Abstract
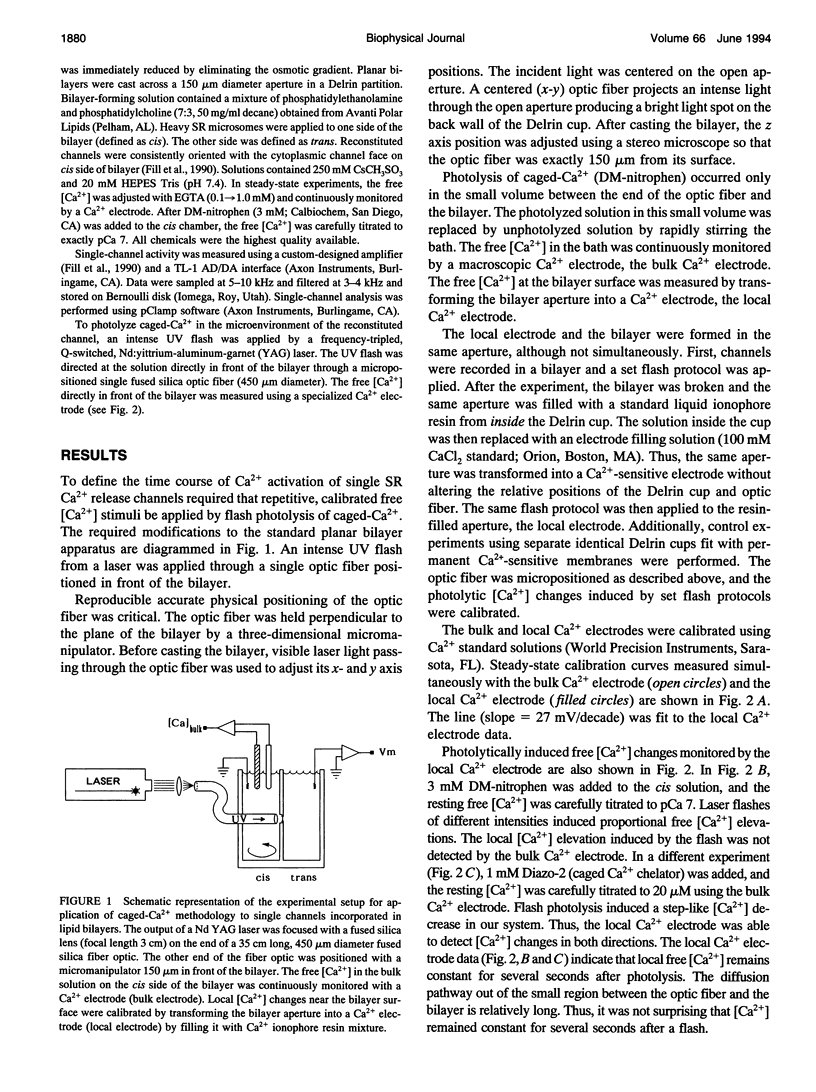
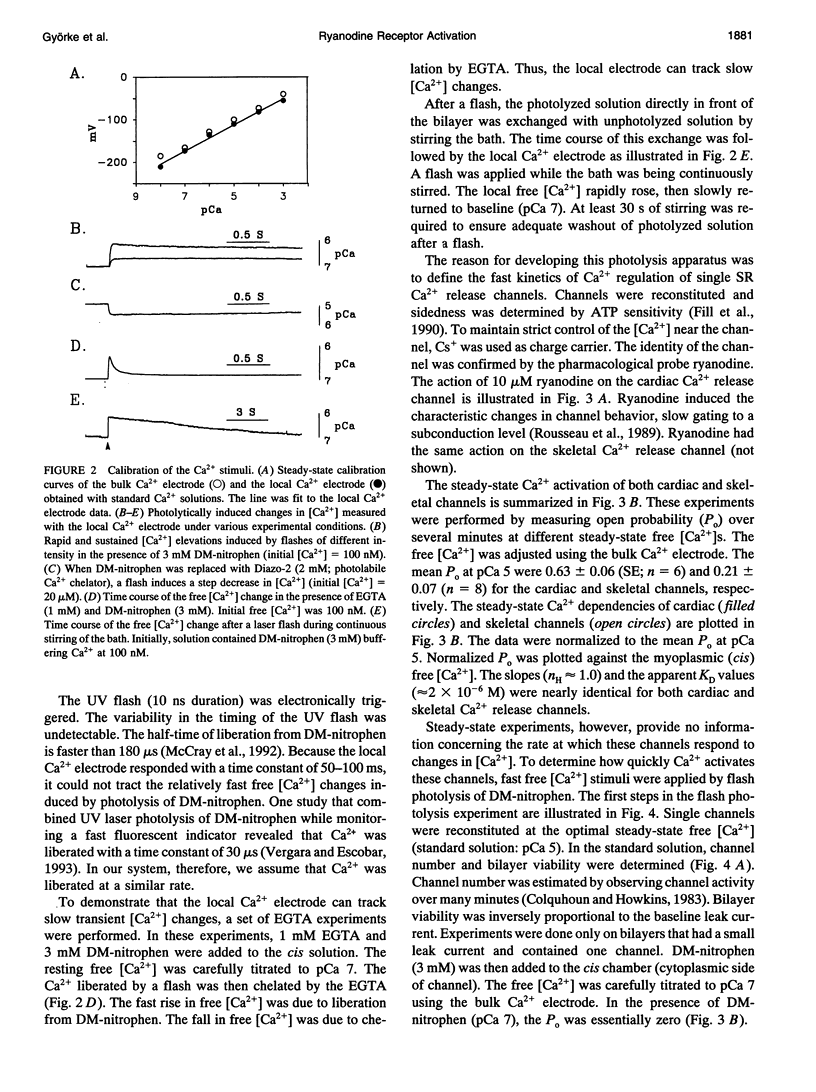
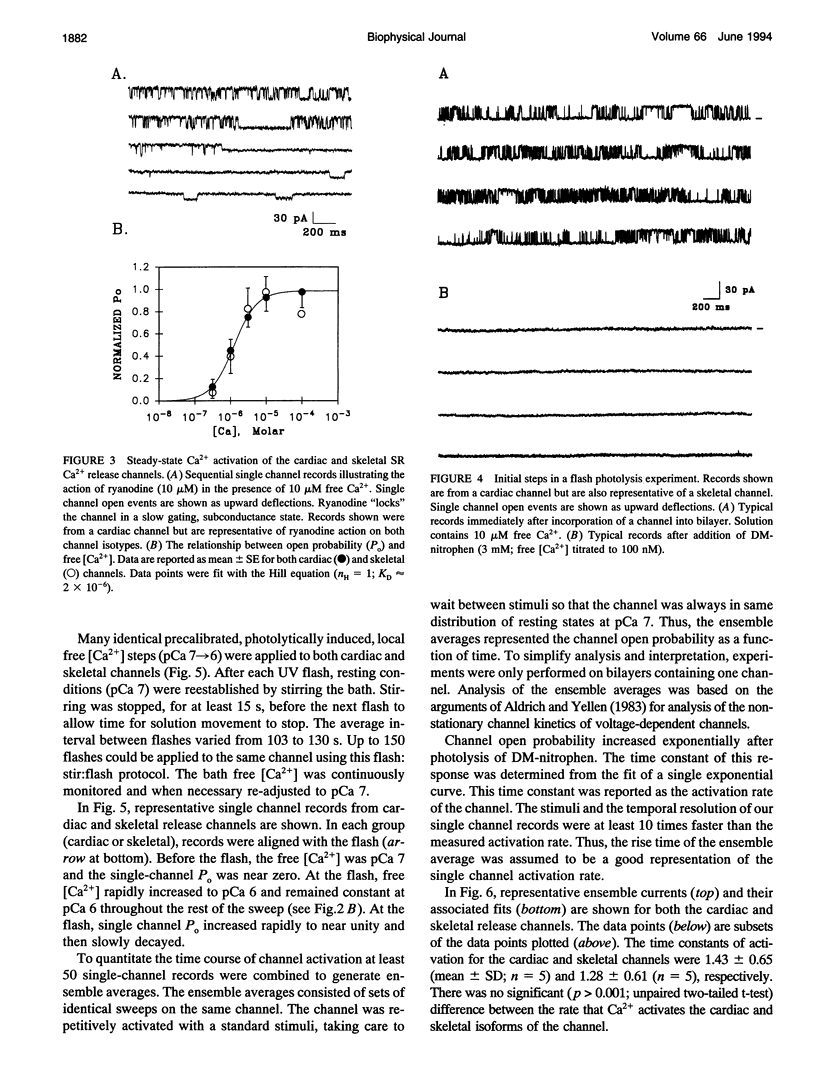
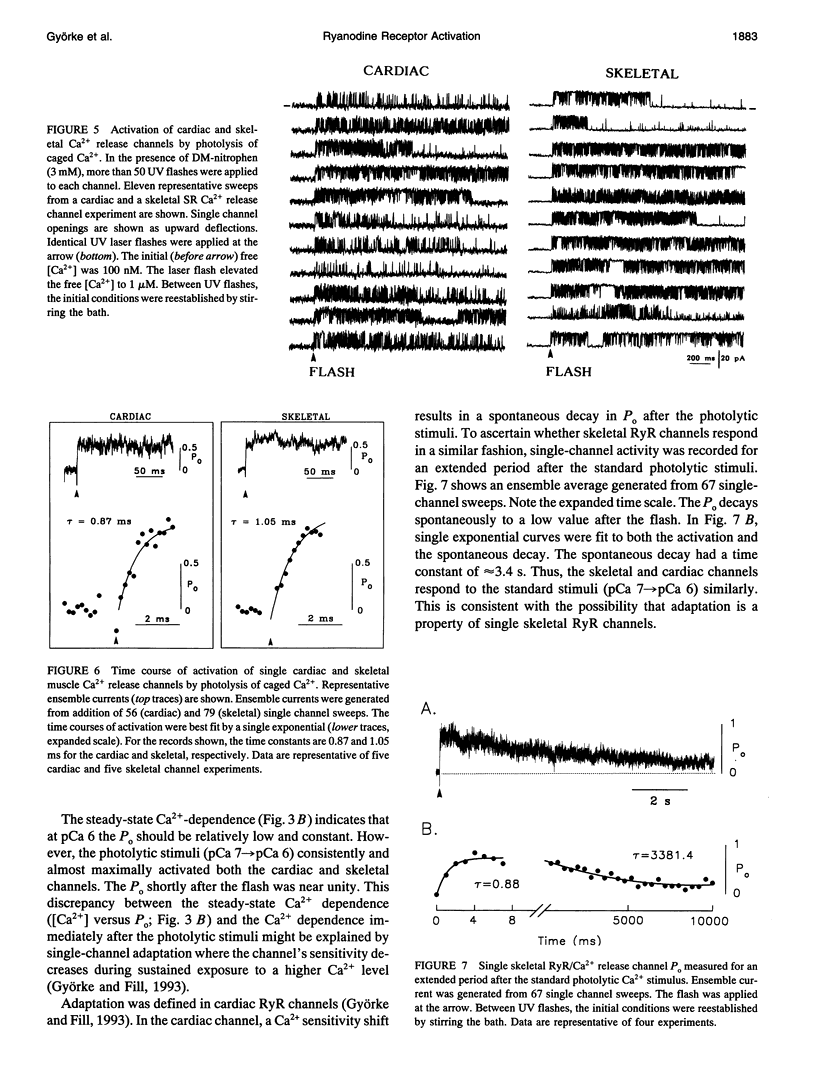
Single ryanodine-sensitive sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ release channels isolated from rabbit skeletal and canine cardiac muscle were reconstituted in planar lipid bilayers. Single channel activity was measured in simple solutions (no ATP or Mg2+) with 250 mM symmetrical Cs+ as charge carrier. A laser flash was used to photolyze caged-Ca2+ (DM-nitrophen) in a small volume directly in front of the bilayer. The free [Ca2+] in this small volume and in the bulk solution was monitored with Ca2+ electrodes. This setup allowed fast, calibrated free [Ca2+] stimuli to be applied repetitively to single SR Ca2+ release channels. A standard photolytically induced free [Ca2+] step (pCa 7-->6) was applied to both the cardiac and skeletal release channels. The rate of channel activation was determined by fitting a single exponential to ensemble currents generated from at least 50 single channel sweeps. The time constants of activation were 1.43 +/- 0.65 ms (mean +/- SD; n = 5) and 1.28 +/- 0.61 ms (n = 5) for cardiac and skeletal channels, respectively. This study presents a method for defining the fast Ca2+ regulation kinetics of single SR Ca2+ release channels and shows that the activation rate of skeletal SR Ca2+ release channels is consistent with a role for CICR in skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. M., Horowicz P. Twitches in the presence of ethylene glycol bis( -aminoethyl ether)-N,N'-tetracetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):605–608. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu A., Fill M., Stefani E., Entman M. L. Cytoplasmic Ca2+ does not inhibit the cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum ryanodine receptor Ca2+ channel, although Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ inactivation of Ca2+ release is observed in native vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1993 Jul;135(1):49–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00234651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleemann L., Morad M. Role of Ca2+ channel in cardiac excitation-contraction coupling in the rat: evidence from Ca2+ transients and contraction. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:283–312. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C1–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Time and calcium dependence of activation and inactivation of calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned canine cardiac Purkinje cell. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Feb;85(2):247–289. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fill M., Coronado R., Mickelson J. R., Vilven J., Ma J. J., Jacobson B. A., Louis C. F. Abnormal ryanodine receptor channels in malignant hyperthermia. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):471–475. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82563-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Podolsky R. J. Regenerative calcium release within muscle cells. Science. 1970 Jan 2;167(3914):58–59. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3914.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. B. The current view of the source of trigger calcium in excitation-contraction coupling in vertebrate skeletal muscle. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Sep 15;29(18):2399–2406. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C., Nunzi G. Junctional feet and particles in the triads of a fast-twitch muscle fibre. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Apr;4(2):233–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00712033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Györke S., Fill M. Ryanodine receptor adaptation: control mechanism of Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in heart. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):807–809. doi: 10.1126/science.8387229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Györke S., Palade P. Role of local Ca2+ domains in activation of Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in crayfish muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jun;264(6 Pt 1):C1505–C1512. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.6.C1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemond V., Csernoch L., Klein M. G., Schneider M. F. Voltage-gated and calcium-gated calcium release during depolarization of skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1991 Oct;60(4):867–873. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82120-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. H., Ellis-Davies G. C. Photolabile chelators for the rapid photorelease of divalent cations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6571–6575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Anderson K., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Evidence for a Ca2+ channel within the ryanodine receptor complex from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):441–449. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90613-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. D., Fryer M. W., Stephenson D. G. Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in response to flash photolysis. Science. 1994 Feb 18;263(5149):986–988. doi: 10.1126/science.8310298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCray J. A., Fidler-Lim N., Ellis-Davies G. C., Kaplan J. H. Rate of release of Ca2+ following laser photolysis of the DM-nitrophen-Ca2+ complex. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 22;31(37):8856–8861. doi: 10.1021/bi00152a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Darling E., Eveleth J. Kinetics of rapid Ca2+ release by sarcoplasmic reticulum. Effects of Ca2+, Mg2+, and adenine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):236–244. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Henderson J. S. Rapid calcium release from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles is dependent on Ca2+ and is modulated by Mg2+, adenine nucleotide, and calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3065–3073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai J., Imagawa T., Hakamat Y., Shigekawa M., Takeshima H., Numa S. Primary structure and functional expression from cDNA of the cardiac ryanodine receptor/calcium release channel. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Meissner G. Single cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-release channel: activation by caffeine. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):H328–H333. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.2.H328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Meissner G. Ryanodine modifies conductance and gating behavior of single Ca2+ release channel. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C364–C368. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Ma J. J., González A. The mechanical hypothesis of excitation-contraction (EC) coupling in skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1991 Apr;12(2):127–135. doi: 10.1007/BF01774031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Pizarro G. Voltage sensor of excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jul;71(3):849–908. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.3.