Abstract
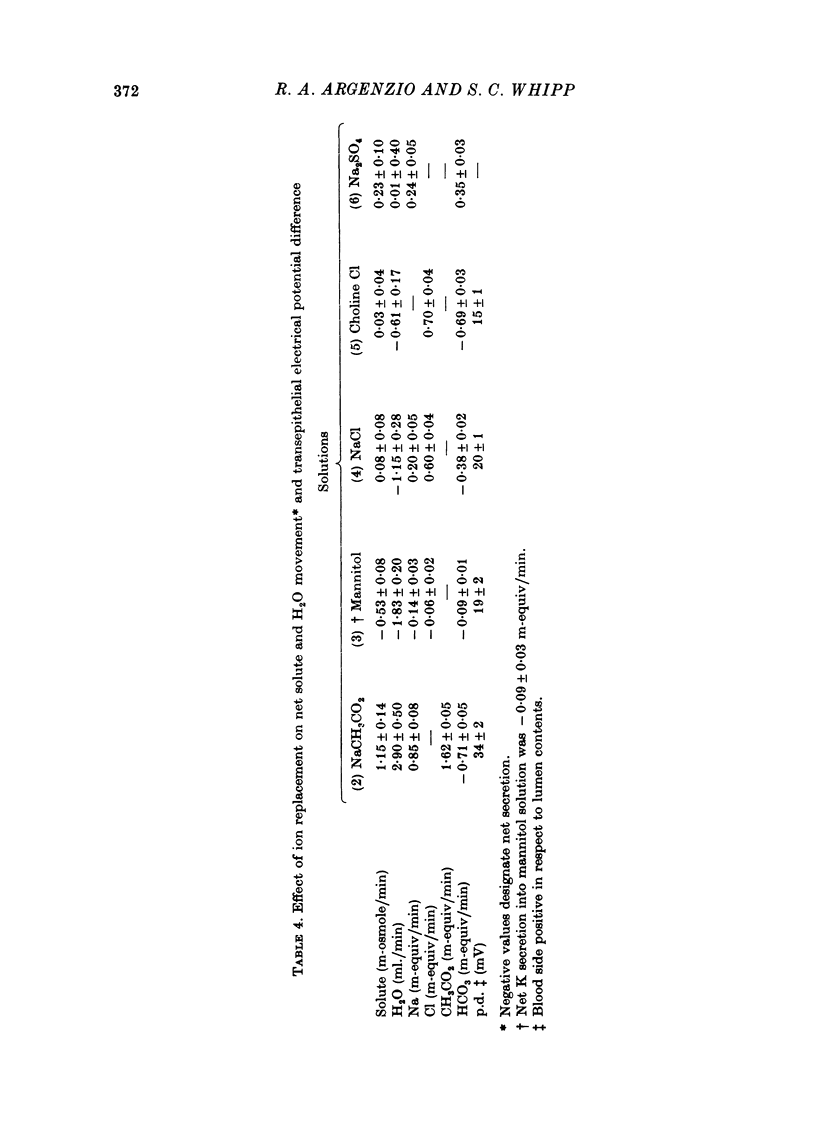
1. Net transport of Na, Cl, HCO3 and acetate was examined in the temporarily isolated colon of conscious pigs weighing 46 +/- 8 kg. 2. The entire colon absorbs 4.1 ml. H2O, 0.8 m-equiv Na, 1.3 m-equiv acetate and secretes 0.5 m-equiv HCO3/min with a solution comparable to the normal contents. The absorptive capacity of the proximal and distal halves of the colon was comparable per unit dry weight of mucosa when each segment was presented with the same solution. 3. A series of studies using ion replacement solutions showed that net Na absorption and net HCO3 accumulation in the lumen solution were both increased in the presence of acetate. Cl absorption was independent of Na absorption and was accompanied by an equivalent net secretion of HCO3 in the absence of Na. When NaCl in the perfusion solution was replaced with Na2SO4, Na and HCO3 were absorbed at equal rates. 4. Final pCO2 values observed in NaCl and Na2SO4 solutions were greater than those observed in plasma while the pCO2 of the Na acetate solution after perfusion was reduced to values below plasma concentrations. 5. Results are consistent with the hypothesis that hydration of CO2 in the lumen solution or mucosal cell provides a continuous source of H ions for absorption of the more permeable undissociated acid. The evidence also suggests an additional source of H ions may be provided by a Na-H exchange process located in one of the limiting cell membranes.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASH R. W., DOBSON A. THE EFFECT OF ABSORPTION ON THE ACIDITY OF RUMEN CONTENTS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:39–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argenzio R. A., Miller N., von Engelhardt W. Effect of volatile fatty acids on water and ion absorption from the goat colon. Am J Physiol. 1975 Oct;229(4):997–1002. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.4.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argenzio R. A., Southworth M., Lowe J. E., Stevens C. E. Interrelationship of Na, HCO3, and volatile fatty acid transport by equine large intestine. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):E469–E478. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.6.E469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argenzio R. A., Southworth M. Sites of organic acid production and absorption in gastrointestinal tract of the pig. Am J Physiol. 1975 Feb;228(2):454–460. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.2.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argenzio R. A., Southworth M., Stevens C. E. Sites of organic acid production and absorption in the equine gastrointestinal tract. Am J Physiol. 1974 May;226(5):1043–1050. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.5.