Full text
PDF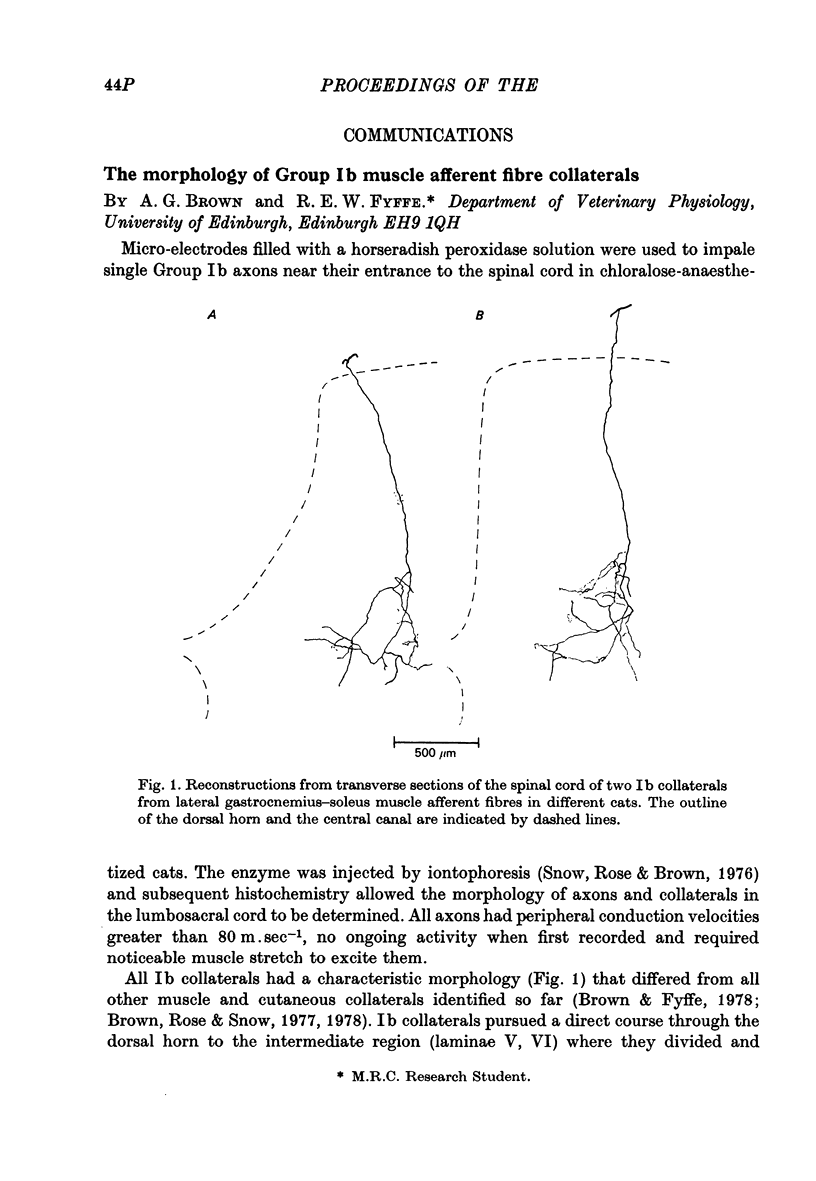




















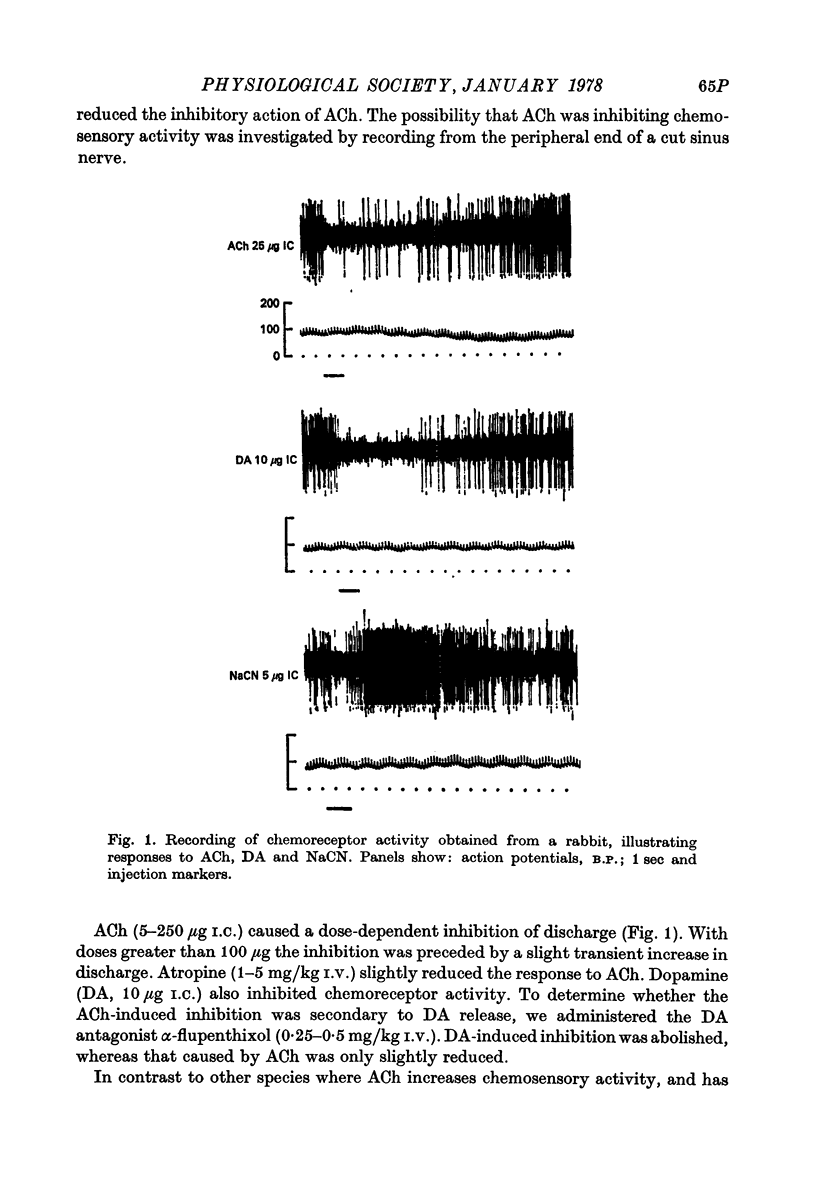


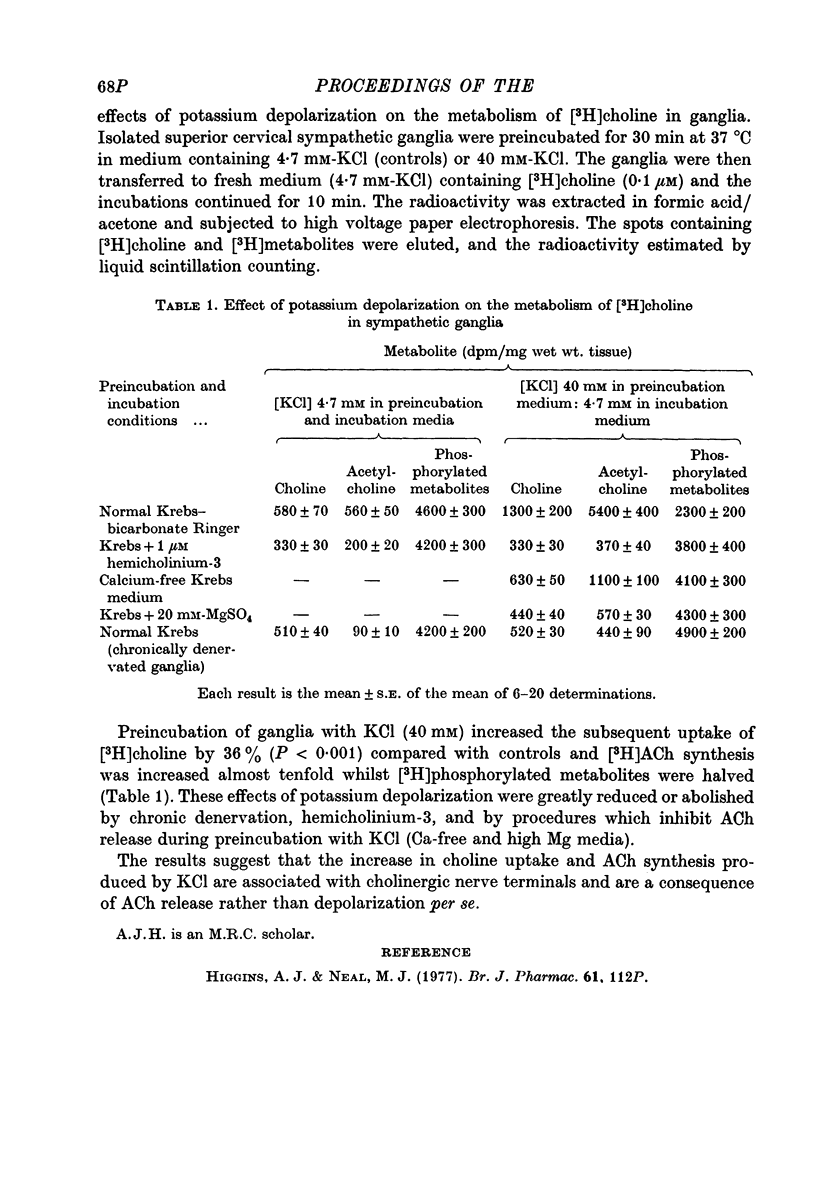
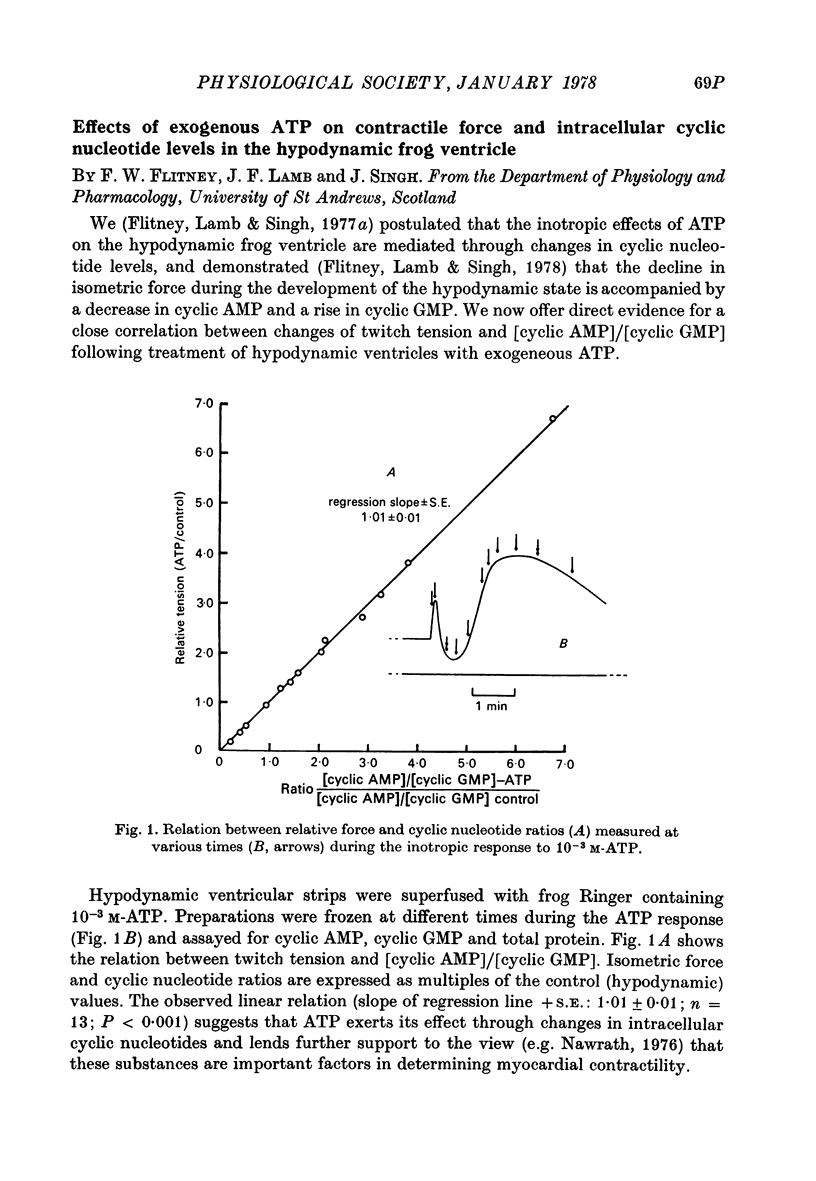
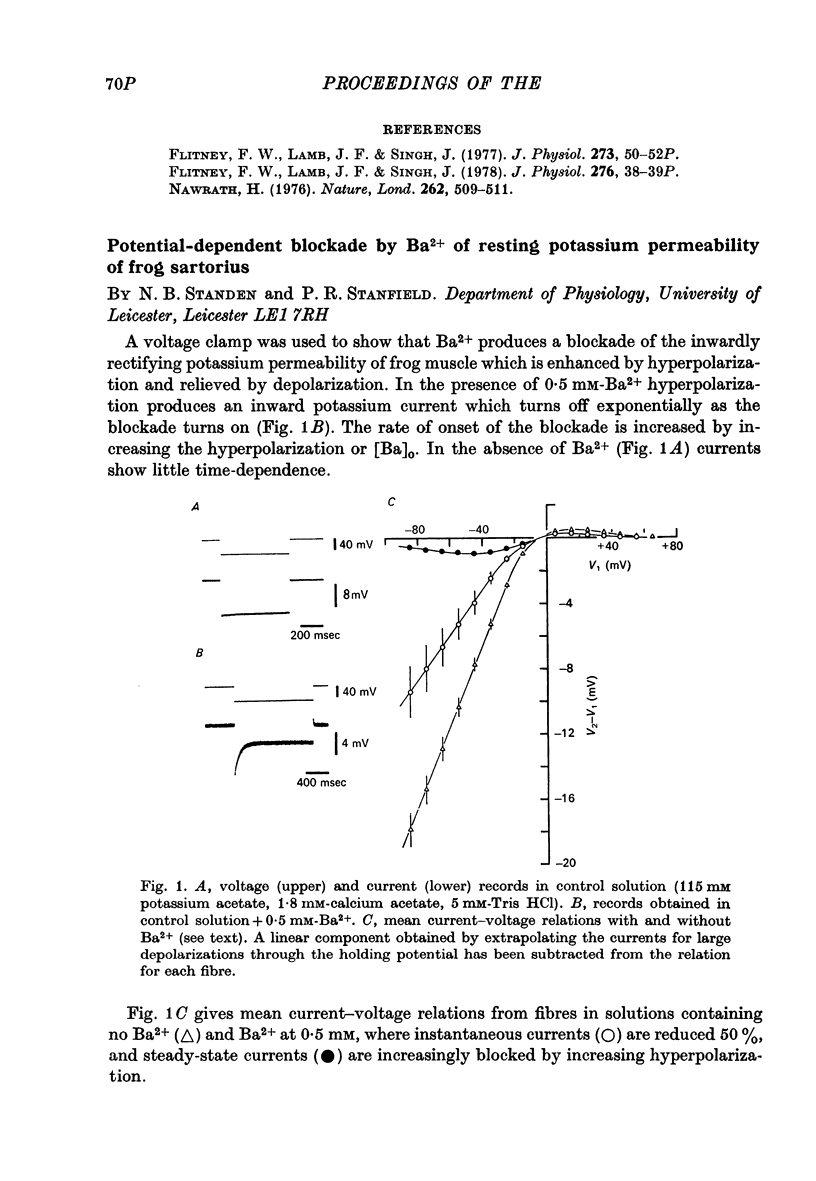

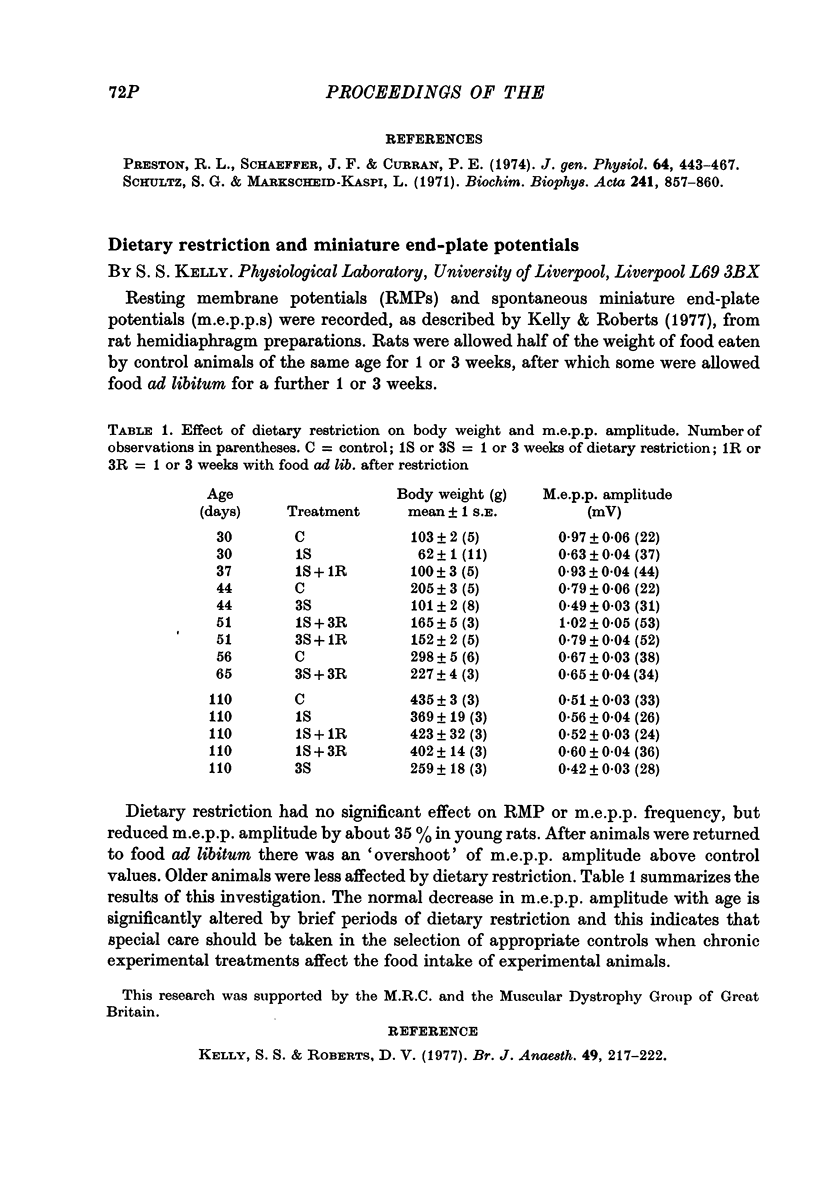





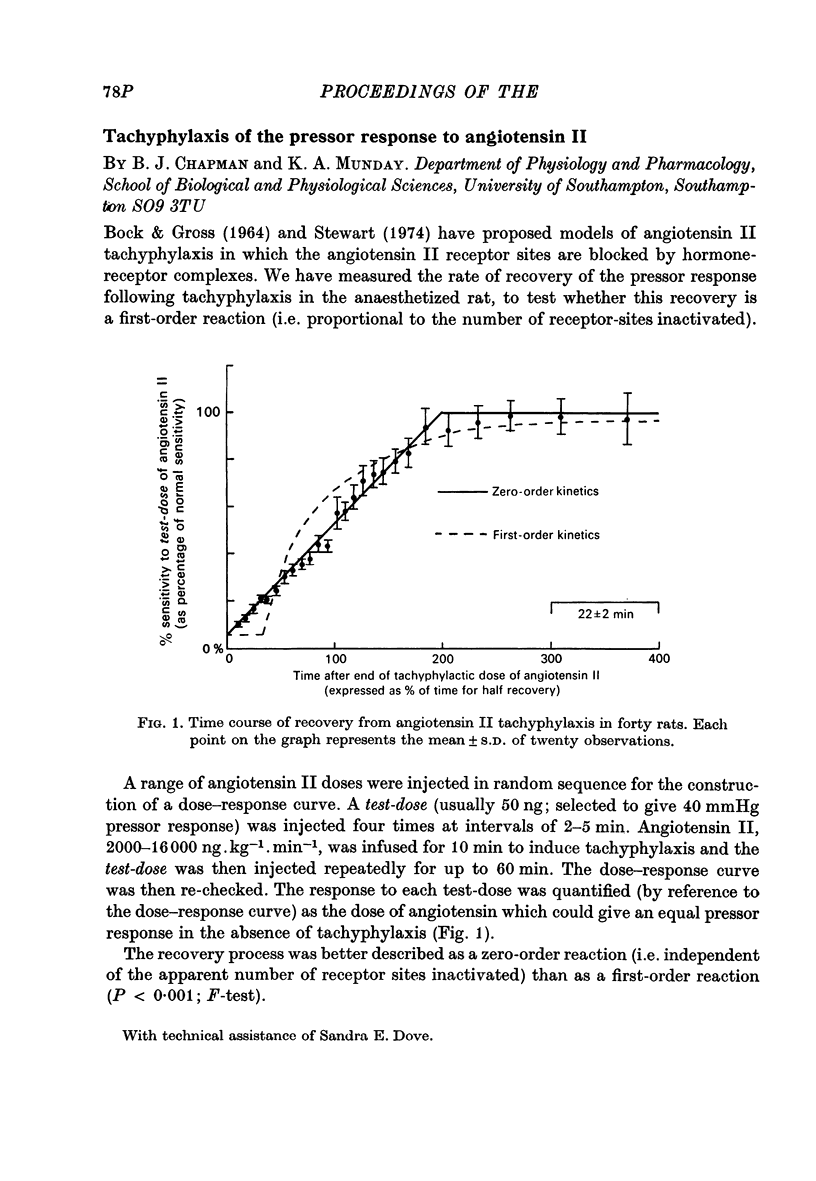




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aars H., Akre S. Reflex changes in sympathetic activity and arterial blood pressure evoked by afferent stimulation of the renal nerve. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Feb;78(2):184–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04654.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiyer M. S., Chiappa S. A., Fink G. A priming effect of luteinizing hormone releasing factor on the anterior pituitary gland in the female rat. J Endocrinol. 1974 Sep;62(3):573–588. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0620573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D. M., Cogdell B., Harvey R. Effects of afferent volleys from the limbs on the discharge patterns of interpositus neurones in cats anaesthetized with alpha-chloralose. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;248(2):489–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton J. C., Pirie S. C. Effects of pregnancy on glomerular filtration rate and sodium reabsorption in the rat kidney [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):82P–83P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Authier L., Sindon A., Chapados R., Barry P. P. Ketamine-induced cataleptogenic effects in the rabbit: potentiation and antagonism. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1972 Jul;19(4):445–452. doi: 10.1007/BF03005969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOCK K. D., GROSS F. Renin and angiotensin tachyphylaxis. Circ Res. 1961 Sep;9:1044–1050. doi: 10.1161/01.res.9.5.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhle Y. S., Vane J. R. Pharmacokinetic function of the pulmonary circulation. Physiol Rev. 1974 Oct;54(4):1007–1045. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.4.