Abstract
The effect of gamma interferon (IFN-γ) on apoptosis due to infection by Chlamydia muridarum (the mouse pneumonitis strain of Chlamydia trachomatis) was studied in epithelial cells in culture and in the genital tracts of mice. IFN-γ concentrations that induce the formation of aberrant, persistent chlamydiae inhibit apoptosis due to C. muridarum infection. In cells treated with an IFN-γ concentration that leads to the development of a heterogenous population of normal and aberrant Chlamydia vacuoles, apoptosis was inhibited preferentially in cells that contained the aberrant vacuoles. The inhibitory effect of IFN-γ appears to be due in part to expression of host cell indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity, since inhibition of apoptosis could be partially reversed through coincubation with exogenous tryptophan. Apoptotic cells were observed in the genital tracts of wild-type mice infected with C. muridarum, and a significantly larger number of apoptotic cells was detected in infected IFN-γ-deficient mice. These results suggest that IFN-γ may contribute to pathogenesis of persistent Chlamydia infections in vivo by preventing apoptosis of infected cells.
Chlamydia trachomatis strains include a causative agent of ocular infection in humans and the most common cause of sexually transmitted bacterial infections (20, 54). An inflammatory response is required for the resolution of primary C. trachomatis infection, but chronic inflammation is also responsible for the scarring process observed in trachoma and chlamydial sexually transmitted disease (2). In addition, the ability of chlamydiae to persist in the host could be an important factor in exacerbating pathogenesis (4, 6). The immune mechanisms responsible for chronic inflammation are not fully understood, but it is believed that repeated exposure to chlamydial antigens contributes to pathogenesis and that bacteria in persistently infected cells may serve as a source of long-lasting pathology (5).
Chlamydia muridarum (also known as the mouse pneumonitis strain of C. trachomatis) (14, 48) infects the genital tracts of mice and has been used to characterize the host immune response to chlamydial genital tract infection. In C. muridarum infections of mice, a major role for CD4+ T cells secreting gamma interferon (IFN-γ) during clearance of the infection has been described (25, 31, 42, 52). Thus, studies with IFN-γ-deficient mice have shown that IFN-γ is required for prevention of dissemination of genital tract infection (9, 26, 42). Similarly, administration of anti-IFN-γ antibodies or recombinant IFN-γ prolongs or resolves the infection, respectively (45).
Chlamydiae are obligate intracellular bacteria that have a distinct biphasic infection cycle: the small elementary bodies are infectious and metabolically inert, and the larger reticulate bodies (RB) are noninfectious and metabolically active (22, 32, 56). A persistent state of chlamydiae can be induced in vitro by IFN-γ treatment, which leads to altered bacterial forms and an antigen profile that is different from that observed during active infection (4, 6). Significantly, there is down-regulation of the chlamydial major outer membrane protein (MOMP), and expression increases or decreases for several other proteins and genes, whereas expression of the immunostimulatory chlamydial antigen, hsp60, remains at high levels during the persistent state (6, 27, 49). The intracellular chlamydiae undergo striking morphological changes, becoming much larger than conventional RB (5, 49). In IFN-γ-treated infected cells, the chlamydiae are noninfectious, but the bacteria are viable and can revert to the infectious state following removal of IFN-γ (3).
Several Chlamydia spp. have joined a growing number of intracellular microorganisms that modulate apoptosis in opposite directions, both promoting and inhibiting apoptosis under different conditions (8, 17, 19, 23, 35, 55). Similar to other pathogens, chlamydiae protect infected cells against apoptosis due to external stimuli during early stages of infection (15) and induce apoptosis of the host cell during later stages (21, 38, 40, 41). Chlamydiae may thus protect infected cells against cytotoxic mechanisms of the immune system, while the apoptosis observed at the end of the infection cycle may contribute to the inflammatory response or facilitate release of bacteria from infected cells.
It has recently been reported that cells infected with C. trachomatis in the presence of IFN-γ resist apoptosis due to external ligands, via inhibition of caspase activation (11). Inhibition of caspase activation has also been shown in the absence of IFN-γ (15), while the apoptosis due to the infection itself is independent of caspases (38, 41). To determine if persistently infected cells are still susceptible to apoptosis at the end of the infection cycle, we characterized apoptosis of cells infected with C. muridarum in the presence or absence of IFN-γ in vitro. The study was then extended to an in vivo infection by measuring the number of apoptotic cells in the genital tracts of wild-type and IFN-γ-deficient mice infected with the same strain of C. muridarum. In both cases, IFN-γ inhibited Chlamydia-induced apoptosis, which could contribute to limiting propagation of the infection during the state of persistence.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cells and animals.
HeLa 229 cells (obtained from the American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, Va.) were cultivated in Dulbecco's modified minimal essential medium with Glutamax-1 (Life Technologies, Inc., Rockville, Md.), supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum and 25 μg of gentamicin per ml. C. muridarum, obtained originally from the American Type Culture Collection, was grown in McCoy cells and purified as previously described (44). Six-week-old female C57BL/6 (C57; H-2b) and IFN-γ-deficient female C57BL/6-Ifgtm1 (IFN-γ−/−) mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, Maine). Recombinant human IFN-γ was obtained from PeproTech (Rocky Hill, N.J.), and l-tryptophan was from Aldrich (Saint Quentin Fallavier, France). All other reagents were previously described (40).
