Abstract
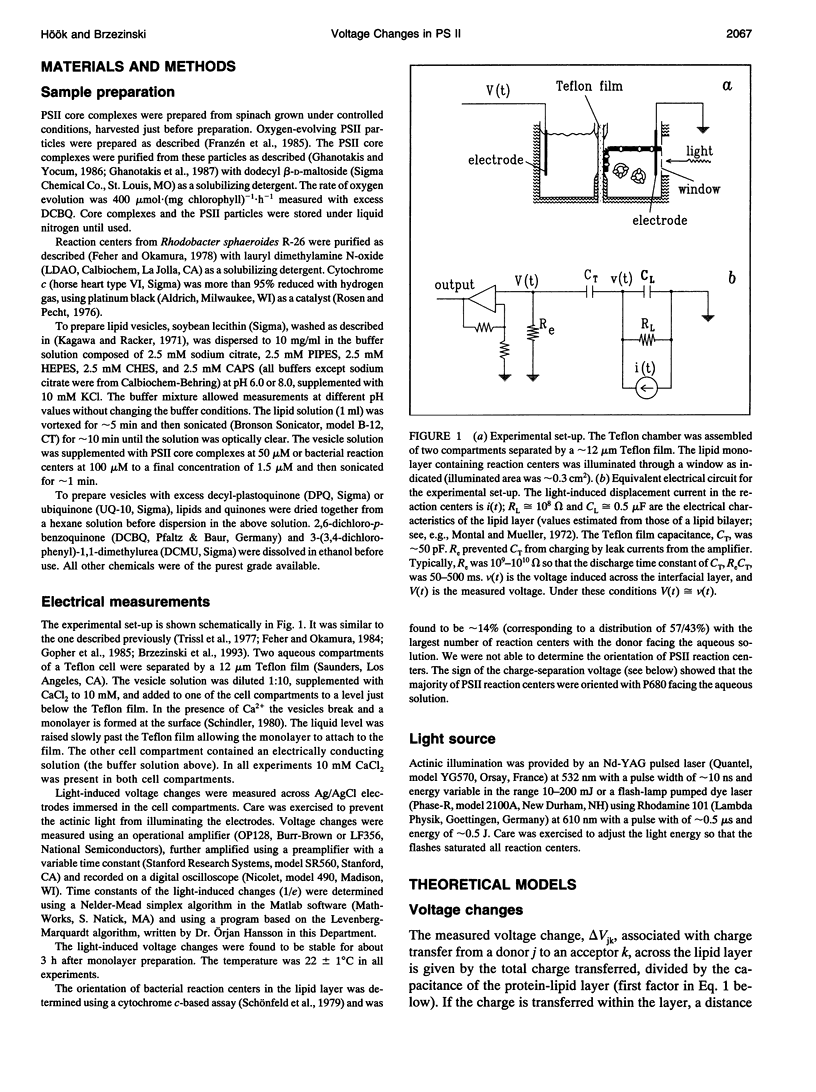
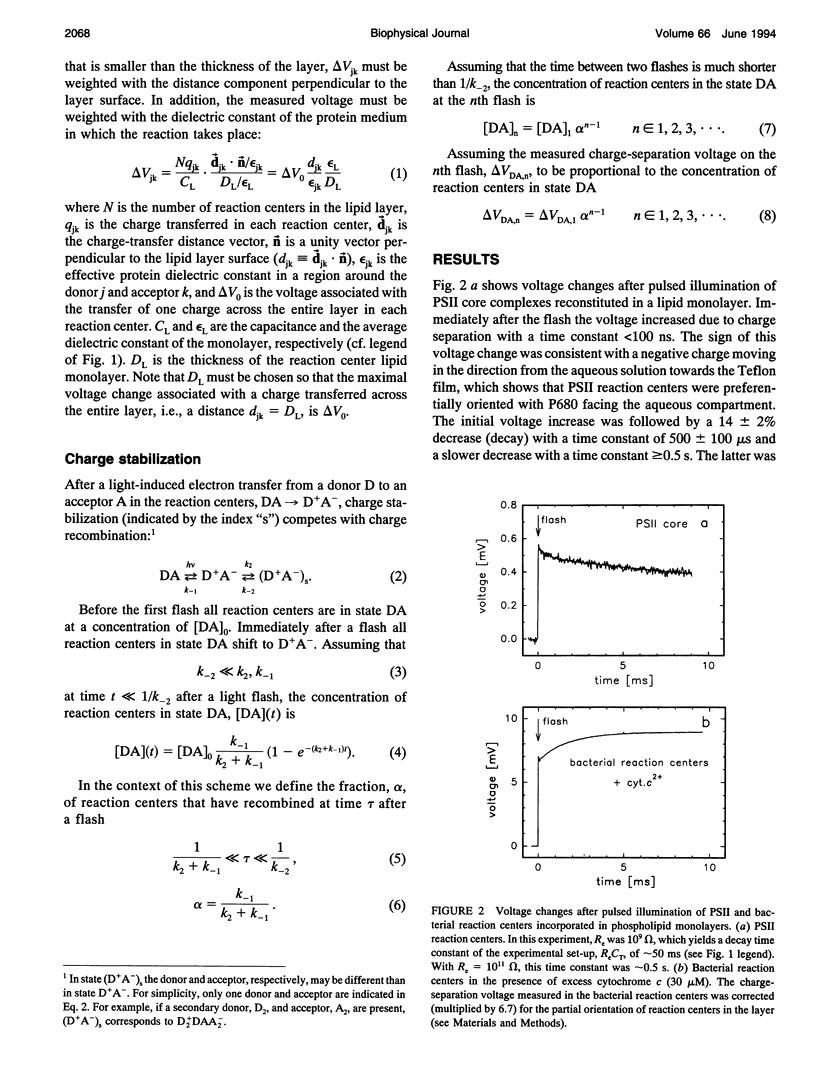
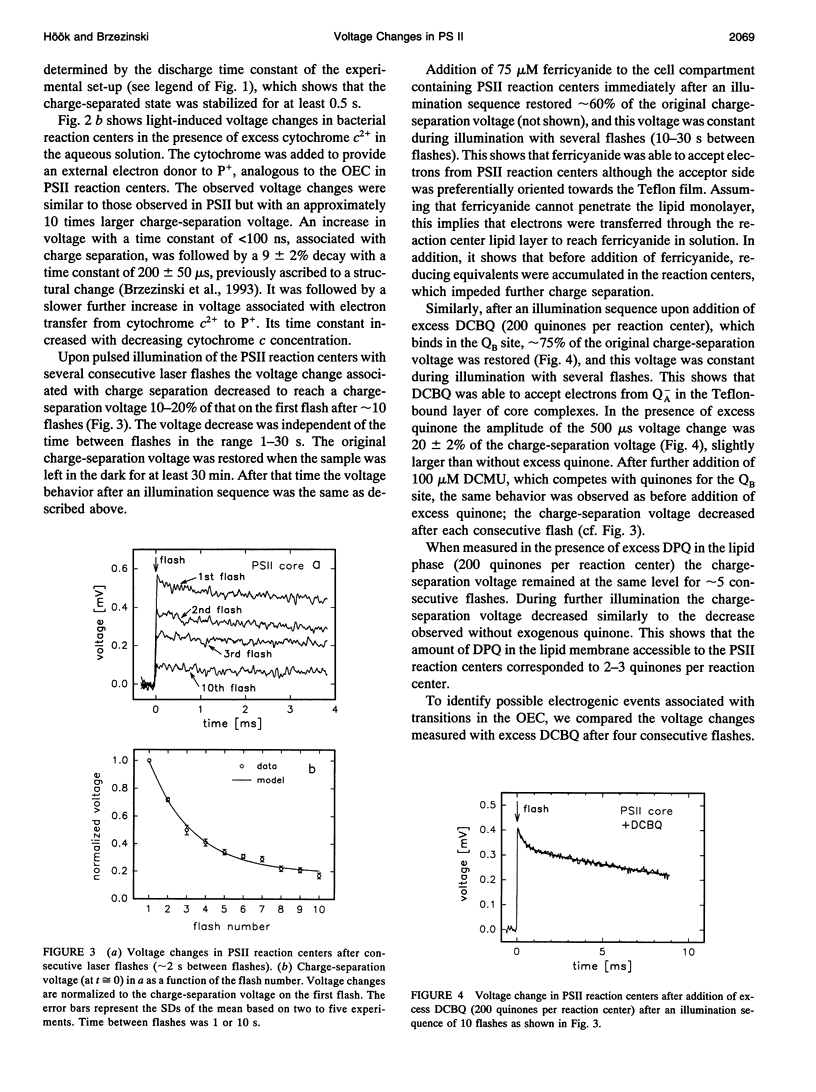
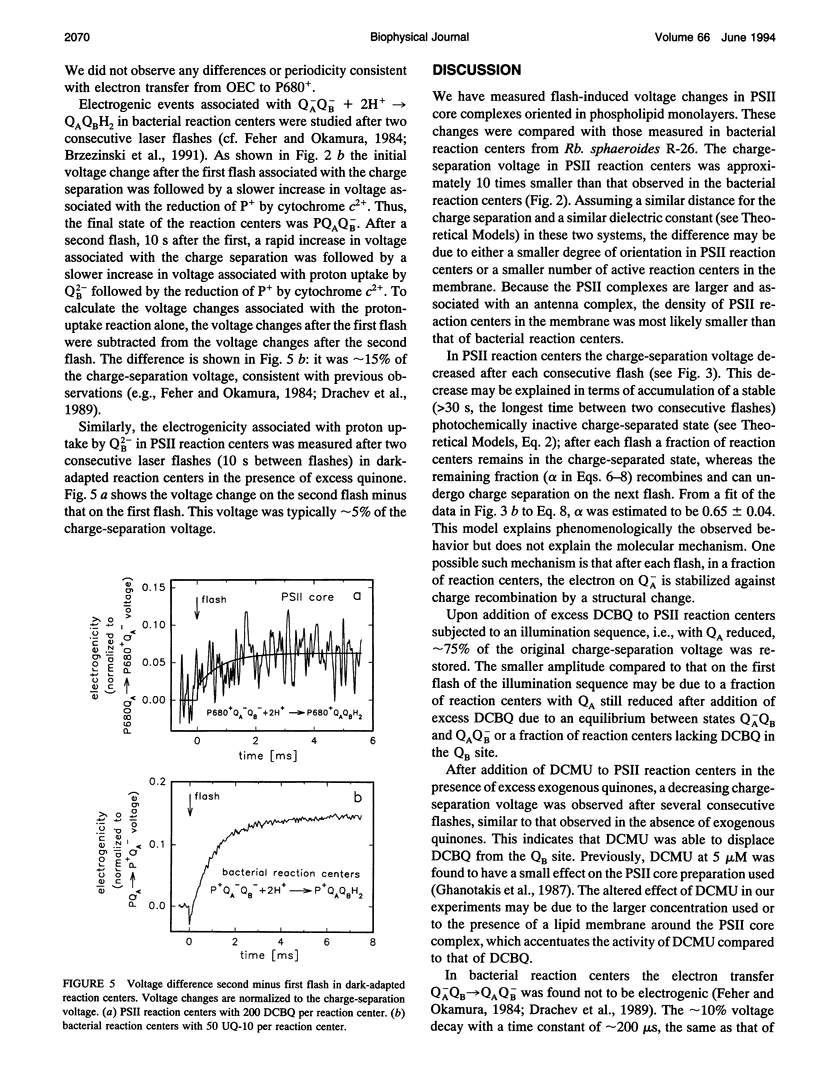
We have measured light-induced voltage changes (electrogenic events) in photosystem II (PSII) core complexes oriented in phospholipid monolayers. These events are compared to those measured in the functionally and structurally closely related reaction centers from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides. In both systems we observed a rapid (< 100 ns) light-induced increase in voltage associated with charge separation. In PSII reaction centers it was followed by a decrease (decay) of approximately 14% of the charge-separation voltage and a time constant of approximately 500 microseconds. In bacterial reaction centers this decay was approximately 9% of the charge-separation voltage, and the time constant was approximately 200 microseconds. The decay was presumably associated with a structural change. In bacterial reaction centers, in the presence of excess water-soluble cytochrome c2+, it was followed by a slower increase of approximately 30% of the charge-separation voltage, associated with electron transfer from the cytochrome to the oxidized donor, P+. In PSII reaction centers, after the decay the voltage remained on the same level for > or = 0.5 s. In PSII reaction centers the electron transfer Q-AQB-->QA Q-B contributed with an electrogenicity of < or = 5% of that of the charge separation. In bacterial reaction centers this electrogenicity was < or = 2% of the charge-separation electrogenicity. Proton transfer to Q2-B in PSII reaction centers contributed with approximately 5% of the charge-separation voltage, which is approximately a factor of three smaller than that observed in bacterial reaction centers.