Abstract
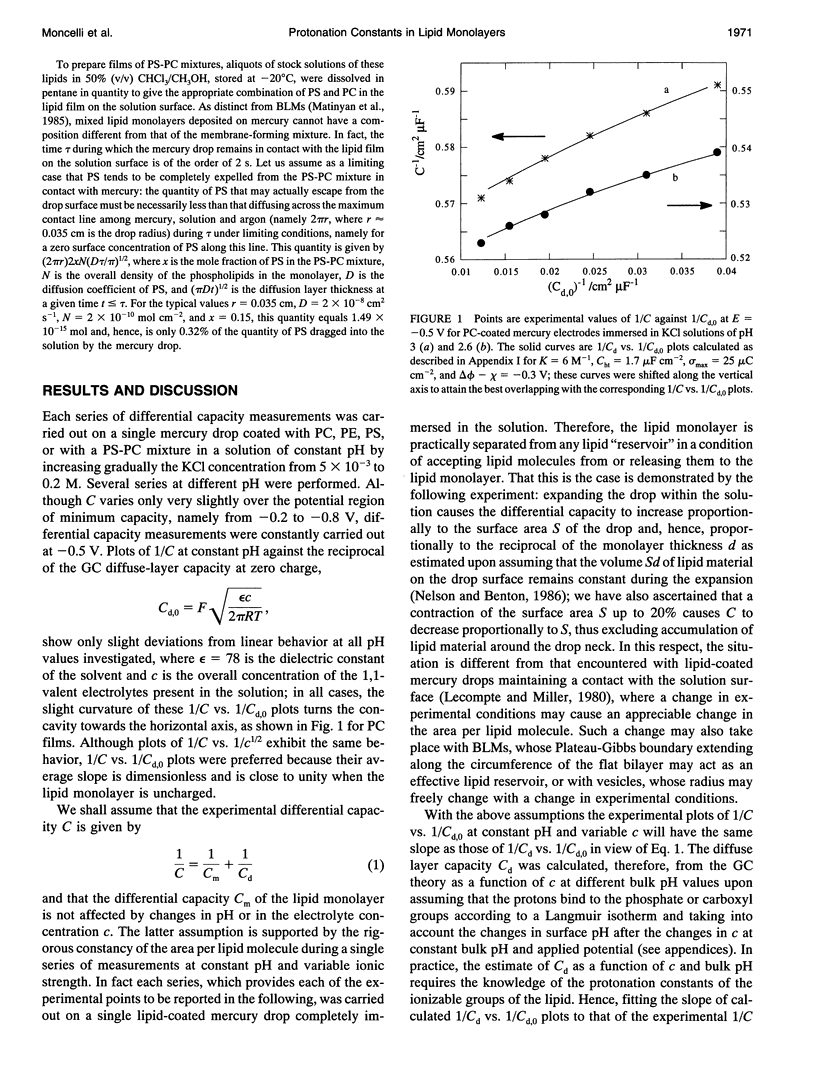
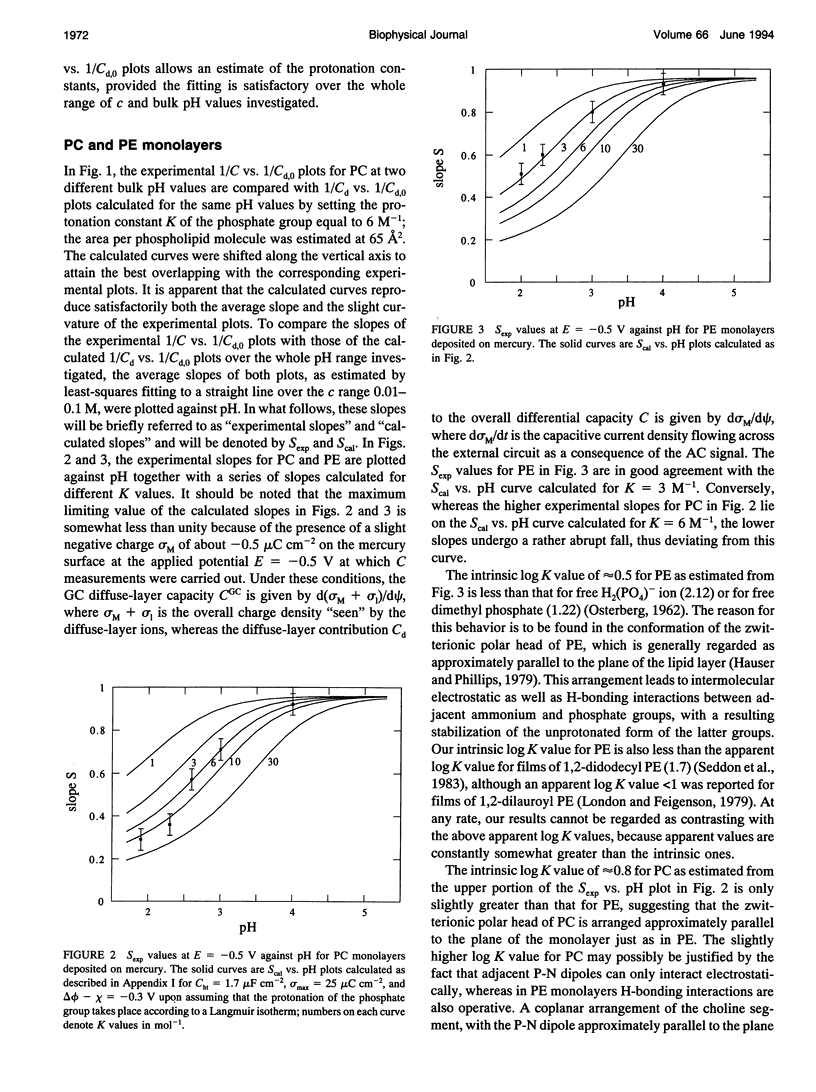
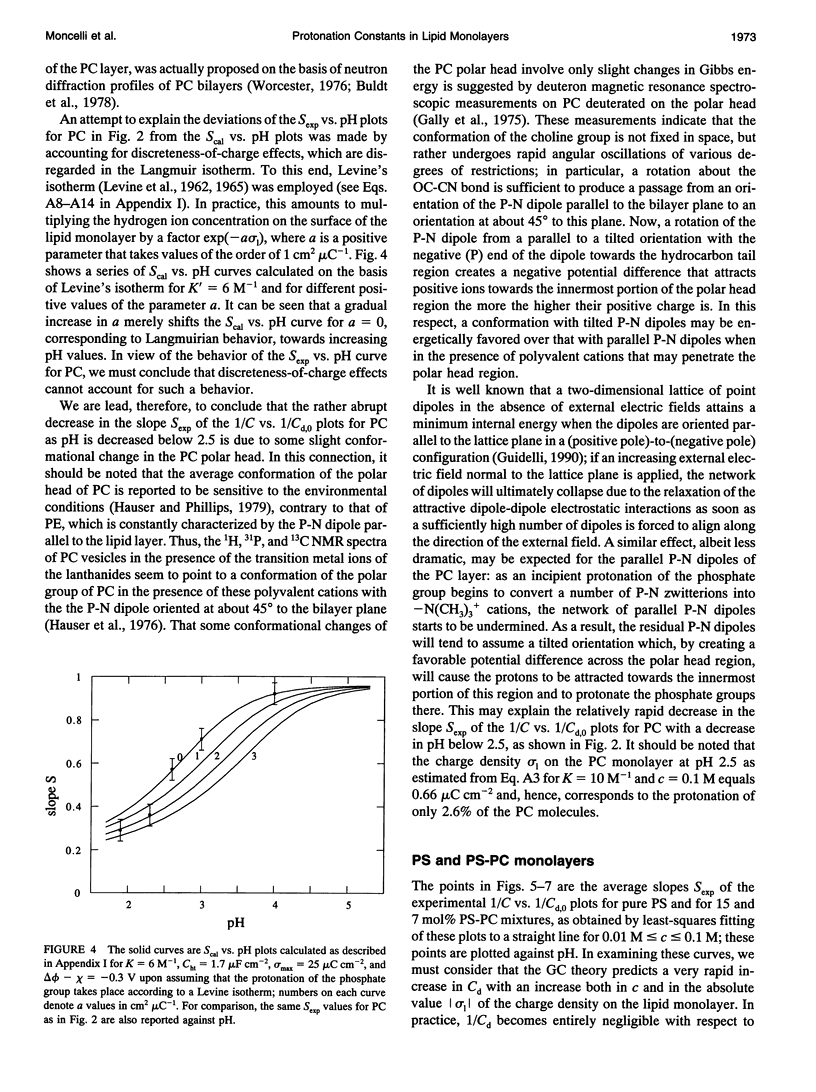
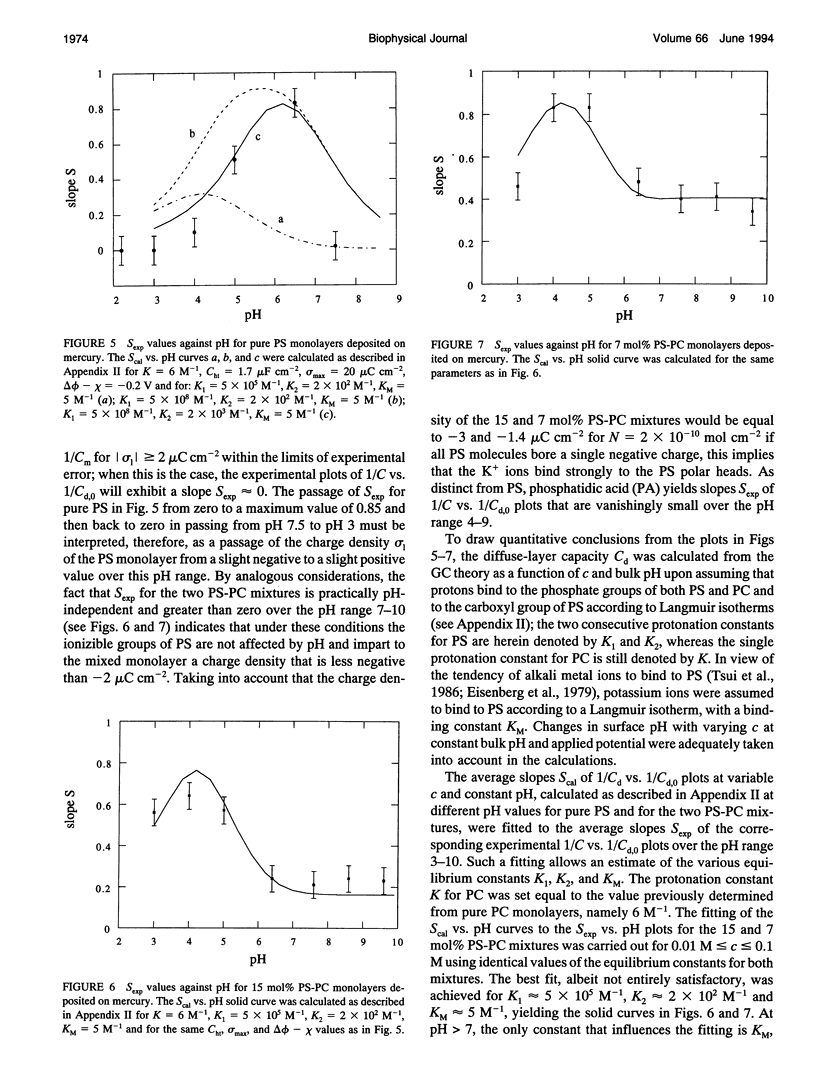
The intrinsic pKa values of the phosphate groups of phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and of the phosphate and carboxyl groups of phosphatidylserine (PS) in self-organized monolayers deposited on a hanging mercury drop electrode were determined by a novel procedure based on measurements of the differential capacity C of this lipid-coated electrode. In view of the Gouy-Chapman theory, plots of 1/C at constant bulk pH and variable KCl concentration against the reciprocal of the calculated diffuse-layer capacity Cd,0 at zero charge exhibit slopes that decrease from an almost unit value to vanishingly low values as the absolute value of the charge density on the lipid increases from zero to approximately 2 microC cm-2. The intrinsic pKa values so determined are 0.5 for PE and 0.8 for PC. The plots of 1/C against 1/Cd,0 for pure PS exhibit slopes that pass from zero to a maximum value and then back to zero as pH is varied from 7.5 to 3, indicating that the charge density of the lipid film passes from slight negative to slight positive values over this pH range. An explanation for this anomalous behavior, which is ascribed to the phosphate group of PS, is provided. Interdispersion of PS and PC molecules in the film decreases the "formal" pKa value of the latter group by about three orders of magnitude.