Abstract
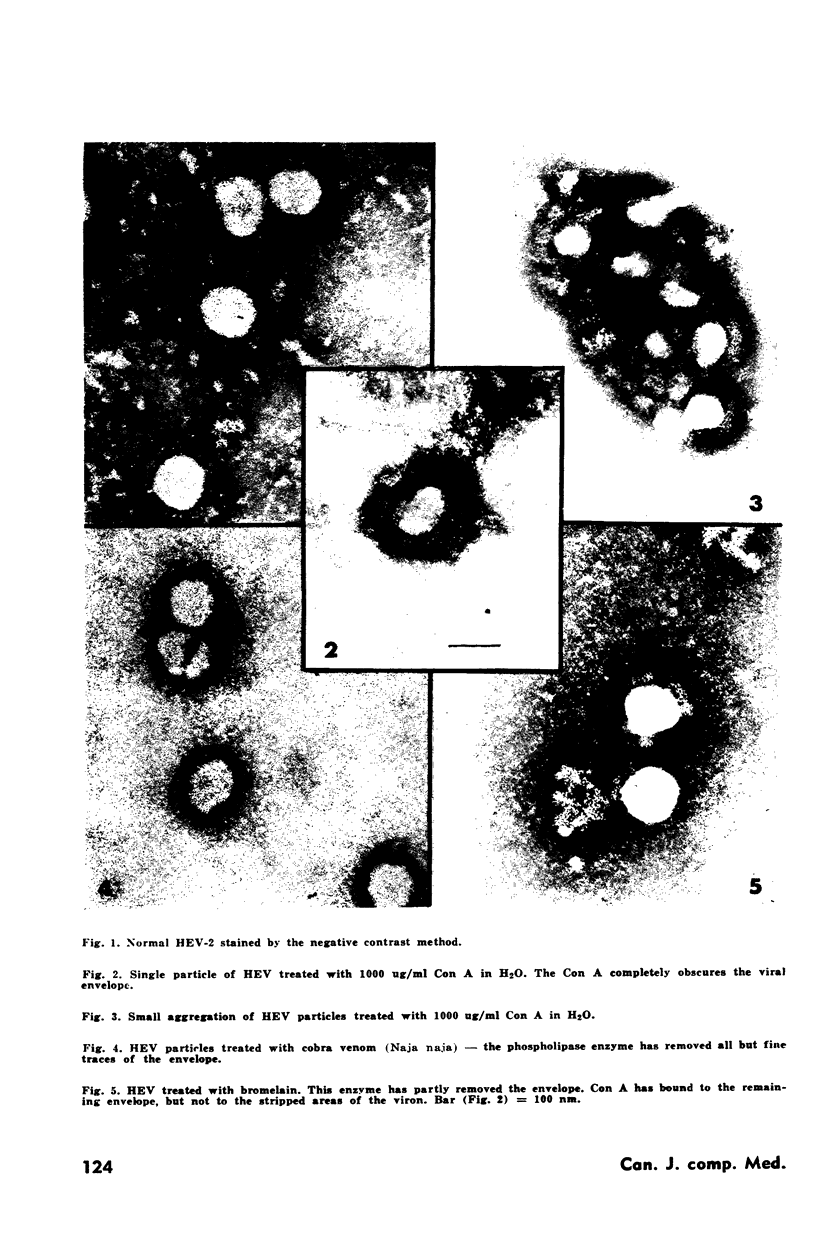
Concanavalin A, a phytagglutinin, binds to the envelope of hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus, a Coronavirus. Concanavalin A treated virus suspensions lose their hemagglutination properties and there is a transient interference with infectivity. Electron micrographs show the Concanavalin A as a granular deposit adhering to the viral envelope and there is aggregation of the virus. Concanavalin A does not bind to virions stripped of their envelopes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becht H., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Effect of Concanavalin A on cells infected with enveloped RNA viruses. J Gen Virol. 1972 Jan;14(1):1–8. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-14-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calafat J., Hageman P. C. Binding of Concanavalin A to the envelope of two murine RNA tumour viruses. J Gen Virol. 1972 Jan;14(1):103–106. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-14-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compans R. W. Location of the glycoprotein in the membrane of Sindbis virus. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 27;229(4):114–116. doi: 10.1038/newbio229114a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig A. S., Girard A. Encephalomyelitis of swine caused by a haemagglutinating virus. V. Response to metabolic inhibitors and other chemical compounds. Res Vet Sci. 1969 Nov;10(6):509–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig A. S., Johnson C. M., Bouillant A. M. Encephalomyelitis of swine caused by a haemagglutinating virus. VI. Morphology of the virus. Res Vet Sci. 1971 Jul;12(4):305–307. doi: 10.1016/S0034-5288(18)34153-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig A. S., Mitchell D., Corner A. H., Bannister G. L., Meads E. B., Julian R. J. A Hemagglutinating Virus Producing Encephalomyelitis in Baby Pigs. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1962 Mar;26(3):49–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Sachs L. Interaction of the carbohydrate-binding protein concanavalin A with normal and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1418–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. H., Shibley G. P., Schidlovsky G., Nakai T., Howatson A. F., Wivel N. W., O'Connor T. E. Action of snake venom on Rauscher virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Jan;40(1):135–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nermut M. V. Further investigation on the fine structure of influenza virus. J Gen Virol. 1972 Dec;17(3):317–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-17-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Kim J. Interaction of concanavalin A with enveloped viruses and host cells. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90401-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. D., Ellwood D. C., Appleyard G., Stanley J. L. Agglutination of an arbovirus by concanavalin A. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 8;233(36):50–51. doi: 10.1038/newbio233050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiloah J., Klibansky C., De Vries A. Phospholipase isoenzymes from Naja naja venom. II. Phospholipase A and B activities. Toxicon. 1973 Oct;11(6):491–497. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(73)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner J. B., Howell S. F. Identification of Hemagglutinin of Jack Bean with Concanavalin A. J Bacteriol. 1936 Aug;32(2):227–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.32.2.227-237.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]