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipido K. R., Wier W. G. Flux of Ca2+ across the sarcoplasmic reticulum of guinea-pig cardiac cells during excitation-contraction coupling. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:605–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single channel measurements of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Activation by Ca2+ and ATP and modulation by Mg2+. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Nov;88(5):573–588. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.5.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Imagawa T., Ma J., Fill M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Purified ryanodine receptor from rabbit skeletal muscle is the calcium-release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):1–26. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiecker W., Melzer W., Lüttgau H. C. Extracellular Ca2+ and excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):158–160. doi: 10.1038/280158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. D., Lakatta E. G. Excitation-contraction coupling in the heart: the state of the question. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3092–3100. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.12.1325933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Mikami A., Numa S., Beam K. G. Cardiac-type excitation-contraction coupling in dysgenic skeletal muscle injected with cardiac dihydropyridine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):451–453. doi: 10.1038/344451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate C. A., Bick R. J., Chu A., Van Winkle W. B., Entman M. L. Nucleotide specificity of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. GTP-induced calcium accumulation and GTPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9618–9623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara J., Delay M. A transmission delay and the effect of temperature at the triadic junction of skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Oct 22;229(1254):97–110. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1986.0077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. The calcium concentration clamp: spikes and reversible pulses using the photolabile chelator DM-nitrophen. Cell Calcium. 1993 Feb;14(2):87–100. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(93)90079-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