Infections of cells with C. muridarum and treatment with IFN-γ.
For infections in vitro, HeLa cells were plated at a density of 2 × 104 cells per well in six-well plates (Costar). After 24 h in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2, the cell monolayers were washed and infected at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.5. At 1 h postinfection, the inoculum was removed and replaced with fresh culture medium. Infected monolayers were maintained in the incubator for 2 days or treated 3 h postinfection with various concentrations of IFN-γ. In some experiments, 200 μg of l-tryptophan per ml was added to the cell cultures at the same time as the IFN-γ (3, 28).
Immunofluorescence.
Infected or uninfected cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and revealed with anti-Chlamydia fluorescein-conjugated antibodies, consisting of a mixture of two monoclonal antibodies specific for the chlamydial MOMP and chlamydial lipopolysaccharide (1:500 dilution; Argene, Varilhes, France), as previously described (37, 38). Host cell and bacterial DNAs were visualized by staining saponin-permeabilized cells with 5 μg of Hoechst 33258 (Sigma, St. Louis, Mo.) per ml. Samples were examined with an Axiovert 135 TV fluorescence microscope (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) attached to a cooled charge-coupled device camera (Photometrics).
To estimate the number of cells with persistent chlamydiae, infected samples were fixed and incubated with an anti-Chlamydia monoclonal antibody, as described above. Using the scale of 1 to 4 for the level of persistent chlamydial development defined previously (3), normal cells correspond to cells with inclusions containing typical chlamydia (level 1), while persistently infected cells included all the cells with inclusions with some evidence of atypical, enlarged chlamydiae (levels 2 and 3) or exclusively atypical chlamydiae (level 4). As the cells were also labeled with Hoechst, apoptotic cells in the same samples were identified by their condensed nuclei.
Analysis of cell death.
In vitro, apoptosis was measured by cytofluorimetry using detergent-permeabilized cells stained with propidium iodide (PI), as previously described (13, 29, 33, 36). Since apoptotic cells were present mainly in the supernatant (38), adherent cells were detached with 1 mM EDTA in phosphate-buffered saline at 37°C, and both adherent cells and cells in suspension were collected and centrifuged. After one washing with phosphate-buffered saline, the cell pellet was resuspended directly in PI-detergent buffer (62.5 μg of PI per ml, 0.1% Triton X-100, and 1 mg of sodium citrate per ml in water) and transferred into 12- by 75-mm Falcon 2052 fluorescence-activated cell sorting tubes (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, Calif.). Data from 10,000 HeLa cells were collected on a FACScan flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson) with an argon ion laser tuned to 488 nm. Apoptosis was measured in the FL-3 range, and the marker used to quantify the number of apoptotic cells was set in such a way as to exclude debris and necrotic cells in the low FL-3 values. Each sample was performed in triplicate, and each experiment was repeated at least three times on separate days.
Infection of mice and histological procedures.
Wild-type or IFN-γ-deficient mice received 2.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate (Depo-Provera; Upjohn, Kalamazoo, Mich.) subcutaneously 7 days before vaginal infection. The mice were infected by placing 30 μl of 250 mM sucrose-10 mM sodium phosphate-5 mM l-glutamic acid (SPG) containing 1.0 × 107 inclusion-forming units of C. muridarum per ml into the vagina of each mouse or 30 μl of SPG without bacteria for negative controls, as described elsewhere (10). Mice were sacrificed 7 days after vaginal infection. Oviducts and uterine horns were removed, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, and embedded in 37°C paraffin. Longitudinal 4-μm sections were cut, deparaffinized, and hydrated through xylene and graded alcohol series.
Apoptotic cells were identified by staining with the terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) method using the apoptosis detection kit from Boehringer Mannheim (Meylan, France), following the manufacturer's instructions. Samples were examined with the Zeiss microscope, and images were acquired and analyzed with the IPLab spectrum program (Signal Analytics Corporation, Vienna, Va.). The relative number of apoptotic cells in each microscope field was quantified with the IPLab spectrum program, as previously described (40).
RESULTS
Effect of IFN-γ on survival of Chlamydia-infected cells in vitro.
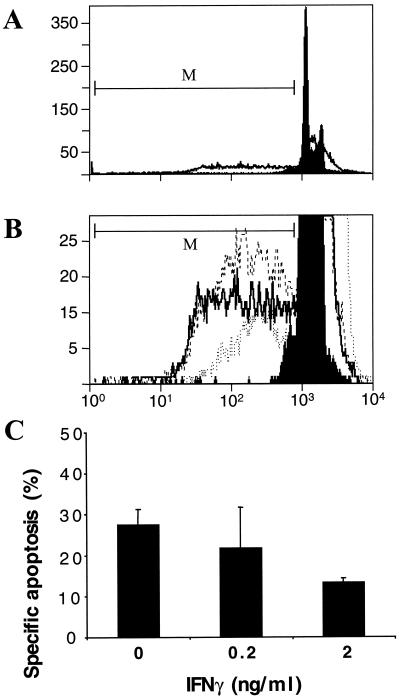
Several strains of C. trachomatis and C. muridarum and the guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis strain of Chlamydia psittaci induce apoptosis of host cells towards the end of the infection cycle (21, 38, 40). IFN-γ has been reported to induce a state of persistence of C. muridarum, human strains of C. trachomatis, and Chlamydia pneumoniae (5, 30, 39), although human strains of C. trachomatis are more sensitive than C. muridarum (30). When incubated 24 or 48 h before the start of infection, IFN-γ had a partial effect on growth of C. muridarum at 0.5 ng/ml and a larger effect at 2.0 ng/ml. The IFN-γ concentrations used in this work had no effect on uninfected cells (data not shown), but IFN-γ concentrations above 5 ng/ml were toxic to the host (HeLa) cells themselves (30). When cells are infected first and then cultured with IFN-γ, growth of the chlamydiae is not inhibited, and instead the chlamydiae assume the biochemical and morphological features of persistence (4). We therefore measured the effect on apoptosis during C. muridarum infection in the presence of IFN-γ at 0, 0.2, and 2 ng/ml, which was added 3 h after the start of infection. Apoptosis, defined by DNA content as measured by cytofluorimetry after 48 h of infection, was not affected by IFN-γ at 0.2 ng/ml but was inhibited by approximately half by IFN-γ at 2 ng/ml (Fig. 1).
