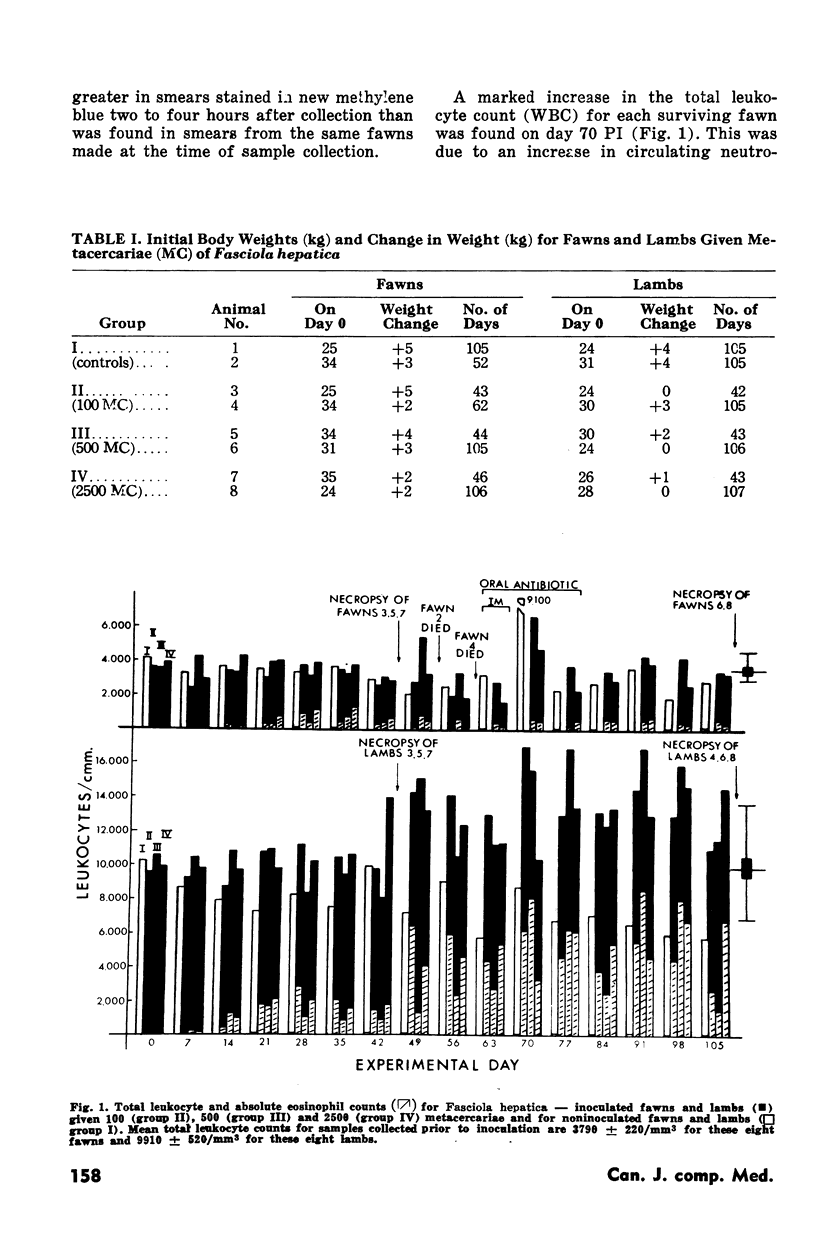
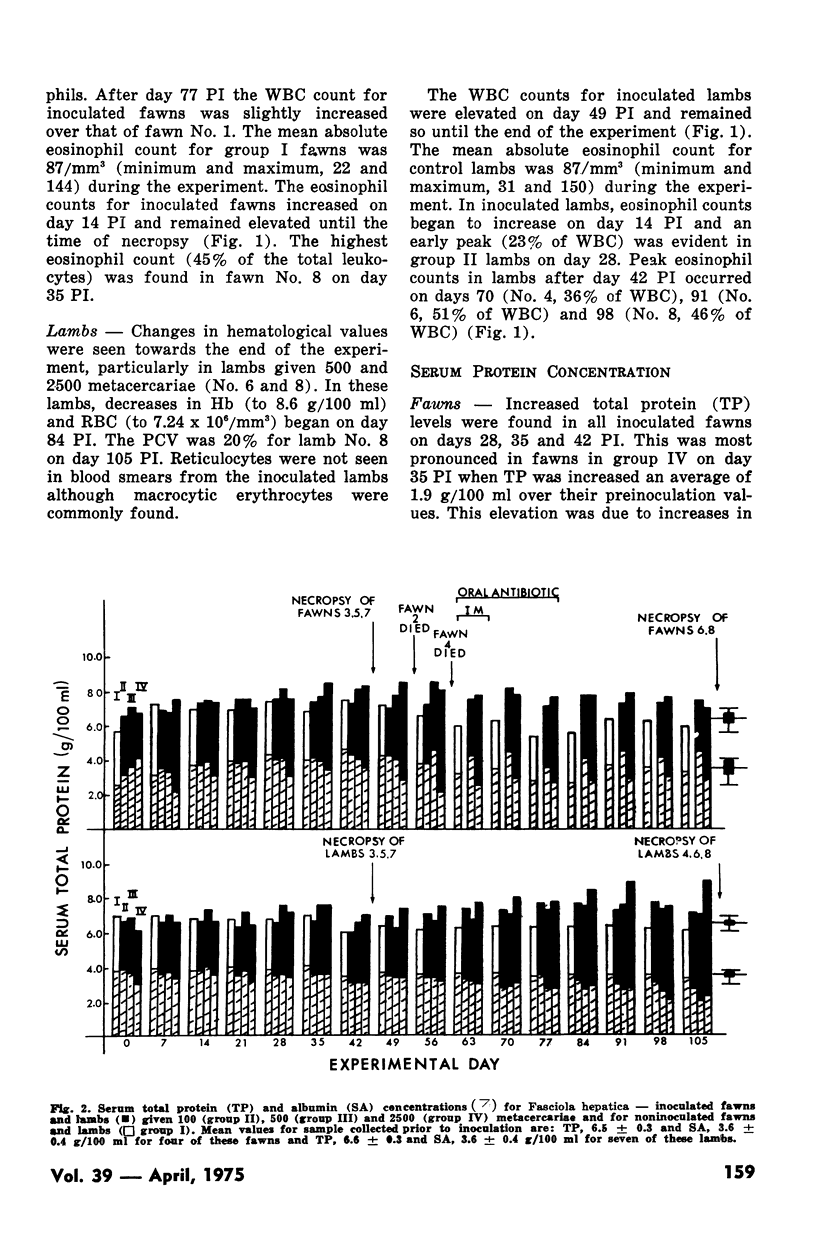
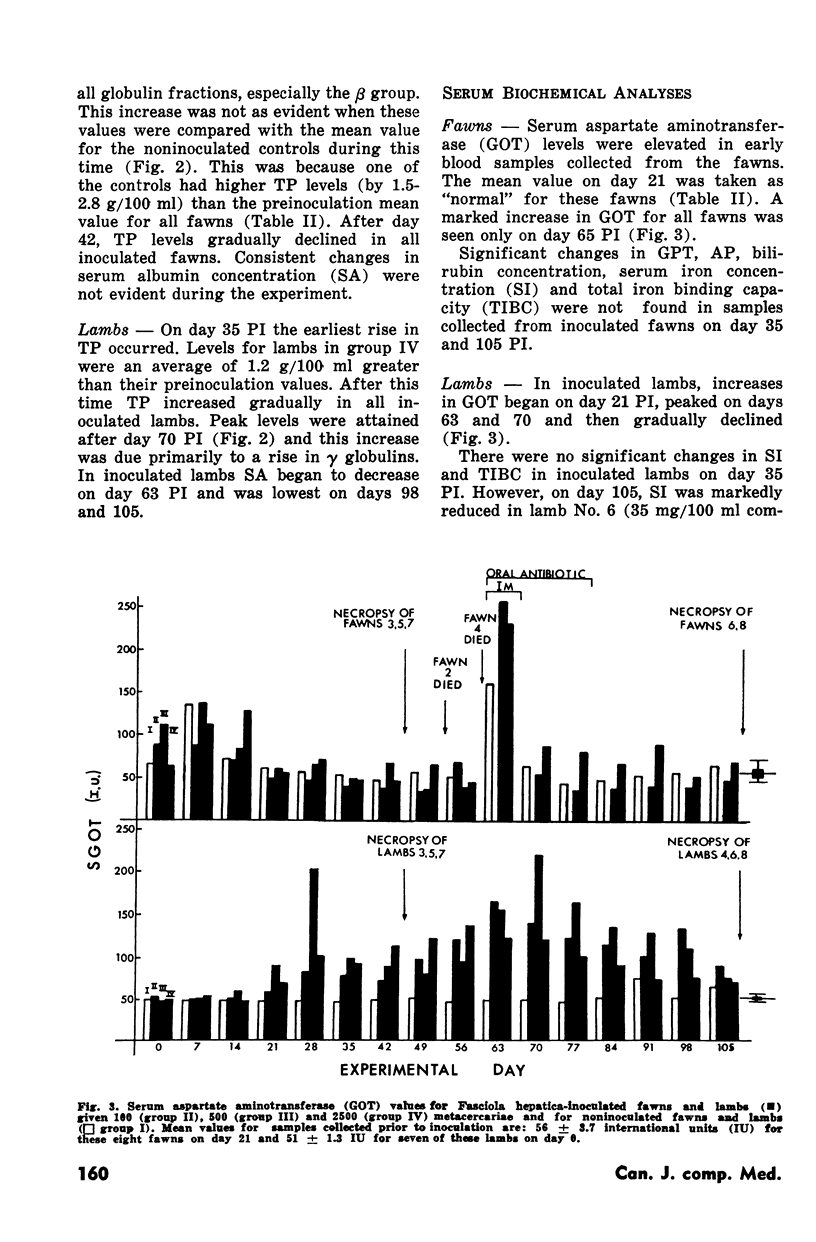
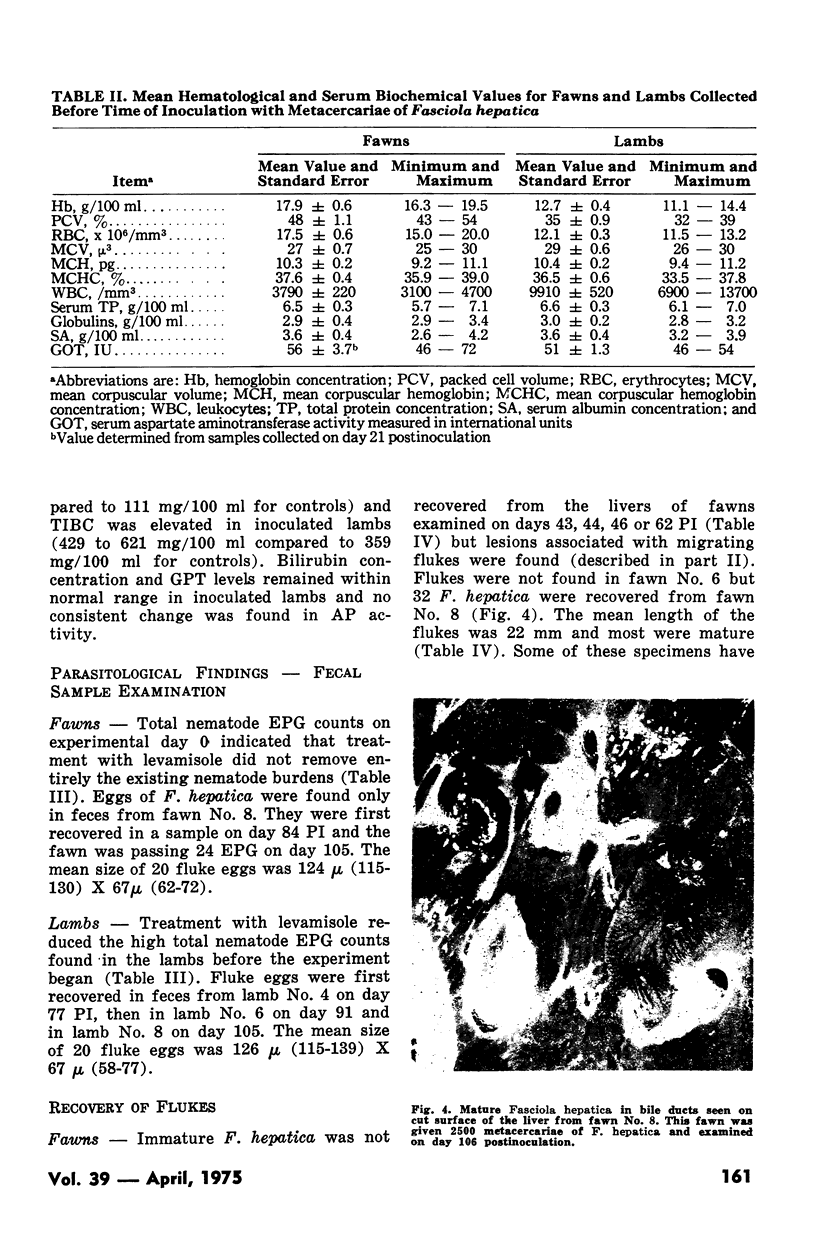
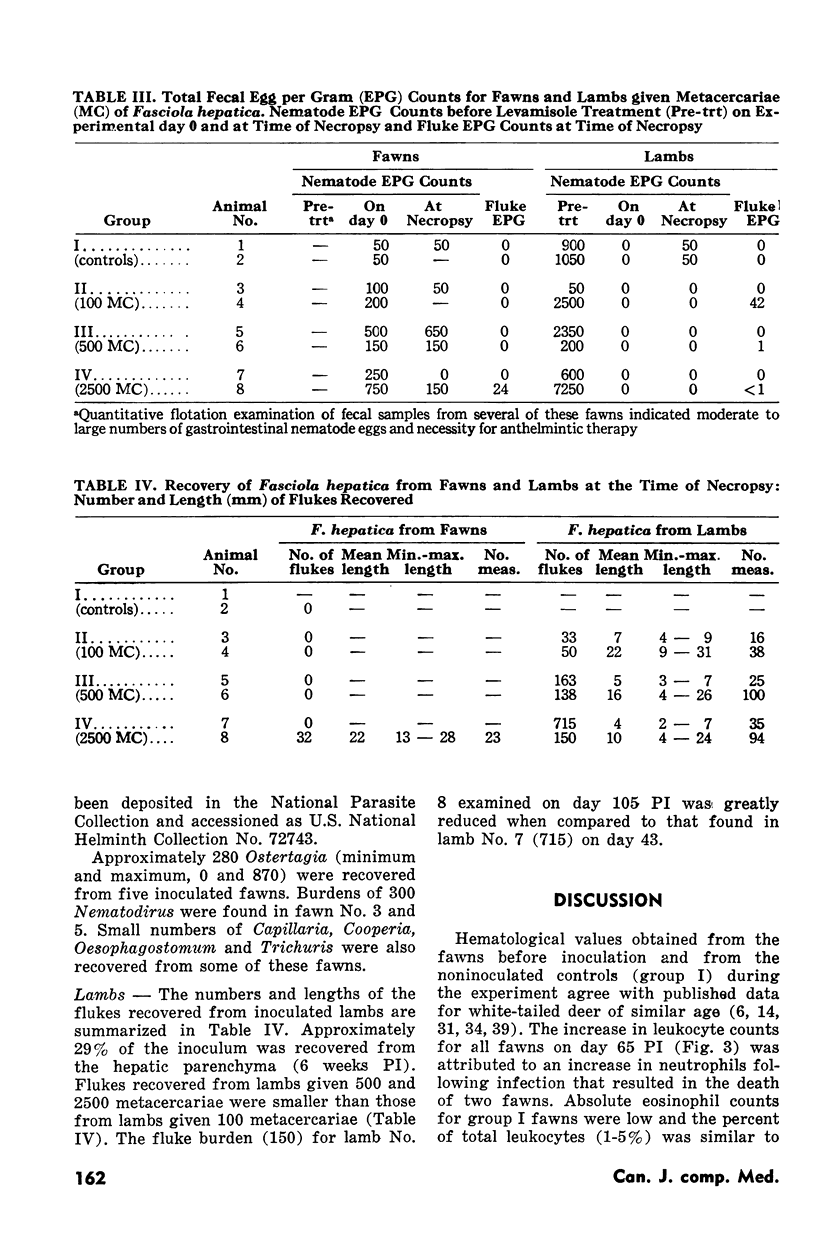
Abstract
Six white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) and six sheep were inoculated with metacercariae of Fasciola hepatica. Two animals of each species were given 100, 500 or 2500 metacercariae. Clinicopathological features of these infections were determined by analyses of blood samples collected each week from inoculated deer and sheep as well as from two noninoculated animals of each species. One animal in each inoculated group was killed and examined at six weeks postinoculation and the remainder at 15 weeks postinoculation. Compared with the values obtained from noninoculated controls, eosinophilia, hyperproteinemia and hyperglobulinemia occured in inoculated deer. There were no other significant changes in hematological values or in serum aspartate aminotransferase levels. Marked leukocytosis and eosinophilia, with hyperproteinemia, hyperglobulinemia, hypoalbuminemia, elevated serum aspartate aminotransferase levels and mild macrocytic normochromic anemia characterized the infection in lambs. Although approximately 29% of the inoculum