Abstract
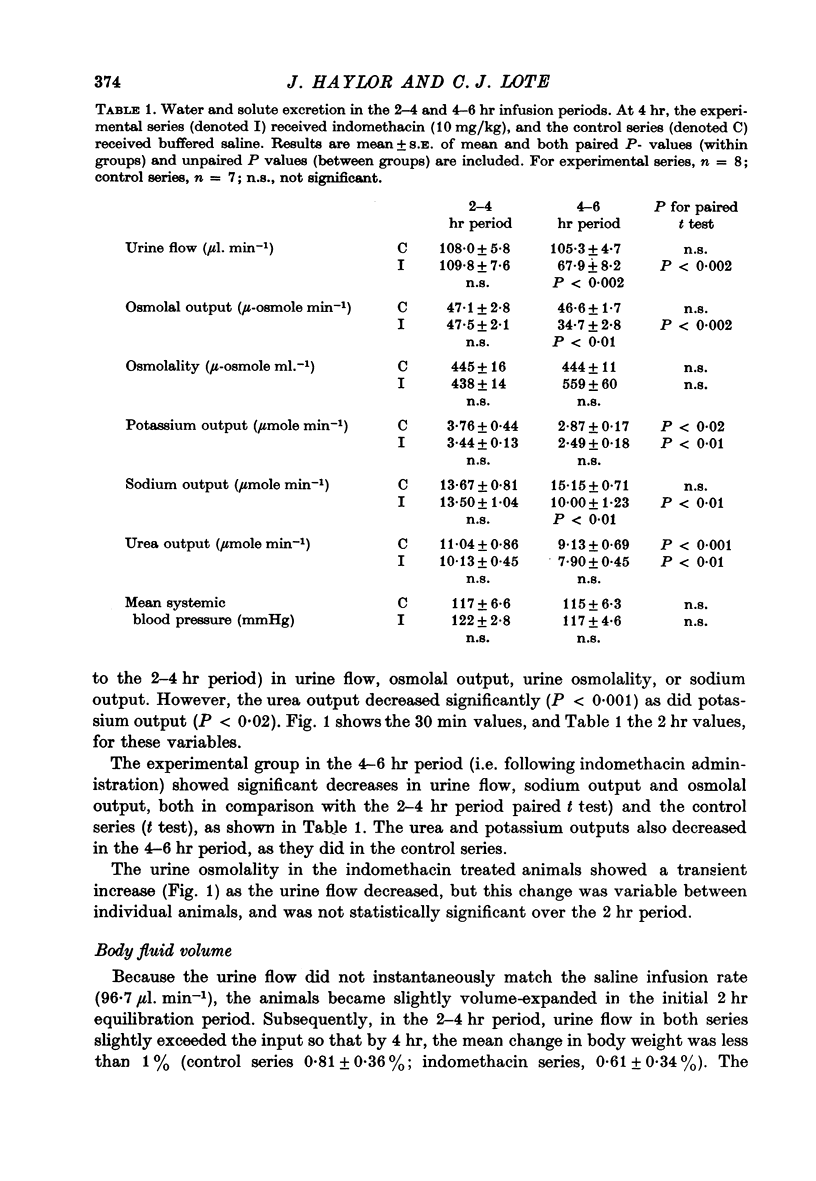
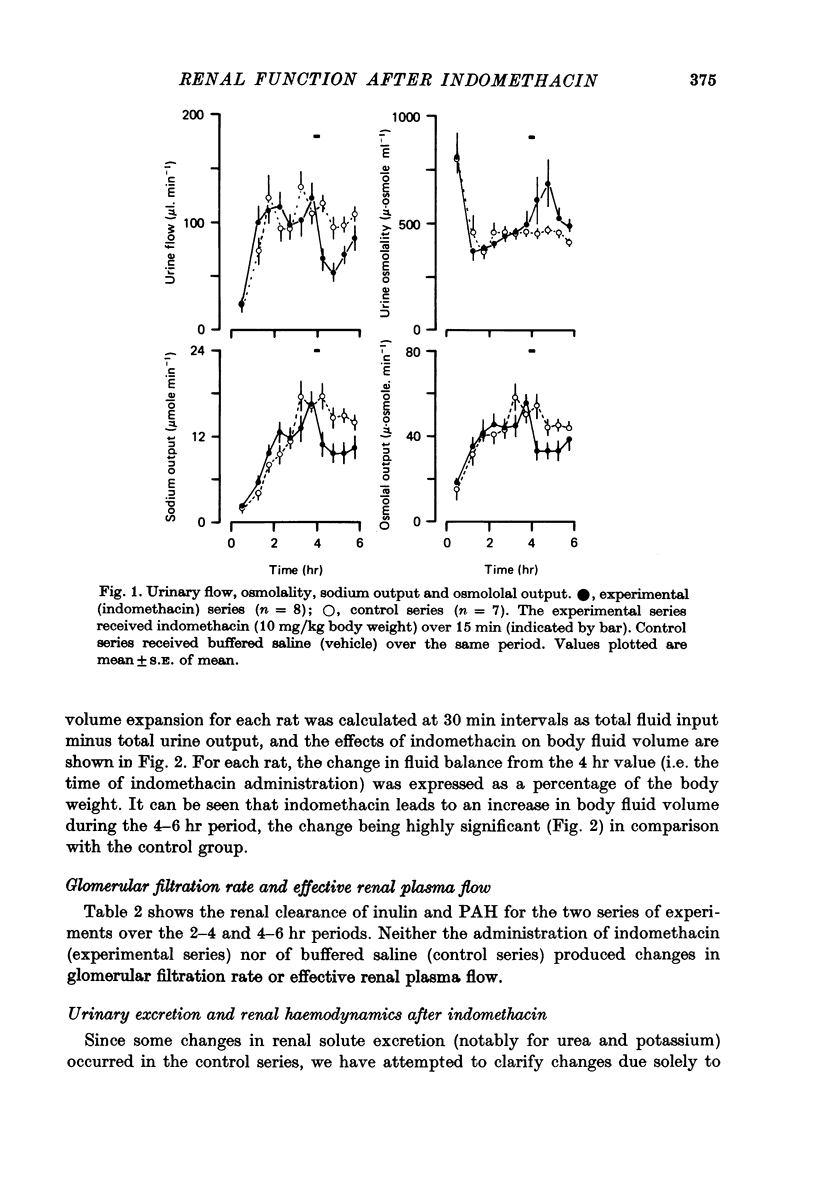
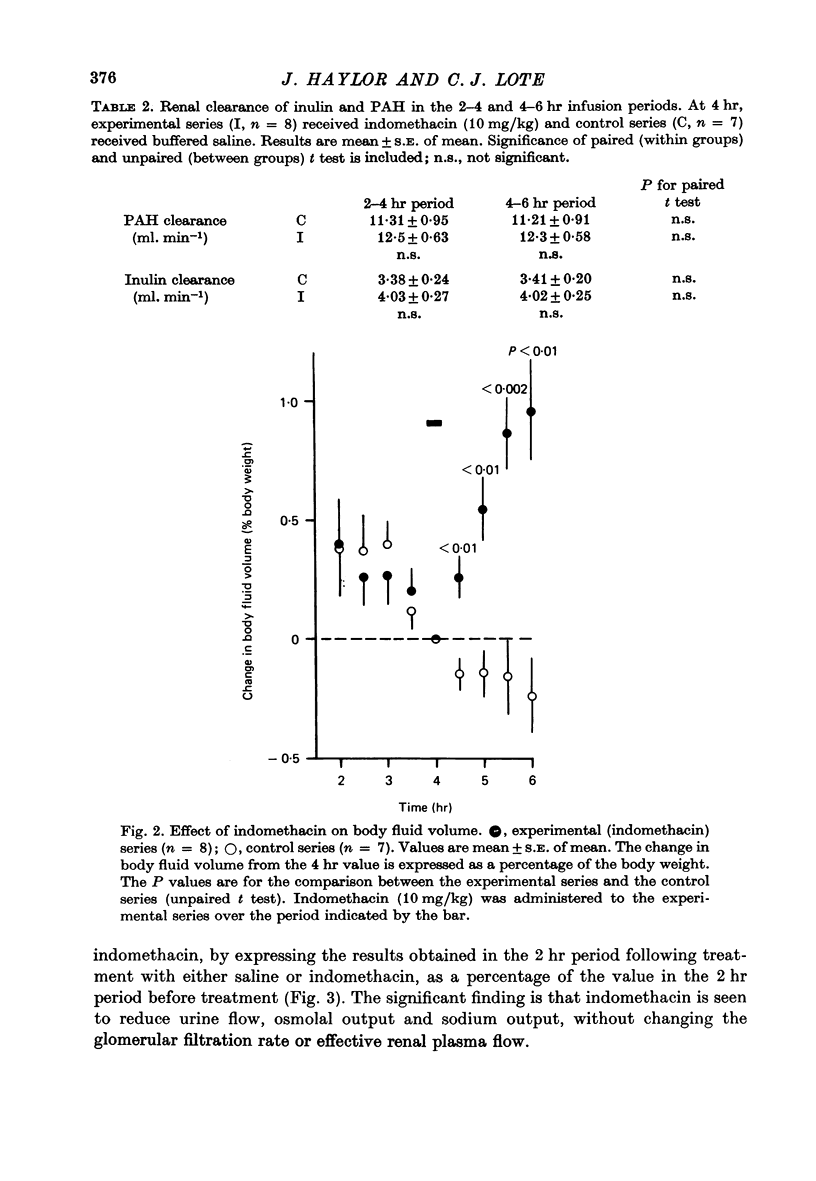
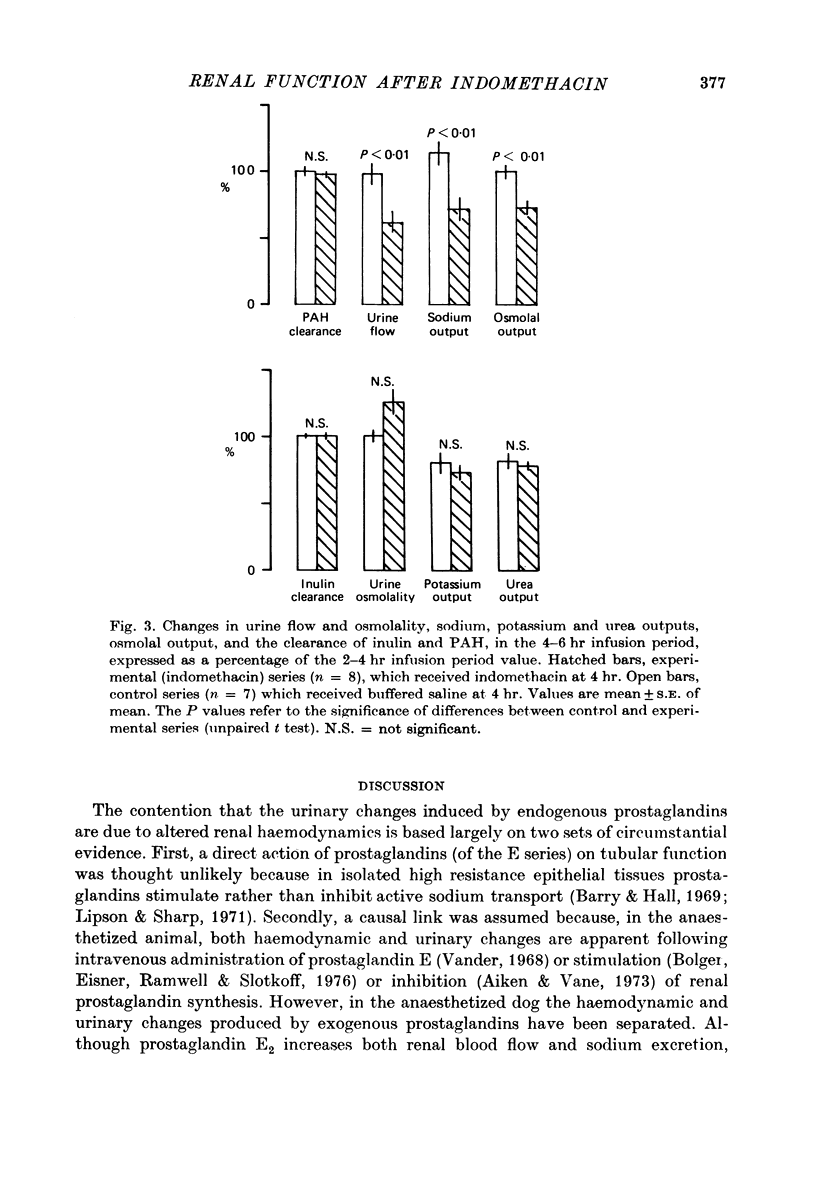
1. Conscious rats, with implanted carotid arterial cannulae, received a saline infusion (5.8 ml./hr) via a tail vein for a 6 hr period. The urinary excretion of water, sodium, potassium, urea and the osmolal output were monitored, together with the systemic blood pressure. Glomerular filtration rate (inulin clearance) and effective renal plasma flow (p-aminohippurate clearance) were also measured. Four hours after the start of the infusion, indomethacin (10 mg/kg body weight) in buffered saline, or buffered saline alone, was administered via the tail vein. 2. Following indomethacin administration, urine flow, sodium output and osmolal output were markedly reduced (P less than 0.01). However, there were no measurable changes in the systemic blood pressure, glomerular filtration rate, or effective renal plasma flow. 3. It is concluded that the changes in urinary excretion observed after indomethacin are not dependent on changes in effective renal plasma flow or glomerular filtration, and it is suggested that indomethacin inhibits the synthesis of endogenous prostaglandins which directly influence renal tubular function.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiken J. W., Vane J. R. Intrarenal prostaglandin release attenuates the renal vasoconstrictor activity of angiotensin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Mar;184(3):678–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. J., Berl T., McDonald K. D., Schrier R. W. Evidence for an in vivo antagonism between vasopressin and prostaglandin in the mammalian kidney. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):420–426. doi: 10.1172/JCI108108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOJESEN E. A method for determination of inulin in plasma and urine. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1952;266:275–282. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1952.tb13376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailie M. D., Barbour J. A., Hook J. B. Effects of indomethacin on furosemide-induced changes in renal blood flow. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Apr;148(4):1173–1176. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry E., Hall W. J. Stimulation of sodium movement across frog skin by prostaglandin E1. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):83P–84P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berl T., Raz A., Wald H., Horowitz J., Czaczkes W. Prostaglandin synthesis inhibition and the action of vasopressin: studies in man and rat. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jun;232(6):F529–F537. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.6.F529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger P. M., Eisner G. M., Ramwell P. W., Slotkoff L. M. Effect of prostaglandin synthesis on renal function and renin in the dog. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):244–245. doi: 10.1038/259244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger P. M., Eisner G. M., Shea P. T., Ramwell P. W., Slotkoff L. M. Effects of PGD2 on canine renal function. Nature. 1977 Jun 16;267(5612):628–630. doi: 10.1038/267628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger B. M., Hopkins T., Tulloch A., Hollenberg N. K. The role of angiotensin in the canine renal vascular response to barbiturate anesthesia. Circ Res. 1976 Mar;38(3):196–202. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.3.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. C., Splawinski J. A., Oates J. A., Nies A. S. Enhanced renal prostaglandin production in the dog. II. Effects on intrarenal hemodynamics. Circ Res. 1975 Jan;36(1):204–207. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.1.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düsing R., Melder B., Kramer H. J. Prostaglandins and renal function in acute extracellular volume expansion. Prostaglandins. 1976 Jul;12(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(76)80002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAWCETT J. K., SCOTT J. E. A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea. J Clin Pathol. 1960 Mar;13:156–159. doi: 10.1136/jcp.13.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigen L. P., Klainer E., Chapnick B. M., Kadowitz P. J. The effect of indomethacin on renal function in pentobarbital-anesthetized dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Aug;198(2):457–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine L. G., Trizna W. Influence of prostaglandins on sodium transport of isolated medullary nephron segments. Am J Physiol. 