FIG. 1.
Effect of IFN-γ on apoptosis and survival of host cells infected with Chlamydia. HeLa cells were infected with C. muridarum at an MOI of 0.5, and the indicated concentration of IFN-γ was added 3 h after the beginning of infection. After 48 h of infection, specific apoptosis of adherent cells and cells in suspension was measured by cytofluorimetry of PI-treated, detergent-permeabilized cells, as described in Materials and Methods. The marker (M) was used to define the population of apoptotic cells. (A) Cytofluorimetry profile of infected and uninfected cells treated with PI. In the absence of infection or IFN-γ treatment, a spontaneous level of apoptosis of 3 to 5% was always observed after 48 h (filled profile). Over 25% of the cells became apoptotic after a 48 h infection (open profile). (B) Cytofluorimetry profile with expanded y axis to show apoptotic cells in a population of infected cells (dashed line) and infected cells incubated with IFN-γ at 0.2 ng/ml (solid line) or 2 ng/ml (dotted line). The fluorescence intensity (FL-3) is given on the x axis, and the number of cells is on the y axis (A and B). (C) Calculated values of specific apoptosis for infected cells treated with 0, 0.2 or 2 ng of IFN-γ per ml. The values are means and standard deviations for three Chlamydia-infected samples treated with IFN-γ on separate days. P is <0.01 for 0 versus 2 ng of IFN-γ per ml.
Correlation between chlamydial persistence and host cell nuclear condensation.
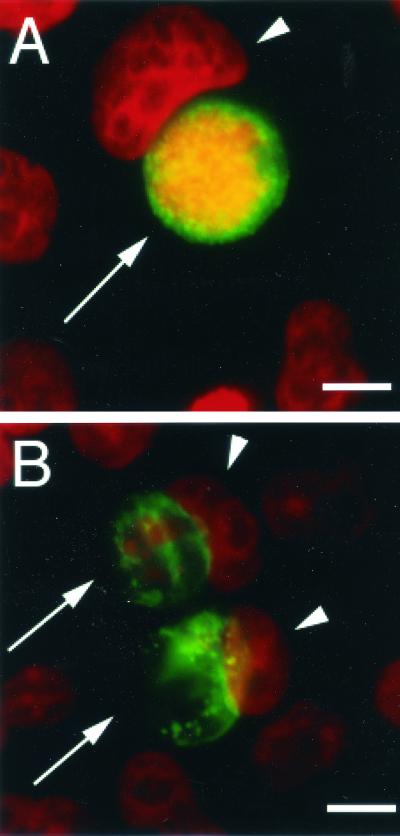
Cells persistently infected with some human C. trachomatis strains in vitro contain abnormally large noninfectious forms of chlamydiae (5, 6). As for C. trachomatis serovar A (3, 49), the number of C. muridarum-infected cells containing persistent chlamydiae was heterogenous for cells treated at the low IFN-γ concentration. At 0.2 ng of IFN-γ per ml, cells with both normal and aberrant inclusions were observed (data not shown), while at 2 ng/ml, most of the inclusions had enlarged chlamydiae, as reflected by the appearance of patches in the inclusions, observed by immunofluorescence (Fig. 2). Thus, unlike C. trachomatis L2, whose form does not change significantly in response to IFN-γ (49), the morphological development of C. muridarum in IFN-γ-treated cells is reminiscent of that of C. trachomatis serovar A.
FIG. 2.
Appearance of Chlamydia inclusions in cells treated with IFN-γ. HeLa cells infected with C. muridarum and treated with IFN-γ at 0 (A) or 2 (B) ng/ml were fixed with paraformaldehyde and prepared for immunofluorescence as described in Materials and Methods, using fluorescein-conjugated anti-Chlamydia antibodies (green) and Hoechst for DNA labeling (red). Chlamydia inclusions were normal in the absence of IFN-γ but were aberrant when infected cells were treated with 2 ng of IFN-γ per ml. Arrows indicate Chlamydia inclusions, and arrowheads show host cell nuclei. Bar, 10 μm.
