Abstract
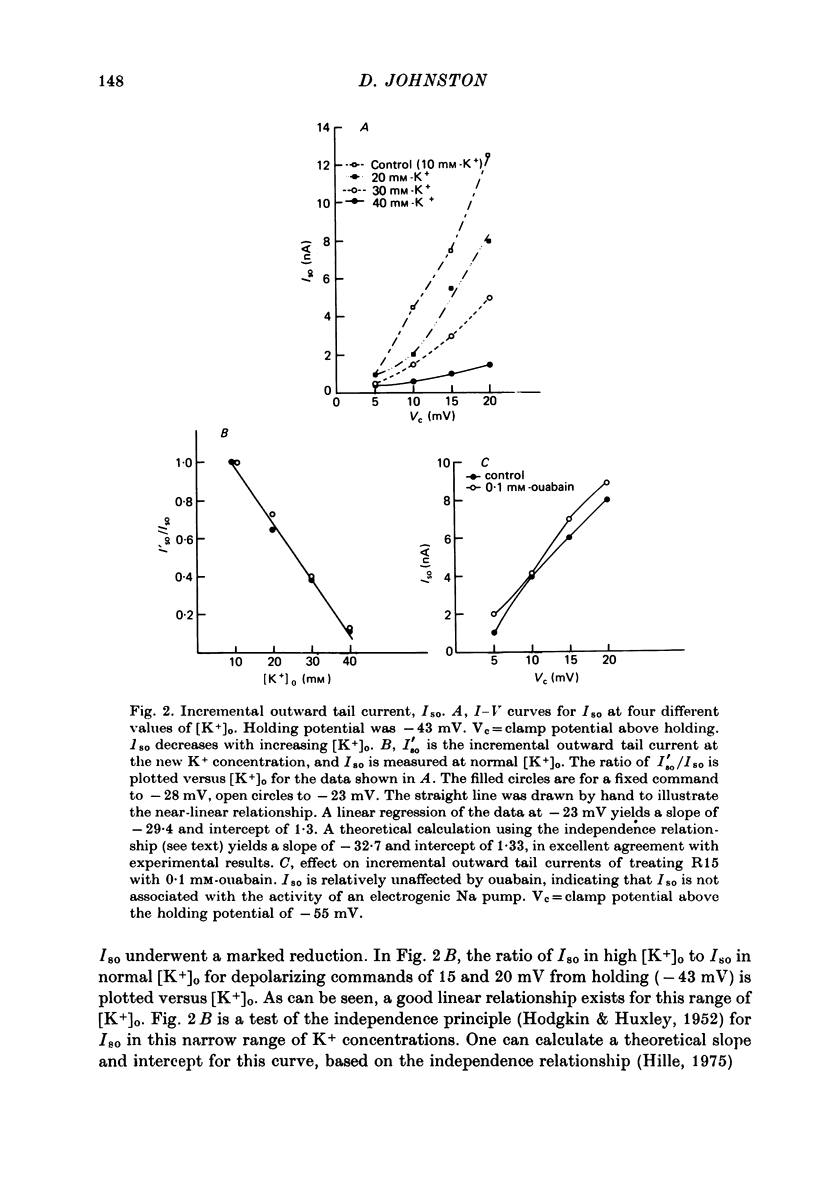
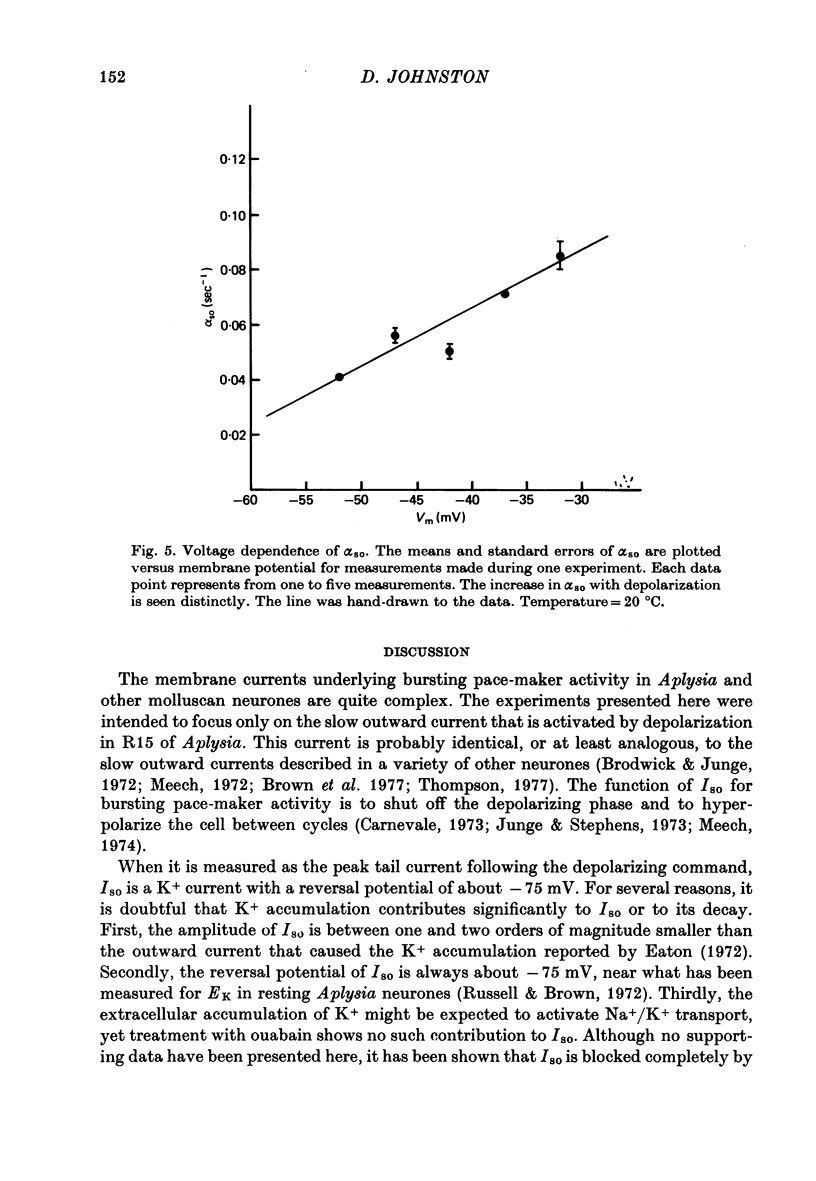
1. The slow outward current in Aplysia burst-firing neurones was studied under voltage-clamp conditions. This current, designated Iso, was measured as the incremental outward tail current following small depolarizing commands. 2. Iso was shown to be a pure K+ current, probably activated by the influx of Ca2+ during the depolarizing command (Johnston, 1976). For small depolarizations, the peak conductance was about 10(-7) mhos. 3. The rate of decay of Iso could be fit by a single exponential and was voltage-dependent, increasing with depolarization. 4. The decay rate of Iso was also temperature-dependent, with a Q10 of about 3. The peak conductance, however, was much less temperature-sensitive, with a Q10 of about 1.5. 5. The voltage dependence of decay rate suggested either the presence of a voltage-dependent Ca2+ pump or that the change in intracellular calcium concentration was not the rate-limiting step in the decay of Iso.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARVANITAKI-CHALAZONITIS A., CHALAZONITIS N. Les potentiels bioélectriques endocytaires du neurone géant d'Aplysia en activité autorythmique. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1955 Jan 17;240(3):349–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARVANITAKI A., CHALAZONITIS N. Configurations modales de l'activité, propres à différents neurones d'un mëme centre. J Physiol (Paris) 1958 Mar;50(2):122–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. The interrelationship between sodium and calcium fluxes across cell membranes. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1974;70:33–82. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Eckert R. Calcium entry leads to inactivation of calcium channel in Paramecium. Science. 1978 Dec 15;202(4373):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.103199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodwick M. S., Junge D. Post-stimulus hyperpolarization and slow potassium conductance increase in Aplysia giant neurone. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(2):549–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Brodwick M. S., Eaton D. C. Intracellular calcium and extra-retinal photoreception of Aplysia Giant neurons. J Neurobiol. 1977 Jan;8(1):1–18. doi: 10.1002/neu.480080102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton R. R., Wenner C. E. Calcium-ion transport by intact Ehrlich ascites-tumour cells. Role of respiratory substrates, Pi and temperature. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):537–544. doi: 10.1042/bj1700537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C. Potassium ion accumulation near a pace-making cell of Aplysia. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):421–440. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Lux H. D. A voltage-sensitive persistent calcium conductance in neuronal somata of Helix. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(1):129–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., MOORE L. E. THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE SODIUM AND POTASSIUM PERMEABILITY CHANGES IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:431–437. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Changes in the intracellular concentration of free calcium ions in a pace-maker neurone, measured with the metallochromic indicator dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:357–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F., KATZ B. Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):424–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D. Voltage clamp reveals basis for calcium regulation of bursting pacemaker potentials in Aplysia neurons. Brain Res. 1976 May 7;107(2):418–423. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junge D., Stephens C. L. Cyclic variation of potassium conductance in a burst-generating neurone in Aplysia. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):155–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel E. R., Tauc L. Anomalous rectification in the metacerebral giant cells and its consequences for synaptic transmission. J Physiol. 1966 Mar;183(2):287–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Shin B. C. Studies on the active transport of calcium in human red cells. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Dec;54(6):713–729. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.6.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmor M. F. The effects of temperature and ions on the current-voltage relation and electrical characteristics of a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):573–598. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Intracellular calcium injection causes increased potassium conductance in Aplysia nerve cells. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1972 Jun 1;42(2):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(72)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. The sensitivity of Helix aspersa neurones to injected calcium ions. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):259–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge L. D., Stevens C. F. A mechanism for spike frequency adaptation. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(2):315–332. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. M., Brown A. M. Active transport of potassium by the giant neuron of the aplysia abdominal ganglion. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Nov;60(5):519–533. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. G., Jr, Barker J. L., Gainer H. Requirements for bursting pacemaker potential activity in molluscan neurones. Nature. 1975 Feb 6;253(5491):450–452. doi: 10.1038/253450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whisler J. W., Johnston D. Epileptogenesis: a model for the involvement of slow membrane events and extracellular potassium. J Theor Biol. 1978 Dec 7;75(3):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(78)90334-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. A., Wachtel H. Negative resistance characteristic essential for the maintenance of slow oscillations in bursting neurons. Science. 1974 Dec 6;186(4167):932–934. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4167.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