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhle Y. S., Youdim M. B. Metabolism of phenylethylamine in rat isolated perfused lung: evidence for monoamine oxidase 'type B' in lung. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Jan;56(1):125–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb06967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes R. J., Comline R. S., Silver M. The effects of bilateral adrenalectomy or hypophysectomy of the foetal lamb in utero. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(2):429–447. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baños G., Daniel P. M., Moorhouse S. R., Pratt O. E. The movement of amino acids between blood and skeletal muscle in the rat. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(2):459–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielecki K. The influence of changes in pH of the perfusion fluid on the occurrence of the calcium paradox in the isolated rat heart. Cardiovasc Res. 1969 Jul;3(3):268–271. doi: 10.1093/cvr/3.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing O. H., Brooks W. W., Messer J. V. Heart muscle viability following hypoxia: protective effect of acidosis. Science. 1973 Jun 22;180(4092):1297–1298. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4092.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Bradley G. W., Purves M. J. The relation between carotid body chemoreceptor discharge, carotid sinus pressure and carotid body venous flow. J Physiol. 1970 May;208(1):99–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J. Carotid body: structure and function. Physiol Rev. 1971 Jul;51(3):437–495. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Davies J., Dray A., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Martin M. R., Watkins J. C. Depression of synaptic excitation and of amino acid induced excitatory responses of spinal neurones by D-alpha-aminoadipate, alpha,epsilon-diaminopimelic acid and HA-966. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Oct 1;45(3):315–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Purves M. J., Sampson S. R. Types of nervous activity which may be recorded from the carotid sinus nerve in the sheep foetus. J Physiol. 