Abstract
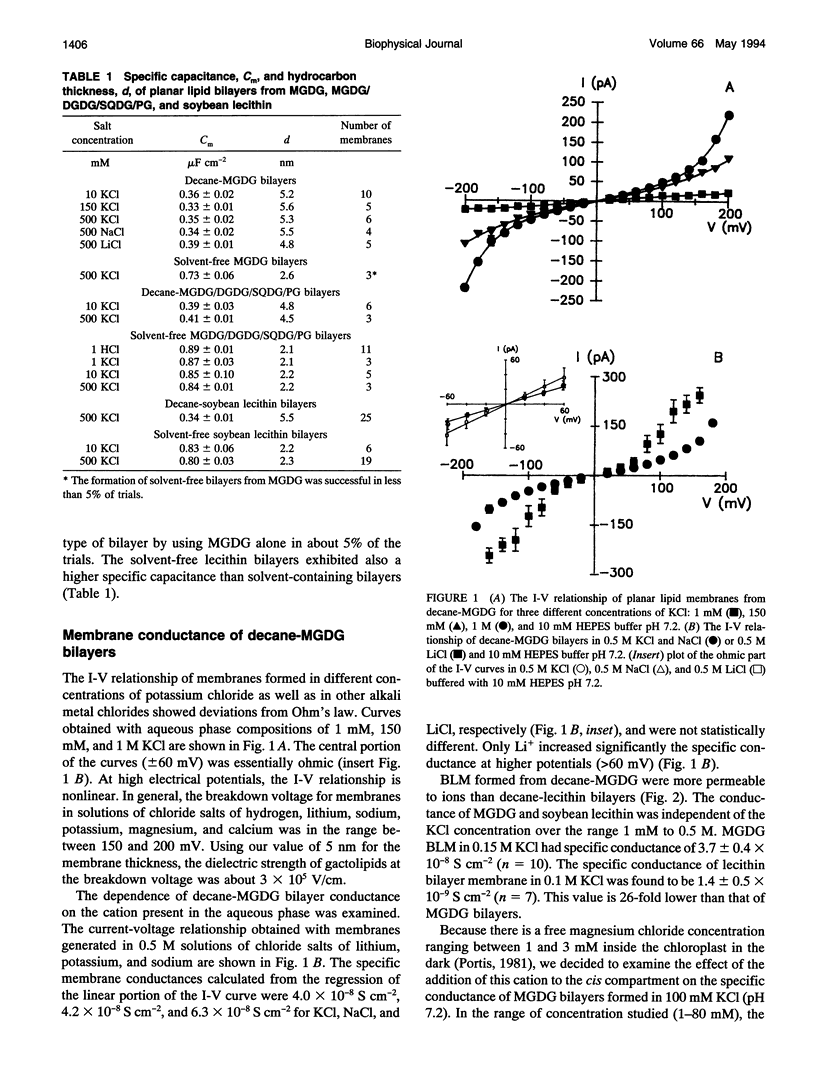
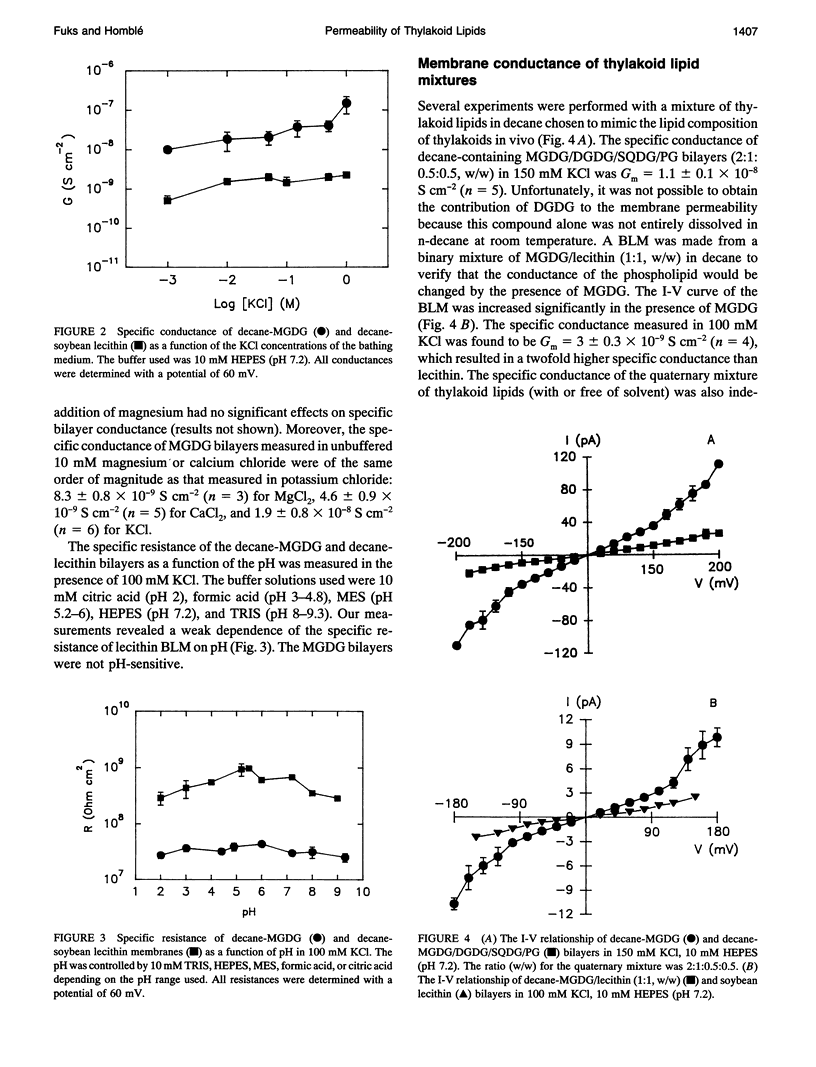
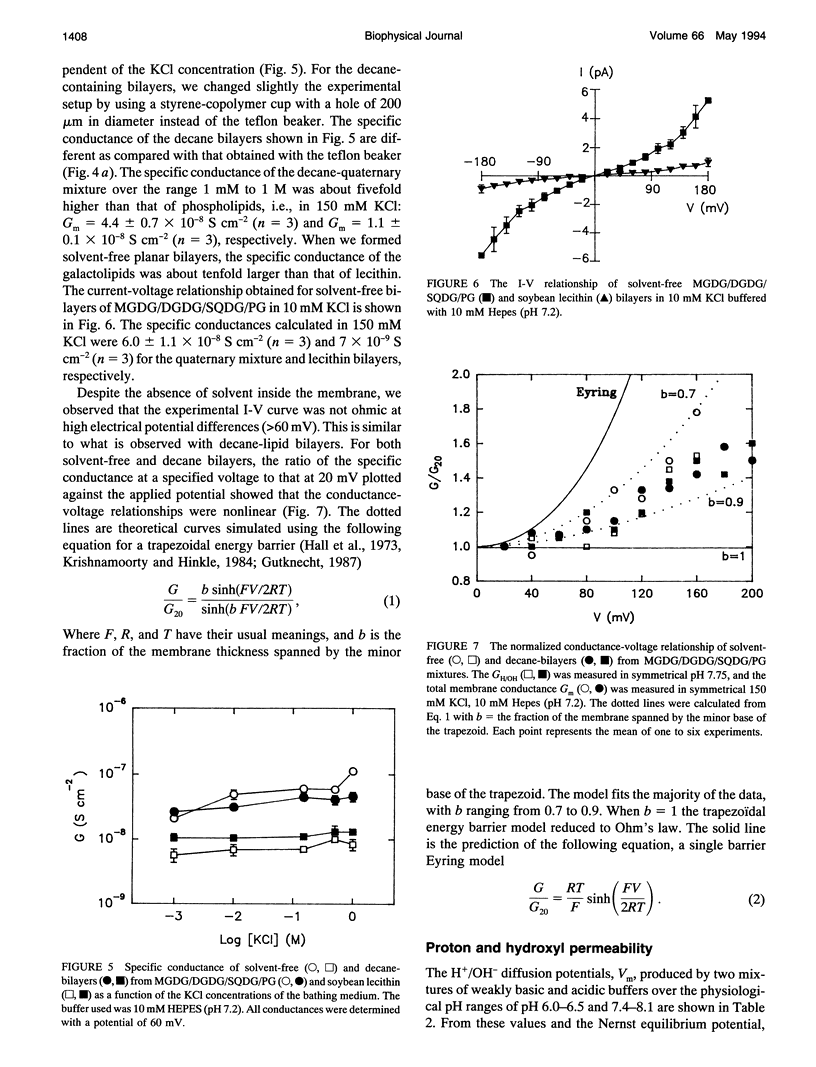
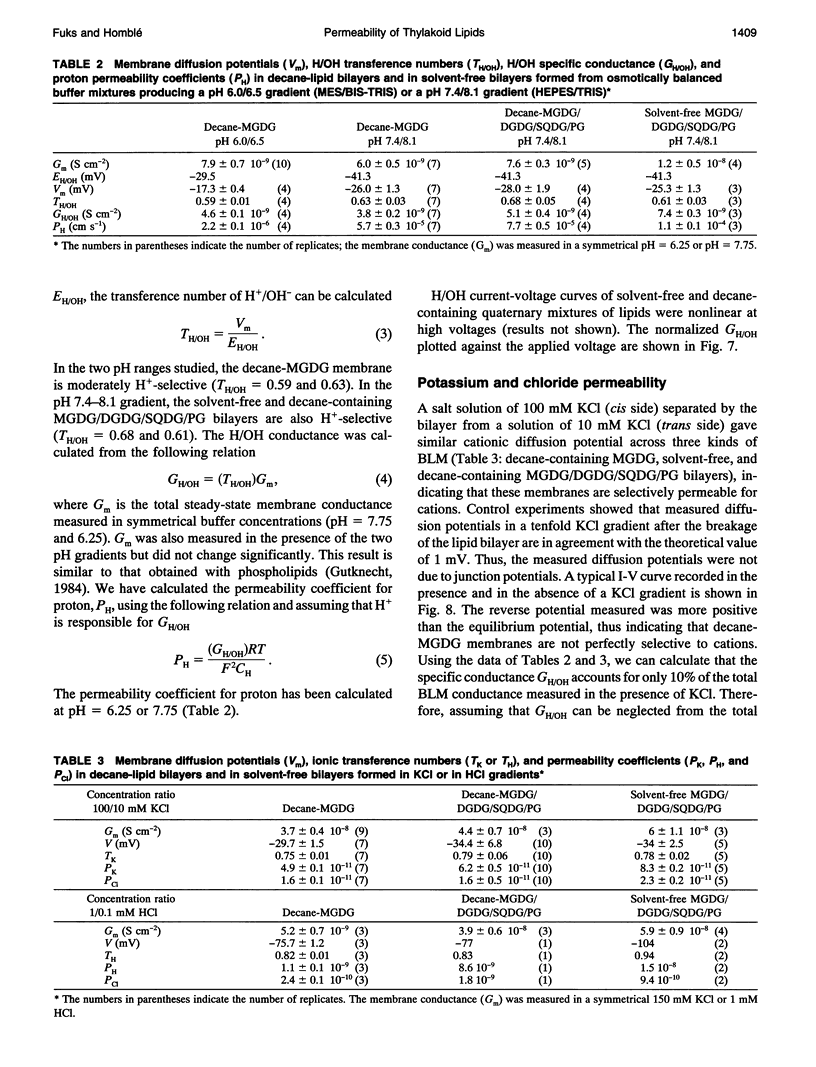
Electrical measurements were carried out on planar lipid membranes from thylakoid lipids. The specific capacitance of membranes formed from decane-containing monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG), which accounts for 57% of the total lipid content of thylakoids, showed that it adopted a bilayer structure. Solvent-free bilayers of MGDG were not formed, with very rare exceptions, indicating that decane is required to stabilize the planar conformation. However, this cone-shaped lipid produces bilayer structures in combination with other cylindrical thylakoid lipids even in the absence of organic solvent. We compared the properties of solvent-free and decane-containing bilayers from MGDG, soybean lecithin, and the quaternary mixture of lipids similar to that found in vivo. The conductance of decane-MGDG was 26 times higher than that of decane-lecithin. The flux through the decane-lecithin bilayer was found to be slightly dependent on pH, whereas the decane-MGDG membrane was not. The specific conductance of bilayers formed from the quaternary mixture of lipids was 5 to 10 times larger than lecithin (with alkane or not). Further experiments with bilayers made in the presence of a KCl gradient showed that decane-MGDG, decane-MGDG/DGDG/SQDG/PG, and solvent-free MGDG/DGDG/SQDG/PG were cation-selective. The permeability coefficient for potassium ranged from 4.9 to 8.3 x 10(-11) cm s-1. The permeability coefficient for protons in galactolipids, however, was determined to be about six orders of magnitude higher than the value for potassium ions. The HCl permeation mechanism through the lipid membranes was determined from diffusion potentials measured in HCl gradients. Our results suggest that HCl was not transported as neutral molecules. The data is discussed with regard to the function of galactolipids in the ion transport through thylakoid membranes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreoli T. E., Bangham J. A., Tosteson D. C. The formation and properties of thin lipid membranes from HK and LK sheep red cell lipids. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6):1729–1749. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.1729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreoli T. E., Tieffenberg M., Tosteson D. C. The effect of valinomycin on the ionic permeability of thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Dec;50(11):2527–2545. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.11.