Abstract
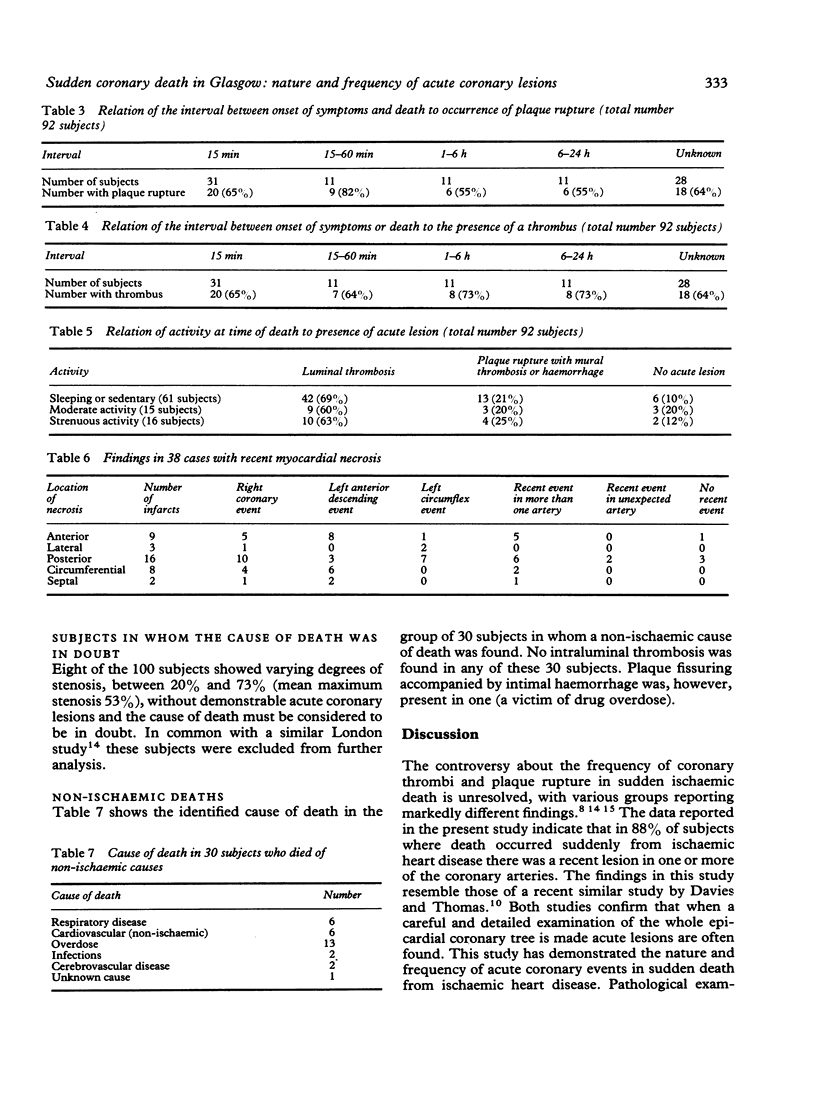
A detailed pathological study of the coronary arteries was carried out on 130 random white subjects (91 male and 39 female) who died suddenly in the Glasgow area. In 30 there was a clearly defined cause of death that was not due to ischaemic heart disease. In eight subjects the cause of death was in doubt. Ninety two of the 130 showed coronary stenosis resulting in a loss of more than 75% of coronary artery cross sectional area and/or acute coronary events with no other cause of death. Of these 92 subjects considered to have died suddenly of ischaemic heart disease, 64% showed plaque rupture and thrombosis which occurred at sites of previous high grades of stenosis. Twenty two subjects had intraluminal thrombosis unrelated to plaque fissuring. Thirty eight (41%) showed histological evidence of recent myocardial necrosis; acute coronary events occurred in 34 of these. There was no correlation between the duration of symptoms before death and the occurrence of acute coronary events. Acute coronary events, mainly in the form of plaque rupture, are a common finding in sudden coronary death when a careful study is made of the whole coronary arterial tree.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baroldi G. Acute coronary occlusion as a cause of myocardial infarct and sudden coronary heart death. Am J Cardiol. 1965 Dec;16(6):859–880. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(65)90704-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt P. W., Partridge J. B., Wattie W. J. Coronary arteriography; method of presentation of the arteriogram report and a scoring system. Clin Radiol. 1977 Jul;28(4):361–365. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(77)80140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. J., Thomas A. C. Plaque fissuring--the cause of acute myocardial infarction, sudden ischaemic death, and crescendo angina. Br Heart J. 1985 Apr;53(4):363–373. doi: 10.1136/hrt.53.4.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. J., Thomas A. Thrombosis and acute coronary-artery lesions in sudden cardiac ischemic death. N Engl J Med. 1984 May 3;310(18):1137–1140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405033101801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erhardt L. R., Unge G., Boman G. Formation of coronary arterial thrombi in relation to onset of necrosis in acute myocardial infarction in man. A clinical and autoradiographic study. Am Heart J. 1976 May;91(5):592–598. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(76)80144-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk E. Plaque rupture with severe pre-existing stenosis precipitating coronary thrombosis. Characteristics of coronary atherosclerotic plaques underlying fatal occlusive thrombi. Br Heart J. 1983 Aug;50(2):127–134. doi: 10.1136/hrt.50.2.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk E. Unstable angina with fatal outcome: dynamic coronary thrombosis leading to infarction and/or sudden death. Autopsy evidence of recurrent mural thrombosis with peripheral embolization culminating in total vascular occlusion. Circulation. 1985 Apr;71(4):699–708. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.71.4.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M., Manwaring J. H., Rosenman R. H., Donlon G., Ortega P., Grube S. M. Instantaneous and sudden deaths. Clinical and pathological differentiation in coronary artery disease. JAMA. 1973 Sep 10;225(11):1319–1328. doi: 10.1001/jama.225.11.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberthson R. R., Nagel E. L., Hirschman J. C., Nussenfeld S. R., Blackbourne B. D., Davis J. H. Pathophysiologic observations in prehospital ventricular fibrillation and sudden cardiac death. Circulation. 1974 May;49(5):790–798. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.49.5.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHLAS M. M., SHNITKA T. K. Macroscopic identification of early myocardial infarcts by alterations in dehydrogenase activity. Am J Pathol. 1963 Apr;42:379–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. C., Buja L. M. The frequency and significance of coronary arterial thrombi and other observations in fatal acute myocardial infarction: a study of 107 necropsy patients. Am J Med. 1972 Apr;52(4):425–443. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper A. G., Cook D. G., Walker M., Macfarlane P. W. Prevalence of ischaemic heart disease in middle aged British men. Br Heart J. 1984 Jun;51(6):595–605. doi: 10.1136/hrt.51.6.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain D. M., Bradess V. A. Sudden death from coronary heart disease. Survival time, frequency of thrombi, and cigarette smoking. Chest. 1970 Aug;58(2):107–110. doi: 10.1378/chest.58.2.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnes C. A., Roberts W. C. Sudden coronary death: comparison of patients with to those without coronary thrombus at necropsy. Am J Cardiol. 1984 Dec 1;54(10):1206–1211. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(84)80068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]