1969 May;202(1):1–23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E. The morphology of group Ia afferent fibre collaterals in the spinal cord of the cat. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:111–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Rose P. K., Snow P. J. Morphology and organization of axon collaterals from afferent fibres of slowly adapting type I units in cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:15–27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Rose P. K., Snow P. J. The morphology of hair follicle afferent fibre collaterals in the spinal cord of the cat. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):779–797. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Marsh S. A very simple method for recording ganglion depolarization. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):24P–26P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Strick P. L., Kanda K., Kim C. C., Walmsley B. Anatomy of medial gastrocnemius and soleus motor nuclei in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1977 May;40(3):667–680. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.3.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caddy K. W., Biscoe T. J. Preliminary observations on the cerebllum in the mutant mouse Lurcher. Brain Res. 1975 Jun 27;91(2):276–280. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caddy K. W., Biscow T. J. The number of Purkinje cells and olive neurones in the normal and Lurcher mutant mouse. Brain Res. 1976 Jul 30;111(2):396–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90783-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calaresu F. R., Stella A., Zanchetti A. Haemodynamic responses and renin release during stimulation of afferent renal nerves in the cat. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):687–700. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell P. C., Walster G. E. The turnover of phosphorus compounds in crab muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;248(1):1–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B., Lee T. F. Do central dopamine receptors have a physiological role in thermoregulation? Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;61(1):83–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb09742.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer H., Johnson D. G., Hanbauer I., Silberstein S. D., Kopin I. J. Accumulation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate induced by catecholamines in the rat superior cervical ganglion in vitro. Brain Res. 1973 Apr 13;53(1):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90769-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Pratt O. E., Spargo E. The mechanism by which glucagon induces the release of amino acids from muscle and its relevance to fasting. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Mar 18;196(1124):347–365. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson A., Sellers A. F., Thorlacius S. O. Limitation of diffusion by blood flow through bovine ruminal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1337–1343. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J., Walsh J. H. Amino terminal gastrin fragment in serum of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome patients. Gastroenterology. 1975 Feb;68(2):222–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drost M., Holm L. W. Prolonged gestation in ewes after foetal adrenalectomy. J Endocrinol. 1968 Mar;40(3):293–296. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0400293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYZAGUIRRE C., LEWIN J. Effect of different oxygen tensions on the carotid body in vitro. J Physiol. 1961 Dec;159:238–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Watkins J. C. Selective antagonism by Mg2+ of amino acid-induced depolarization of spinal neurones. Experientia. 1977 Apr 15;33(4):489–491. doi: 10.1007/BF01922227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evarts E. V., Thach W. T. Motor mechanisms of the CNS: cerebrocerebellar interrelations. Annu Rev Physiol. 1969;31:451–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.31.030169.