of small peptides at the bilayer interface: implications for the insertion of transbilayer helices. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3421–3437. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay D., Cantley L. Structural aspects of the red cell anion exchange protein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:511–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIMM S. Infrared spectra and chain conformation of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:528–540. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano K., Fendler J. H. Pyranine as a sensitive pH probe for liposome interiors and surfaces. pH gradients across phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 18;509(2):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear J. D., Wasserman Z. R., DeGrado W. F. Synthetic amphiphilic peptide models for protein ion channels. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1177–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.2453923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G., Elias S. R., Hautman J. M. Number of water molecules coupled to the transport of sodium, potassium and hydrogen ions via gramicidin, nonactin or valinomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 22;512(2):436–451. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimms L. T., Zampighi G., Nozaki Y., Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Phospholipid vesicle formation and transmembrane protein incorporation using octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):833–840. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers V. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. II. The ion selectivity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Tristram-Nagle S. Hydrogen bonded chain mechanisms for proton conduction and proton pumping. J Membr Biol. 1983;74(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01870590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. W., Deamer D. W. Net proton-hydroxyl permeability of large unilamellar liposomes measured by an acid-base titration technique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2038–2042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa S. Molecular mechanism of proton translocation by the cytochrome system and the ATPase of mitochondria. Role of proteins. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1982 Apr;14(2):69–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00745021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parente R. A., Nadasdi L., Subbarao N. K., Szoka F. C., Jr Association of a pH-sensitive peptide with membrane vesicles: role of amino acid sequence. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8713–8719. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington R. M., Fisher R. R. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide modification of bovine heart mitochondrial transhydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8963–8969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins W. R., Cafiso D. S. An electrical and structural characterization of H+/OH- currents in phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2270–2276. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portlock S. H., Clague M. J., Cherry R. J. Leakage of internal markers from erythrocytes and lipid vesicles induced by melittin, gramicidin S and alamethicin: a comparative study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 30;1030(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90231-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman A. Theoretical studies on the formation and properties of bundles of alpha-helices and their aptitude to form ion-channels. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;273:113–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romans A. Y., Allen T. M., Meckes W., Chiovetti R., Jr, Sheng L., Kercret H., Segrest J. P. Incorporation of the transmembrane hydrophobic domain of glycophorin into small unilamellar phospholipid vesicles. Ion flux studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 20;642(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., De Loof H., Dohlman J. G., Brouillette C. G., Anantharamaiah G. M. Amphipathic helix motif: classes and properties. Proteins. 1990;8(2):103–117. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Thomas D. E., Separovic F., Atkins A. R., Cornell B. A. Determination of the structure of a membrane-incorporated ion channel. Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance studies of gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1989 Aug;56(2):307–314. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82677-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susi H., Byler D. M. Protein structure by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: second derivative spectra. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson D. C., Andreoli T. E., Tieffenberg M., Cook P. The effects of macrocyclic compounds on cation transport in sheep red cells and thin and thick lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1968 May;51(5 Suppl):373S+–373S+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A. Membrane protein folding: motifs and predictions. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;273:133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M., Krab K., Saraste M. Proton-translocating cytochrome complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:623–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]