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley P. J., Smith M. W. Transport of electrolytes across the helicoidal colon of the new-born pig. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(1):103–117. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Rawlins C. L. Electrolyte transport across isolated large intestinal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1973 Nov;225(5):1232–1239. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.5.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. H., Jr, Levitt M. D. Fate of soluble carbohydrate in the colon of rats and man. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1158–1164. doi: 10.1172/JCI108383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien W. J., Stevens C. E. Coupled active transport of Na and Cl across forestomach epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1972 Oct;223(4):997–1003. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.4.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens E. T., Stevens C. E., Southworth M. Sites of organic acid production and pattern of digesta movement in the gastrointestinal tract of swine. J Nutr. 1975 Jun;105(6):759–768. doi: 10.1093/jn/105.6.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOBSON A. Active transport through the epithelium of the reticulo-rumen sac. J Physiol. 1959 May 19;146(2):235–251. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOBSON A., PHILLIPSON A. T. The absorption of chloride ions from the retie-ulo-rumen sac. J Physiol. 1958 Jan 23;140(1):94–104. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Koch M. J., Schultz S. G. Ion transport by rabbit colon. I. Active and passive components. J Membr Biol. 1976;27(3):297–316. doi: 10.1007/BF01869142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebisch G., Malnic G. Studies on the mechanism of tubular acidification. Physiologist. 1976 Nov;19(4):511–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning S. J., Hird F. J. Ketogenesis from butyrate and acetate by the caecum and the colon of rabbits. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):785–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1300785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
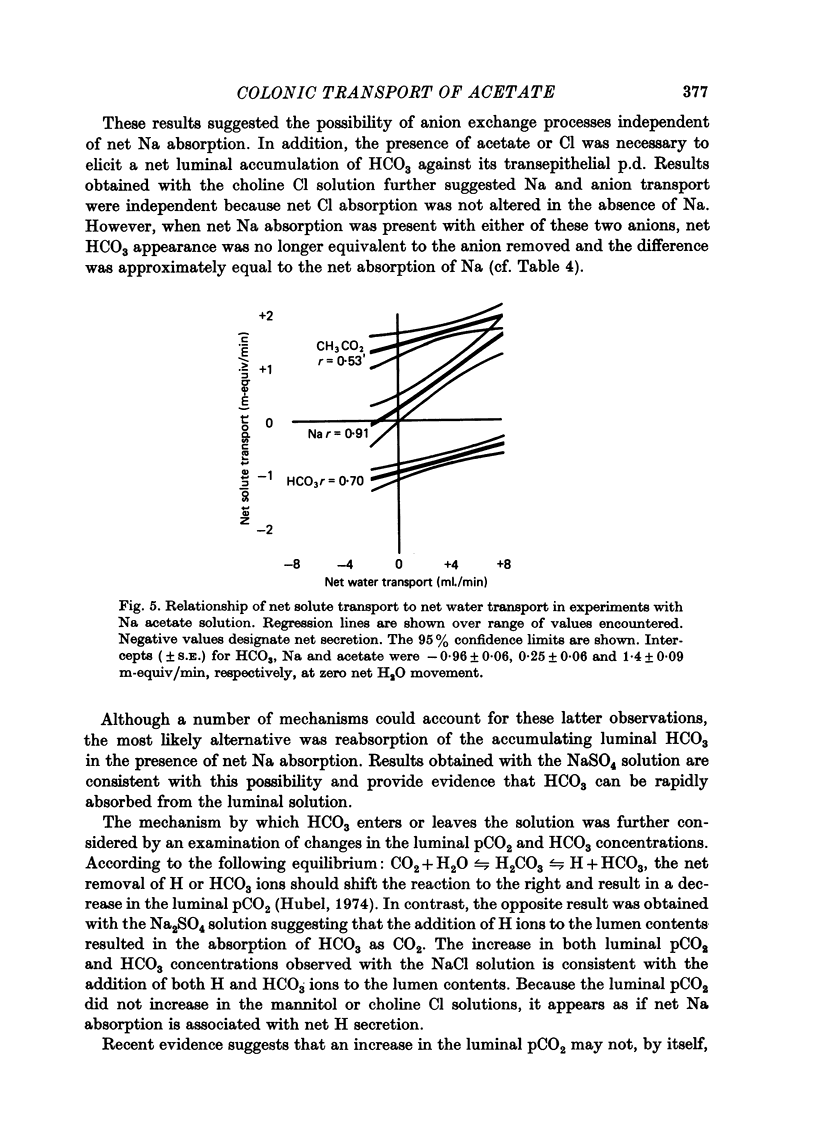
- Hubel K. A. The mechanism of bicarbonate secretion in rabbit ileum exposed to choleragen. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):964–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI107662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hénin S., Smith M. W. Electrical properties of pig colonic mucosa measured during early post-natal development. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;262(1):169–187. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P. S., Smith M. W. Methionine transport by pig colonic mucosa measured during early post-natal development. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;262(1):151–168. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