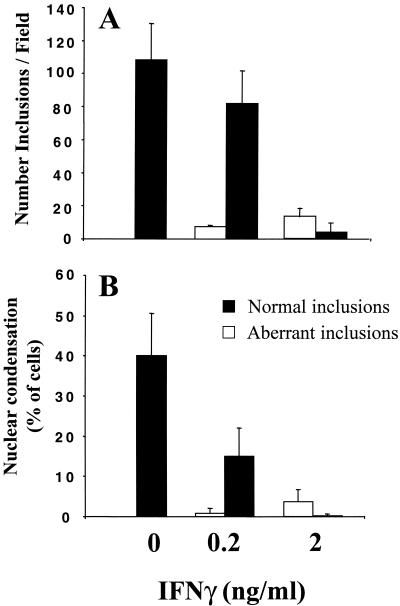
Approximately 1/10 of the infected cells had persistent chlamydiae at 0.2 ng of IFN-γ per ml, compared to over 3/4 of the cells that had been treated with 2 ng of IFN-γ per ml (Fig. 3A). At the MOI of 0.5 used here and in the absence of IFN-γ, half of the infected cells had apoptotic nuclei after 48 h of infection and the other half still had normal nuclei (data not shown). Interestingly, at the lower IFN-γ concentration, inhibition of nuclear condensation, as assayed by immunofluorescence of Hoechst-stained nuclei, was limited preferentially to cells containing the aberrant chlamydial inclusions (Fig. 3B). Thus, IFN-γ inhibits apoptosis mainly of persistently infected cells.
FIG. 3.
Sensitivity to the effects of IFN-γ and correlation between the developmental state of Chlamydia vacuoles and sensitivity to apoptosis. HeLa cells were infected with C. muridarum at an MOI of 0.5 for 48 h in the presence of the indicated concentrations of IFN-γ. (A) The number of cells containing normal inclusions (black bars) or inclusions with persistent chlamydiae (white bars) was determined and defined as described in Materials and Methods. For cells containing normal inclusions, P is <0.01 for 0 versus 0.2 and 0 versus 2 ng of IFN-γ per ml. (B) Host cells were identified as containing normal or persistent chlamydiae, and apoptotic cells were counted based on the condensation of Hoechst-labeled nuclei, as described in Materials and Methods. For cells containing normal inclusions and condensed nuclei, P is <0.001 for 0 versus 2 ng of IFN-γ per ml and <0.01 for 0 versus 0.2 ng of IFN-γ per ml. Each series of experiments was performed at least three times.
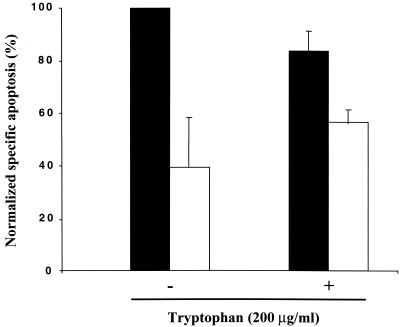
Effect of tryptophan on apoptosis of IFN-γ-treated cells.
The persistent phenotype of Chlamydia-infected cells can be reversed through incubation of cell cultures with an excess of extracellular tryptophan (3, 28, 53). Similarly, coincubation of Chlamydia-infected cells with IFN-γ and tryptophan partially reverses the inhibitory effect of IFN-γ on Chlamydia-induced apoptosis (Fig. 4), suggesting that IFN-γ exerts its effect mainly via host cell indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity (5). Thus, IFN-γ inhibits infection-dependent apoptosis by approximately 60% in the absence of tryptophan and by approximately 30% in the presence of tryptophan (Fig. 4). However, tryptophan did not completely reverse the inhibitory effect of IFN-γ, suggesting that this cytokine may have some effects on chlamydiae independent of IDO activity. As controls, addition of tryptophan to the extracellular medium in the absence of IFN-γ did not affect Chlamydia-induced apoptosis, and 2 ng of IFN-γ per ml with or without tryptophan had no effect on apoptosis in the absence of infection (data not shown).
FIG. 4.
Reversal by tryptophan of IFN-γ-dependent inhibition of apoptosis. HeLa cells were infected with C. muridarum at an MOI of 0.5 for 48 h. Infected cells were treated with (white bars) or without (black bars) IFN-γ (2 ng/ml) and with or without 200 μg of l-tryptophan per ml. Apoptosis was measured by cytofluorimetry using PI-stained, detergent-permeabilized cells, as described in Materials and Methods. The values were normalized to the highest level of apoptosis (infected cells in the absence of IFN-γ or l-tryptophan), and the values are means and standard deviations for three samples infected with C. muridarum on separate days.
Apoptosis in wild-type and IFN-γ-deficient mice.
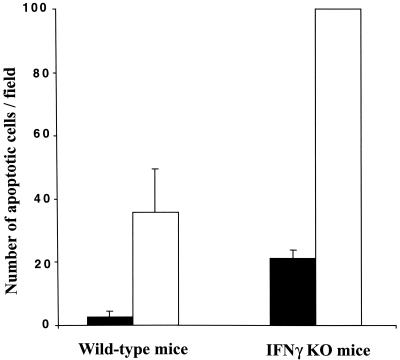
Both C. muridarum and human strains of C. trachomatis are sensitive to the inhibitory effects of IFN-γ in mouse models, although, as in the case of the chlamydiae in vitro (30), human strains are more sensitive than C. muridarum (43). The effect of IFN-γ on apoptosis during infection with C. muridarum in vivo was evaluated by quantifying the apoptotic cells, revealed by the TUNEL technique, in the upper genital tracts of wild-type and IFN-γ-deficient mice infected for 7 days. There was a large increase in the level of apoptosis in infected wild-type mice compared to uninfected controls (Fig. 5), as previously reported (40). The extent of apoptosis increased even further, more than twofold, in the IFN-γ-deficient mice that had been infected (Fig. 5), suggesting that secretion of IFN-γ may protect against Chlamydia-induced apoptosis in vivo.
