Abstract
A magnetically driven bead micro-rheometer for local quantitative measurements of the viscoelastic moduli in soft macromolecular networks such as an entangled F-actin solution is described. The viscoelastic response of paramagnetic latex beads to external magnetic forces is analyzed by optical particle tracking and fast image processing. Several modes of operation are possible, including analysis of bead motion after pulse-like or oscillatory excitations, or after application of a constant force. The frequency dependencies of the storage modulus, G'(omega), and the loss modulus, G''(omega), were measured for frequencies from 10(-1) Hz to 5 Hz. For low actin concentrations (mesh sizes epsilon > 0.1 micron) we found that both G'(omega) and G''(omega) scale with omega 1/2. This scaling law and the absolute values of G' and G'' agree with conventional rheological measurements, demonstrating that the magnetic bead micro-rheometer allows quantitative measurements of the viscoelastic moduli. Local variations of the viscoelastic moduli (and thus of the network density and mesh size) can be probed in several ways: 1) by measurement of G' and G'' at different sites within the network; 2) by the simultaneous analysis of several embedded beads; and 3) by evaluation of the bead trajectories over macroscopic distances. The latter mode yields absolute values and local fluctuations of the apparent viscosity eta(x) of the network.
Full text
PDF
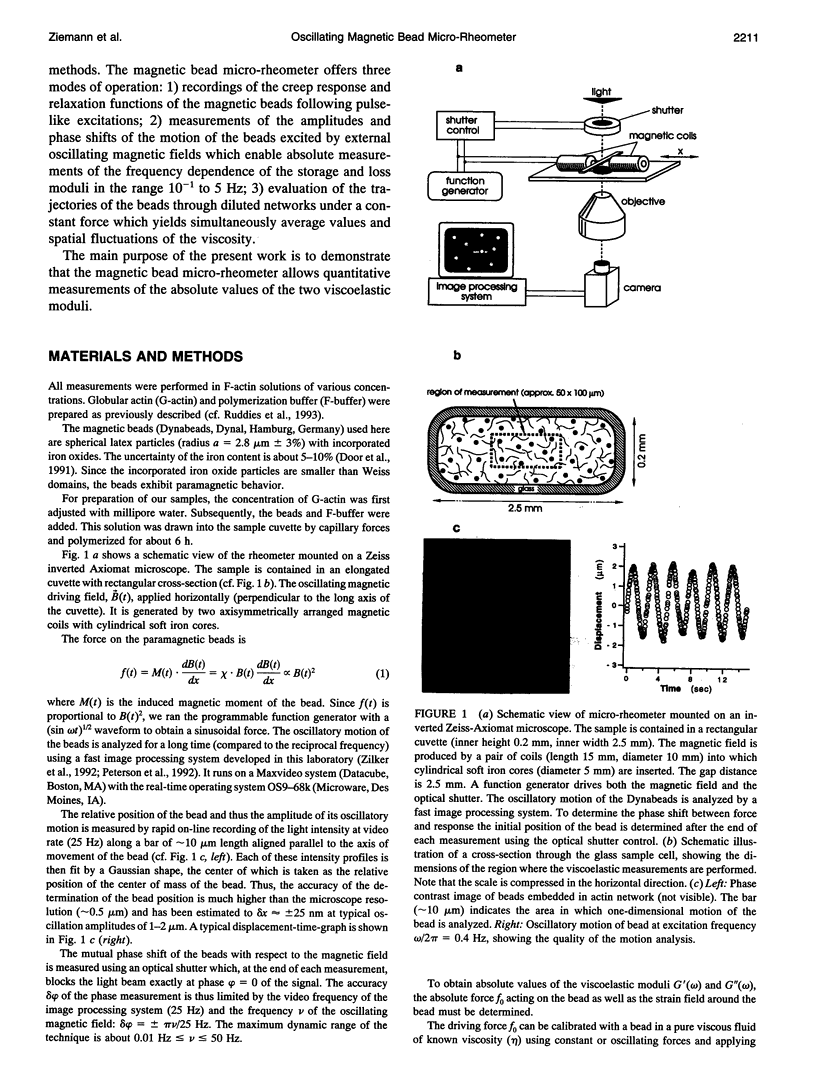
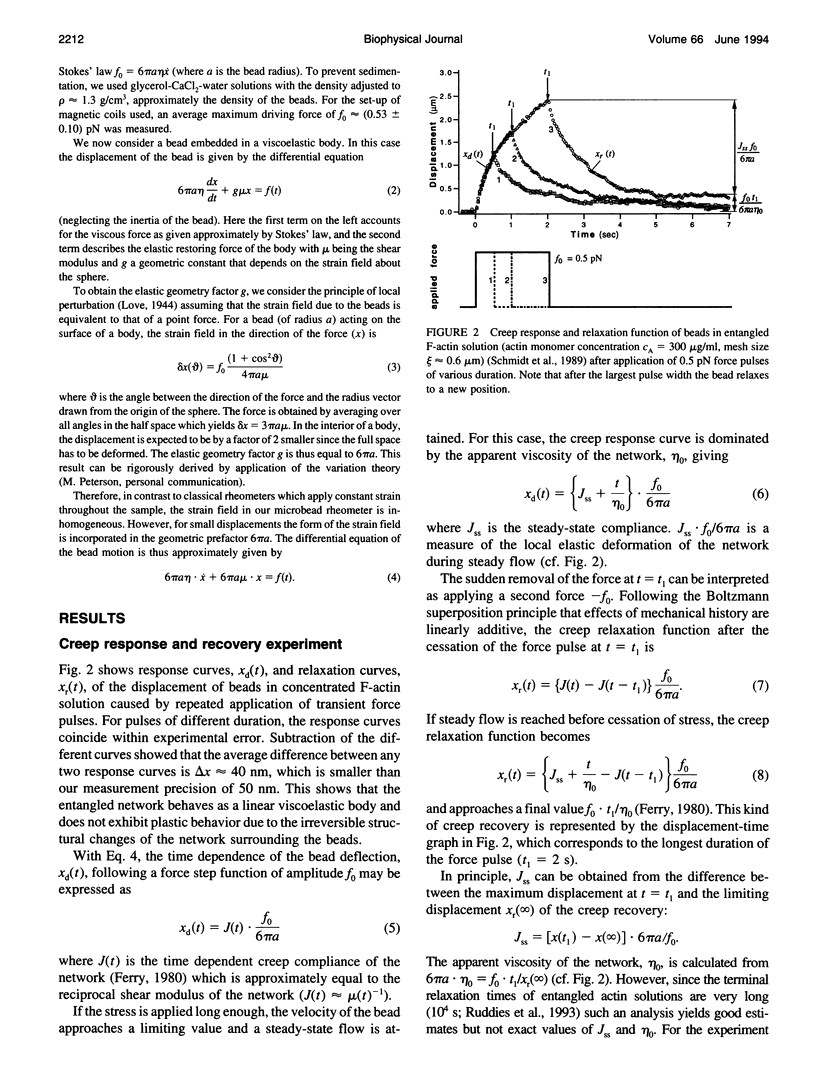

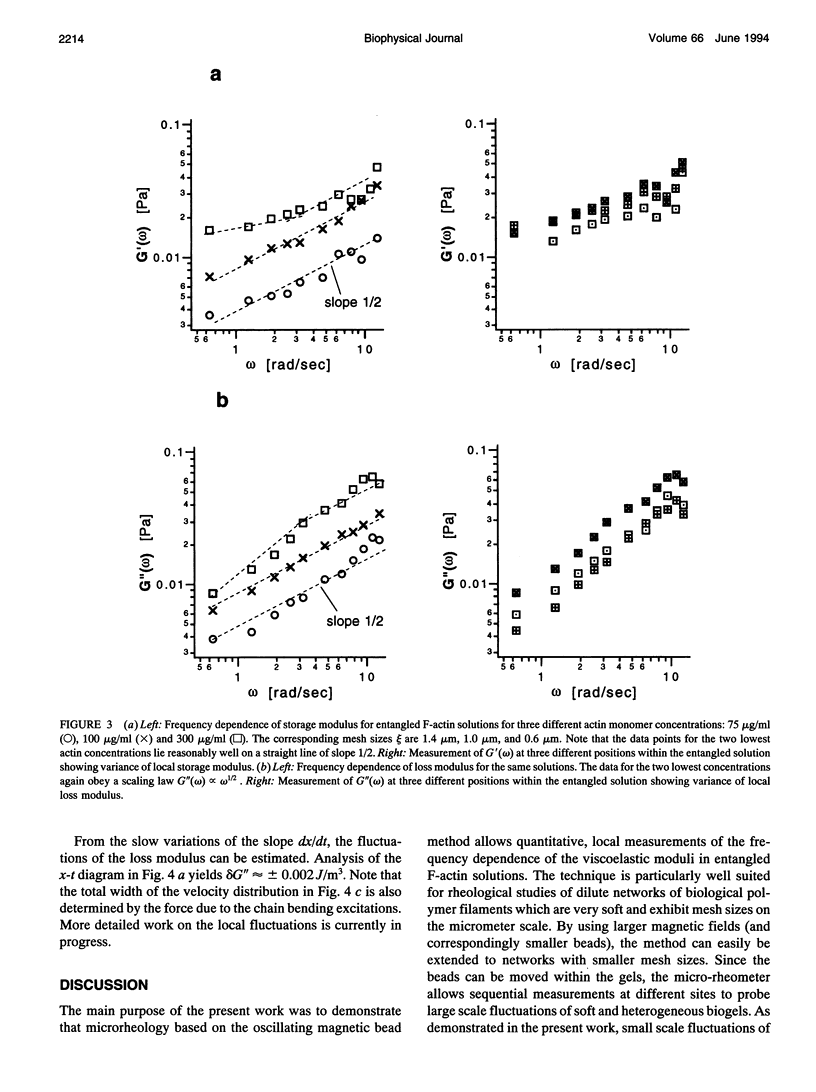

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Janmey P. A., Hvidt S., Lamb J., Stossel T. P. Resemblance of actin-binding protein/actin gels to covalently crosslinked networks. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):89–92. doi: 10.1038/345089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A. Mechanical properties of cytoskeletal polymers. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):4–11. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90159-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerst A., Chmielewski C., Livesay C., Buxbaum R. E., Heidemann S. R. Liquid crystal domains and thixotropy of filamentous actin suspensions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4241–4245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Litt M., Buchsbaum G. Rheology of the vitreous body. Part I: Viscoelasticity of human vitreous. Biorheology. 1992 Sep-Dec;29(5-6):521–533. doi: 10.3233/bir-1992-295-612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddies R., Goldmann W. H., Isenberg G., Sackmann E. The viscoelasticity of entangled actin networks: the influence of defects and modulation by talin and vinculin. Eur Biophys J. 1993;22(5):309–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00213554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Wong T. Z., Brown D. T., Allen R. D. Rheological properties of living cytoplasm: a preliminary investigation of squid axoplasm (Loligo pealei). Cell Motil. 1984;4(1):7–23. doi: 10.1002/cm.970040103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. B., Finzi L., Bustamante C. Direct mechanical measurements of the elasticity of single DNA molecules by using magnetic beads. Science. 1992 Nov 13;258(5085):1122–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.1439819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N., Butler J. P., Ingber D. E. Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1124–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.7684161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAGI K. The mechanical and colloidal properties of Amoeba protoplasm and their relations to the mechanism of amoeboid movement. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1961 Aug;3:73–91. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(61)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaner K. S., Valberg P. A. Viscoelasticity of F-actin measured with magnetic microparticles. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2233–2243. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilker A, Ziegler M, Sackmann E. Spectral analysis of erythrocyte flickering in the 0.3-4- microm-1 regime by microinterferometry combined with fast image processing. Phys Rev A. 1992 Dec 15;46(12):7998–8001. doi: 10.1103/physreva.46.7998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]