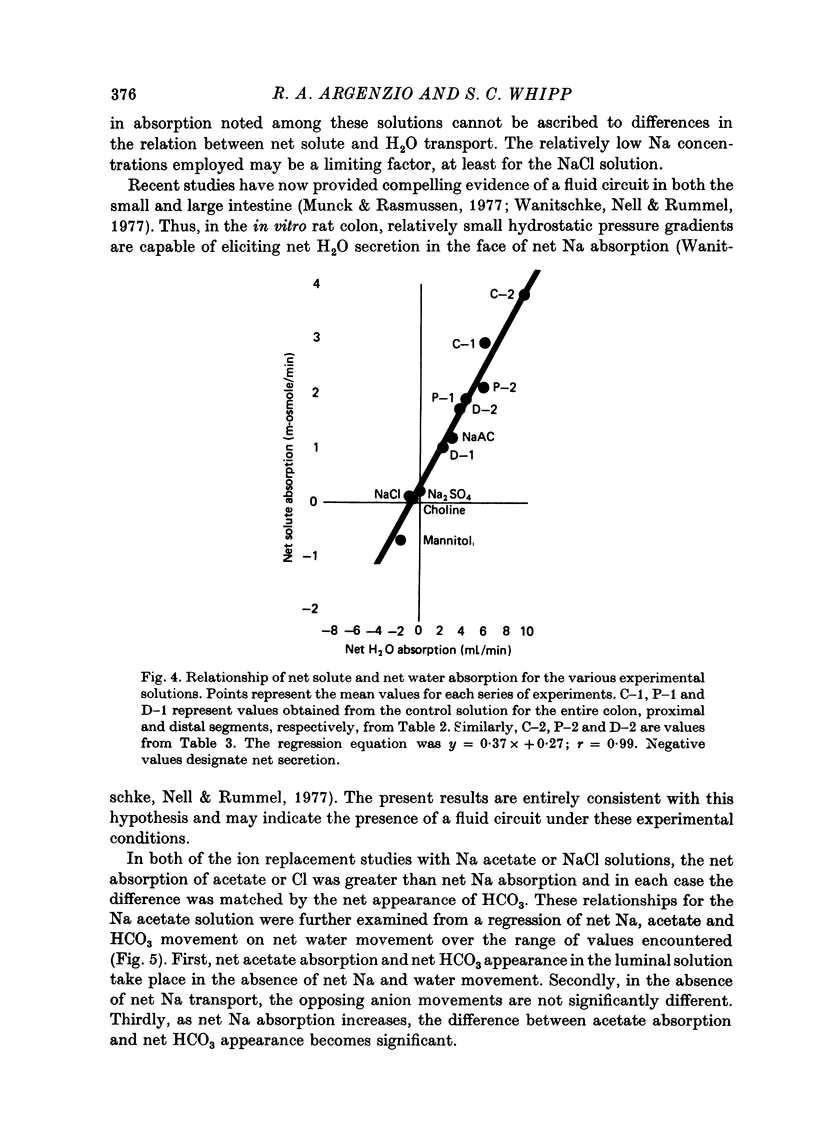
- Munck B. G., Rasmussen S. N. Paracellular permeability of extracellular space markers across rat jejunum in vitro. Indication of a transepithelial fluid circuit. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(2):473–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podesta R. B., Mettrick D. F. HCO3 transport in rat jejunum: relationship to NaCl and H2O transport in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jan;232(1):E62–E68. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.232.1.E62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein R., Howard A. V., Wrong O. M. In vivo dialysis of faeces as a method of stool analysis. IV. The organic anion component. Clin Sci. 1969 Oct;37(2):549–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMYTH D. H., TAYLOR C. B. Intestinal transfer of short-chain fatty acids in vitro. J Physiol. 1958 Apr 3;141(1):73–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salanitro J. P., Muirhead P. A. Quantitative method for the gas chromatographic analysis of short-chain monocarboxylic and dicarboxylic acids in fermentation media. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Mar;29(3):374–381. doi: 10.1128/am.29.3.374-381.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. G., Jr, Soergel K. H., Wood C. M. Absorption of short chain fatty acids from the human jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1976 Feb;70(2):211–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. G., Jr, Soergel K. H., Wood C. M., Steff J. J. Absorption of short-chain fatty acids from the human ileum. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Apr;22(4):340–347. doi: 10.1007/BF01072192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. E., Dobson A., Mammano J. H. A transepithelial pump for weak electrolytes. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):983–987. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Bieberdorf F. A., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Interrelationships of chloride, bicarbonate, sodium, and hydrogen transport in the human ileum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):557–567. doi: 10.1172/JCI106266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanitschke R., Nell G., Rummel W. Influence of hydrostatic pressure gradients on net transfer of sodium and water across isolated rat colonic mucosa. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;297(2):191–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00499930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


