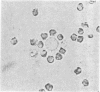
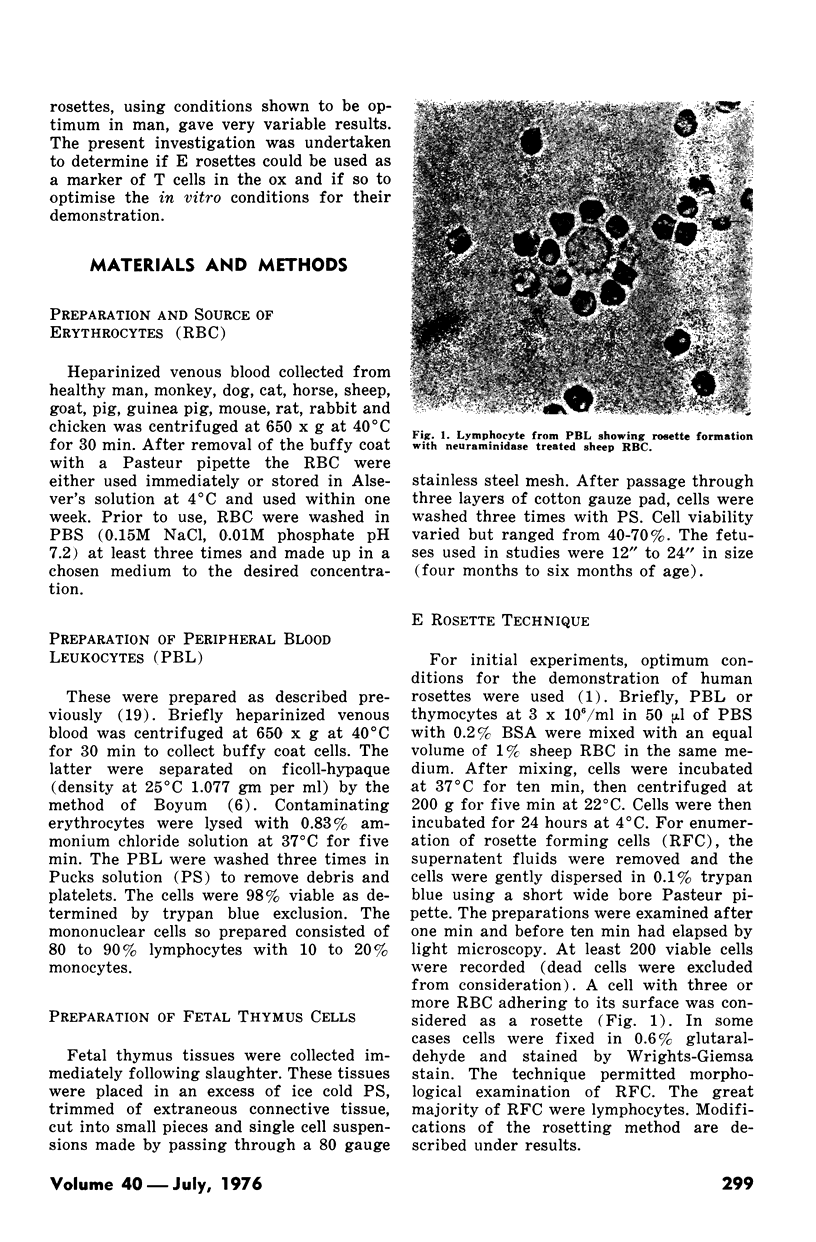
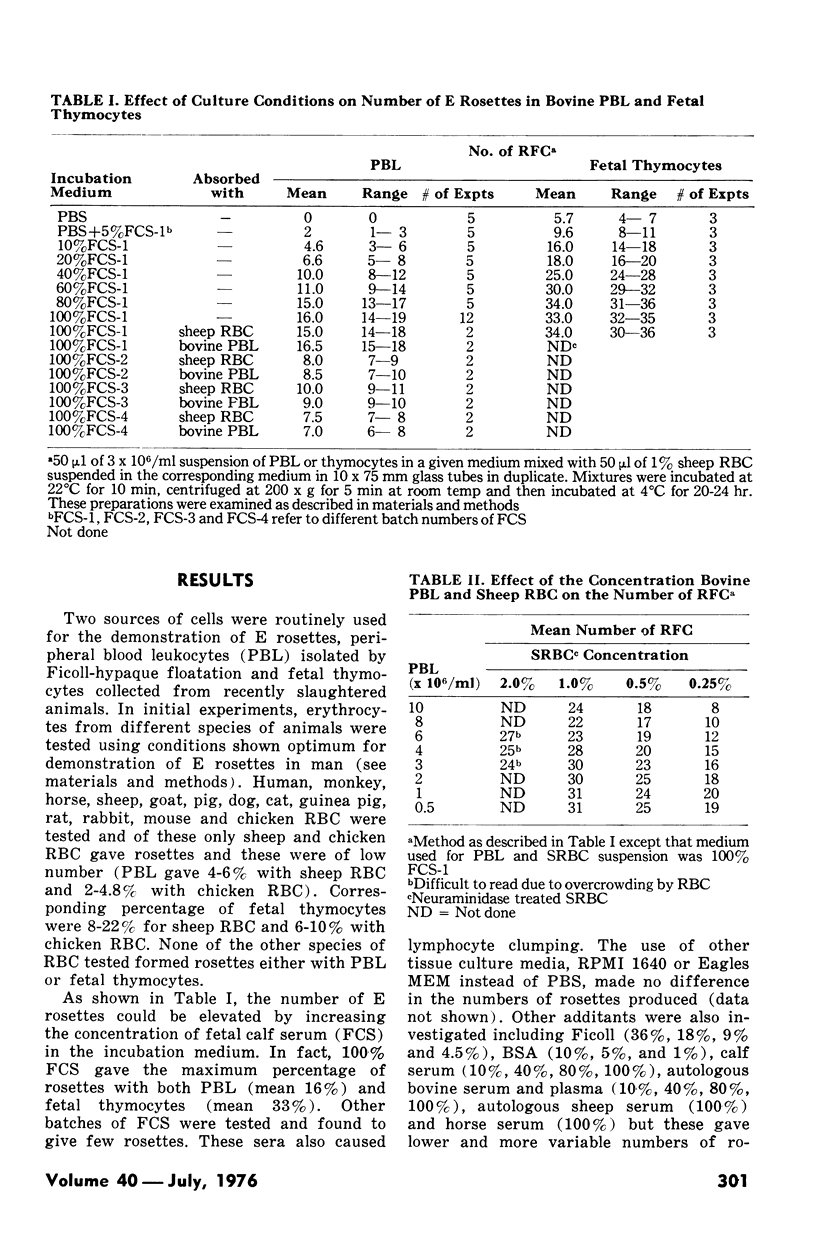
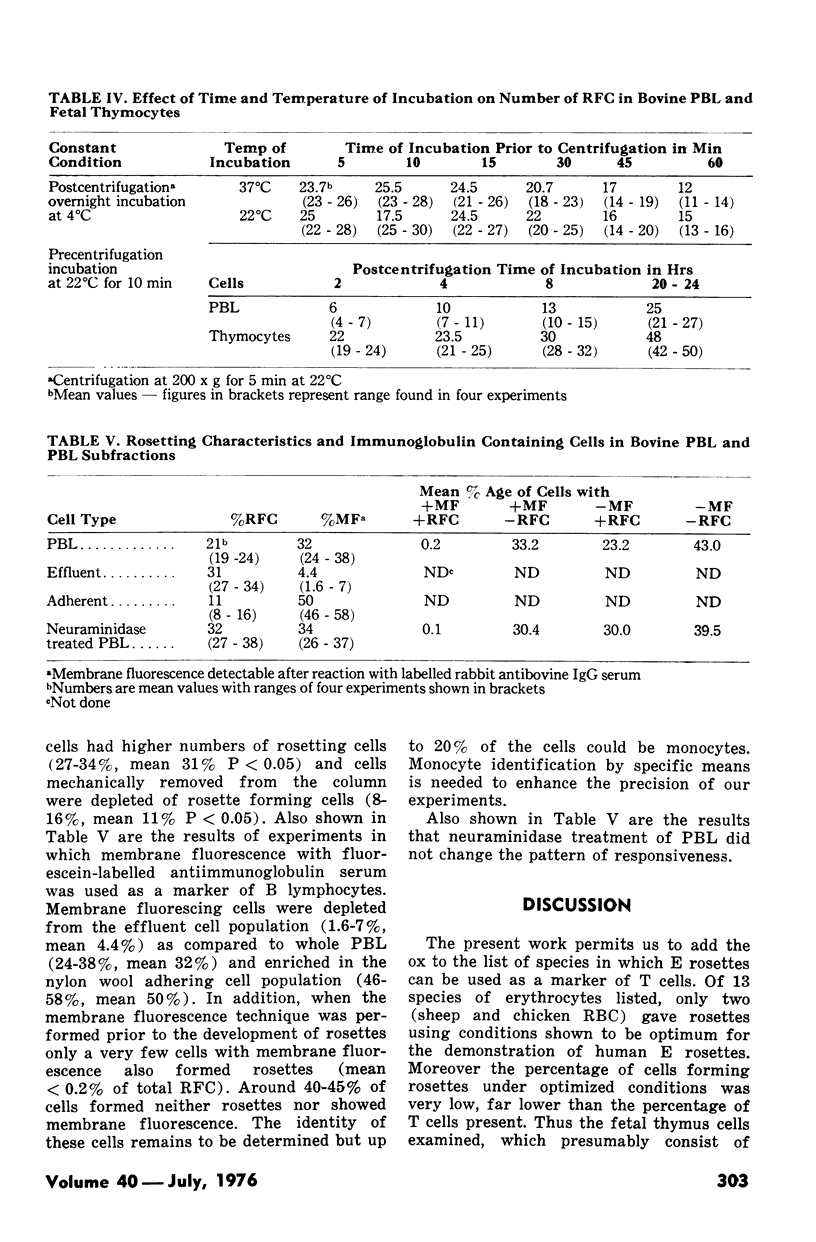
Abstract
Many species of erythrocytes were investigated for their ability to form spontaneous rosette with bovine peripheral blood leukocytes and fetal thymocytes. Only sheep and chicken red blood cells gave rosettes. Using conditions shown optimum for the demonstration of human rosette forming cells, only low numbers of bovine rosettes were demonstrable. By changing culture conditions to include 100% fetal calf serum, neuraminidase treated erythrocytes and/or lymphocytes and optimizing the incubation times and temperature, up to 38% of peripheral blood leukocytes and 52% of thymocytes formed rosettes. A thymic origin of rosetting cells was ascribed to T cells for the following reasons: 1) thymocytes gave higher numbers than did peripheral blood leukocytes, 2) rosette forming cell numbers were increased in peripheral blood leukocyte subpopulations enriched in T cells by nylon column separation and 3) only very few rosette forming cells had surface immunoglobulin, a marker of B lymphocytes. The reasons why all T cells were not detected by the technique were discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach J. F. Evaluation of T-cells and thymic serum factors in man using the rosette technique. Transplant Rev. 1973;16(0):196–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxley G., Bishop G. B., Cooper A. G., Wortis H. H. Rosetting of human red blood cells to thymocytes and thymus-derived cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Nov;15(3):385–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentwich Z., Douglas S. D., Skutelsky E., Kunkel H. G. Sheep red cell binding to human lymphocytes treated with neuraminidase; enhancement of T cell binding and identification of a subpopulation of B cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Jun 1;137(6):1532–1537. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.6.1532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentwich Z., Kunkel H. G. Specific properties of human B and T lymphocytes and alterations in disease. Transplant Rev. 1973;16:29–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowles C. A., White G. S., Lucas D. Rosette formation by canine peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):399–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain P., Marston R. H. Rosette formation by human T and B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Jan;3(1):6–9. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapel H. M. The effects of papain, trypsin and phospholipase A on rosette formation. Transplantation. 1973 Mar;15(3):320–325. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197303000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer J. M., Bullock W. E., Fields J. P. Disturbance of the blood T:B lymphocyte ratio in lepromatous leprosy. Clinical and immunologic correlations. N Engl J Med. 1973 May 17;288(20):1036–1039. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197305172882002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escajadillo C., Binns R. M. Rosette formation with sheep erythrocytes--a possible T-cell marker in the pig. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(2):261–275. doi: 10.1159/000231312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen K. S., Johansen T. S., Talmage D. W. T cell rosette formation in primates, pigs, and guinea pigs. The influence of immunosuppresive agents. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1974 Aug;54(2):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(74)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly G. E., Mears D. C., Sheil A. G. Relationship of the immunosuppressive potency of antilymphocyte globulin to three in vitro tests. Close correlation with rosette inhibition. Transplantation. 1971 Dec;12(6):443–447. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197112000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Mendes N. F., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Binding of sheep red blood cells to a large population of human lymphocytes. Nature. 1971 Apr 23;230(5295):531–532. doi: 10.1038/230531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackey L., Jarrett W., Jarrett O., Wilson L. B and T cells in a cat with thymic lymphosarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jun;54(6):1483–1487. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.6.1483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscoplat C. C., Johnson D. W., Teuscher E. Surface immunoglobulin of circulating lymphocytes in chronic bovine diarrhea: abnormalities in cell populations and cell function. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Aug;34(8):1101–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Host defense mechanisms against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. II. Inhibition of viral plaque formation by immune peripheral blood lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1975 May;17(1):43–56. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Host responses to infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. III. Isolation and immunologic activities of bovine T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1391–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiigi S. M., Fujikawa L. S., Mishell R. I. Sera and the in vitro induction of immune responses. II. Inhibitory effects of newborn calf sera on primary humoral responses. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):745–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiigi S. M., Mishell R. I. Sera and the in vitro induction of immune responses. I. Bacterial contamination and the generation of good fetal bovine sera. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):741–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. S., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Enhanced binding of neuraminidase-treated sheep erythrocytes to human T lymphocytes. Blood. 1973 Dec;42(6):939–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. B., Gurner B. W., Coombs R. R. Observations on rabbit thymocytes and peripheral T cells. II. Rosette formation with rabbit erythrocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(3):383–394. doi: 10.1159/000231323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Levin A. S., Spitler L. E., Fudenberg H. H. Rosette-forming cells, immunologic deficiency diseases and transfer factor. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 5;288(14):710–713. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304052881405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]