FIG. 5.
Level of apoptosis in the genital tracts of wild-type and IFN-γ-deficient mice infected with Chlamydia. Mice were infected with C. muridarum for 7 days, histological samples were stained by TUNEL, and the number of apoptotic cells in the uterine horns and oviducts was determined as described in Materials and Methods. All apoptosis values were normalized to the value obtained with infected IFN-γ-deficient (IFNγ KO) mice, which was defined as 100. Histological sections were prepared from three uninfected mice and three infected mice from each group.
DISCUSSION
We show here that IFN-γ produces a state of persistence of C. muridarum, as previously reported for human strains of C. trachomatis (5, 6, 39, 49). After treatment with a low concentration of IFN-γ (0.2 ng/ml), we observed a heterogenous population of Chlamydia inclusions, some being normal and others being aberrant. A homogeneous population of persistent, aberrant chlamydiae arises after treatment with a higher concentration (2 ng/ml) of IFN-γ, as reported for the human strain C. trachomatis serovar A (3). In infected cells in vitro, IFN-γ treatment also results in inhibition of Chlamydia-induced apoptosis. As measured by immunofluorescence, there is near-complete inhibition of apoptosis at 2 ng of IFN-γ per ml and partial inhibition at 0.2 ng/ml. However, at the lower concentration, the inhibitory effect is restricted mainly to cells containing inclusions with the persistent phenotype. The inhibitory effect of IFN-γ on apoptosis was smaller when assayed by cytofluorimetry, which allowed us to measure apoptosis of both adherent cells and cells in suspension. Thus, the extent of apoptosis is most likely underestimated when measured by immunofluorescence, which is limited to adherent cells. We also quantified the number of apoptotic cells in the upper genital tract of IFN-γ−/− mice infected with C. muridarum and found that, consistent with the in vitro results, there are more apoptotic cells in the IFN-γ−/− mice than in wild-type mice.
The concentration dependence and the timing of the effects of IFN-γ on Chlamydia-induced apoptosis are consistent with previous work on the persistent state of chlamydiae in vitro. It has been reported that multiplication of C. trachomatis is inhibited in a dose-dependent manner when IFN-γ treatment begins before infection (50). However, when treatment begins concomitantly with infection or shortly after infection, as in our experiments, a persistent state develops in which the RB are morphologically abnormal and are unable to develop into elementary bodies (4), remaining in an undividing but viable state. In addition, pretreatment of HeLa cells with IFN-γ before infection with the murine species used in this study, C. muridarum, had little effect on the production of infectious chlamydiae at IFN-γ concentrations of ≤0.2 ng/ml, but there was more than a threefold reduction in the number of infectious chlamydiae starting at 0.5 ng/ml (30). The concentrations of IFN-γ that cause persistence in vitro are thus comparable to those found in endocervical secretions from women infected with C. trachomatis (1, 5).
Chlamydia spp. have been reported to modulate apoptosis in opposite directions (19, 55), both protecting acutely infected cells against apoptosis due to external ligands and inducing apoptosis towards the end of the infection cycle (15, 38, 40, 41). In a recent study, the effect of persistence on the protective activity of C. trachomatis serovar A was evaluated in HeLa cells incubated with 0.2 and 2.0 ng of IFN-γ per ml (11). During acute infection in vitro, infected cells are resistant to apoptosis due to inhibition of cytochrome c release from mitochondria and inactivation of host cell caspases (15). Similarly, cytochrome c was not translocated from mitochondria to the cytosol in persistently infected cells, suggesting that caspase-9 and consequently caspase-3 were not activated (11). Thus, the mechanism of protection in persistently infected cells appears to be the same as that observed in the absence of IFN-γ (15). The effect of IFN-γ on apoptosis at the end of the infection cycle was not evaluated.
Chlamydia species are endowed with a type III secretion apparatus that could be used by the bacteria to secrete virulence factors into the inclusion or the host cell cytosol (16, 24, 51). Although specific Chlamydia factors that could induce or inhibit apoptosis have not been identified yet, it is tempting to speculate that proteins secreted by Chlamydia may modulate apoptosis in the infected cell, as reported for other intracellular bacteria (18, 55). It also remains to be seen whether IFN-γ could alter the expression of chlamydial proteins that modify survival pathways in the infected cell. A recent proteomic analysis of the regulation of chlamydial proteins revealed that the expression of chlamydial MOMP and several other proteins decreases markedly early in the developmental cycle of C. trachomatis serovar A, while modifications were also found for other proteins (49). However, no significant down-regulation was observed for the expression of MOMP or other proteins in cells infected with C. trachomatis serovar L2. If it turns out that chlamydial virulence factors are involved in IFN-γ-dependent inhibition of host cell apoptosis, then one may expect that IFN-γ affects Chlamydia-mediated apoptosis differentially, depending on the Chlamydia strain.