1977 Apr;232(4):F383–F390. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.4.F383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores A. G., Sharp G. W. Endogenous prostaglandins and osmotic water flow in the toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1972 Dec;223(6):1392–1397. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.6.1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fülgraff G., Brandenbusch G. Comparison of the effects of the prostaglandins A1, E2, and F2alpha on kidney function in dogs. Pflugers Arch. 1974 May 24;349(1):9–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00587912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fülgraff G., Meiforth A. Effects of prostaglandin E 2 on excretion and reabsorption of sodium and fluid in rat kidneys (micropuncture studies). Pflugers Arch. 1971;330(3):243–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00588615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haylor J., Lote C. J. Proceedings: The role of endogenous prostaglandin synthesis in the maintenance of frog skin permeability. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(1):50P–51P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haylor J. Prostaglandin synthesis and renal function in man. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:383–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino Y., Imai M. Effects of prostaglandins on Na transport in isolated collecting tubules. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Feb 22;373(2):125–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00584850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. H., Herzog J. P., Lauler D. P. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on renal hemodynamics, sodium and water excretion. Am J Physiol. 1967 Oct;213(4):939–946. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.4.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalisker A., Dyer D. C. In vitro release of prostaglandins from the renal medulla. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Sep;19(3):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschenbaum M. A., Stein J. H. The effect of inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis on urinary sodium excretion in the conscious dog. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):517–521. doi: 10.1172/JCI108304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschenbaum M. A., White N., Stein J. H., Ferris T. F. Redistribution of renal cortical blood flow during inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1974 Oct;227(4):801–805. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.4.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyssac P. P., Christensen P., Hill R., Skinner S. L. Indomethacin blockade of renal PGE-synthesis: effect on total renal and tubular function and plasma renin concentration in hydropenic rats and on their response to isotonic saline. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Aug;94(4):484–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson L. C., Sharp G. W. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on sodium transport and osmotic water flow in the toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1046–1052. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonigro A. J., Itskovitz H. D., Crowshaw K., McGiff J. C. Dependency of renal blood flow on prostaglandin synthesis in the dog. Circ Res. 1973 Jun;32(6):712–717. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.6.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lote C. J., Rider J. B., Thomas S. The effect of prostaglandin E1 on the short-circuit current and sodium, potassium, chloride and calcium movements across isolated frog (Rana temporaria) skin. Pflugers Arch. 1974;352(2):145–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00587513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lote C. J., Snape B. M. Collecting duct dlow rate as a determinant of equilibration between urine and renal papilla in the rat in the presence of a maximal antidiuretic hormone concentration. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):533–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum G. M., Aisenbrey G. A., Dunn M. J., Berl T., Schrier R. W., McDonald K. M. In vivo effect of indomethacin to potentiate the renal medullary cyclic AMP response to vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):8–13. doi: 10.1172/JCI108624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEIERS H. G., WETZELS E. PHENYLBUTAZON UND NIERENFUNKTIONEN. Arzneimittelforschung. 1964 Apr;14:252–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Crowshaw K., Itskovitz H. D. Prostaglandins and renal function. Fed Proc. 1974 Jan;33(1):39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papanicoulaou N. Nature and origin of the released prostaglandins following expansion of the blood volume. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;27(9):704–707. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1975.tb09538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman R. J., Kauker M. L. Renal effect of prostaglandin synthetase inhibition in rats: micropuncture studies. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):F111–F118. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.2.F111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Finkelstein N., Aliminosa L., Crawford B., Graber M. THE RENAL CLEARANCES OF SUBSTITUTED HIPPURIC ACID DERIVATIVES AND OTHER AROMATIC ACIDS IN DOG AND MAN. J Clin Invest. 1945 May;24(3):388–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI101618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., Kokko J. P. Inhibition of sodium transport by prostaglandin E2 across the isolated, perfused rabbit collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1099–1104. doi: 10.1172/JCI108733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandhoy J. W., Ott C. E., Schneider E. G., Willis L. R., Beck N. P., Davis B. B., Knox F. G. Effects of prostaglandins E1 and E2 on renal sodium reabsorption and Starling forces. Am J Physiol. 1974 May;226(5):1015–1021. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.5.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain J. A., Heyndrickx G. R., Boettcher D. H., Vatner S. F. Prostaglandin control of renal circulation in the unanesthetized dog and baboon. Am J Physiol. 1975 Sep;229(3):826–830. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.3.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terragno N. A., Terragno D. A., McGiff J. C. Contribution of prostaglandins to the renal circulation in conscious, anesthetized, and laparotomized dogs. Circ Res. 1977 Jun;40(6):590–595. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.6.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Direct effects of prostaglandin on renal function and renin release in anesthetized dog. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):218–221. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zins G. R. Renal prostaglandins. Am J Med. 1975 Jan;58(1):14–24. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


