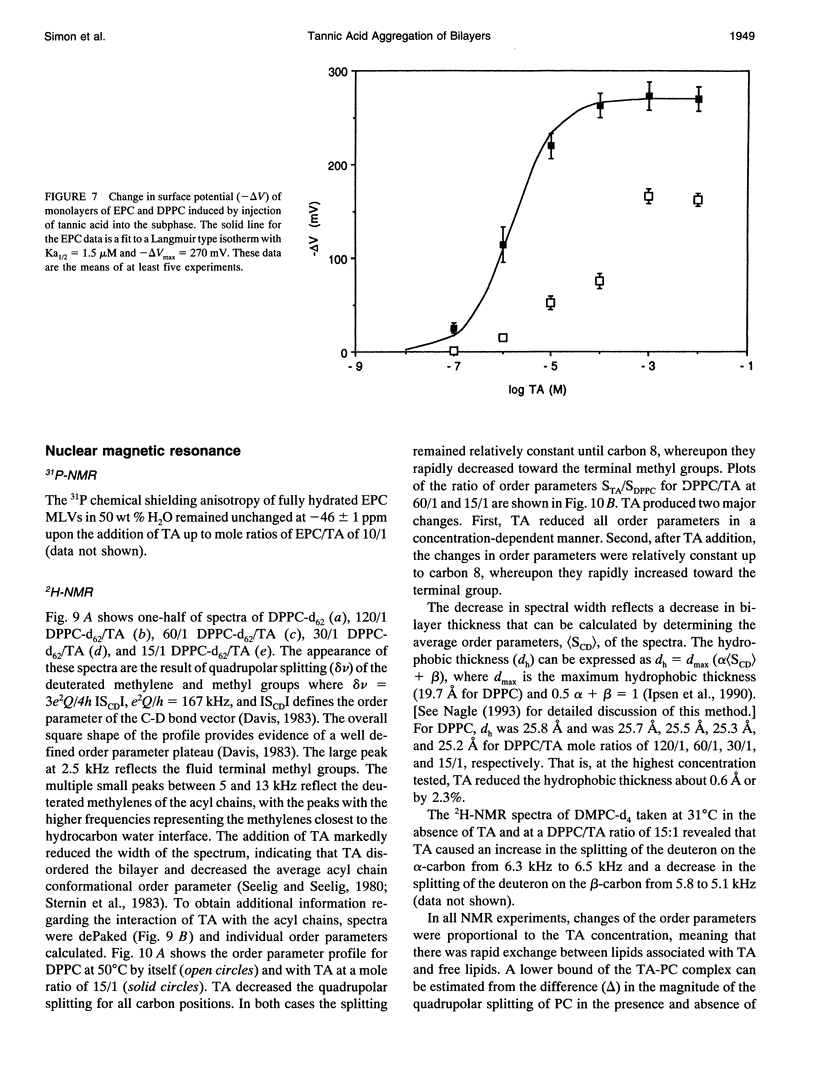
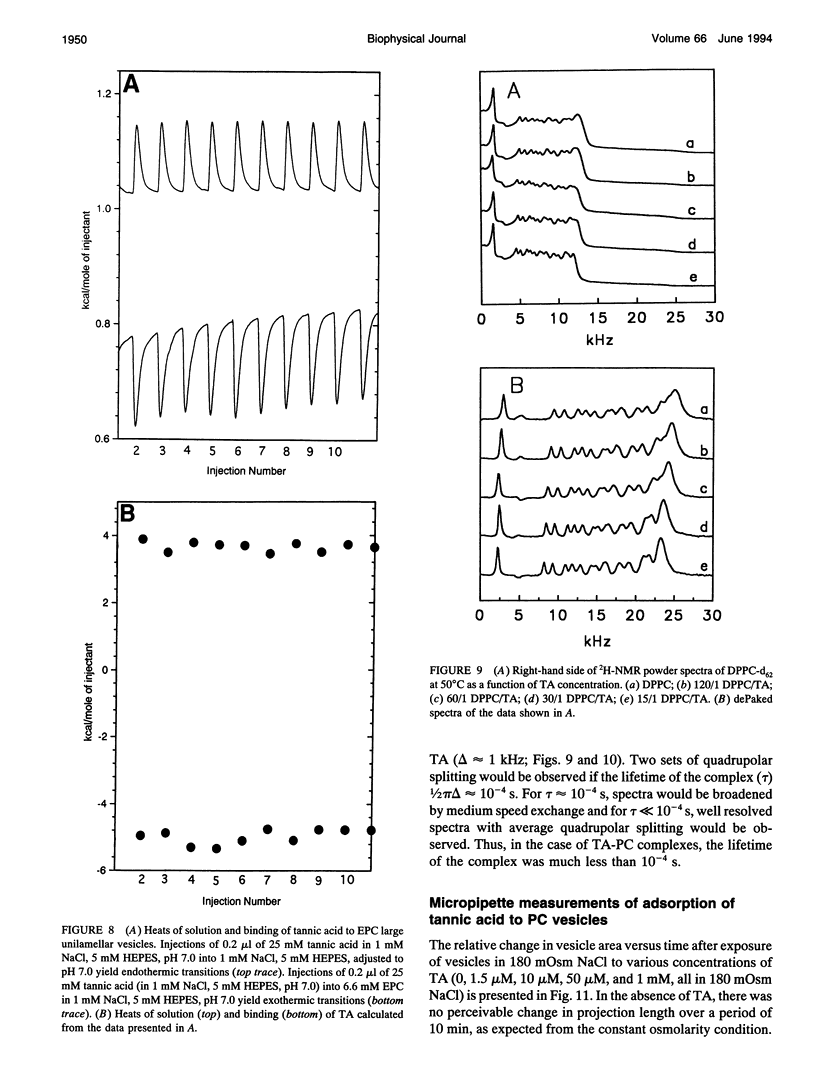
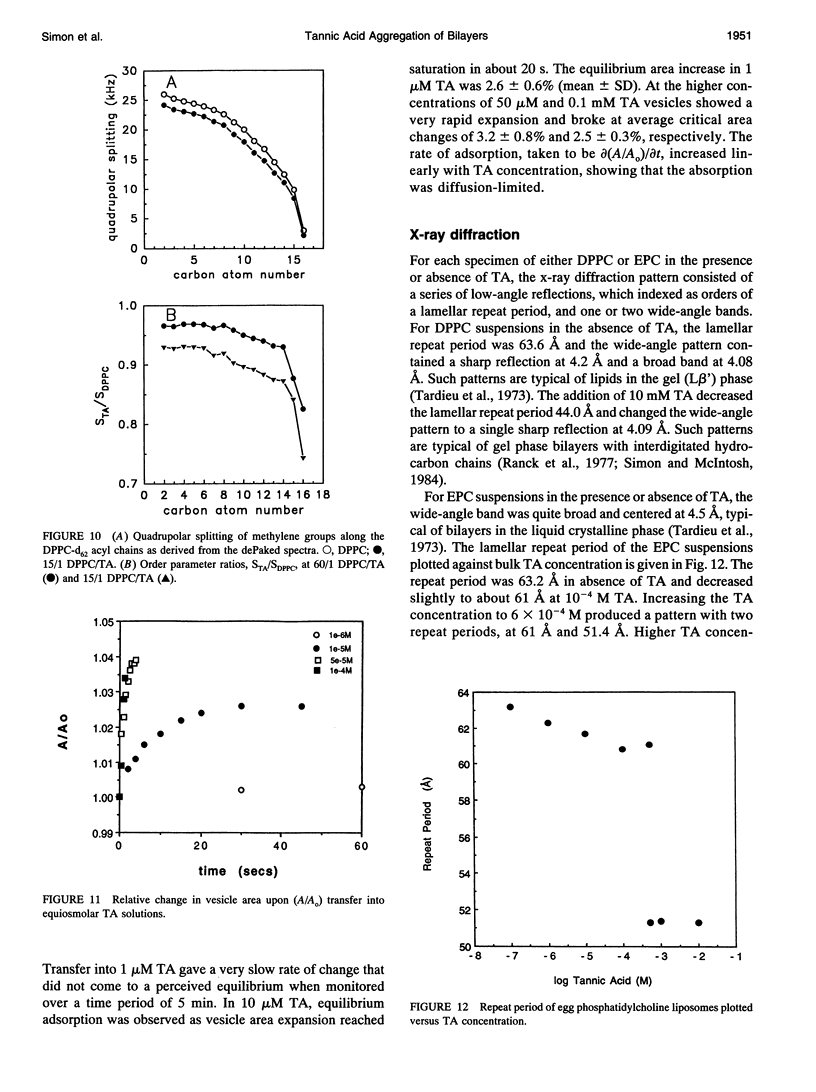
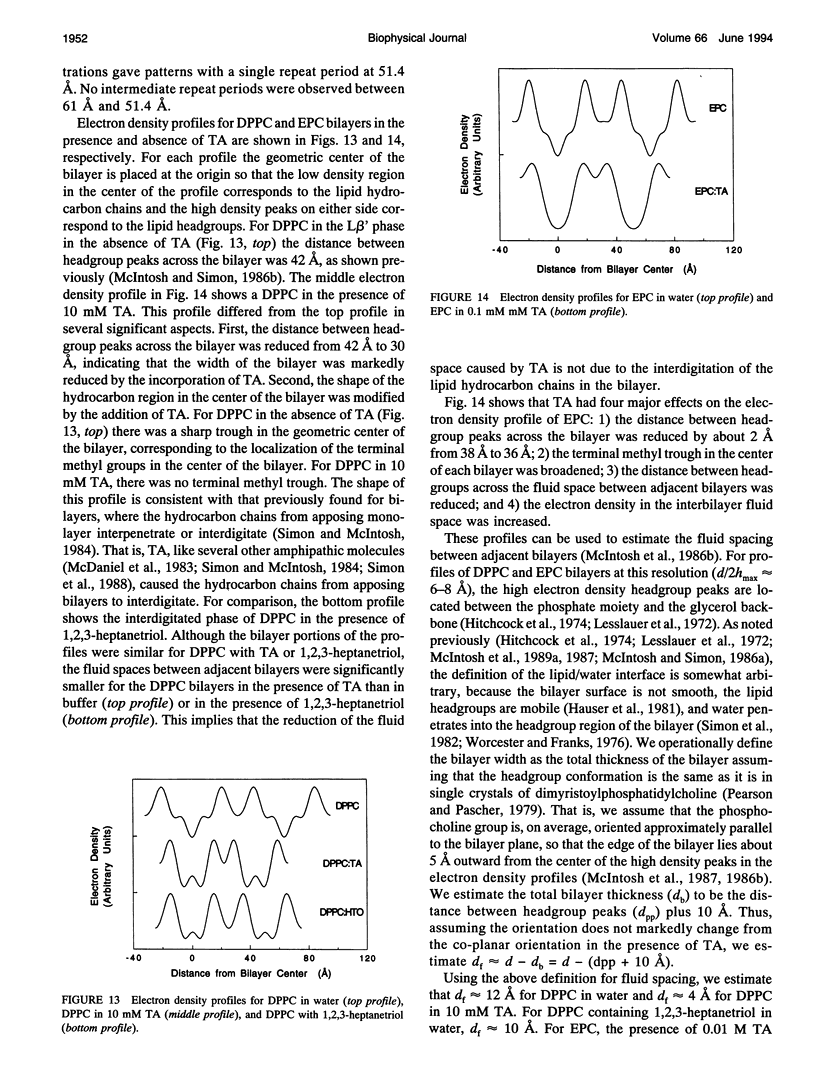
Abstract
Tannic acid (TA) is a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound that aggregates membranes and neutral phosolipid vesicles and precipitates many proteins. This study analyzes TA binding to lipid membranes and the ensuing aggregation. The optical density of dispersions of phosphatidylcholine (PC) vesicles increased upon the addition of TA and electron micrographs showed that TA caused the vesicles to aggregate and form stacks of tightly packed disks. Solution calorimetry showed that TA bound to PC bilayers with a molar binding enthalpy of -8.3 kcal/mol and zeta potential measurements revealed that TA imparted a small negative charge to PC vesicles. Monolayer studies showed that TA bound to PC with a dissociation constant of 1.5 microM and reduced the dipole potential by up to 250 mV. Both the increase in optical density and decrease in dipole potential produced by TA could be reversed by the addition of polyvinylpyrrolidone, a compound that chelates TA by providing H-bond acceptor groups. NMR, micropipette aspiration, and x-ray diffraction experiments showed that TA incorporated into liquid crystalline PC membranes, increasing the area per lipid molecule and decreasing the bilayer thickness by 2 to 4%. 2H-NMR quadrupole splitting measurements also showed that TA associated with a PC molecule for times much less than 10(-4) s. In gel phase bilayers, TA caused the hydrocarbon chains from apposing monolayers to fully interdigitate. X-ray diffraction measurements of both gel and liquid crystalline dispersions showed that TA, at a critical concentration of about 1 mM, reduced the fluid spacing between adjacent bilayers by 8-10 A. These data place severe constraints on how TA can pack between adjacent bilayers and cause vesicles to adhere. We conclude that TA promotes vesicle aggregation by reducing the fluid spacing between bilayers by the formation of transient interbilayer bridges by inserting its digallic acid residues into the interfacial regions of adjacent bilayers and spanning the interbilayer space.
Full text
PDF
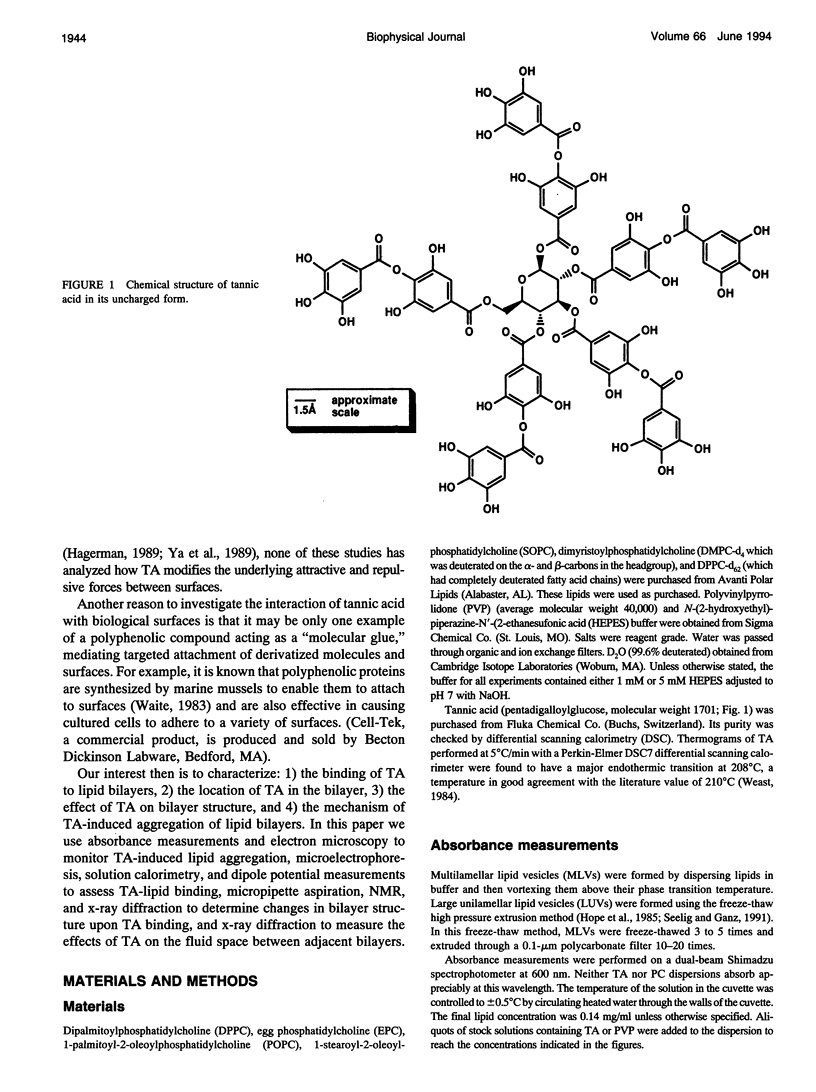








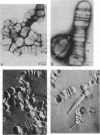
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S., Feldberg S., Nakadomari H., Levy S., McLaughlin S. Electrostatic interactions among hydrophobic ions in lipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1978 Jan;21(1):35–70. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85507-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S., Finkelstein A., Katz I., Cass A. Effect of phloretin on the permeability of thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):749–771. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechinger B., Macdonald P. M., Seelig J. Deuterium NMR studies of the interactions of polyhydroxyl compounds and of glycolipids with lipid model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 18;943(2):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beschiaschvili G., Seelig J. Peptide binding to lipid bilayers. Nonclassical hydrophobic effect and membrane-induced pK shifts. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 20;31(41):10044–10053. doi: 10.1021/bi00156a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaurock A. E., Worthington C. R. Treatment of low angle x-ray data from planar and concentric multilayered structures. Biophys J. 1966 May;6(3):305–312. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(66)86658-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borovyagin V. L., Sabelnikov A. G. Lipid polymorphism of model and cellular membranes as revealed by electron microscopy. Electron Microsc Rev. 1989;2(1):75–115. doi: 10.1016/0892-0354(89)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger Y., Schreier S., Smith I. C. Molecular details of anesthetic--lipid interaction as seen by deuterium and phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6824–6830. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. H. The description of membrane lipid conformation, order and dynamics by 2H-NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):117–171. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day E. P., Kwok A. Y., Hark S. K., Ho J. T., Vail W. J., Bentz J., Nir S. Reversibility of sodium-induced aggregation of sonicated phosphatidylserine vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4026–4029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebihara L., Hall J. E., MacDonald R. C., McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. Effect of benzyl alcohol on lipid bilayers. A comparisons of bilayer systems. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):185–196. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85170-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellena J. F., Dominey R. N., Archer S. J., Xu Z. C., Cafiso D. S. Localization of hydrophobic ions in phospholipid bilayers using 1H nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4584–4592. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Parsegian V. A. Energetics of membrane deformation and adhesion in cell and vesicle aggregation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983;416:13–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb35176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E, Rawicz W. Entropy-driven tension and bending elasticity in condensed-fluid membranes. Phys Rev Lett. 1990 Apr 23;64(17):2094–2097. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.64.2094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewelling R. F., Hubbell W. L. The membrane dipole potential in a total membrane potential model. Applications to hydrophobic ion interactions with membranes. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):541–552. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83664-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin J. C., Cafiso D. S. Internal electrostatic potentials in bilayers: measuring and controlling dipole potentials in lipid vesicles. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):289–299. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81051-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawrisch K., Ruston D., Zimmerberg J., Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P., Fuller N. Membrane dipole potentials, hydration forces, and the ordering of water at membrane surfaces. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1213–1223. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81931-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER F. R. The effect of tannic acid on the permeability of erythrocytes to non-electrolytes. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1960 Apr;55:175–188. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030550209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam E. Polyphenol-protein interactions. Biochem J. 1974 Apr;139(1):285–288. doi: 10.1042/bj1390285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Pascher I., Pearson R. H., Sundell S. Preferred conformation and molecular packing of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 16;650(1):21–51. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Hladky S. B. Ion transport across thin lipid membranes: a critical discussion of mechanisms in selected systems. Q Rev Biophys. 1972 May;5(2):187–282. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfrich W. Out-of-plane fluctuations of lipid bilayers. Z Naturforsch C. 1975 Nov-Dec;30(6):841–842. doi: 10.1515/znc-1975-11-1230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbette L., Marquardt J., Scarpa A., Blasie J. K. A direct analysis of lamellar x-ray diffraction from hydrated oriented multilayers of fully functional sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1977 Nov;20(2):245–272. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85547-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. B., Mason R., Thomas K. M., Shipley G. G. Structural chemistry of 1,2 dilauroyl-DL-phosphatidylethanolamine: molecular conformation and intermolecular packing of phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3036–3040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert J. P., Jr, Kiernan P. D., Beahrs O. H., McConahey W. M., Woolner L. B. Occult papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. Arch Surg. 1980 Apr;115(4):394–398. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1980.01380040028004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Mouritsen O. G., Bloom M. Relationships between lipid membrane area, hydrophobic thickness, and acyl-chain orientational order. The effects of cholesterol. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):405–412. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82557-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalina M., Pease D. C. The preservation of ultrastructure in saturated phosphatidyl cholines by tannic acid in model systems and type II pneumocytes. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):726–741. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelusky E. C., Smith I. C. The influence of local anesthetics on molecular organization in phosphatidylethanolamine membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;26(2):314–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakhdar-Ghazal F., Tichadou J. L., Tocanne J. F. Effect of pH and monovalent cations on the ionization state of phosphatidylglycerol in monolayers. An experimental (surface potential) and theoretical (Gouy-Chapman) approach. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 15;134(3):531–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesslauer W., Cain J. E., Blasie J. K. X-ray diffraction studies of lecithin bimolecular leaflets with incorporated fluorescent probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1499–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. C., Simon S. A. Lipid monolayer states and their relationships to bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4089–4093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Seelig J. Anion binding to neutral and positively charged lipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6769–6775. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marassi F. M., Macdonald P. M. Response of the phosphatidylcholine headgroup to membrane surface charge in ternary mixtures of neutral, cationic, and anionic lipids: a deuterium NMR study. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 20;31(41):10031–10036. doi: 10.1021/bi00156a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra J., Israelachvili J. Direct measurements of forces between phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine bilayers in aqueous electrolyte solutions. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4608–4618. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel R. V., Simon S. A., McIntosh T. J., Borovyagin V. Interaction of benzene with bilayers. Thermal and structural studies. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):4116–4126. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Holloway P. W. Determination of the depth of bromine atoms in bilayers formed from bromolipid probes. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1783–1788. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Magid A. D., Simon S. A. Range of the solvation pressure between lipid membranes: dependence on the packing density of solvent molecules. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7904–7912. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Magid A. D., Simon S. A. Repulsive interactions between uncharged bilayers. Hydration and fluctuation pressures for monoglycerides. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):897–904. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82888-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Magid A. D., Simon S. A. Steric repulsion between phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7325–7332. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. Area per molecule and distribution of water in fully hydrated dilauroylphosphatidylethanolamine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4948–4952. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. Contributions of hydration and steric (entropic) pressures to the interactions between phosphatidylcholine bilayers: experiments with the subgel phase. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 17;32(32):8374–8384. doi: 10.1021/bi00083a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. Hydration force and bilayer deformation: a reevaluation. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4058–4066. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A., MacDonald R. C. The organization of n-alkanes in lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 24;597(3):445–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S., Harary H. The hydrophobic adsorption of charged molecules to bilayer membranes: a test of the applicability of the stern equation. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1941–1948. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F. Area/lipid of bilayers from NMR. Biophys J. 1993 May;64(5):1476–1481. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81514-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T., Allison A. C., Harington J. S. Physico-chemical properties of silica in relation to its toxicity. Nature. 1966 Apr 16;210(5033):259–261. doi: 10.1038/210259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham D., Nunn R. S. Elastic deformation and failure of lipid bilayer membranes containing cholesterol. Biophys J. 1990 Oct;58(4):997–1009. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82444-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian V. A., Fuller N., Rand R. P. Measured work of deformation and repulsion of lecithin bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2750–2754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. H., Pascher I. The molecular structure of lecithin dihydrate. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):499–501. doi: 10.1038/281499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranck J. L., Keira T., Luzzati V. A novel packing of the hydrocarbon chains in lipids. The low temperature phases of dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl-glycerol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):432–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux M., Neumann J. M., Hodges R. S., Devaux P. F., Bloom M. Conformational changes of phospholipid headgroups induced by a cationic integral membrane peptide as seen by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2313–2321. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman S. S., Suggs M. S., Simon S. A. Astringent compounds suppress taste responses in gerbil. Brain Res. 1992 Nov 6;595(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91445-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrijvers A. H., Frederik P. M., Stuart M. C., Burger K. N., Heijnen V. V., Van der Vusse G. J., Reneman R. S. Formation of multilamellar vesicles by addition of tannic acid to phosphatidylcholine-containing small unilamellar vesicles. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Nov;37(11):1635–1643. doi: 10.1177/37.11.2809174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Ganz P. Nonclassical hydrophobic effect in membrane binding equilibria. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9354–9359. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Macdonald P. M., Scherer P. G. Phospholipid head groups as sensors of electric charge in membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7535–7541. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Seelig A. Lipid conformation in model membranes and biological membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Feb;13(1):19–61. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager P. G., Macey R. I., Strickholm A. Internal perfusion of crayfish, giant axons: action of tannic acid, DDT, and TEA. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Aug;74(1):77–90. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040740111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuchter S. H., Franki N., Hays R. M. The effect of tanning agents on the permeability of the toad bladder to water and solutes. J Membr Biol. 1973 Dec 31;14(2):177–191. doi: 10.1007/BF01868076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., Fink C. A., Kenworthy A. K., McIntosh T. J. The hydration pressure between lipid bilayers. Comparison of measurements using x-ray diffraction and calorimetry. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):538–546. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82270-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., Hall W. L., Schiffman S. S. Astringent-tasting compounds alter ion transport across isolated canine lingual epithelia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1992 Sep;43(1):271–283. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(92)90668-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., McIntosh T. J. Interdigitated hydrocarbon chain packing causes the biphasic transition behavior in lipid/alcohol suspensions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 13;773(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90562-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., McIntosh T. J., Latorre R. Influence of cholesterol on water penetration into bilayers. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):65–67. doi: 10.1126/science.7063872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., McIntosh T. J. Magnitude of the solvation pressure depends on dipole potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9263–9267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smaby J. M., Brockman H. L. Surface dipole moments of lipids at the argon-water interface. Similarities among glycerol-ester-based lipids. Biophys J. 1990 Jul;58(1):195–204. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82365-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smejtek P., Wang S. R. Adsorption to dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine membranes in gel and fluid state: pentachlorophenolate, dipicrylamine, and tetraphenylborate. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1285–1294. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82468-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaralingam M. Discussion paper: molecular structures and conformations of the phospholipids and sphingomyelins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Jun 20;195:324–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatulian S. A. Effect of lipid phase transition on the binding of anions to dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 21;736(2):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90283-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatulian S. A., Gordeliy V. I., Sokolova A. E., Syrykh A. G. A neutron diffraction study of the influence of ions on phospholipid membrane interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 18;1070(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocanne J. F., Teissié J. Ionization of phospholipids and phospholipid-supported interfacial lateral diffusion of protons in membrane model systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Feb 28;1031(1):111–142. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90005-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G. L., Oldfield E. Effect of a local anaesthetic on hydrocarbon chain order in membranes. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):669–670. doi: 10.1038/277669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite J. H. Evidence for a repeating 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine- and hydroxyproline-containing decapeptide in the adhesive protein of the mussel, Mytilus edulis L. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2911–2915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcester D. L., Franks N. P. Structural analysis of hydrated egg lecithin and cholesterol bilayers. II. Neutrol diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 25;100(3):359–378. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. S., Skita V., Mason R. P., Herbette L. G. Molecular basis for the inhibition of 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel drugs binding to their receptors by a nonspecific site interaction mechanism. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1244–1255. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81933-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C., Vanderkooi G. Molecular origin of the internal dipole potential in lipid bilayers: calculation of the electrostatic potential. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):935–941. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81673-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]