In human epithelial cells, IFN-γ treatment results in depletion of tryptophan via IFN-γ-induced expression of IDO. IDO activity leads to tryptophan catabolism, thus decreasing the intracellular concentration of tryptophan available for chlamydiae (3). C. trachomatis and C. pneumoniae can be rescued from IFN-γ-treated or tryptophan-depleted cell cultures through the addition of extracellular tryptophan (3, 28, 53), but IFN-γ may also induce or inhibit apoptosis of eukaryotic cells in the absence of infection (7, 34, 57). In order to distinguish between the effects of IFN-γ on host cell apoptosis and chlamydial development, apoptosis of IFN-γ-treated infected cells was measured in the presence and absence of exogenous tryptophan. IFN-γ by itself (at 2 ng/ml) or with tryptophan in the absence of infection had no effect on survival of the host cells. However, reversal by tryptophan of the effect of IFN-γ in infected cells suggests that IDO activity is responsible for the IFN-γ-dependent inhibition of apoptosis observed during C. trachomatis infection of human host cells.
The increase in apoptosis observed in the genital tracts of infected IFN-γ-deficient mice may also have been due to their inability to induce IDO. Unlike the case for infected human host cells (3, 4), the anti-C. muridarum activity of IFN-γ in murine host cells was not dependent on induction of IDO and tryptophan catabolism in vitro (12). However, in a murine model of C. pneumoniae infection, IFN-γ was necessary for accumulation of IDO transcripts in the lung (46), and in a murine model of malaria, IDO was induced in wild-type mice but not in IFN-γ-deficient mice (47). It is thus likely that IDO activity may also be responsible for IFN-γ-dependent inhibition of apoptosis in the murine genital tract.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Institut Pasteur, INSERM, Université Paris 7, a fellowship from the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (to J.L.P.), and National Institutes of Health grant AI43337 (to T.D.).
We thank Thomas Jungas for excellent technical assistance, Iris Motta for advice on experiments, and Philippe Kourilsky for support and encouragement.
Editor: S. H. E. Kaufmann
REFERENCES
- 1.Arno, J. N., V. A. Ricker, B. E. Batteiger, B. P. Katz, V. A. Caine, and R. B. Jones. 1990. Interferon-gamma in endocervical secretions of women infected with Chlamydia trachomatis. J. Infect. Dis. 162:1385-1389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bavoil, P. M., R.-C. Hsia, and R. G. Rank. 1996. Prospects for a vaccine against Chlamydia genital disease. I. Microbiology and pathogenesis. Bull. Inst. Pasteur 94:5-54. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Beatty, W. L., T. A. Belanger, A. A. Desai, R. P. Morrison, and G. I. Byrne. 1994. Tryptophan depletion as a mechanism of gamma interferon-mediated chlamydial persistence. Infect. Immun. 62:3705-3711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Beatty, W. L., G. I. Byrne, and R. P. Morrison. 1993. Morphologic and antigenic characterization of interferon γ-mediated persistent Chlamydia trachomatis infection in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:3998-4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Beatty, W. L., G. I. Byrne, and R. P. Morrison. 1994. Repeated and persistent infection with Chlamydia and the development of chronic inflammation and disease. Trends Microbiol. 2:94-98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Beatty, W. L., R. P. Morrison, and G. I. Byrne. 1994. Persistent chlamydiae: from cell culture to a paradigm for chlamydial pathogenesis. Microbiol. Rev. 58:686-699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Castelli, J. C., B. A. Hassel, K. A. Wood, X. L. Li, K. Amemiya, M. C. Dalakas, P. F. Torrence, and R. J. Youle. 1997. A study of the interferon antiviral mechanism: apoptosis activation by the 2-5A system. J. Exp. Med. 186:967-972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen, X. M., S. A. Levine, P. L. Splinter, P. S. Tietz, A. L. Ganong, C. Jobin, G. J. Gores, C. V. Paya, and N. F. LaRusso. 2001. Cryptosporidium parvum activates nuclear factor κB in biliary epithelia preventing epithelial cell apoptosis. Gastroenterology 120:1774-1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cotter, T. W., K. H. Ramsey, G. S. Miranpuri, C. E. Poulsen, and G. I. Byrne. 1997. Dissemination of Chlamydia trachomatis chronic genital tract infection in gamma interferon gene knockout mice. Infect. Immun. 65:2145-2152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Darville, T., C. W. Andrews, J. D. Sikes, P. L. Fraley, and R. G. Rank. 2001. Early local cytokine profiles in strains of mice with different outcomes from chlamydial genital tract infection. Infect. Immun. 69:3556-3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dean, D., and V. C. Powers. 2001. Persistent Chlamydia trachomatis infections resist apoptotic stimuli. Infect. Immun. 69:2442-2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.de la Maza, L. M., E. M. Peterson, C. W. Fennie, and C. W. Czarniecki. 1985. The anti-chlamydial and anti-proliferative activities of recombinant murine interferon-gamma are not dependent on tryptophan concentrations. J. Immunol. 135:4198-4200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Douglas, R. S., A. D. Tarshis, C. H. Pletcher, P. C. Nowell, and J. S. Moore. 1995. A simplified method for the coordinate examination of apoptosis and surface phenotype of murine lymphocytes. J. Immunol. Methods 188:219-228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Everett, K. D. E., R. M. Bush, and A. A. Andersen. 