was recovered from the hepatic parenchyma of the sheep, F. hepatica was found in only one of six inoculated deer. A patent infection was established in this deer and constitutes the second report of mature F. hepatica in this host.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth D., Schaich K. Zum Vorkommen von Fasciola hepatica bei Reh- (Capreolus capreolus) und Rotwild (Cervus elaphus) und deren Bekämpfung mit Rafoxanid. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1973 Sep 15;80(18):420–contd. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boray J. C. Studies on experimental infections with Fasciola hepatica, with particular reference to acute fascioliasis in sheep. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1967 Dec;61(4):439–450. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1967.11686513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalchow W., Hörchner F. Zur experimentellen Fasciola hepatica-Infektion bei verschiedenen Tierarten. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1972 Jul 15;85(14):271–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreyt W. J., Tood A. C. The occurrence of Fascioloides magna and Fasciola hepatica together in the livers of naturally infected cattle in south Texas, and the incidence of the flukes in cattle, white-tailed deer, and feral hogs. J Parasitol. 1972 Oct;58(5):1010–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjerpe C. A., Tennant B. C., Crenshaw G. L., Baker N. F. Ovine fascioliasis in California. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1971 Nov;159(10):1266–1271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörchner F., Dalchow W. Zur experimentellen Fasciola hepatica-Infektion beim Schwein. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1972 May 15;85(10):184–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistner T. P., Koller L. D. Experimentally induced Fasciola hepatica infections in black-tailed deer. J Wildl Dis. 1975 Apr;11(2):214–220. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-11.2.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nansen P., Andersen S., Harmer E., Riising H. J. Experimental fascioliasis in the pig. Exp Parasitol. 1972 Apr;31(2):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(72)90115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presidente P. J., Knapp S. E., Nicol K. D. Pathogenicity of experimentally induced concurrent infections of Fasciola hepatica and Haemonchus contortus in sheep. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Jan;34(1):51–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presidente P. J., Lumsden J. H., Presnell K. R., Rapley W. A., McCraw B. M. Combination of etorphine and zylazine in captive white-tailed deer. II. Effects on hematologic, serum biochemical and blood gas values. J Wildl Dis. 1973 Oct;9(4):342–348. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-9.4.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presidente P. J., McCraw B. M., Lumsden J. H. Early pathological changes associated with Fasciola hepatica infections in white-tailed deer. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Jul;38(3):271–279. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presnell K. R., Presidente P. J., Rapley W. A. Combination of etorphine and xylazine in captive white-tailed deer. I. Sedative and immobilization properties. J Wildl Dis. 1973 Oct;9(4):336–341. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-9.4.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullan N. B., Sewell M. M., Hammond J. A. Studies on the pathogenicity of massive infections of Fasciola hepatica L. in lambs. Br Vet J. 1970 Oct;126(10):543–558. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)48141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts H. E. Observations on experimental acute fascioliasis in sheep. Br Vet J. 1968 Oct;124(10):433–450. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)39152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell M. M., Hammond J. A., Dinning D. C. Studies on the aetiology of anaemia in chronic fascioliasis in sheep. Br Vet J. 1968 Apr;124(4):160–170. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)39455-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons L. E., Boray J. C. The anaemia of acute and chronic ovine fascioliasis. Z Tropenmed Parasitol. 1968 Dec;19(4):451–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe E., Ford E. J. Serum enzyme and hepatic changes in sheep infested with Fasciola hepatica. J Pathol. 1969 Apr;97(4):619–629. doi: 10.1002/path.1710970406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tumbleson M. E., Cuneio J. D., Murphy D. A. Serum biochemical and hematological parameters of captive white-tailed fawns. Can J Comp Med. 1970 Jan;34(1):66–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M., Cook R. S. Blood characteristics of free-ranging white-tailed deer in southern Texas. J Wildl Dis. 1974 Jan;10(1):18–24. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-10.1.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]