Abstract
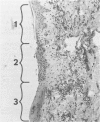
Heat-inactivated pseudorabies virus caused cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitive reactions when injected intradermally on the dorsolateral aspect of the thorax and tips of the ears of pigs previously exposed to the homologous virus. The reaction induced by subcutaneous injection in the lower eyelid was more easily administered and evaluated. Nonexposed control pigs did not react to the antigen and exposed and control pigs did not react when injected with a cell control antigen prepared in a similar manner. A positive response was detectable as early as seven days after exposure, reached near maximal levels by 28 days, and remained at similar levels for at least 90 days.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Darcel C. le Q., Dorward W. J. Skin reactivity and infectious bovine rhinotracheitis. Can Vet J. 1972 Apr;13(4):100–101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haralambiev H., Yotov M. On allergy in the Aujeszky disease of swine. C R Acad Bulg Sci. 1967;20(8):853–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAWETZ E., COLEMAN V., ALLENDE M. F. Studies on herpes simplex virus. II. A soluble antigen of herpes virus possessing skin-reactive properties. J Immunol. 1951 Sep;67(3):197–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. C., Cutlip R. C., Ritchie A. E., Young J. K. A bovine herpesvirus associated with a disease of the upper respiratory tract of feedlot cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Nov 15;161(10):1134–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]