1999. Emended description of the order Chlamydiales, proposal of Parachlamydiaceae fam. nov. and Simkaniaceae fam. nov., each containing one monotypic genus, revised taxonomy of the family Chlamydiaceae, including a new genus and five new species, and standards for the identification of organisms. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49:415-440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fan, T., H. Lu, L. Shi, G. A. McCarthy, D. M. Nance, A. H. Greenberg, and G. Zhong. 1998. Inhibition of apoptosis in Chlamydia-infected cells: blockade of mitochondrial cytochrome c release and caspase activation. J. Exp. Med. 187:487-496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fields, K. A., and T. Hackstadt. 2000. Evidence for the secretion of Chlamydia trachomatis CopN by a type III secretion mechanism. Mol. Microbiol. 38:1048-1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Galvan, V., and B. Roizman. 1998. Herpes simplex virus 1 induces and blocks apoptosis at multiple steps during infection and protects cells from exogenous inducers in a cell-type-dependent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:3931-3936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gao, L.-Y., and Y. Abu Kwaik. 2000. Hijacking of apoptotic pathways by bacterial pathogens. Microbes Infect. 2:1705-1719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gao, L.-Y., and Y. Abu Kwaik. 2000. The modulation of host cell apoptosis by intracellular bacterial pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 8:306-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gerbase, A. C., J. T. Rowley, and T. E. Mertens. 1998. Global epidemiology of sexually transmitted diseases. Lancet 351:2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gibellini, D., R. Panaya, and F. Rumpianesi. 1998. Induction of apoptosis by Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis infection in tissue culture cells. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. 288:35-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hackstadt, T. 1999. Cell biology, p. 101-138. In R. S. Stephens (ed.), Chlamydia: intracellular biology, pathogenesis, and immunity. ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
- 23.Hisaeda, H., T. Sakai, H. Ishikawa, Y. Maekawa, K. Yasutomo, R. A. Good, and K. Himeno. 1997. Heat shock protein 65 induced by γδ T cells prevents apoptosis of macrophages and contributes to host defense in mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 159:2375-2381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hsia, R.-C., Y. Pannekoek, E. Ingerowski, and P. M. Bavoil. 1997. Type III secretion genes identify a putative virulence locus of Chlamydia. Mol. Microbiol. 5:351-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Igietseme, J. U., K. H. Ramsey, D. M. Magee, D. M. Williams, T. J. Kincy, and R. G. Rank. 1993. Resolution of murine chlamydial genital infection by the adoptive transfer of a biovar-specific, Th1 lymphocyte clone. Reg. Immunol. 5:317-324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ito, J. I., and J. M. Lyons. 1999. Role of gamma interferon in controlling murine chlamydial genital tract infections. Infect. Immun. 67:5518-5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mathews, S., C. George, C. Flegg, D. Stenzel, and P. Timms. 2001. Differential expression of ompA, ompB, pyk, nlpD and Cpn0585 genes between normal and interferon-gamma treated cultures of Chlamydia pneumoniae. Microb. Pathog. 30:337-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mehta, S. J., R. D. Miller, J. A. Ramirez, and J. T. Summersgill. 1998. Inhibition of Chlamydia pneumoniae replication in Hep-2 cells by interferon-gamma: role of tryptophan catabolism. J. Infect. Dis. 177:1326-1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mok, C.-L., G. Gil-Gómez, O. Williams, M. Coles, S. Taga, M. Tolaini, T. Norton, D. Kioussis, and H. J. M. Brady. 1999. Bad can act as a key regulator of T cell apoptosis and T cell development. J. Exp. Med. 189:575-586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Morrison, R. P. 2000. Differential sensitivities of Chlamydia trachomatis strains to inhibitory effects of gamma interferon. Infect. Immun. 68:6038-6040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Morrison, R. P., K. Feilzer, and D. B. Tumas. 1995. Gene knockout mice establish a primary protective role for major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted responses in Chlamydia trachomatis genital tract infection. Infect. Immun. 63:4661-4668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Moulder, J. W. 1991. Interaction of chlamydiae and host cells in vitro. Microbiol. Rev. 55:143-190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Müller, M., S. Wilder, D. Bannasch, D. Israeli, K. Lehlbach, M. Li-Weber, S. L. Friedman, P. R. Galle, W. Stremmel, M. Oren, and P. H. Krammer. 1998. p53 activates the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) gene in response to DNA damage by anticancer drugs. J. Exp. Med. 188:2033-2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Munn, D. H., A. C. Beall, D. Song, R. W. Wrenn, and D. C. Throckmorton. 1995. Activation-induced apoptosis in human macrophages: developmental regulation of a novel cell death pathway by macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interferon gamma. J. Exp. Med. 181:127-136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nash, P. B., M. B. Purner, R. P. Leon, P. Clarke, R. C. Duke, and T. J. Curiel. 1998. Toxoplasma gondii-infected cells are resistant to multiple inducers of apoptosis. J. Immunol. 160:1824-1830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nicoletti, I., G. Migliorati, M. C. Pagliacci, F. Grignani, and C. Riccardi. 1991. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 139:271-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ojcius, D. M., F. Niedergang, A. Subtil, R. Hellio, and A. Dautry-Varsat. 1996. Immunology and the confocal microscope. Res. Immunol. 147:175-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ojcius, D. M., P. Souque, J. L. Perfettini, and A. Dautry-Varsat. 1998. Apoptosis of epithelial cells and macrophages due to infection with the obligate intracellular pathogen Chlamydia psittaci. J. Immunol. 161:4220-4226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pantoja, L. G., R. D. Miller, J. A. Ramirez, R. E. Molestina, and J. T. Summersgill. 2000. Inhibition of Chlamydia pneumoniae replication in human aortic smooth muscle cells by gamma interferon-induced indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity. Infect. Immun. 68:6478-6481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Perfettini, J.-L., T. Darville, G. Gachelin, P. Souque, M. Huerre, A. Dautry-Varsat, and D. M. Ojcius. 2000. Effect of Chlamydia trachomatis infection and subsequent tumor necrosis factor alpha secretion on apoptosis in the murine genital tract. Infect. Immun. 68:2237-2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Perfettini, J. L., J. C. Reed, N. Israël, J. C. Martinou, A. Dautry-Varsat, and D. M. Ojcius. 2002. Role of Bcl-2 family members in caspase-independent apoptosis during Chlamydia infection. Infect. Immun. 70:55-61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Perry, L. L., K. Feilzer, and H. D. Caldwell. 1997. Immunity to Chlamydia trachomatis is mediated by T helper 1 cells through IFN-γ-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Immunol. 158:3344-3352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Perry, L. L., H. Su, K. Feilzer, R. Messer, S. Hughes, W. Whitmire, and H. D. Caldwell. 1999. Differential sensitivity of distinct Chlamydia trachomatis isolates to IFN-gamma-mediated inhibition. J. Immunol. 162:3541-3548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ramsey, K. H., W. J. Newhall, and R. G. Rank. 1989. Humoral immune response to chlamydial genital infection of mice with the agent of mouse pneumonitis. Infect. Immun. 57:2441-2446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rank, R. G., K. H. Ramsey, E. A. Pack, and D. M. Williams. 1992. Effect of gamma interferon on resolution of murine chlamydial genital infection. Infect. Immun. 60:4427-4429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rottenberg, M. E., A. Gigliotti Rothfuchs, D. Gigliotti, M. Ceausu, C. Une, V. Levitsky, and H. Wigzell. 2000. Regulation and role of IFN-gamma in the innate resistance to infection with Chlamydia pneumoniae. J. Immunol. 164:4812-4818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sanni, L. A., S. R. Thomas, B. N. Tattam, D. E. Moore, G. Chaudhri, R. Stocker, and N. H. Hunt. 1998. Dramatic changes in oxidative tryptophan metabolism along the kynurenine pathway in experimental cerebral and noncerebral malaria. Am. J. Pathol. 152:611-619. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Schachter, J., R. S. Stephens, P. Timms, C. Kuo, P. M. Bavoil, S. Birkelund, J. Boman, H. Caldwell, L. A. Campbell, M. Chernesky, G. Christiansen, I. N. Clarke, C. Gaydos, J. T. Grayston, T. Hackstadt, R. Hsia, B. Kaltenboeck, M. Leinonnen, D. Ojcius, G. McClarty, J. Orfila, R. Peeling, M. Puolakkainen, T. C. Quinn, R. G. Rank, J. Raulston, G. L. Ridgeway, P. Saikku, W. E. Stamm, D. Taylor-Robinson, S.-P. Wang, and P. B. Wyrick. 2001. Radical changes to chlamydial taxonomy are not necessary just yet. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Bacteriol. 51:249, 251-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Shaw, A. C., G. Christiansen, and S. Birkelund. 1999. Effects of interferon gamma on Chlamydia trachomatis serovar A and L2 protein expression investigated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 20:775-780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Shemer, Y., and I. Sarov. 1985. Inhibition of growth of Chlamydia trachomatis by human gamma interferon. Infect. Immun. 48:592-596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Stephens, R. S., S. Kalman, C. Lammel, J. Fan, R. Marathe, L. Aravind, W. Mitchell, L. Olinger, R. L. Tatusov, Q. Zhao, E. V. Koonin, and R. W. Davis. 1998. Genome sequence of an obligate intracellular pathogen of humans: Chlamydia trachomatis. Science 23:638-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Su, H., and H. D. Caldwell. 1995. CD4+ T cells play a significant role in adoptive immunity to Chlamydia trachomatis infection of the mouse genital tract. Infect. Immun. 63:3302-3308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Summersgill, J. T., N. N. Sahney, C. A. Gaydos, T. C. Quinn, and J. A. Ramirez. 1995. Inhibition of Chlamydia pneumoniae growth in Hep-2 cells pretreated with gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Infect. Immun. 63:2801-2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Thylefors, B., A. D. Negrel, R. Pararajasegaram, and K. Y. Dadzie. 1995. Global data on blindness. Bull. W. H. O. 73:115-121. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Weinrauch, Y., and A. Zychlinsky. 1999. The induction of apoptosis by bacterial pathogens. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 53:155-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wyrick, P. B. 2000. Intracellular survival by Chlamydia. Cell. Microbiol. 2:275-282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Xaus, J., M. Cardo, A. F. Valledor, C. Soler, J. Lloberas, and A. Celada. 1999. Interferon gamma induces the expression of p21waf-1 and arrests macrophage cell cycle, preventing induction of apoptosis. Immunity 11:103-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]