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber J. Stimulation of millisecond delayed light emission by KCl and NaCl gradients as a means of investigating the ionic permeability properties of the thylakoid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 12;275(1):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Fröhlich O., Läuger P., Montal M. Electrical capacity of black lipid films and of lipid bilayers made from monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 3;394(3):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Nichols J. W. Proton-hydroxide permeability of liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):165–168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W. Proton permeation of lipid bilayers. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1987 Oct;19(5):457–479. doi: 10.1007/BF00770030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorne A. J., Joyard J., Douce R. Do thylakoids really contain phosphatidylcholine? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):71–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas D. L., Korenstein R., Malkin S. Electrophotoluminescence and the electrical properties of the photosynthetic membrane. I. Initial kinetics and the charging capacitance of the membrane. Biophys J. 1984 Feb;45(2):363–373. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84160-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewelling R. F., Hubbell W. L. The membrane dipole potential in a total membrane potential model. Applications to hydrophobic ion interactions with membranes. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):541–552. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83664-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzesiek S., Dencher N. A. Dependency of delta pH-relaxation across vesicular membranes on the buffering power of bulk solutions and lipids. Biophys J. 1986 Aug;50(2):265–276. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83460-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J. Proton conductance through phospholipid bilayers: water wires or weak acids? J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1987 Oct;19(5):427–442. doi: 10.1007/BF00770028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J. Proton/hydroxide conductance through lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1984;82(1):105–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01870737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J., Tosteson D. C. Ionic peremability of thin lipid membranes. Effects of n-alkyl alcohols, polyvalent cations, and a secondary amine. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Mar;55(3):359–374. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J., Walter A. Hydroxyl ion permeability of lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 6;645(1):161–162. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90525-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J., Walter A. Transport of protons and hydrochloric acid through lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 20;641(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90582-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Oldani D., Phillips M. C. Mechanism of ion escape from phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine single bilayer vesicles. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4507–4517. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hind G., Nakatani H. Y., Izawa S. Light-dependent redistribution of ions in suspensions of chloroplast thylakoid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1484–1488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamoorthy G., Hinkle P. C. Non-ohmic proton conductance of mitochondria and liposomes. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1640–1645. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER P., RUDIN D. O., TIEN H. T., WESCOTT W. C. Reconstitution of cell membrane structure in vitro and its transformation into an excitable system. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:979–980. doi: 10.1038/194979a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Mueller P. Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers and a study of their electrical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3561–3566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F. Theory of passive proton conductance in lipid bilayers. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1987 Oct;19(5):413–426. doi: 10.1007/BF00770027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Tristram-Nagle S. Hydrogen bonded chain mechanisms for proton conduction and proton pumping. J Membr Biol. 1983;74(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01870590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. W., Deamer D. W. Net proton-hydroxyl permeability of large unilamellar liposomes measured by an acid-base titration technique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2038–2042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki S. The electrical capacitance of phospholipid membranes. Biophys J. 1969 Oct;9(10):1195–1205. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86445-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki S. The variation of the direct current resistance of lipid bilayers. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1969 Jul;30(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(69)90410-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldani D., Hauser H., Nichols B. W., Phillips M. C. Monolayer characteristics of some glycolipids at the air-water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 28;382(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A. R. Evidence of a Low Stromal Mg Concentration in Intact Chloroplasts in the Dark: I. STUDIES WITH THE IONOPHORE A23187. Plant Physiol. 1981 May;67(5):985–989. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.5.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redwood W. R., Pfeiffer F. R., Weisbach J. A., Thompson T. E. Physical properties of bilayer membranes formed from a synthetic saturated phospholipid in n-decane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes J., Latorre R. Effect of the anesthetics benzyl alcohol and chloroform on bilayers made from monolayers. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):259–279. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85175-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. N., Thompson T. E. The function of phospholipid polar groups in membranes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 1;76(1):16–19. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossignol M., Thomas P., Grignon C. Proton permeability of liposomes from natural phospholipid mixtures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 22;684(2):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. G., Green J. P., Nichols B. W. The phase behavior of monogalactosyl, digalactosyl, and sulphoquinovosyl diglycerides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 18;311(4):531–544. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., Lis L. J., MacDonald R. C., Kauffman J. W. The noneffect of a large linear hydrocarbon, squalene, on the phosphatidylcholine packing structure. Biophys J. 1977 Jul;19(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85570-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tester M., Blatt M. R. Direct measurement of k channels in thylakoid membranes by incorporation of vesicles into planar lipid bilayers. Plant Physiol. 1989 Sep;91(1):249–252. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.1.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima Y., Thompson T. E. Chloride flux in bilayer membranes: the electrically silent chloride flux in semispherical bilayers. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 8;14(7):1518–1524. doi: 10.1021/bi00678a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H., Petersen D. C., Simon S., Yafuso M. Formation of planar bilayer membranes from lipid monolayers. A critique. Biophys J. 1976 May;16(5):481–489. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85703-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