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMSON M. B., KATZMAN R., GREGOR H. P. AQUEOUS DISPERSIONS OF PHOSPHATIDYLSERINE. IONIC PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:70–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM A. D., DAWSON R. M. The relation between the activity of a lecithinase and the electrophoretic charge of the substrate. Biochem J. 1959 Jul;72:486–492. doi: 10.1042/bj0720486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangham A. D., Papahadjopoulos D. Biophysical properties of phospholipids. I. Interaction of phosphatidylserine monolayers with metal ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Sep 5;126(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büldt G., Gally H. U., Seelig A., Seelig J., Zaccai G. Neutron diffraction studies on selectively deuterated phospholipid bilayers. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):182–184. doi: 10.1038/271182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cevc G., Watts A., Marsh D. Titration of the phase transition of phosphatidylserine bilayer membranes. Effects of pH, surface electrostatics, ion binding, and head-group hydration. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4955–4965. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg M., Gresalfi T., Riccio T., McLaughlin S. Adsorption of monovalent cations to bilayer membranes containing negative phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5213–5223. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally H. U., Niederberger W., Seelig J. Conformation and motion of the choline head group in bilayers of dipalmitoyl-3-sn-phosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 12;14(16):3647–3652. doi: 10.1021/bi00687a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Phillips M. C., Barratt M. D. Differences in the interaction of inorganic and organic (hydrophobic) cations with phosphatidylserine membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 16;413(3):341–353. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Phillips M. C. Conformation of the lecithin polar group in charged vesicles. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):390–394. doi: 10.1038/261390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakhdar-Ghazal F., Tichadou J. L., Tocanne J. F. Effect of pH and monovalent cations on the ionization state of phosphatidylglycerol in monolayers. An experimental (surface potential) and theoretical (Gouy-Chapman) approach. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 15;134(3):531–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecompte M. F., Miller I. R. Interaction of prothrombin and its fragments with monolayers containing phosphatidylserine. 2. Electrochemical determination of lipid layer perturbation by interacting prothrombin and its fragments. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3439–3446. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London E., Feigenson G. W. Phosphorus NMR analysis of phospholipids in detergents. J Lipid Res. 1979 Mar;20(3):408–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. C., Simon S. A., Baer E. Ionic influences on the phase transition of dipalmitoylphosphatidylserine. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):885–891. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki S., Kurland R. Surface potential of phosphatidylserine monolayers. II. Divalent and monovalent ion binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 20;645(2):170–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90187-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D. Surface properties of acidic phospholipids: interaction of monolayers and hydrated liquid crystals with uni- and bi-valent metal ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 17;163(2):240–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Weiss L. Amino groups at the surfaces of phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):417–426. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROJAS E., TOBIAS J. M. MEMBRANE MODEL: ASSOCIATION OF INORGANIC CATIONS WITH PHOSPHOLIPID MONOLAYERS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 29;94:394–404. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAH D. O., SCHULMAN J. H. BINDING OF METAL IONS TO MONOLAYERS OF LECITHINS, PLASMALOGEN, CARDIOLIPIN, AND DICETYL PHOSPHATE. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:341–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddon J. M., Cevc G., Marsh D. Calorimetric studies of the gel-fluid (L beta-L alpha) and lamellar-inverted hexagonal (L alpha-HII) phase transitions in dialkyl- and diacylphosphatidylethanolamines. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1280–1289. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seimiya T., Oki S. Accessibility of calcium ions to anionic sites of lipid monolayers. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 6;239(88):26–27. doi: 10.1038/newbio239026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. O., Schulman J. H. The ionic structure of lecithin monolayers. J Lipid Res. 1967 May;8(3):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui F. C., Ojcius D. M., Hubbell W. L. The intrinsic pKa values for phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine in phosphatidylcholine host bilayers. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83655-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



