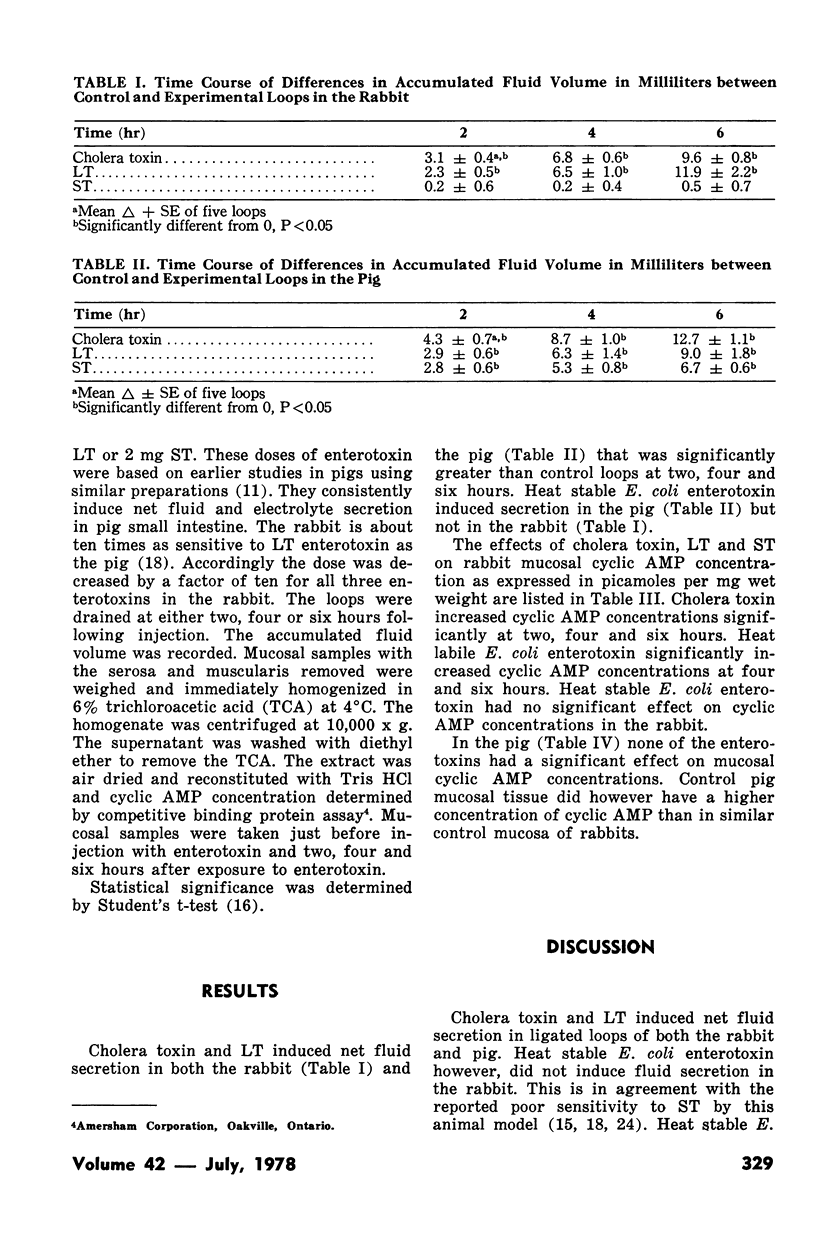
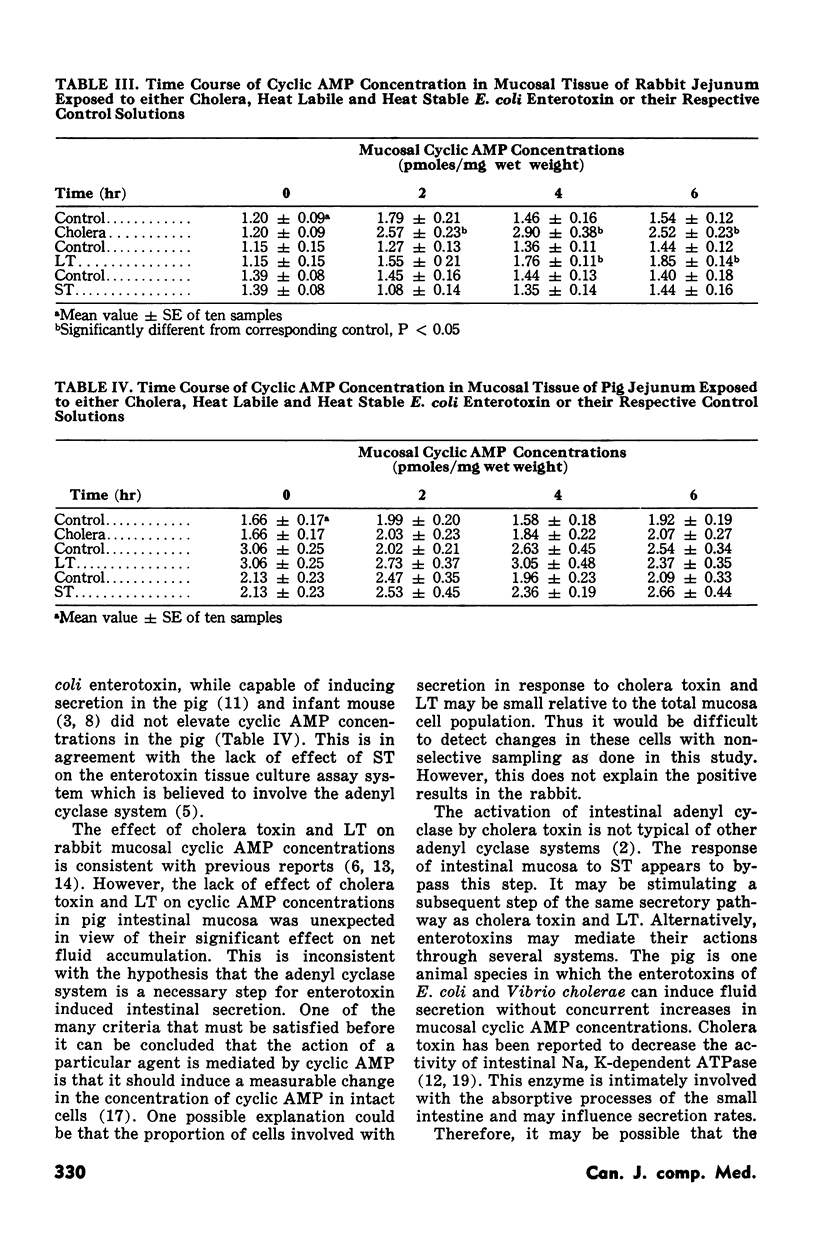
Abstract
The effect of cholera toxin, heat labile and heat stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin on mucosal cyclic AMP concentrations was determined on the proximal jejunum of weanling pigs and young rabbits. Ligated loops were injected with solutions containing no enterotoxin for control and either cholera toxin, heat labile or heat stable E. coli enterotoxin. The loops were drained after either two, four or six hours incubation at which time accumulated fluid was recorded and mucosal samples removed for determination of cyclic AMP concentration. In the rabbit, cholera toxin and heat labile, but not heat stable E. coli enterotoxin stimulated intestinal secretion while in the pig all three enterotoxins induced net fluid accumulation. Cholera toxin and heat labile, but not heat stable E. coli enterotoxin elevated rabbit mucosal cyclic AMP concentrations. In the pig these enterotoxins had no significant effect on mucosal cyclic AMP concentrations. The results are inconsistent with the hypothesis that the adenyl cyclase system is an essential step for enterotoxin induced intestinal secretion. The activation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by bacterial enterotoxins may only be an associated and not a necessary event for the stimulation of intestinal secretion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banwell J. G., Sherr H. Effect of bacterial enterotoxins on the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1973 Sep;65(3):467–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., King M., Sloper K. Induction of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by cholera enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 20;243(129):246–247. doi: 10.1038/newbio243246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Chen L. C., Curlin G. T., Evans D. G. Stimulation of adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):137–138. doi: 10.1038/newbio236137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., al-Awqati Q., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effect of cholera enterotoxin on ion transport across isolated ileal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):796–804. doi: 10.1172/JCI106874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Chen L. C., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in canine cholera: correlation with fluid accumulation. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):377–381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Ganguly U., Casper A. G., Moore E. J., Pierce N. F., Carpenter C. C. Effect of Escherichia coli on fluid transport across canine small bowel. Mechanism and time-course with enterotoxin and whole bacterial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1707–1714. doi: 10.1172/JCI107352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton D. L., Roe W. E., Nielsen N. O. Effect of heat stable and heat labile Escherichia coli enterotoxins, cholera toxin and theophylline on unidirectional sodium and chloride fluxes in the proximal and distal jejunum of weanling swine. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Jul;41(3):306–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn N., Rosenberg I. H. Sodium-potassium stimulated adenosine triphosphatase of the small intestine of man: studies in cholera and other diarrheal diseases. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jul;72(1):28–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor H. S., Tao P., Gorbach S. L. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin: comparison of strains from an infant and an adult with diarrhea. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larivière S., Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A comparative study of the rabbit and pig gut loop systems for the assay of Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Can J Comp Med. 1972 Oct;36(4):319–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddle G. W., Hardman J. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate as a mediator of hormone action. N Engl J Med. 1971 Sep 2;285(10):560–566. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197109022851007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson D. K., Ebel H., DiBona D. R., Sharp G. W. Localization of the action of cholera toxin on adenyl cyclase in mucosal epithelial cells of rabbit intestine. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2292–2298. doi: 10.1172/JCI107039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Carpenter C. C., Jr, Elliott H. L., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effects of prostaglandins, theophylline, and cholera exotoxin upon transmucosal water and electrolyte movement in the canine jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jan;60(1):22–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. E., Lust W. D., Sircar B., Goldberg N. D. Elevated concentration of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in intestinal mucosa after treatment with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):851–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The effect of cell-free fluids prepared from cultures of human and animal enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli on ligated intestinal segments of rabbits and pigs. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):403–409. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between two apparently different enterotoxins produced by enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli of porcine origin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):387–401. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Studies on Escherichia coli enterotoxin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):531–543. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Awqati Q., Cameron J. L., Greenough W. B., 3rd Electrolyte transport in human ileum: effect of purified cholera exotoxin. Am J Physiol. 1973 Apr;224(4):818–823. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.4.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