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields H. L., Basbaum A. I., Clanton C. H., Anderson S. D. Nucleus raphe magnus inhibition of spinal cord dorsal horn neurons. Brain Res. 1977 May 13;126(3):441–453. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90596-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flitney F. W., Lamb J. F., Singh J. Intracellular cyclic nucleotides and contractility of the hypodynamic frog ventricle [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:38P–39P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forn J., Krueger B. K., Greengard P. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate content in rat caudate nucleus: demonstration of dopaminergic and adrenergic receptors. Science. 1974 Dec 20;186(4169):1118–1120. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4169.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADDUM J. H., HAMEED K. A., HATHWAY D. E., STEPHENS F. F. Quantitative studies of antagonists for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1955 Jan;40(1):49–74. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1955.sp001097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The spinal origin of the motor and inhibitory innervation of the rat anococcygeus muscles. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):659–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Possible role for cyclic nucleotides and phosphorylated membrane proteins in postsynaptic actions of neurotransmitters. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):101–108. doi: 10.1038/260101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G. W. Electrical stimulation of the hypothalamus and the mechanism of neural control of the adenohypophysis. J Physiol. 1948 Sep 30;107(4):418–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1948.sp004286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch R. C. Ketamine catalepsy and anesthesia in dogs pretreated with antiserotonergic or antidopaminergic neuroleptics or with anticholinergic agents. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1974 Jun;6(3):289–299. doi: 10.1016/s0031-6989(74)80048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haymet B. T., McCloskey D. I. Baroreceptor and chemoreceptor influences on heart rate during the respiratory cycle in the dog. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;245(3):699–712. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins A. J., Neal M. J. Activation of high affinity choline uptake in sympathetic ganglia by potassium depolarization [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;61(1):112P–113P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbauer M., Youdim M. B. The oestrous cycle and monoamine oxidase activity. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Aug;48(4):600–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D., Spyer K. M. Studies on the termination of sinus nerve afferents. Pflugers Arch. 1977 May 6;369(1):65–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00580812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly S. S., Roberts D. V. The effect of age on the safety factor in neuromuscular transmission in the isolated diaphragm of the rat. Br J Anaesth. 1977 Mar;49(3):217–222. doi: 10.1093/bja/49.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y., Kubota K., Shuto S., Sumino R. Possible interneurons responsible for reflex inhibition of motoneurons of jaw-closing muscles from the inferior dental nerve. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Sep;31(5):709–716. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.5.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensson K., Olsson Y. Retrograde axonal transport of protein. Brain Res. 1971 Jun 18;29(2):363–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landis S. C. Ultrastructural changes in the mitochondria of cerebellar Purkinje cells of nervous mutant mice. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jun;57(3):782–797. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.3.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer G. A., Poole-Wilson P. A. The effect of acidosis and manganese on calcium exchange in the myocardium of the rabbit [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):20P–21P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M. The effect of denervation on the mechanical and electrical responses of fast and slow mammalian twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):51–75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J., McAllen R. M., Spyer K. M. The carotid chemoreceptor input to the respiratory neurones of the nucleus of tractus solitarus. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;269(3):797–810. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J., McAllen R. M., Spyer K. M. The sinus nerve and baroreceptor input to the medulla of the cat. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;251(1):61–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston A., Waterman A. E. Effects of repeated doses of ketamine on sleeping times in rats [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;57(3):457P–457P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. F. Growth of the maternal kidneys in pregnant mice [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):84P–84P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S., van der Meché F. G. Coordinated stepping of all four limbs in the high spinal cat. Brain Res. 1976 Jun 11;109(2):395–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90541-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N., Fleck A. Recent developments in the measurement of nucleic acids in biological materials. A supplementary review. Analyst. 1966 Feb;91(79):78–88. doi: 10.1039/an9669100078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawrath H. Cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP may play opposing roles in influencing force of contraction in mammalian myocardium. Nature. 1976 Aug 5;262(5568):509–511. doi: 10.1038/262509b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijima A. Afferent discharges from arterial mechanoreceptors in the kidney of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(2):477–485. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveras J. L., Redjemi F., Guilbaud G., Besson J. M. Analgesia induced by electrical stimulation of the inferior centralis nucleus of the raphe in the cat. Pain. 1975 Jun;1(2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(75)90098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestronk A., Drachman D. B., Griffin J. W. Effect of botulinum toxin on trophic regulation of acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):787–789. doi: 10.1038/264787a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole-Wilson P. A., Langer G. A. Effect of pH on ionic exchange and function in rat and rabbit myocardium. Am J Physiol. 1975 Sep;229(3):570–581. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.3.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston R. L., Schaeffer J. F., Curran P. F. Structure-affinity relationships of substrates for the neutral amino acid transport system in rabbit ileum. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Oct;64(4):443–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.4.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. I. Quantitative aspects. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Apr;81(4):557–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers A. F., Sutherland R. J. Proceedings: Clo values of Polar clothing and their relation to 'total number of layers' counts. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(2):22P–24P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Markscheid-Kaspi L. Competitive interactions between L-alanine and L-phenylalanine in rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 14;241(3):857–860. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow P. J., Rose P. K., Brown A. G. Tracing axons and axon collaterals of spinal neurons using intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase. Science. 1976 Jan 23;191(4224):312–313. doi: 10.1126/science.54936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegemann H., Stalder K. Determination of hydroxyproline. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 Nov;18(2):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten S. M. Dissociation of limbic and neocortical EEG patterns in cats under ketamine anesthesia. J Neurosurg. 1972 Oct;37(4):429–433. doi: 10.3171/jns.1972.37.4.0429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



