Abstract
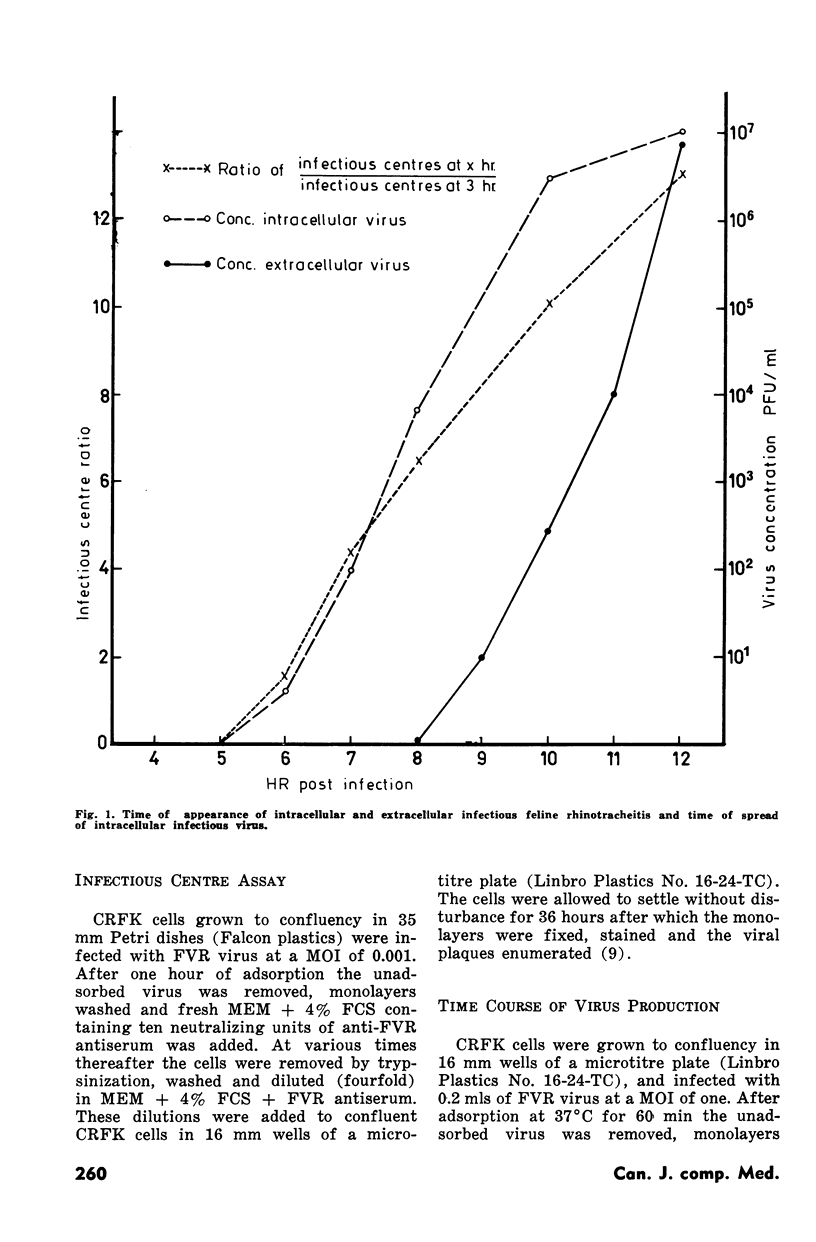
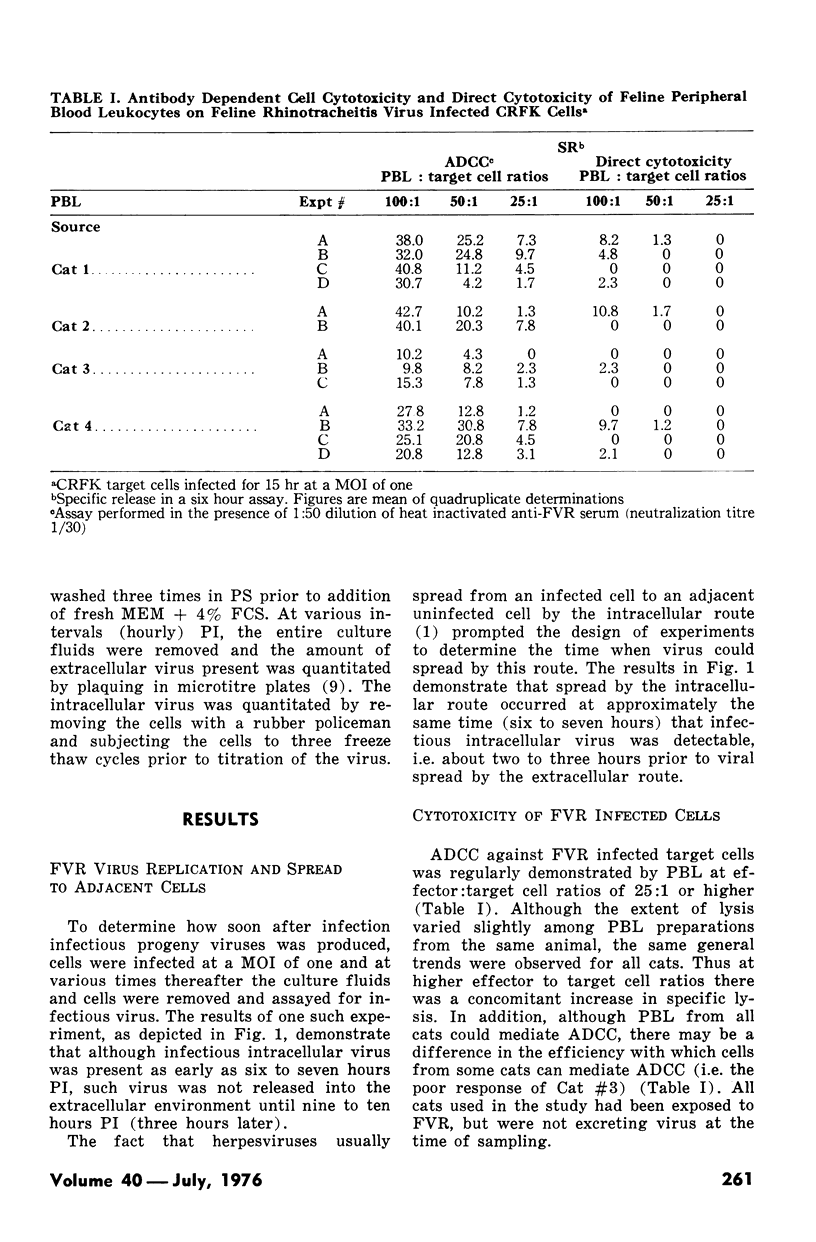
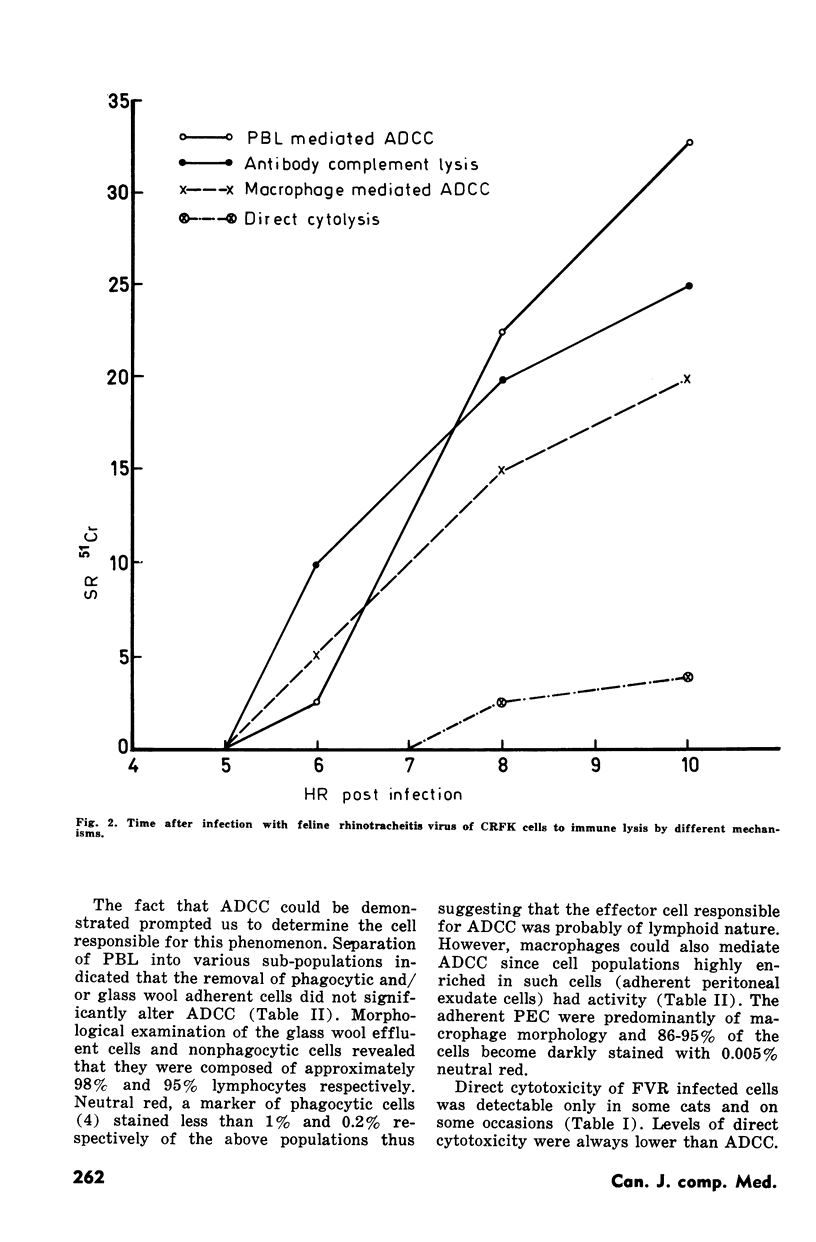
Experiments were designed to determine immunological mechanisms responsible for controlling dissemination of feline rhinotracheitis virus in feline cell cultures. Virus infected cells could be destroyed by three mechanisms--antibody and complement mediated lysis, direct lymphocyte cytotoxicity and antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. This latter immune parameter was mediated by both lymphocytes and macrophages and varied in extent in different cats. To ascertain the potential importance of the immunological parameters in curtailing viral spread, the time when virus infected cells could be destroyed by each component was related to the chronological events of viral replication and dissemination. Intracellular infectious virus and intracellular spread occurred at six to seven hours postinfection and extracellular spread at nine to ten hours postinfection. Antibody complement lysis and antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity occurred at six hours postinfection and direct cytotoxicity at eight hours postinfection. The relevance that these findings might have in relation to the occurrence and frequency of recrudescent disease is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crandell R. A. Feline viral rhinotracheitis (FVR). Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1973;17:201–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. J., Chopan M. The latent herpes simplex virus. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Dec;38(4):337–355. doi: 10.1128/br.38.4.337-355.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potgieter L. N. The influence of complement on the neutralization of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus by globulins derived from early and late bovine antisera. Can J Comp Med. 1975 Oct;39(4):427–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povey R. C., Johnson R. H. Observations on the epidemiology and control of viral respiratory disease in cats. J Small Anim Pract. 1970 Jul;11(7):485–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-5827.1970.tb05599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchase H. G. Recent advances in the knowledge of Marek's disease. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1972;16:223–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Host defense mechanisms against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. II. Inhibition of viral plaque formation by immune peripheral blood lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1975 May;17(1):43–56. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Wardley R. C., Babiuk L. A. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in cows: comparison of effector cell activity against heterologous erthrocyte and herpesvirus-infected bovine target cells. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1433–1441. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1433-1441.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Clark I. A., Taylor G. A. Different effector cell types in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nature. 1975 Jan 31;253(5490):376–377. doi: 10.1038/253376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