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. P., Feher G., Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Rees D. C. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26: the cofactors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5730–5734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. P., Feher G., Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Rees D. C. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26: the protein subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6162–6166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aro E. M., Virgin I., Andersson B. Photoinhibition of Photosystem II. Inactivation, protein damage and turnover. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 5;1143(2):113–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler C. F., Kok B. Direct observation of a light-induced electric field in chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 23;357(2):308–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopher A., Blatt Y., Schönfeld M., Okamura M. Y., Feher G., Montal M. The effect of an applied electric field on the charge recombination kinetics in reaction centers reconstituted in planar lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1985 Aug;48(2):311–320. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83784-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Mueller P. Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers and a study of their electrical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3561–3566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura M. Y., Feher G. Proton transfer in reaction centers from photosynthetic bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:861–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham N. K., Dutton P. L., Mueller P. Photoelectric currents across planar bilayer membranes containing bacterial reaction centers. Response under conditions of single electron turnover. Biophys J. 1982 Feb;37(2):465–473. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84693-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen P., Pecht I. Conformational equilibria accompanying the electron transfer between cytochrome c (P551) and azurin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):775–786. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H. Formation of planar bilayers from artificial or native membrane vesicles. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 15;122(1):77–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönfeld M., Montal M., Feher G. Functional reconstitution of photosynthetic reaction centers in planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6351–6355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl H. W., Darszon A., Montal M. Rhodopsin in model membranes: charge displacements in interfacial layers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):207–210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A., Russell S. T., Churg A. K. Macroscopic models for studies of electrostatic interactions in proteins: limitations and applicability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4785–4789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt H. T., Zickler A. Electrical evidence for the field indicating absorption change in bioenergetic membranes. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 1;37(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80484-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



